Lecture 10 - circulation 1
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
What does every organism exchange substances with
Its environment
how do exchanges occur at the cellular level
By crossing the plasma membrane
How does exchange occur in unicellular organisms
Directly with the environment via diffusion.
What is the distance of exchange in unicellular organisms
Only across the cell membrane
When does diffusion play an important role
When distances are short (less than 100 um)
What distance does diffusion become ineffective
Over 100 um
In what cells is direct exchange with the environment not possible
Most cells of multicellular organisms.
What do most multicellular cells require for exchange
Specialised transport system.
Fick's law
Rate of diffusion is proportional to;
Surface area x concentration difference
Thickness of membrane
What is diffusion
The movement of molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration
What is osmosis
A special type of diffusion linking to fluids through a semi permeable membrane - the movement o water molecules from a high to a low concentration.
Gas exchange is via _________
Diffusion
Fluid exchange is via _______
Osmosis
Why do we need exchange
Cells have to get rid of waste products.
What are cells engaged in, in multicellular organisms
Metabolic activities.
What does every cell require
Nutrients
Oxygen ( if it uses aerobic respiration )
Example of waste products
Carbon dioxide
Nitrogenous compounds ( animals )
What is the special transport system in animals
Circulation
3 components of a circulatory system
Circulatory fluid
Interconnecting vessels
Muscular pump.
What does the circulatory system do
Connects the fluid which surrounds cells with the organs that exchange gases, absorb nutrients & dispose of waste products.
What are the 2 types of circulatory system.
Open and closed
Open circulatory system fluid
Hemolymph
What does the hemolymph do in an open circuit
Bathes the body cells and organs.
What is hemolymph composed of
Blood, lymph & interstitial fluid
What organisms have an open circulatory system
Arthropods (eg. Grass hoppers & molluscs)
Describe an open circulatory system
Heart contractions pump the hemolymph through the circulatory vessels and into the interconnected sinuses (spaces surrounding the organs)
The hemolymph exchanges gases and other chemicals with body cells within the sinuses
The heart relaxes, drawing hemolymph back in through pores which have valves that close when the heart contracts
What do body movements cause in an open circulatory system
Periodically squeeze the sinuses which helps to circulate the hemolymph
What does the open circulatory system of larger crustaceans include
More extensive vessels and an accessory pump.
What is the fluid in a closed circulatory system
Blood
Where is the blood in a closed circulatory system
Confined to vessels
What is blood distinct from
Interstitial fluid
What happens in a closed circulatory system
One or more hearts pump blood into large vessels which branch into smaller ones that infiltrate the tissues and organs
Chemical exchange occurs between blood and interstitial fluid
Chemical exchange also occurs between interstitial fluid and body cells
What organisms have a closed circulatory system
Annelids (including earthworms)
Cephalopods (including squid and octopuses)
All vertebrates
What is the pump in a closed circulatory system
Heart
Name of the closed circulatory system in humans
Cardiovascular system
What does the cardiovascular system consist of
Blood, interconnecting vessels arteries, capillaries & veins) & heart
Three types of main blood vessels
Arteries
Veins
Capillaries
What do arteries branch into
Arterioles
What do veins branch into
Venules
What direction do arteries carry blood
Away from heart to the capillaries
What are capillary beds
Networks of capillaries which are the sites of chemical exchange between blood and interstitial fluid
What direction do veins take blood
Towards the heart from the capillaries
How are arteries and veins distinguished
By the direction of blood flow
The two types of vertebrate closed circulatory systems
Single and double
What do single circulatory systems consist of
One atrium and one ventricle
Only one circuit
Organisms with a single circulatory system
Bony fish, rays & sharks
Blood pressure level in single systems
Low
What happens in a double circulatory system
Oxygen poor and oxygen rich blood are separately pumped from the left and right sides of the heart
What does a double circulatory system comprise of
3-4 heart chambers
Has 2 loops
Blood pressure level in double circulatory systems
Higher blood pressure than single
Organisms with a double circulation
Amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals.
Single circulation system in fish
Deoxygenated Blood is pumped out of the ventricle
Travels up artery to the gill capillaries where it picks up oxygen
Oxygenated blood travels to the body capillaries where the oxygen is removed
Blood returns to the heart via a vein
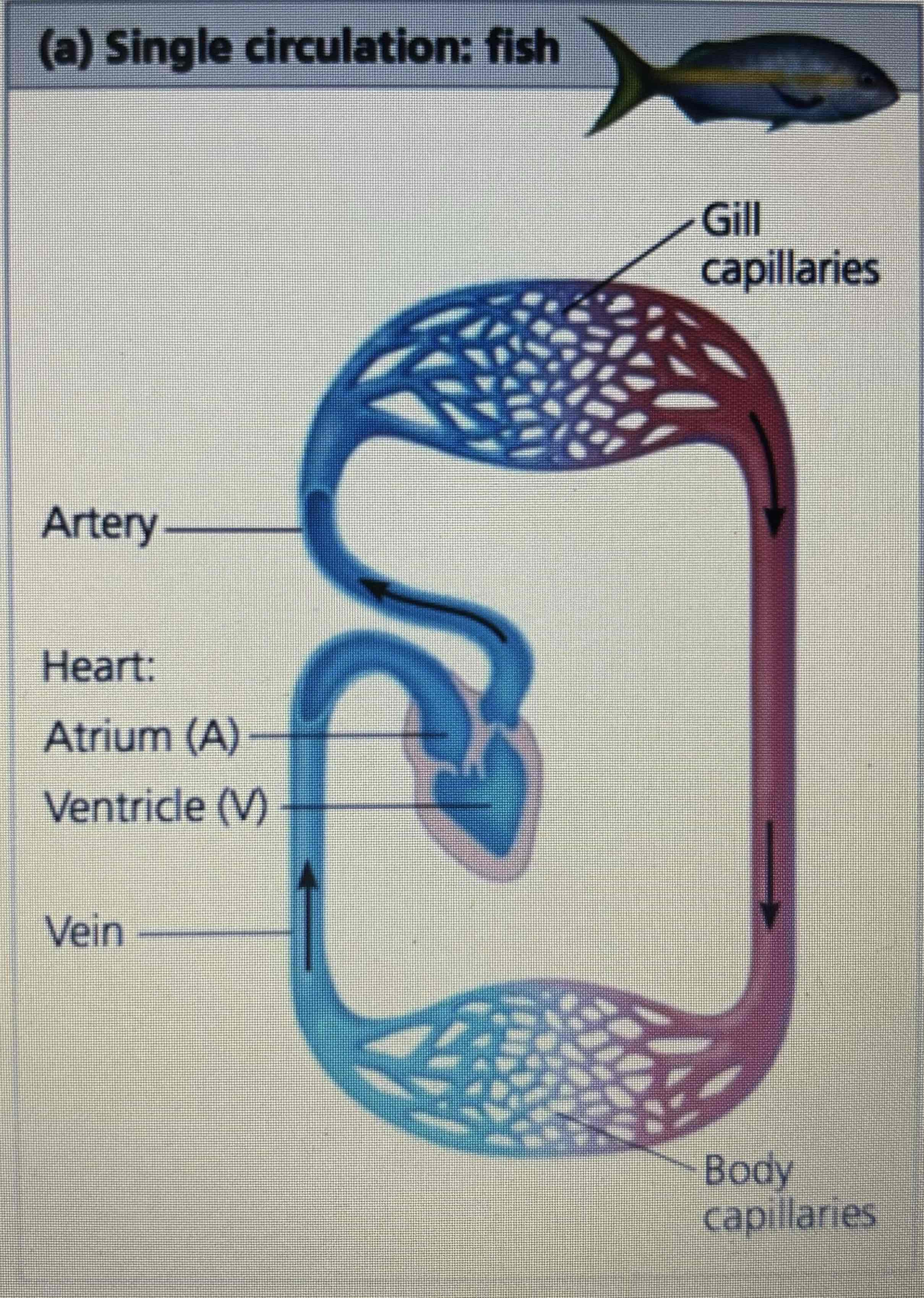
How many heart chambers do bony fish, rays & sharks have
2: one atrium & one ventricle
What systems are 'in series ‘ within fish circulation
Gill and systemic capillaries
When does blood reach the tissues in fish
After first passing through the gills
Pressure of blood flow in systemic part of fish circulation
Low pressure ( lost at gill capillary)
Ectothermic
Regulate temperature via environmental heat sources
What is blood pressure in the artery of a fish like
High
Where is the high blood pressure lost in a fish
The gill capillaries
Type of circulation in amphibians
Double
How many heart chambers do amphibians have
3: 2 atria and one ventricle
Amphibian circulation
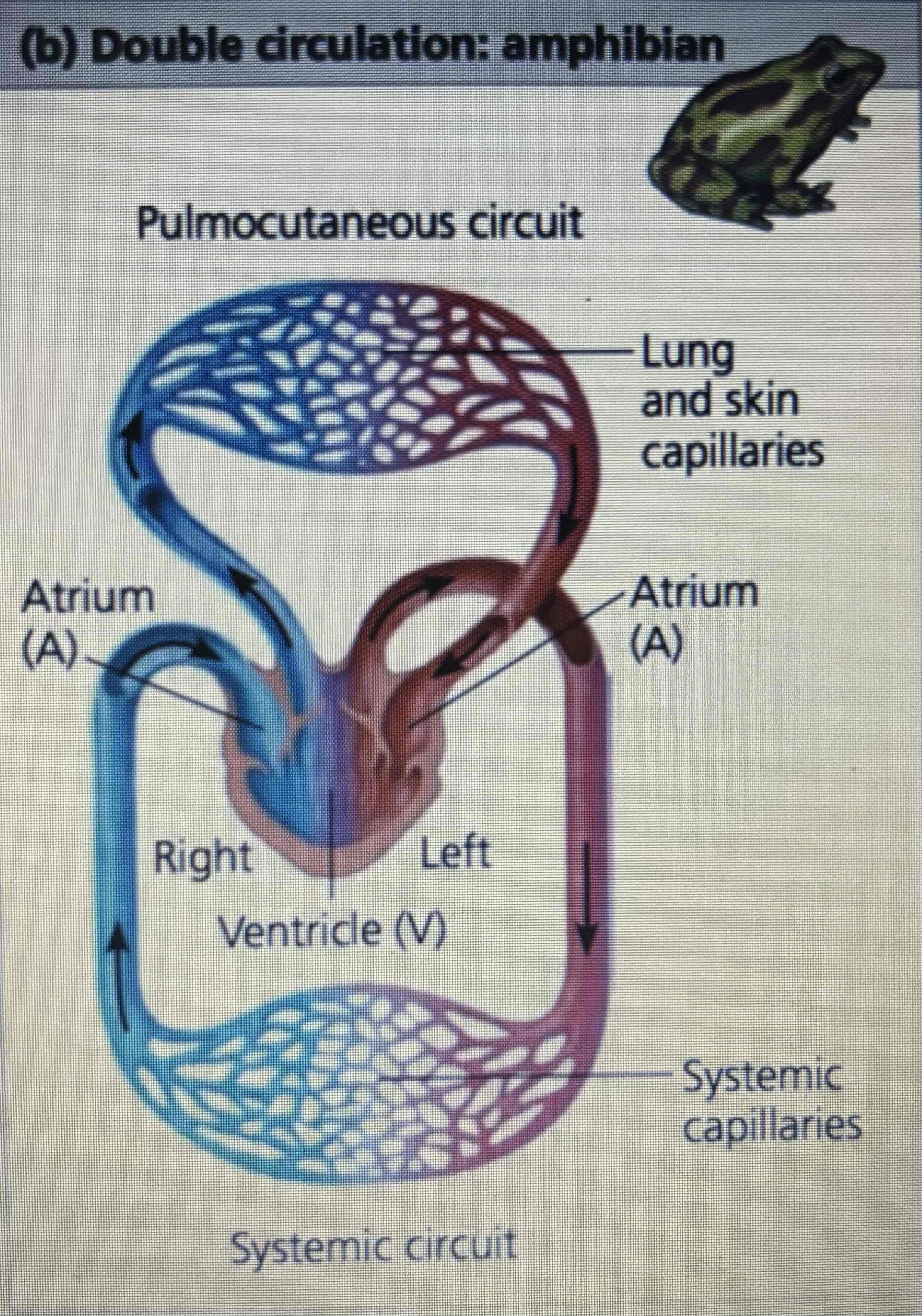
Oxygen poor blood flows through what kind of circuit
Pulmocutaneous circuit to pick up oxygen
How do amphibians breathe
Through nose/mouth and skin
Amphibian circulation blood flow
Ventricle → artery → lung & skin capillaries → vein → ventricle → left atrium → systemic capillaries → right atrium
What does the ridge in the ventricle of amphibians do
Diverts majority of the oxygen-rich blood into the systemic circuit (bottom) & most of the oxygen poor blood into the pulmocutaneous circuit (top)
Is blood in the ventricle of an amphibian oxygenated
There is some mixing of oxygenated & deoxygenated
When do amphibians breathe via the skin
Blood flow to the lungs is nearly shut off when underwater
Type of circulation in reptiles
Double
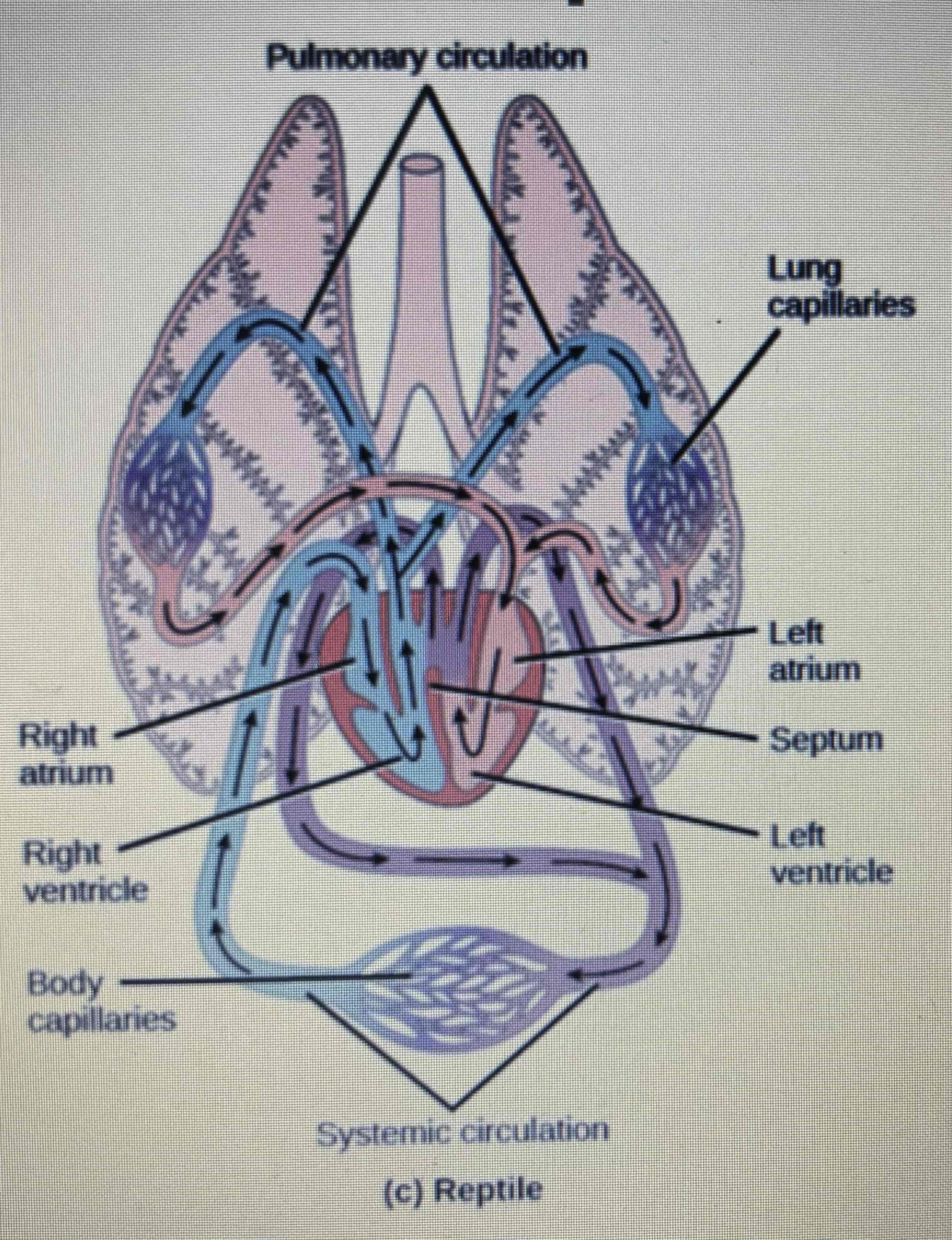
How many heart chambers do reptiles have
2 atria and one ventricle (except from crocodilians which have 2 atria & 2 ventricles)
Do reptiles have a septum
An incomplete septum
How many aortas do reptiles have
2
Blood flow in reptiles
Left ventricle side → aorta → body capillaries (systemic circulation) → right atrium → right ventricle → lung capillaries (pulmonary circulation) → left atrium
Circulation in mammals & birds
Double
How many heart chambers do mammals & birds have
4: 2 atria & 2 ventricles
What do the left and right sides of the heart in mammals & birds do
left: receives and pumps oxygen rich blood
Right: receives and pumps oxygen poor blood
Blood flow in mammals and birds
Right ventricle → lung capillaries (pulmonary circuit) → left atrium → left ventricle → systemic capillaries (systemic circuit) → right atrium
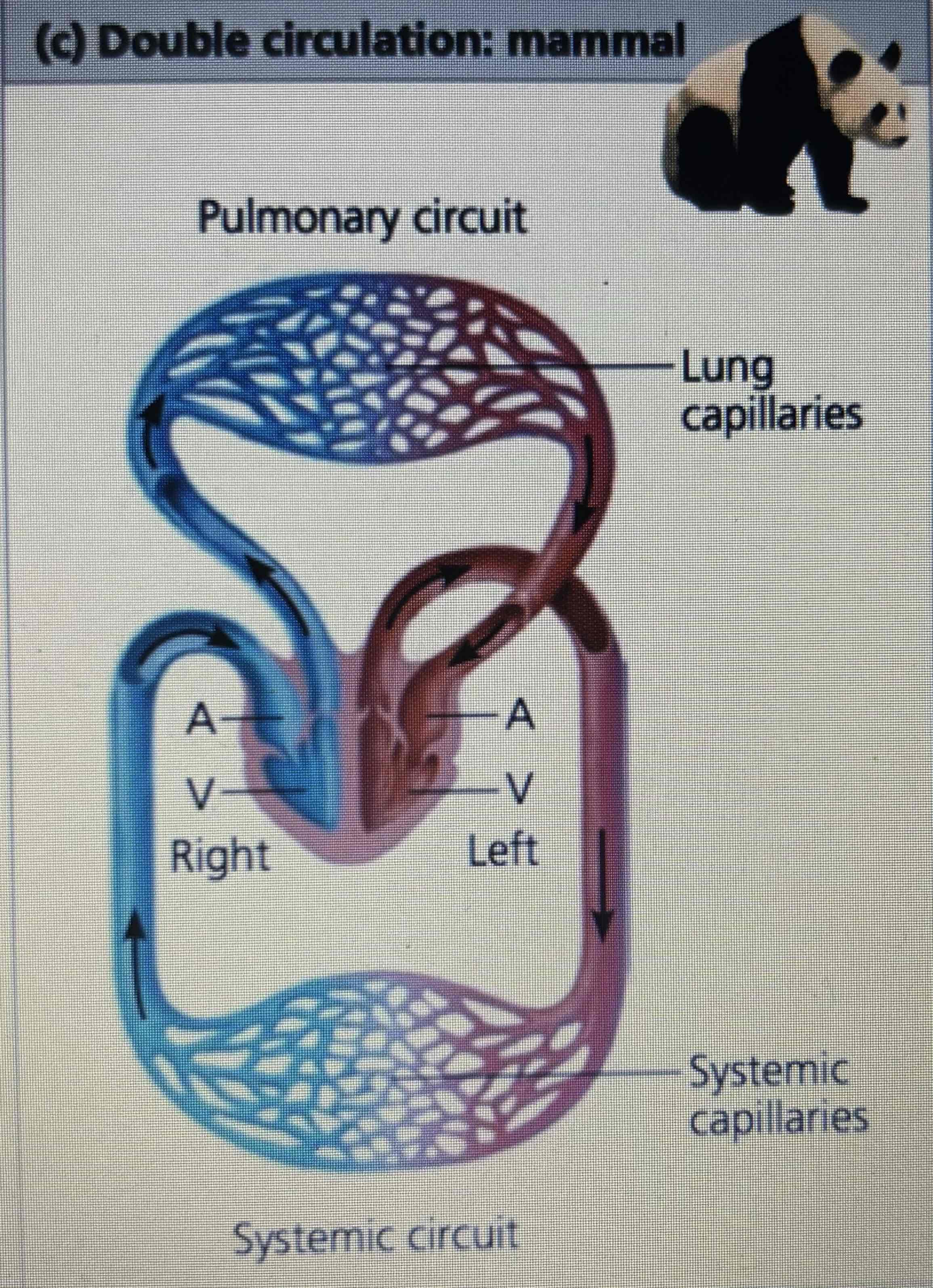
Mammals & birds are endothermic what does this mean
They require more oxygen as they have to generate their own heat
Do mammals and birds have a septum
Yes: the ventricles are separated
What is the human circulatory system composed of
Four contracting chambers and 2 loops of blood vessels
2 types of circulation systems in humans
Pulmonary and systemic
What are the blood distribution percentages in humans
Heart = 7%
Pulmonary circulation = 9%
Systemic circulation = 84%
Blood distribution in the systemic circulation
Arterioles and capillaries = 7%
Arteries = 13%
Veins, venues and venous sinuses = 64%
Structure and function of human atria
Have very thin walls
Collect the blood that is returning to heart and allow it to trickle down into the ventricles
Structure and function of human ventricles
Thicker wall
Contract more forcefully
Right one pumps blood to the pulmonary circulation
Left one pumps blood to the systemic circulation so has a higher pressure and thicker muscular wall than right
The cardiac cycle
The rhythmic cycle of heart contractions and relaxing
Name of the contracting phase of the cardiac cycle
Systole
Right atrium
Receives deoxygenated blood from the body (systemic circulation)
Right ventricle
Pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs via the pulmonary arteries (pulmonary circulation)
Left atrium
Receives oxygenated blood from pulmonary veins
Left ventricle
Pumps oxygenated blood to the body via the aorta
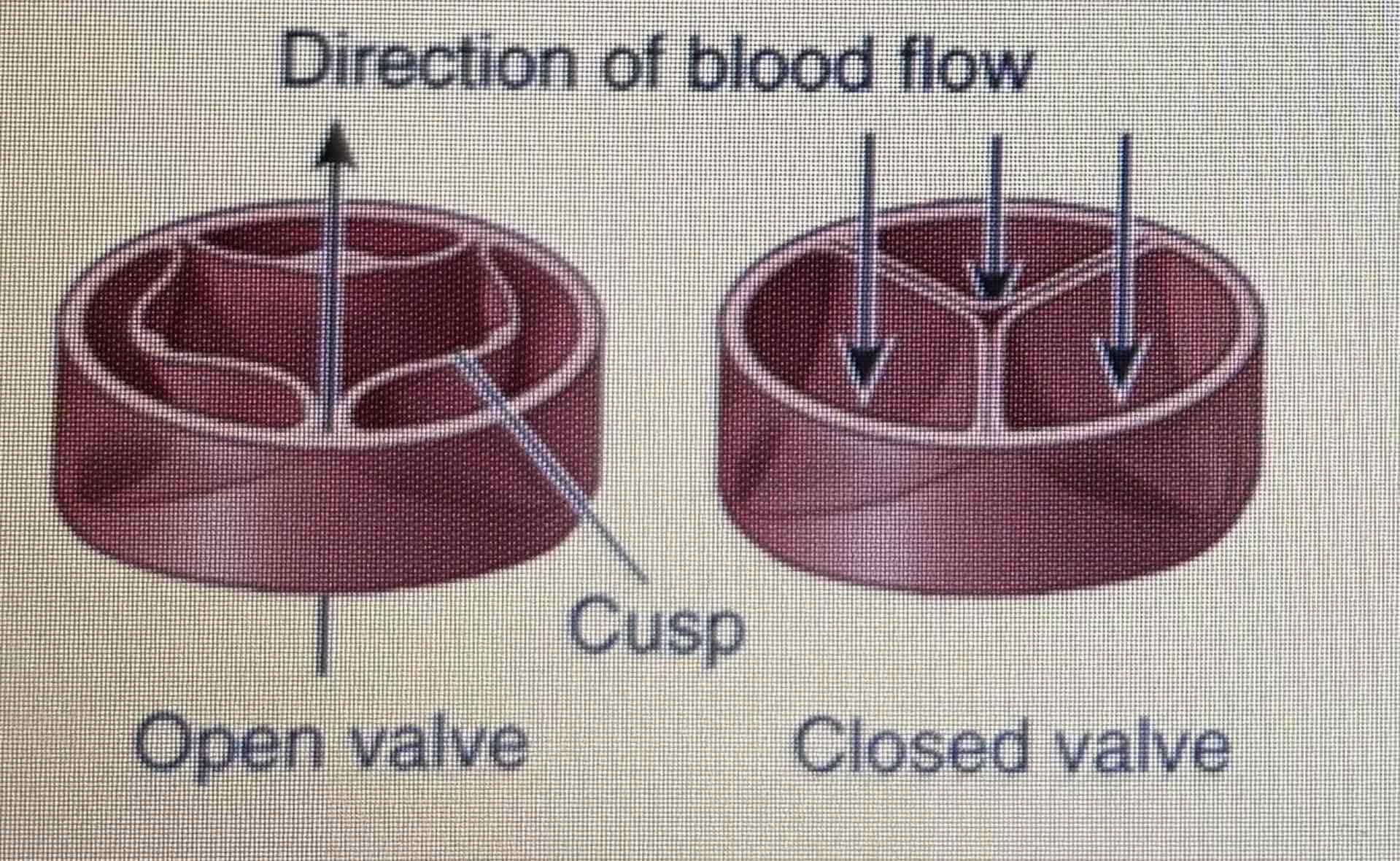
Function of valves
Ensures blood flows in the correct direction by preventing the backflow
What causes the lub- dub sound on a stethoscope
Closure of valves
What is a heart murmur
Extra sounds on a stethoscope (e.g. The backflow of blood through a defective valve)
The atrioventricular valves
Tricuspid valve: between right atrium and ventricle
Mitral valve: between left atrium and ventricle
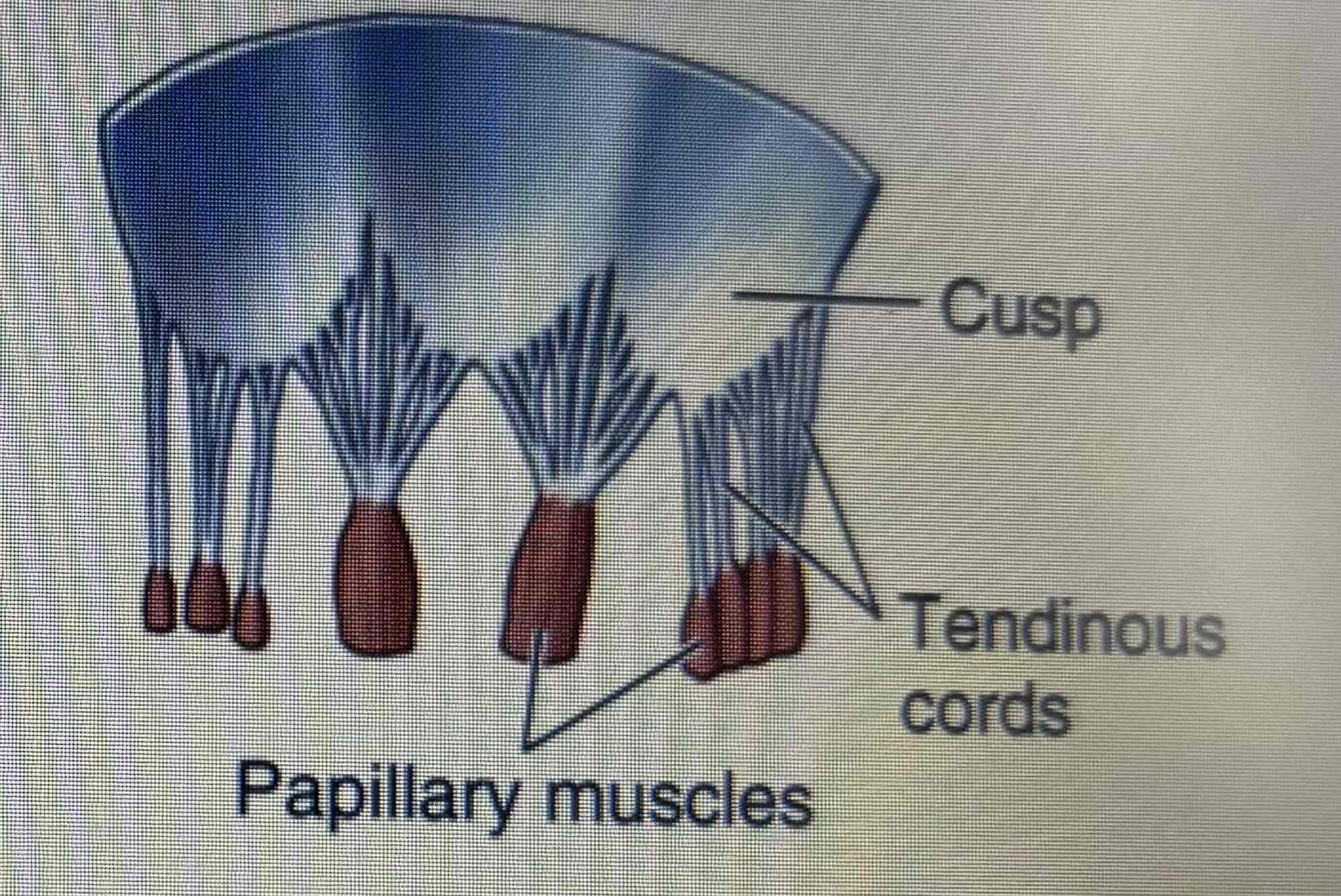
Semilunar valves
Aortic: between left ventricle and aorta
Pulmonary: between right ventricle and pulmonary valve