Chapter 3 - Prenatal Development -> Influences and Birthing
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Maternal Influences
nutrition
stress
age
Environmental Influences
teratogens
Nutrition
mother is the child’s sole source of nutrition
should increase calorie intake by about 10% to 20%
expect to gain between 25-35 lbs
many proteins, vitamins, and minerals are essential for normal prenatal development
not enough macronutrients and micronutrients
causes issues with attention, memory, intelligence
Stress
links between maternal anxiety → child outcome
babies are born sooner
lower birth weight
attention problems
behavioral issues
research examining the children of women who were pregnant during Sept. 11 found stress effected
physical growth
language development
cognitive development
Maternal Age
maternal age at both extremes (youth & advanced age) can be considered a “risk factor” during pregnancy
Youth Issues
premature birth
low birth weight
lower academic performance
behavioral issues
Youth Reasons and Protective Factors
social stigmas and challenges faced by teen moms
certain characteristics are more prevalent in teen mom populations
protective factors
living with a supportive relative
home-visiting programs
Advanced Age (40-45) Issues
miscarriage
low birth weight
down syndrome
however
older mothers have been shown to provide effective mothering (sensitivity, responsibility, stability)
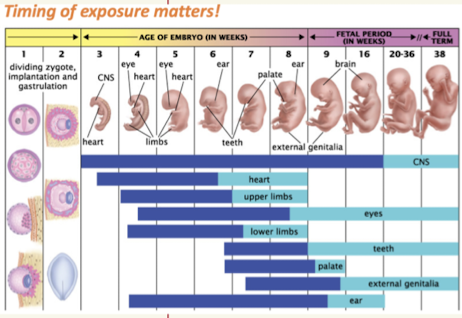
Teratogens
any environmental agent that causes birth defects
severity and type of damage depends on:
dose, genetic susceptibility, presence of other negative factors, timing of exposure

Fetal Alcohol Syndrom (FAS)
physical traits: slow growth and facial anomalies
leading cause of developmental delay in the US
Ultrasound
procedure that uses sound waves to generate a picture of the fetus
can include
due date, position, major anomalies, multiples, determine sex (after 20 weeks)
Amniocentesis
a needle that is inserted through the mother’s abdomen to obtain a sample of amniotic fluid
typically done at 16 weeks
ultrasound is used to guide the needle
results take 2 week
can detect birth defects
Chronic Villus Sampling (CVS)
a sample of tissue is obtained from the chorion (a part of the placenta)
can be done at 9-12 weeks
results take up to 7-10 days
about a .6%-1.3% risk of miscarriage following
can detect birth defects
Labor
38 weeks after conception
on average takes 12-26 hours
divided into 3 stages
Stage 1 (12-24 hours)
cervix enlarges to 10 cm
contractions activated through hormonal pathways
are weak and irregular at first and end up intense and sometimes without interruption
Stage 2 (1 hour)
baby moves through the birth canal and out the woman’s body
crowning
breech presentation
Crowning
the baby’s head becomes visable
Breech Presentation
when the baby moves down the birth canal feet or bottom first
Stage 3 (10-15 minutes)
placenta and fetal membranes expelled
“after birth”
small contractions will start again as the placenta detaches from the uterus
The Baby Blues
a range of negative emotions that typically lasts 1-2 weeks post-birth
occurs in 50% of women
commonly attributed to adjusting to the demands of a newborn and physiological changes while the body heals
Postpartum Depression (PPD)
mood disorder that affects women after child birth (goes on longer than the “baby blues”)
10%-15% of all members
PPD Symptoms
irritability
crying spells
anxiety
feelings of low self-worth
disturbed sleep
poor appetite
apathy
PPD Risk Factors
depression pre-pregnancy
family members have suffered depression
previous episodes of PPD
additional life stressors
unplanned pregnancy
lack of support system