Chemistry- Semester 2 Exam 3 Review
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
149 Terms
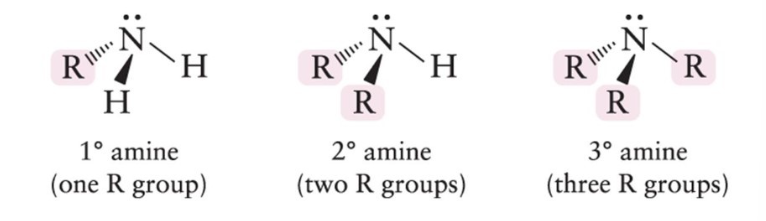
Amine
Nitrogen attached to hydrogen and R groups.
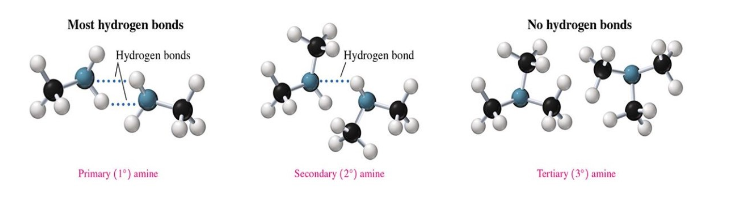
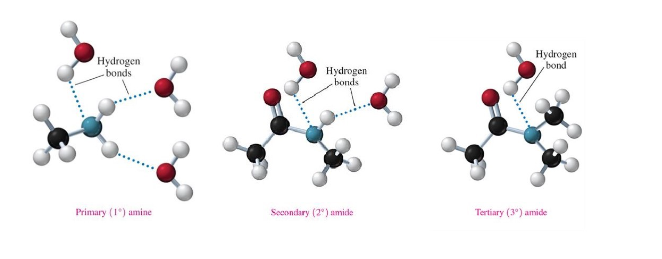
Hydrogen Bonding of Amines
primary and secondary can form hydrogen bonds with themselves and with water molecules.
tertiary amines lack an N-H bond, so they cannot hydrogen bond with themselves, but they can hydrogen bond with water.
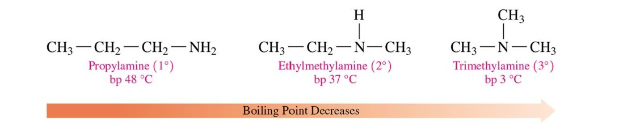
Boiling Points of Amines
primary amines and secondary amines have higher boiling points than tertiary amines of similar molecular mass (decreases from primary to secondary to tertiary)
larger amines (longer carbon chains) have higher boiling points
Solubility of Amines
insoluble with 4+ carbons
nonpolar hydrocarbon chains decrease solubility.
Amines are…
weak organic bases- accept protons (H)
accept a proton in water
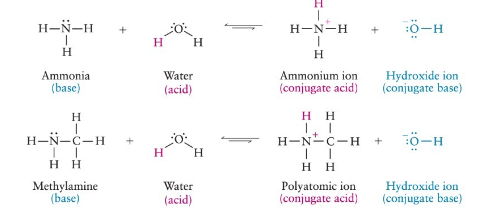
Neutralization of Amines
reaction of amine with acid
forms amine salt (ammonium salt) (N+ and Cl-)
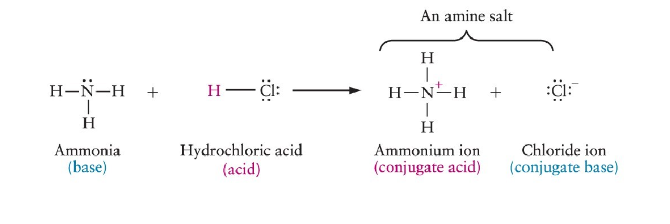
Ammonium Salts
ionic compounds with strong attractions between the positively charged ammonium ion and an anion (chloride)
solids at room temperature, odorless, soluble in water
amines are usually converted to their ammonium salt before being used as drugs
Heterocyclic Amines
cyclic organic compound with a ring of 5 or 6 atoms in which one or two are nitrogen atoms
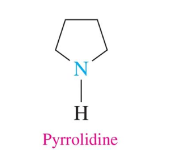
Pyrrolidine
simplest five-atom ring (four C and 1 N)
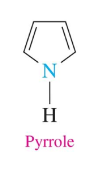
Pyrrole
2 double bonds
Imidazole
2 N atoms and 2 double bonds
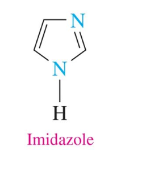
Piperidine
simplest 6 atom ring (5 C, 1 N)
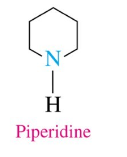
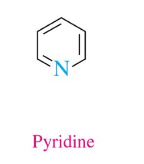
Pyridine
1 N, 3 double bonds
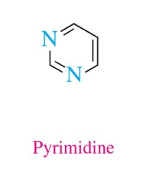
Pyrimidine
2 N, 3 double bonds
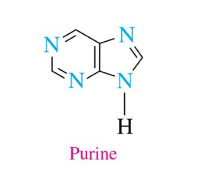
Purine
imidazole + pyrimidine
Neurotransmitters
chemical compound that transmits an impulse from a nerve cell to a target cell.
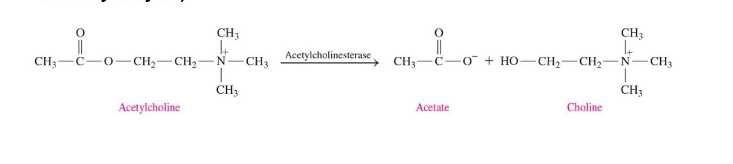
Acetylcholine
communicates between nervous system and muscle
regulates muscle activation (contraction)
degraded by hydrolysis to enable continual nerve transmission
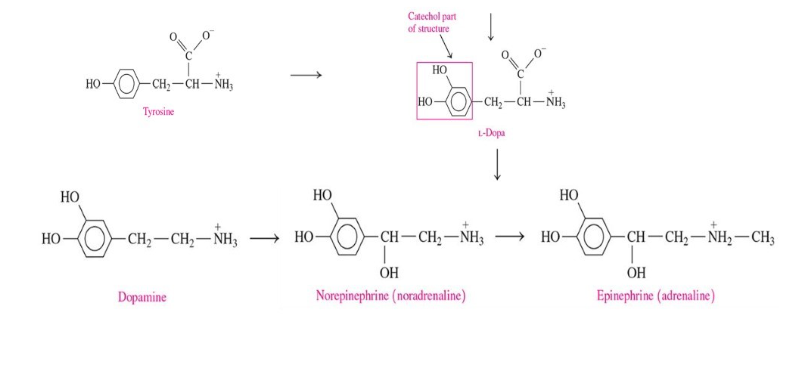
Catecholamines
include dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine
synthesize from amino acid tyrosine after it is converted to L-dopa
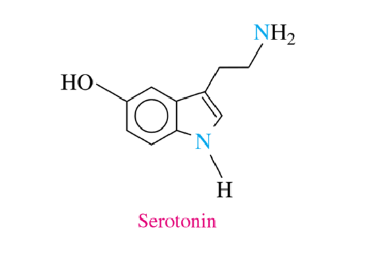
Serotonin
helps us relax, sleep, think rationally
well-being, calmness
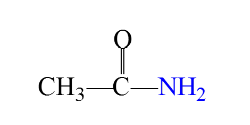
Amides
derivatives of carboxylic acids in which a nitrogen group (NH2) of a primary or secondary amine replaces the hydroxyl (OH) group of carboxylic acids
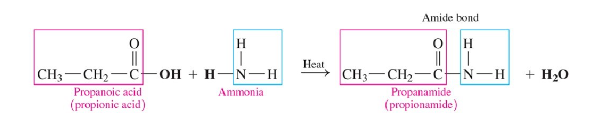
Amidation
carboxylic acid reacts with ammonia or a primary or secondary amine
forms amide
requires heat
tertiary do not react
produces water
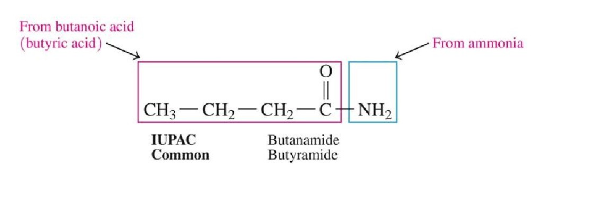
Naming Amides
drop -oic acid (IUPAC) or -ic acid (common) from the carboxylic acid name and add the suffix amide
Boiling Point of Amides
amides are not bases
solid at room temperature
higher boiling points than carboxylic acids
Solubility of Amides
primary amides are more soluble than secondary amides, which are more soluble than tertiary amides
more soluble than amines
vs carboxylic acids- primary and secondary amides are comparable
vs esters/ketones/aldehydes- tertiary are comparable
Amides Hydrolysis
reverse of amidation
water and an acid or a base split an amide
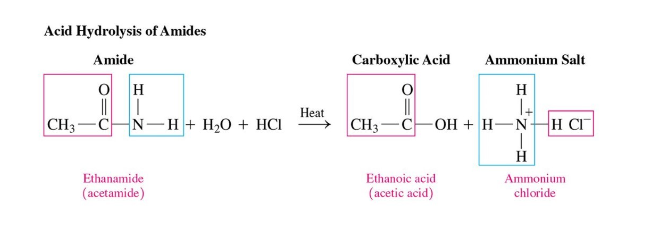
Amides Acid Hydrolysis
requires heat + acid
produces a carboxylic acid and an ammonium salt
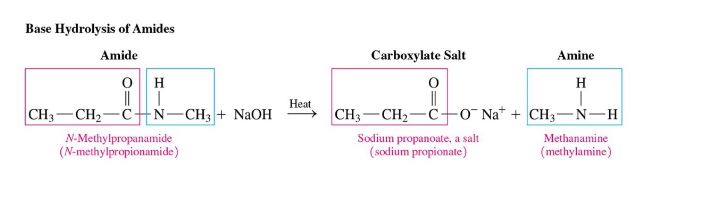
Amides Base Hydrolysis
requires base + heat
produces amine (or ammonia) and carboxylate salt
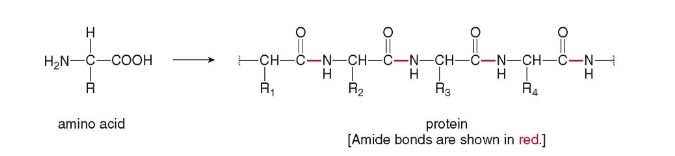
Proteins
biomolecular polymers that contain many amide bonds, formed by joining amino acids.
Structural Proteins
provide structural components
collagen- in tendons and cartilage
keratin- in hair, skin, wool, and nails
Contractile Proteins
make muscles move
myosin and actin contract muscle fibers
Transport Proteins
carry essential substances throughout the body
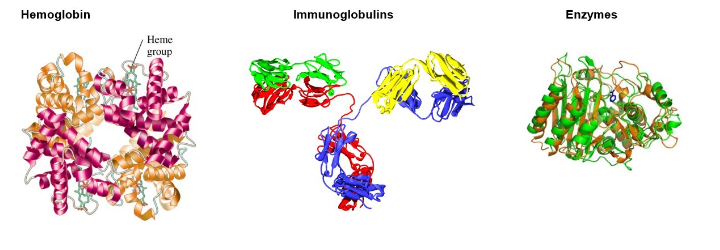
hemoglobin transports oxygen
lipoproteins transport lipids
Storage Proteins
store nutrients
casein stores protein in milk
ferritin stores iron in the spleen and liver
Hormone Proteins
regulate body metabolism and the nervous system
insulin regulates blood glucose levels
growth hormone regulates body growth
Enzyme Proteins
catalyze biochemical reactions in cells
sucrase catalyzes hydrolysis of sucrose
trypsin catalyzes hydrolysis of proteins
Protection Proteins
recognize and destroy foreign substances
immunoglobulins stimulate immune responses
Amino Acid Structure
contain an amino group (NH2), a carboxyl group (COOH), and a R group
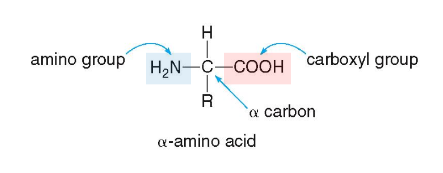
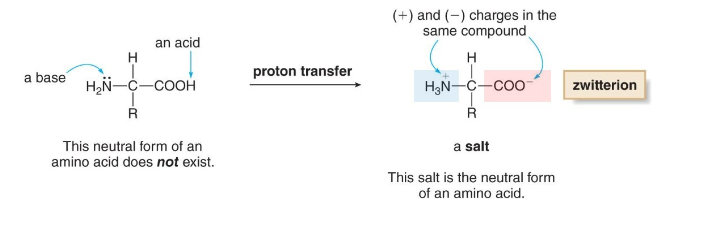
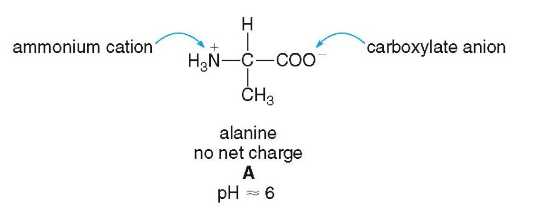
Zwitterions
neutral form of an amino acid
at 7.4 pH
protonated amino
deprotonated carboxyl
Deprotonation
loss of a proton (H)
Protonation
gain of a proton (H)
Nonpolar amino acids
contain alkyl groups, aromatic, benzene, many carbon atoms
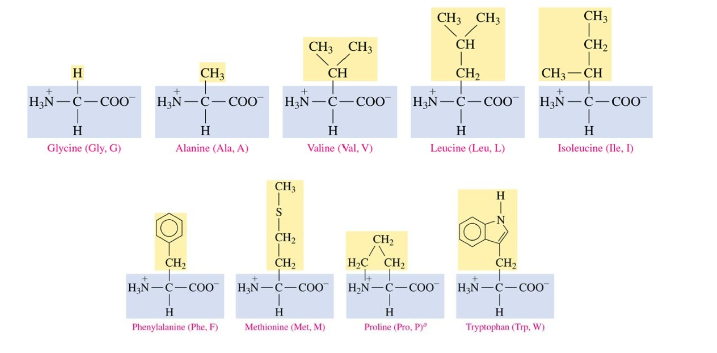
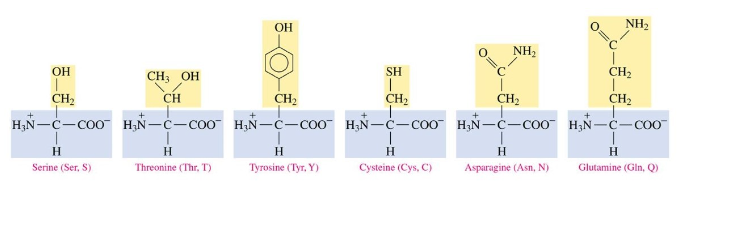
Polar amino acids
contain OH, SH, and amides
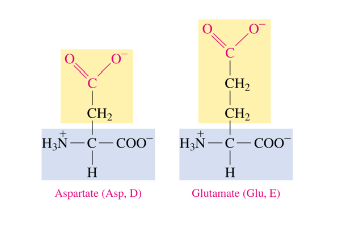
Polar Acidic Amino Acids
have a carboxylic acid side chain
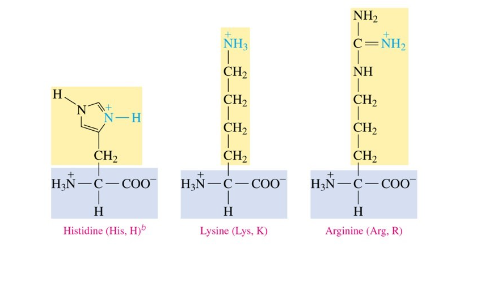
Polar Basic Amino Acids
have an amine group
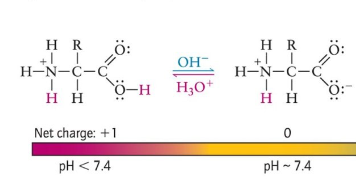
If pH decreases…
carboxylic acid group gains a proton
+ net charge
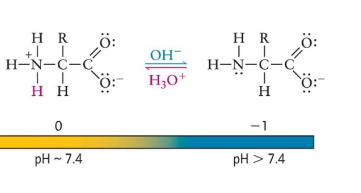
if pH increases…
a proton is lost from the amino group
- net charge
deprotonates
An amino acid exists as a…
neutrally charged zwitterion, at 7.4 pH (neutral pH)
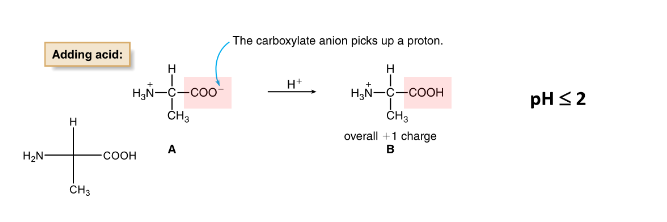
Amino Acids- Acid Behavior
when pH is low (or acidic), the carboxylate anion gains a proton
+ 1 charge
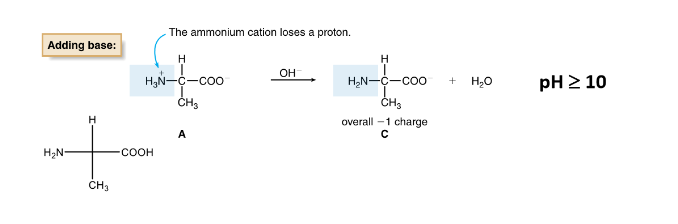
Amino Acids- Base Behavior
when pH is high (or basic), the ammonium cation loses a proton
-1 charge
Acid Behavior of Side Chains
polar acidic amino acids have a deprotonated carboxylic acid side chain at 7.4 pH
loses H
COO-
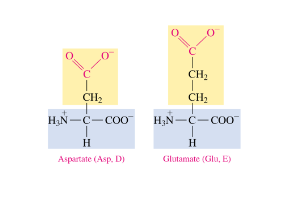
Base Behavior of Side Chains
polar basic amino acids have a protonated basic side chains at 7.4 pH
NH+
N-terminus
start of a protein that contains the amine group
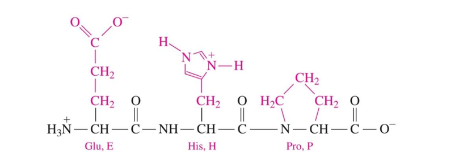
Peptide Bond
an amide bond that forms when the COO- group of one amino acid reacts with the NH3+ group of the next amino acid
C-terminus
end of the protein that contains the carboxylic acid group
Naming Peptides
begin with name of N-terminal amino acid
change -ine and -ate endings to -yl
c-terminal amino acid retains complete name
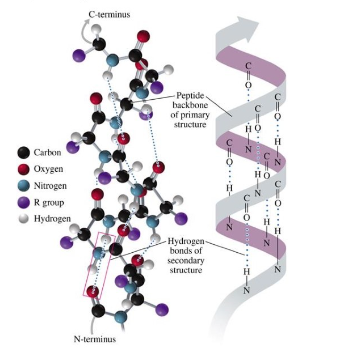
Primary Structure
the sequence of amino acids held together by peptide bonds
Secondary Structure
describes any regular folding patterns in the polypeptide backbone
stabilized by hydrogen bonds between N-H of amide from one part of the protein and the C=O from carboxylic acid in another part
alpha helix + beta sheet
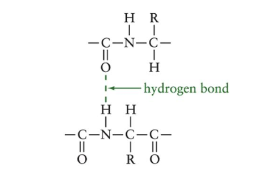
Alpha Helix
hydrogen bonds form between the oxygen of C=O group and hydrogen of N-H groups of amide bonds in the next turn of the helix
R groups extend out of the helix
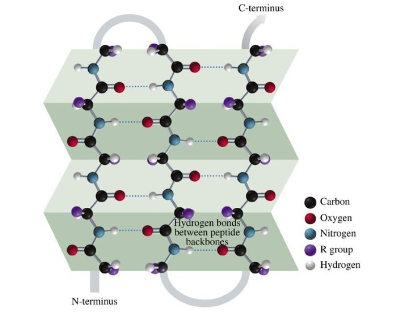
Beta Sheet
two or more sections of a polypeptide folded in a pleated pattern
hydrogen bonds between amide N-H of one strand and the C=O of another
R groups project above and below the sheet
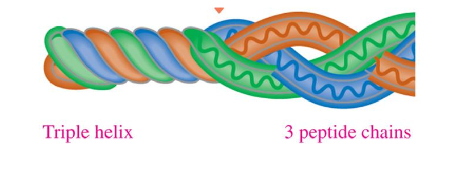
Collagen Structure
triple helix
three polypeptide chains woven together
hydrogen bonds holds 3 together
adds strength
Tertiary Structure
folding of a single polypeptide as a result of interactions between
side chains in the polypeptide
side chains and the surrounding environment
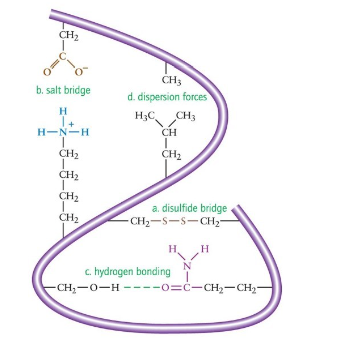
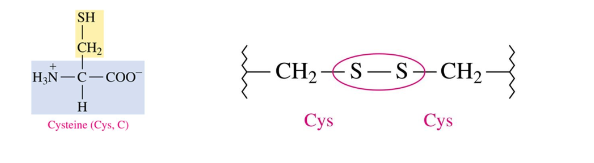
Tertiary Structure: Disulfide Bonds
covalent bonds that form between -SH groups of cysteine
strongest type of interaction between two side chains
Tertiary Structure: Salt Bridges
ionic attractions between ionized R groups of polar basic and polar acidic amino acids
form between the carboxylate ion of an acidic side chain and the cation of a basic side chain
very strong
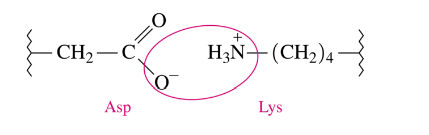
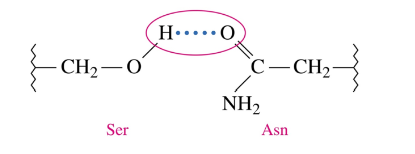
Tertiary Structure: Hydrogen Bonds
form between the H of a polar R group and the O or N of another polar amino acid
weaker than disulfide bonds and salt bridges, but contribute to overall tertiary structure because there are many more hydrogen bonds
Tertiary Structure: Hydrophobic Interactions
dispersion forces between two nonpolar R groups
amino acids with nonpolar r groups are pushed away from the aqueous environment to form a hydrophobic center at the protein’s interior
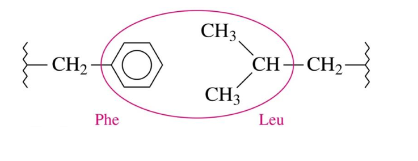
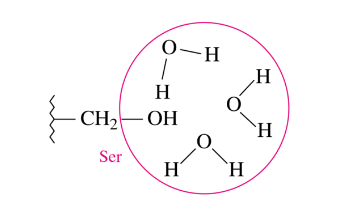
Tertiary Structure: Hydrophilic Interactions
occur between external aqueous environment and the R-groups of polar amino acid residues that are pulled to the outer surface of most proteins
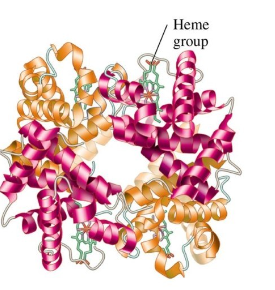
Quaternary Structure
biologically active proteins with two or more polypeptide chains or subunits
not all proteins have a quaternary structure
Fibrous
insoluble in water

Globular
water soluble
complex, spherical shapes
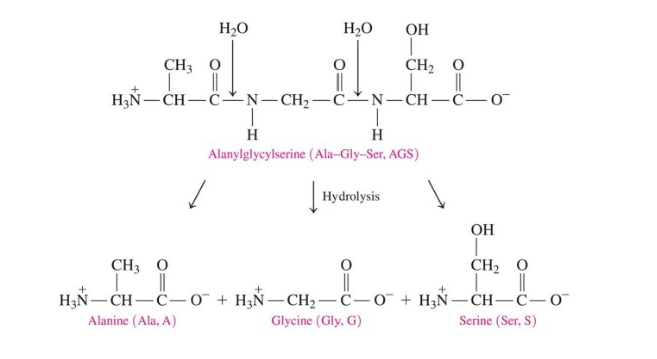
Protein Hydrolysis
breaks the amide/peptide bond
adds water
occurs in the stomach when enzymes catalyze hydrolysis of proteins to give amino acids
breaks up primary structure by breaking peptide bonds
Denaturation of Proteins
occurs when changes disrupt the ineractions among residues that stabilize the 2, 3, 4 structures
does not affect amind bond in primary structure
causes protein to no longer be biologically active
Denaturation- Heat
denatured above 50 degrees C
disrupts hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions among nonpolar residues
Denaturation: pH
breaks hydrogen bonds
disrupts ionic and salt bridges
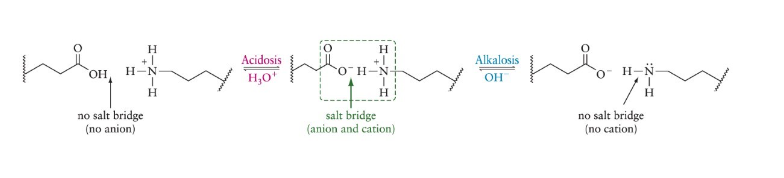
Acidosis
a proton is added to carboxyl, disrupting salt bridge
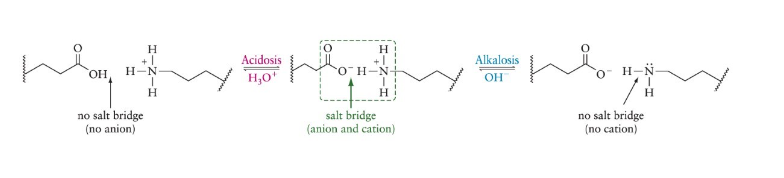
Alkalosis
a proton is removed from the amine, disrupting the salt bridge
Denaturation: Organic Compounds
isopropyl alcohol, ethanol
disrupts hydrogen bonding
used as disinfectants
Denaturation: Heavy Metal Ions
Ag+, Pb2+. Hg2+ denature proteins by forming bonds with ionic residues or reacting with disulfide bonds
Denaturation: Agitation/Mechanical
mechanical agitation stretches polypeptide chains until the stabilizing interactions are disrupted.
hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions disrupted
Enzymes
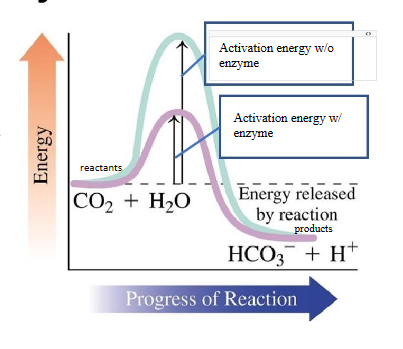
biological catalysts
increases rate of reaction by lowering activation energy required to start the reaction
are globular proteins
recognizes and binds a small group of reacting molecules (substrates)
have a tertiary sturcture that includes a region called the active site where substrates bind to create a chemical reaction
Active Sites
contain specific amino acid residues that interact with functional groups of the substrate to form hydrogen bonds, salt bridges, and hydrophobic interactions
Absolute Enzyme
catalyzes one type of reaction for one substrate
urease catalyzes only the hydrolysis of urea
Group Enzyme
catalyzes one type of reaction for similar substances
hexokinase adds a phosphate group to hexoses
Linkage Enzyme
catalyzes one type of reaction for a specific type of bond
chymotrypsin catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds
Enzyme-Catalyzed Reactions
combination of an enzyme and substrate forms an enzyme substrate complex
the Es provides an alternative pathway for the reaction with lower activation energy
within the active site, amino acid R groups catalyze the reaction to form an enzyme product complex
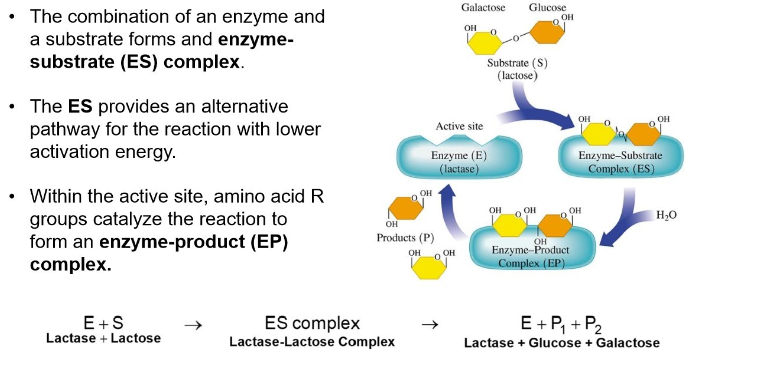
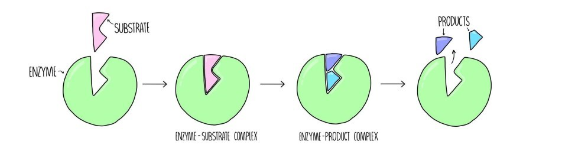
Lock-and-Key Model
active site has a rigid, nonflexible shape
enzyme binds only substrates that exactly fit the active site
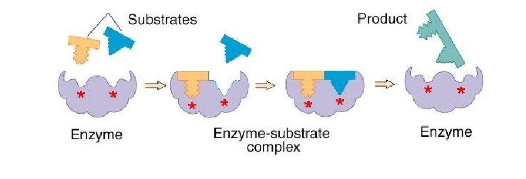
Induced-Fit Model
enzyme structure is flexible and adjusts to the shape of the active site in order to bind the substrate
shape changes improve catalysis during reaction
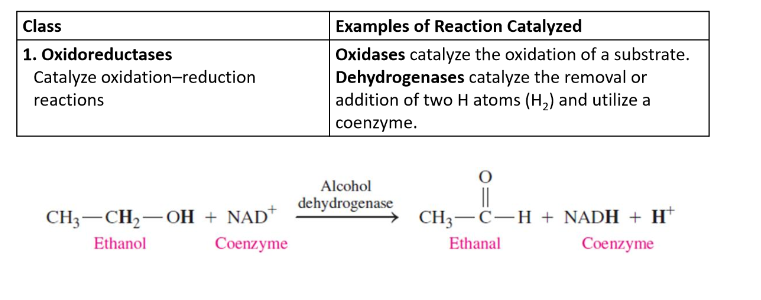
Classification of Enzymes
the name of an enzyme usually ends in -ase and identifies the reaction substrate
describes function of enzyme
can be common names
Oxidoreductases
catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions
gain of O, loss of H
Transferases
catalyze the transfer of a functional group between two compounds
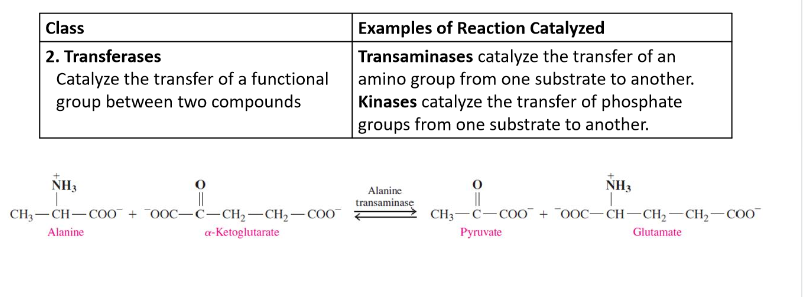
Hydrolases
catalyze hydrolysis (addition of water) reactions
add water to split a compound into two products
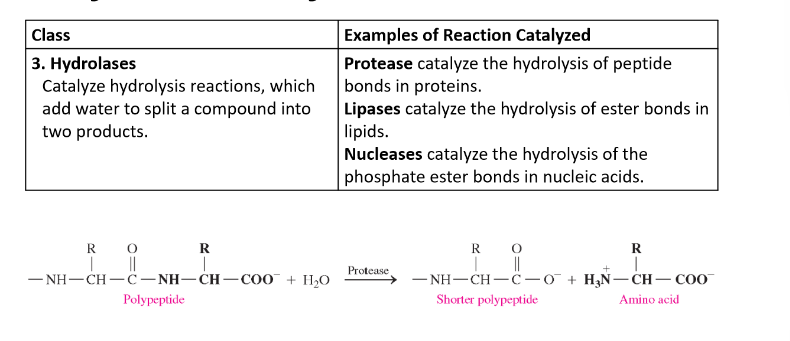
Lyases
catalyze the addition or removal of a group (without water)
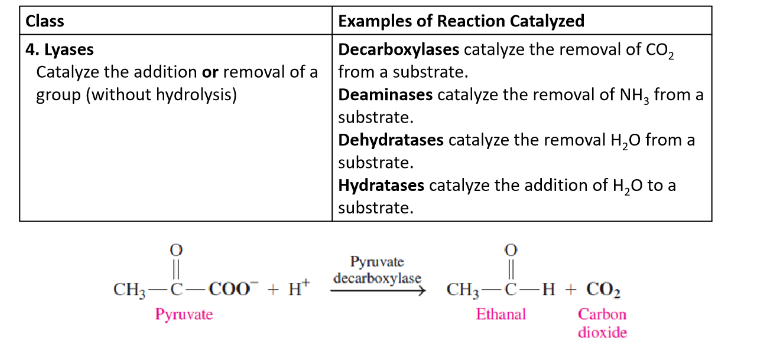
Isomerases
catalyze the rearrangement (isomerization) of atoms within a substrate
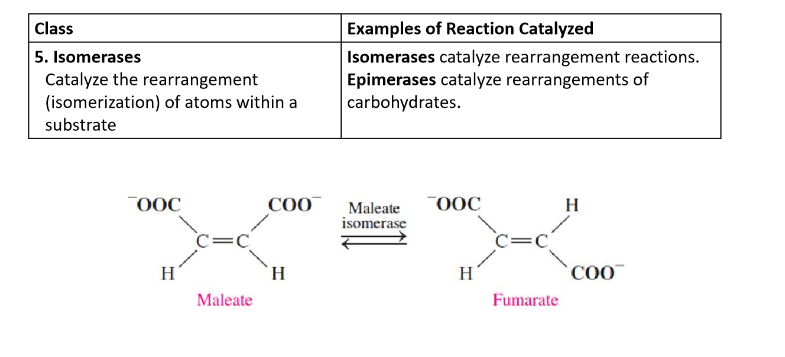
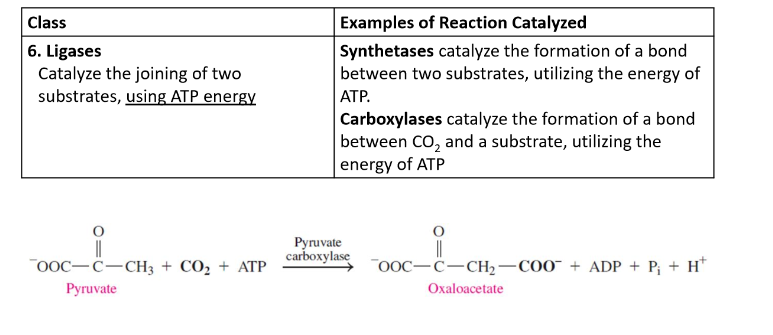
Ligases
catalyze the joining of two substrates, using ATP
pH Dependence of Enzymes
enzymes are most active at an optimal pH, where proper tertiary structure of the protein is maintained
enzymes lose activity in a too low or too high pH
changes in pH alter the acidic and basic side chains
acidosis (making more acidic) and alkalosis (making more basic) are detrimental to the function of enzymes- can lead to denaturation
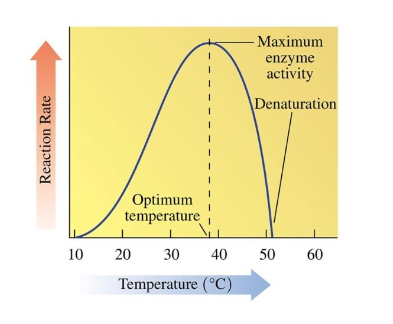
Temperature Dependence of Enzymes
the optimal temperature for most proteins is 37 C
enzymes show little activity at low temperatures
denaturation occurs at high temperature and enzyme function is lost
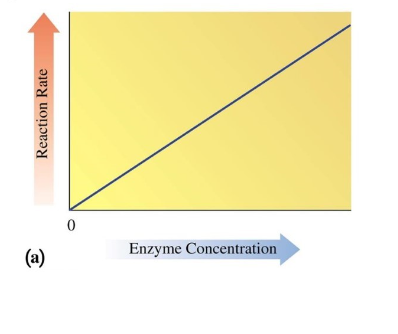
Enzyme Concentration on Activity
increasing enzyme concentration increases the rate of reaction
binds more substrate with enzyme (since there is more enzyme)
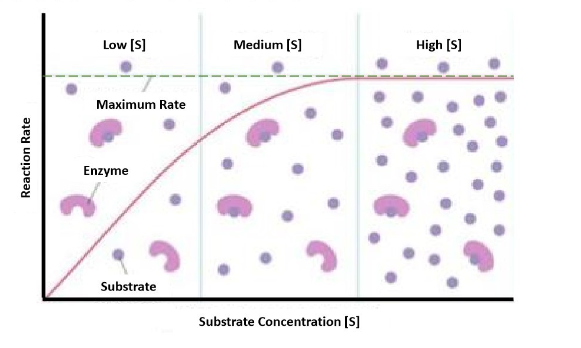
Substrate Concentration on Activity
increasing substrate concentration increases rate of reaction
eventually saturates an enzyme with substrate to give maximum activity
run out of enzymes for substrates to bind to
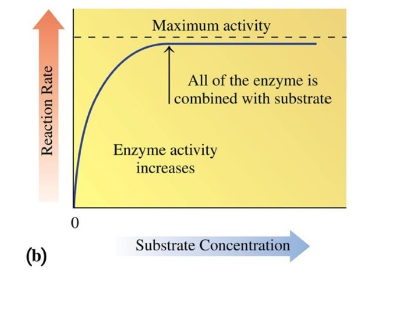
Regulation of Enzyme Activity
rates of enzyme-catalyzed reactions are controlled by regulatory enzymes that
increases the reaction rate when more of a particular substance is needed
decreases the reaction rate when the substance is not needed
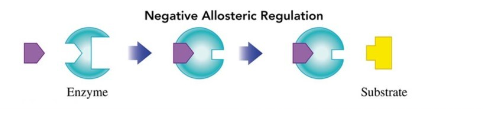
Regulation by Allosteric Enzymes
allosteric sites are sites on the enzyme that is different from the active site
binding to the allosteric site changes the shape of the active site
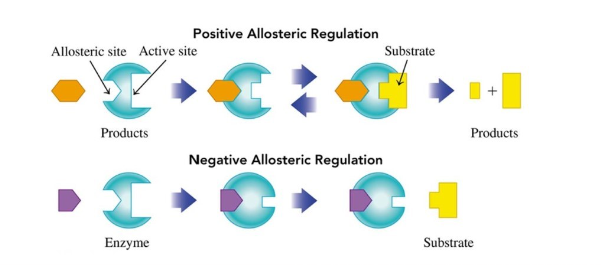
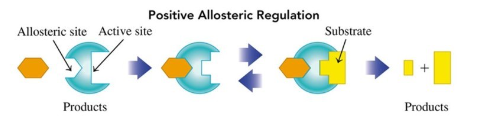
Positive Regulator (allosteric enzymes)
changes the shape of the active site to allow the substrate to bind more effectively
Negative Regulator (allosteric enzymes)
changes the shape of the active site to prevent proper binding of the substrate
decreases rate of reaction