AQA Psychology - Research Methods Quiz
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Self-report techniques
Any method in which a person is asked to state or explain their own feelings, opinions, behaviors and experiences related to a given topic.

Questionnaire
A set of written questions (sometimes called items) used to access a persons' thoughts/experiences

Open Questions
Questions with no fixed answer/response and respondents can answer in any way they wish.

Closed Question
Questions with a fixed answer/ the choice of response is determined by the question setter.

Interview
A live encounter (face to face or on the phone) where one person asks a set of questions to assess an interviewees thoughts/experiences. They can be structured, semi structured or unstructured.

Structured Interview
Made up of pre-determined questions and are asked in a fixed order. Basically like a questionnaire but conducted face to face.
Unstructured Interview
Works like a conversation. There are no set questions. There is a general aim that a certain topic will be discussed and interaction tends to be free flowing.
Semi-structured Interview
There is a list of questions that have been worked out in advance but interviewers are also free to ask follow up questions when they feel it is appropriate.
Aim
A general statement that the researcher intends to investigate.

Hypothesis
A detailed statement which is clear, precise and testable that states the relationship between variables being tested.

Directional Hypothesis
The researcher makes it clear what difference is anticipated between the 2 conditions or groups.
(One tailed).
Non-directional Hypothesis
Simply states that there is a difference but not what the difference will be.

Null Hypothesis
the hypothesis that there is no significant difference between specified populations, any observed difference being due to sampling or experimental error.
Meta-analysis
A particular form of research method that uses secondary data. Data from a large number of studies which have involved the same research question and method are combined.
Quantitative Data
Data that focuses on numbers and frequencies which can be counted. e.g. experiments, questionnaires and psychometric tests.

Qualitative Data
Data that describes meaning and experiences which is expresses in words e.g. case studies, interviews and observations.
Primary Data
Information that has been obtained first hand by the researcher. It is also known as field research.
Secondary Data
Information that has already been collected by previous researchers. It is also known as 'desk research' and can be found in journal articles, books or websites.I
Variable
Any "thing" that can vary or change with in an investigation. They are generally in experiments to determine if changes in one result in changes to another.
Independent Variable - IV
An aspect of the experimental situation that is manipulated by the researcher or changes naturally so the effect on the DV can be measured.
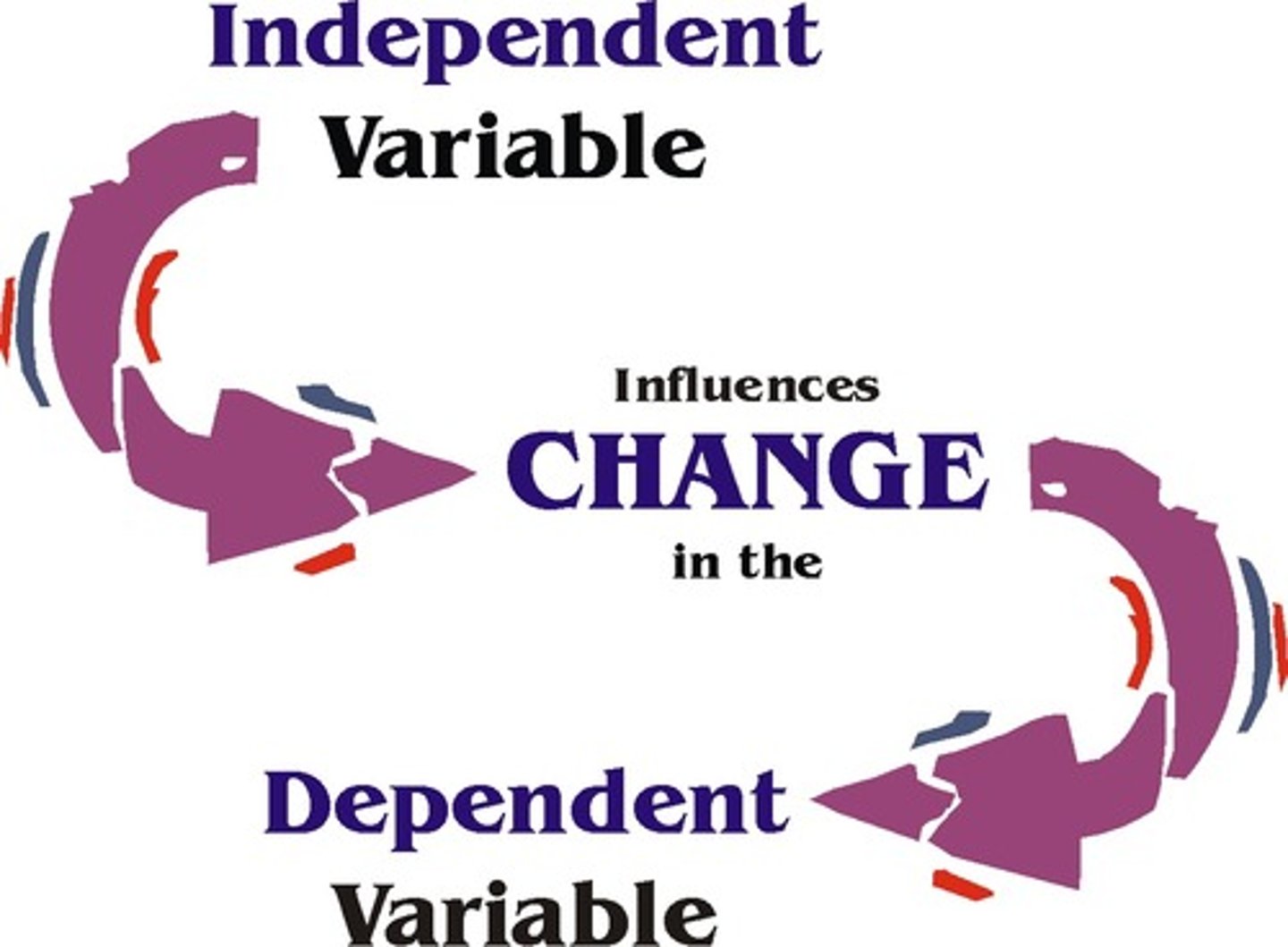
Dependent Variable - DV
The variable that is measured by the researcher. Any result/change on the DV should be caused by the change in the IV.

Operationalising Variables
The process of devising a way of measuring a variable. It is a clear statement of what the variable is.
Lab Experiment
An experiment that takes place in a controlled environment where the researcher manipulates the IV and records the effect on the DV while maintaining strict control of extraneous variables.

Field Experiment
An experiment that takes place in a natural setting where the researcher manipulates the IV and records the effect on the DV.

Natural Experiment
An experiment where the change in the IV is not caused by the researcher as it would have happened if the researcher wasn't there. The researcher records the effect on the DV.
extraneous variable
any aspect of the experimental setting that must be held constant to prevent unplanned environmental variation
confounding variable
a factor other than the independent variable that might produce a similar effect on the DV
Control Condition
A condition where the IV isn't changed and provides a baseline measure.
Experimental Condition
A condition where the IV has been manipulated.
Random Allocation
Allocating participants to experimental groups or conditions using random techniques
Ecological Validity
The extent to which a study is realistic or representative of real life.
Demand Characteristics
Any cue from the researcher or research situation that can be interpreted by participants as revealing the purpose of the investigation leading them to change their behaviour.
Experimenter Effects
when a researcher unintentionally affects the results
Experimental Methods
A research method that tests causal hypotheses by manipulating independent variables and measuring the effects on dependent variables.
Experimental Designs
How participants are arranged across the conditions of an experiment
Independent Groups Design
Different participants are used in each condition in an experiment
Repeated Measures Design
The same participants are used in all the conditions in an experiment.
Matched Pairs Design
A method of assigning subjects to groups in which pairs of subjects are first matched on some characteristic and then individually assigned randomly to groups.
Counterbalancing
All possible orders of presentation are included in the experiment
Order Effects
A problem in research design when the results of the study are attributed to the sequence of tasks in the experiment rather than to the independent variable.
Naturalistic Observation
watching behavior in real-world settings without trying to manipulate the situation
Controlled Observation
A form of investigation in which behaviour is observed but under controlled conditions.
Participant Observation
The researcher is involved in/with the observational setting. The researcher joins the group either overtly of covertly.
Non-Participant Observation
The researcher is not involved in what is going on. The researcher is external to what is going on/the people being observed.
Covert Observation
Where the researchers status is not made clear to the group and the researcher doesn't get consent.

Overt Observation
The researcher is open about their intentions and seeks consent. People know they are being observed.
Event Sampling
a procedure in observational research in which only certain types of behaviors occurring under precisely defined conditions are sampled
Inter-Observer Reliability
Two or more researchers observe the same behaviour at the same time then check results for consistency
Content Analysis
A kind of observational study where behaviour is observed indirectly in pictorial or verbal material.
Target Population
The entire group a researcher is interested in. The researchers wishes to draw conclusions from this group.

Generalisation
The extent to which findings and conclusions from a particular experiment can be broadly applied to the population. This is possible if the sample is representative of the population.
Peer Review
The assessment of work by others who are specialists in the same field to ensure that any research set for publication is high quality.

Case Study
A research method that involves a detailed study of a single individual, institution or event.
Sampling Techniques
The method used to select participants from the target population.
Opportunity Sampling
A sample of participants produced by selecting people who are most easily available at the time of the study.
Random Sampling
A sample of participants produced by using a random technique so that every member of the target population has an equal chance of being selected.

Volunteer Sampling
A sample of participants produced by a sampling technique that relies solely on inviting people to take part.

Systematic Sampling
A method of obtaining a sample by selecting systematically from a list e.g. every 5th or 7th person.
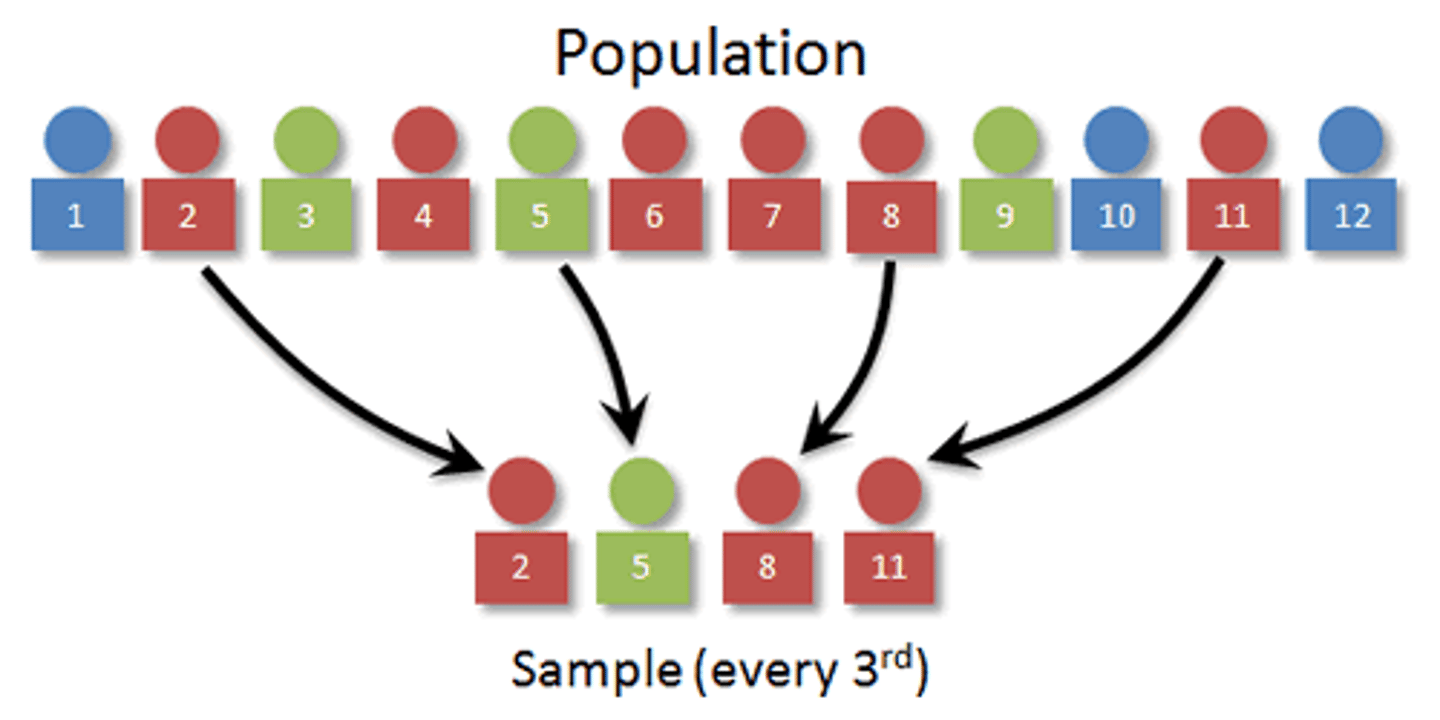
Stratified Sampling
A sampling technique where groups of participants are selected in proportion to their frequency in the population in order to obtain a representative sample.
Correlation
A mathematical technique, where a researcher investigates an association between two variables call co-variables.

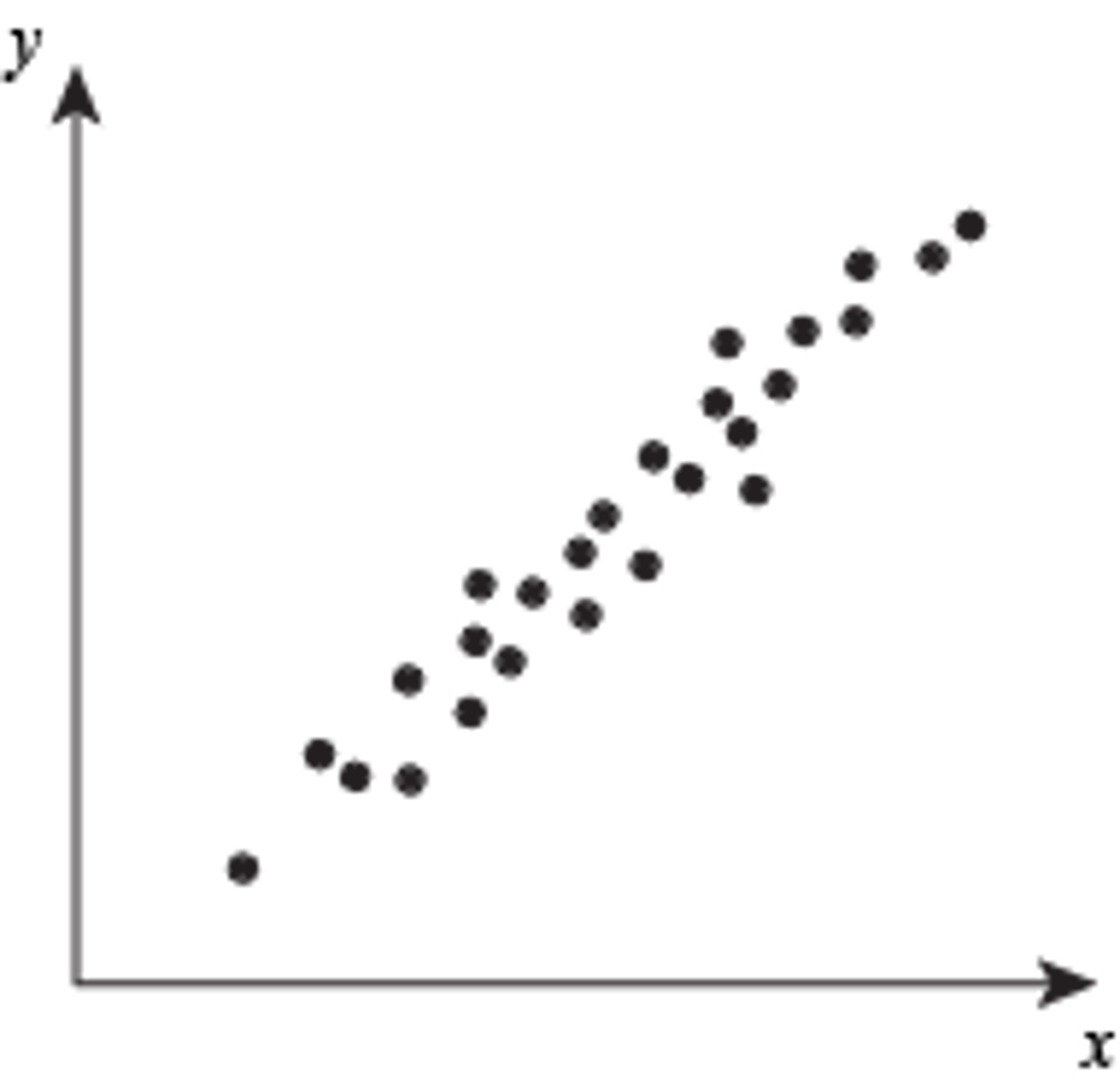
Positive Correlation
As one variable increase the other variable increases.
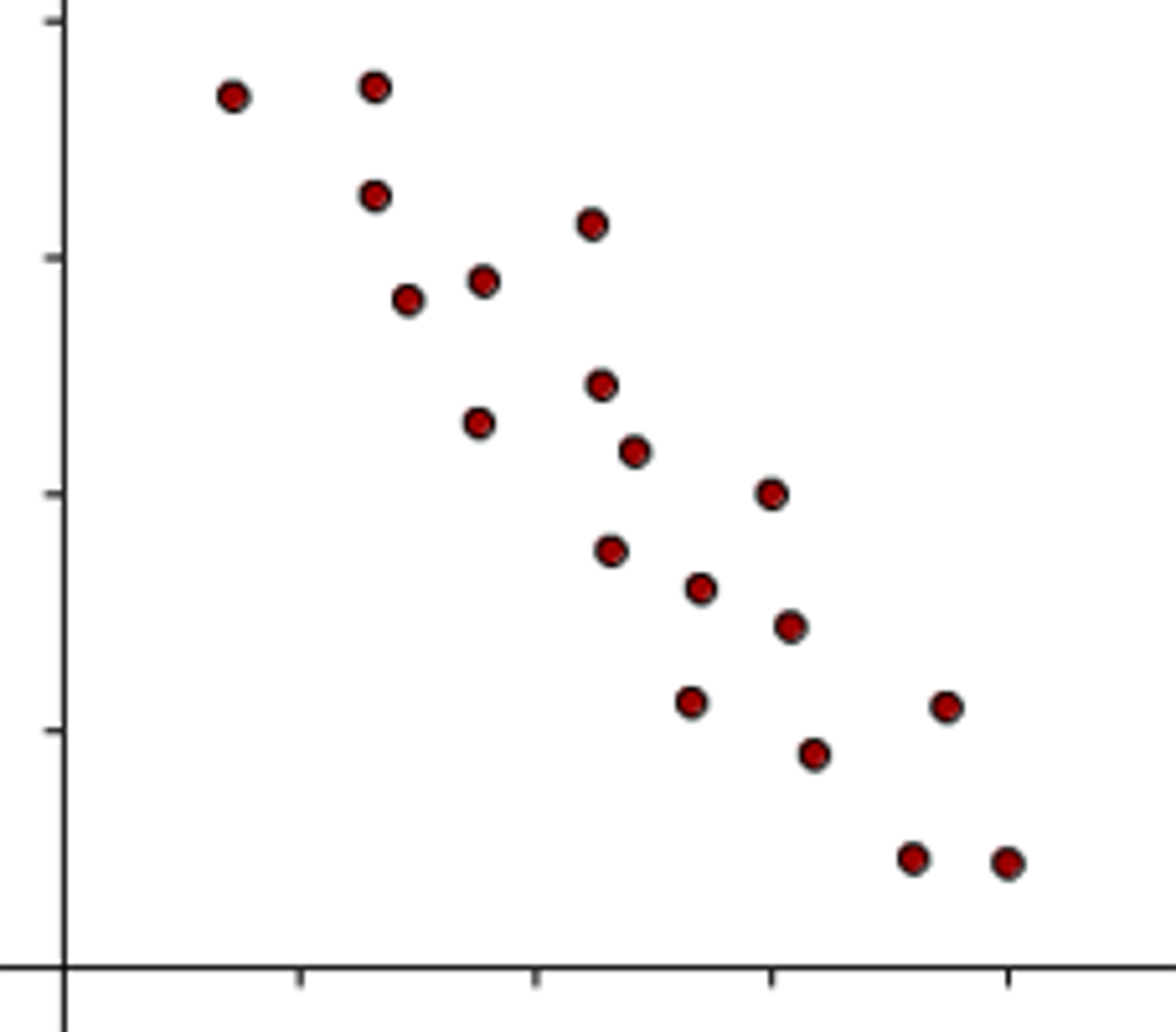
Negative Correlation
As one variable increase the other variable decreases.
Zero Correlation
When there is no relationship between the co-variables.
Measures of Central Tendency
The general term for any measure of the average value in the set of data.
Measures of Dispersion
The general term for any measure of the spread or variation in a set of scores.
Descriptive Statistics
The use of graphs, tables and summary statistics to identify trends and analyse sets of data.
Pilot Study
A small scale trial carried out at the start of an experiment to check for any flaws e.g. do the questions in the questionnaire make sense.
Mean
The arithmetic average. Calculated by adding up all of the values in a set of data and dividing by the number of values.
Median
The central value in a set of data when it is ordered from lowest to highest value.
Mode
The value that appears most frequently in a set of data
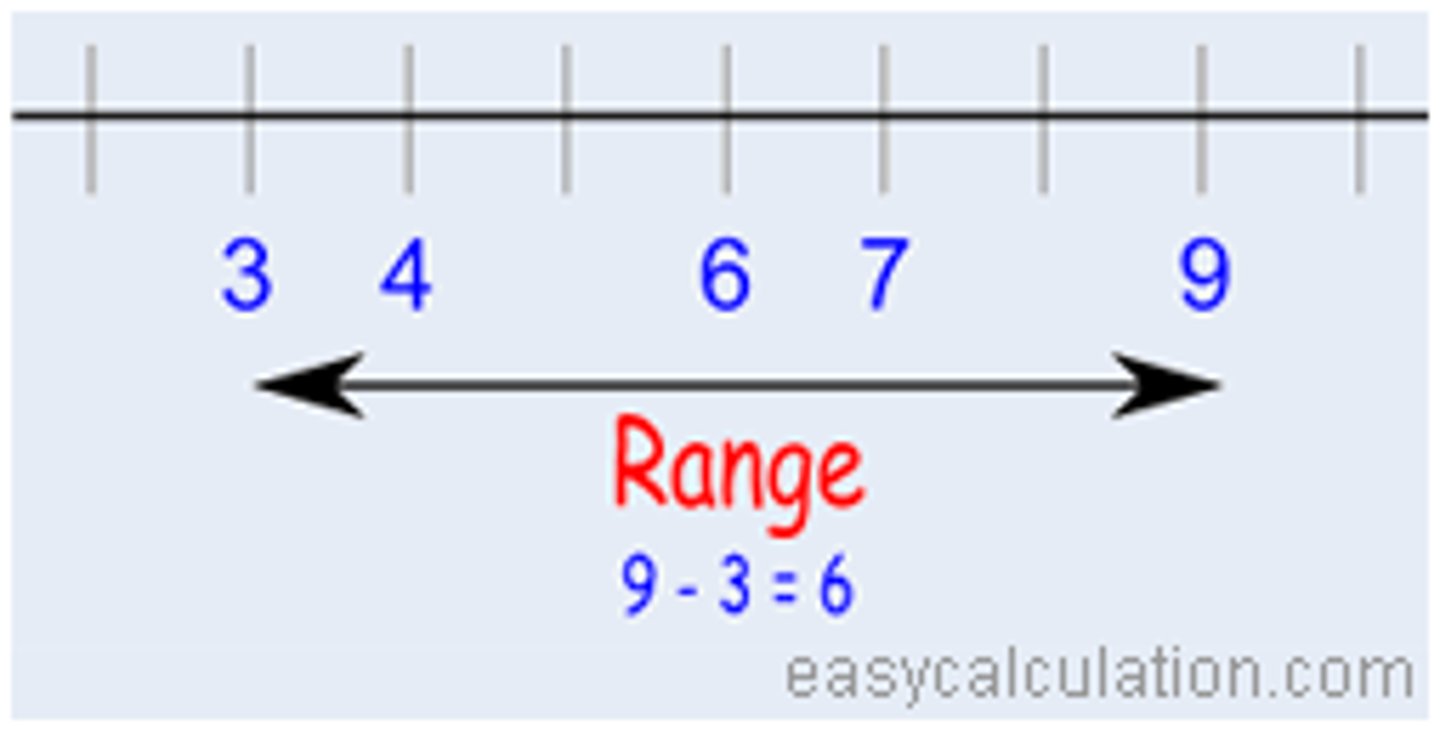
Range
Calculation of the dispersion in a set of scores. Worked out by minusing the lowest value from the highest value and adding one as a mathematical correction.
Standard Deviation
How far each score in a data set deviates from the mean
Normal Distribution
There is a symmetrical spread of frequency data that forms a bell shaped pattern
Skewed Distributions
When the spread of data is not symmetrical meaning the data clusters to one end.
Time Sampling
The procedure of observing and recording behavior during intervals or at specific moments
Accepted level of probability
In psychology the accepted level is 0.05 / 5%
Sometime researchers need more confidence so have a more stringent significance level of 0.01 / 1% e.g. when humans lives are involved.
Calculated Value
The number the researcher is left with after the statistical test has been calculated. It is compared to the critical value to see whether the results are significant.