RADIOLOGY QUIZ 4
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
177 Terms
35%
for caries to be visible on radiograph, at least X% of mineral needs to be demineralized
false
T/F these are root caries
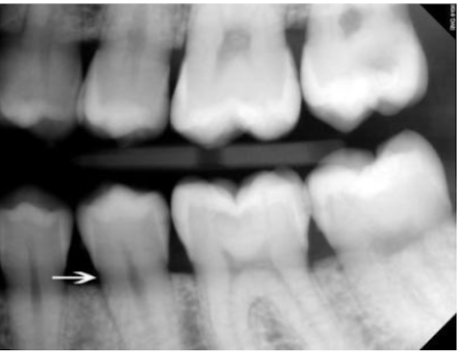
mach band effect
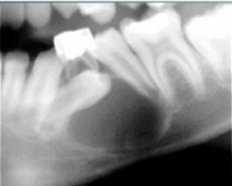
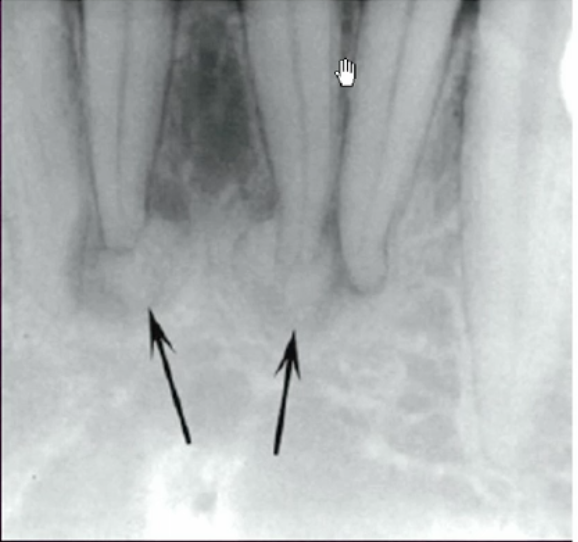
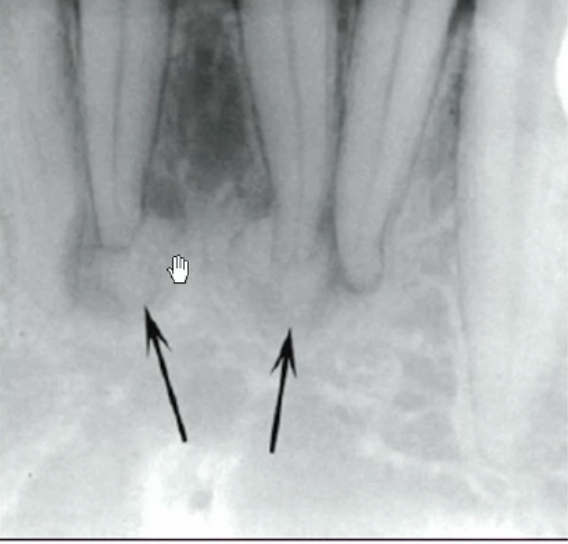
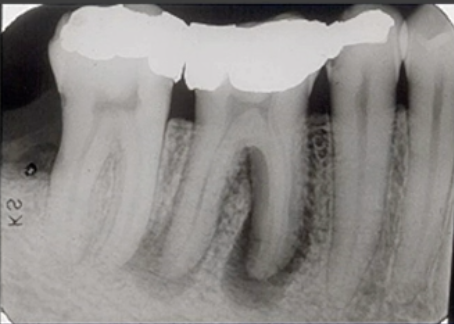
cause of this thin dark line at the root of #13
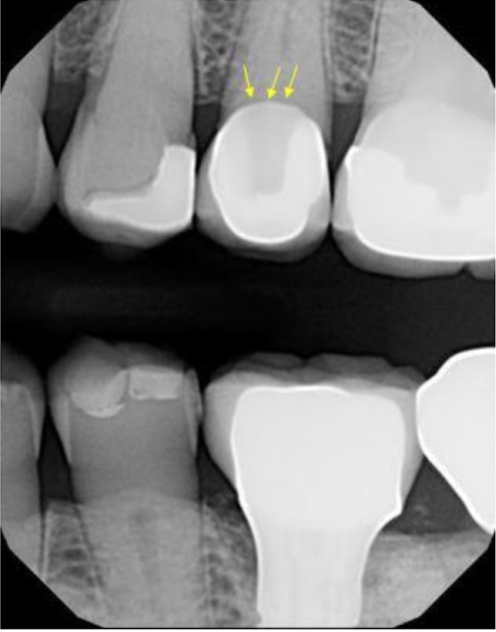
radiolucent composite
most likely cause of this radiolucency
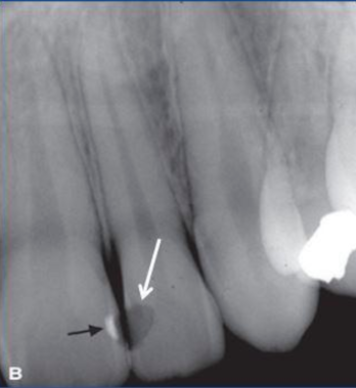
false
T/F one can determine from this periapical if the lesion. is a periapical granuloma or cyst
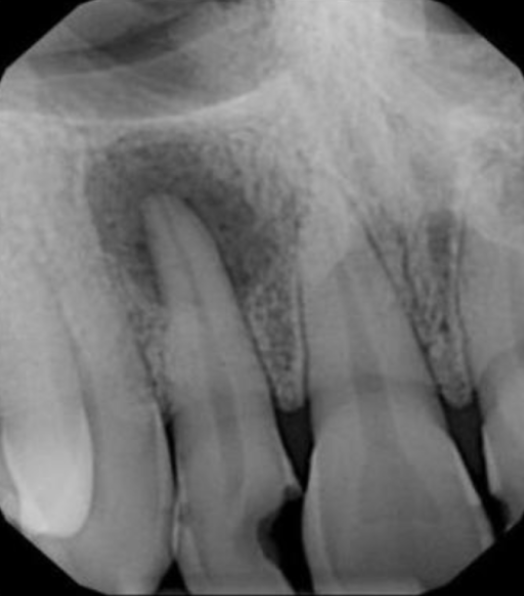
widened PDL, moderately well defined periapical radiolucency
radiographic features of rarefying osteitis
false
T/F vertical bone loss at #19 mesial
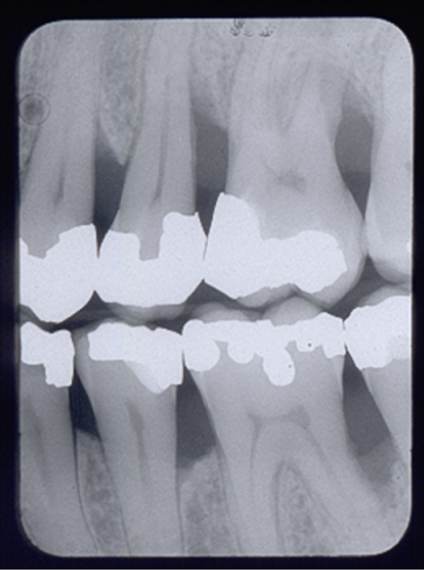
vertical bitewings
best tool to view bone loss in patient with moderate to severe periodontitis (pocket ≥ 6mm)
estimating interproximal bone loss
what are radiographs useful for in periodontal disease
intraoral xray
highest spatial resolution imaging, best for disease involving teeth and supporting structure
CBCT/MDCT
best for evaluating anatomy in multiple dimensions without anatomical superimposition
periapical xray
main image for periapical diagnosis
bitewings
best for interproximal caries
no
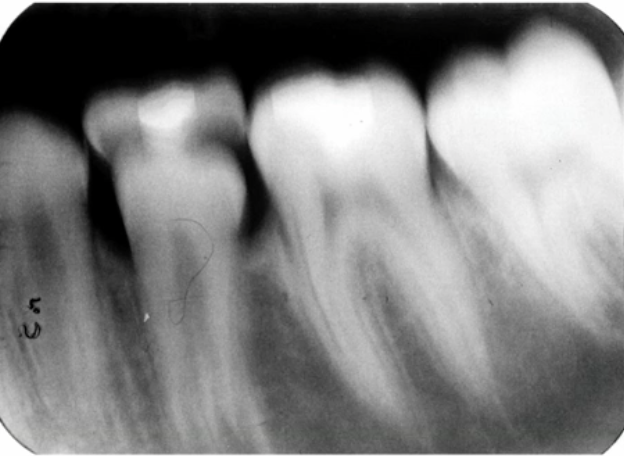
would you consider this image diagnostic?
non-analytic strategy
diagnostic reasoning through deliberate search for features that support the hypothesis
analytical strategy
diagnostic reasoning through step-by-step analysis of features
location, edge, shape/size, internal content, other structures, number (LESION)
analytical strategy for lesion description
epicenter
geometric center of lesion
neural/vascular origin
lesion WITHIN inferior alveolar canal
odontogenic origin
lesion ABOVE inferior alveolar canal
non-odontogenic/osseous origin
lesion BELOW inferior alveolar canal
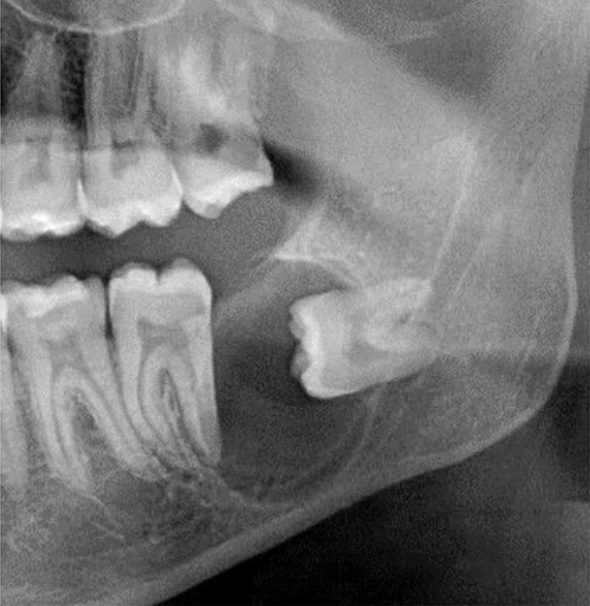
left posterior mandibular pericoronal lesion
how would you descrribe the location on this lesion
poorly defined
how would you describe the border of this lesion
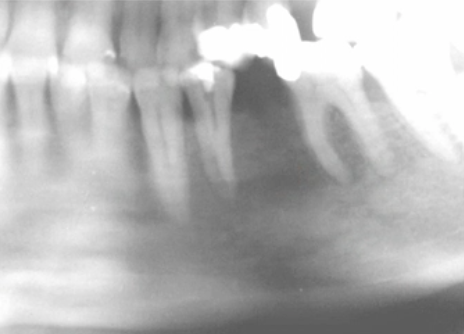
well defined, corticated
how would you describe the border of this image
poorly defined
border that tends to be malignant
corticated
thin, radioopaque line of bone at lesion periphery
sclerotic
well-defined wider more diffuse zone of transition at lesion borders
radiolucent periphery
rim of radiolucency indicating soft tissue, generally with corticated outer border
radiolucent periphery
how would you describe the BORDER of this lesion
invasive
wide zone of transition with few or no trabeculae between periphery and normal bone
blending
poorly defined gradual wide zone of transition
entirely radiopaque
how would you describe the internal structure of this lesion
idiopathic osteosclerosis
most likely diagnosis
well defined mildly sclerotic
how would describe the border of this lesion
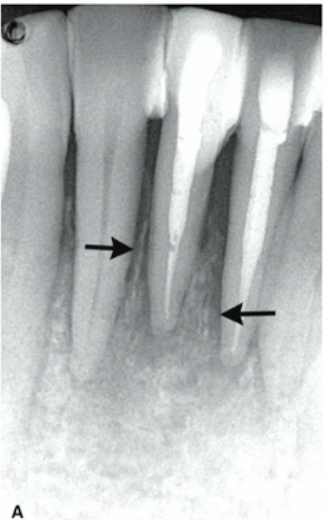
mixed (radiolucent and radiopaque)
how would you describe the internal structure of this lesion
multilocular
lesion with multiple compartments or septations
dystrophic calcification
mineralization in damaged soft tissue
amorphous bone
dense often cortical-like poorly organized bone
rarefaction
decrease in bone density, causing radiolucency
sclerosis
abnormal hardening or thickening of bone, causing radiopacity
benign lesions
tend to have smooth borders of resorption with lesion
malignancies
likely to have thinning or spiked root appearance
pulpal origin
PDL widening with epicenter at apex
periodontal origin
PDL widening with coronal epicenter
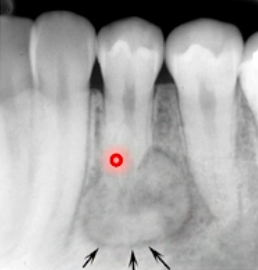
irregular PDL widening
what are the arrows pointing to
closure
visual connection or continuity between sets of elements which do not actually touch each other
class 2 and 3 (interproximal)
radiographs are most helpful for detecting which type of caries
true
T/F CBCT is NOT recommended to be used as a routine method of caries diagnosis
primary
caries on unrestored tooth structure that involves DEJ or EXTENDS through
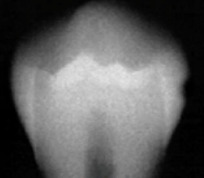
E1
caries classification?
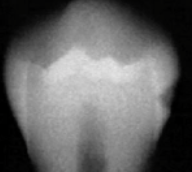
E2
caries classification?
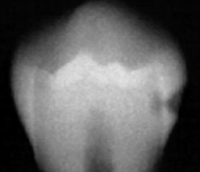
D1
caries classification?
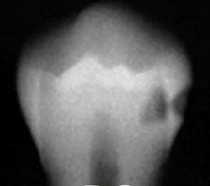
D2
caries classification?
D3
caries classification?
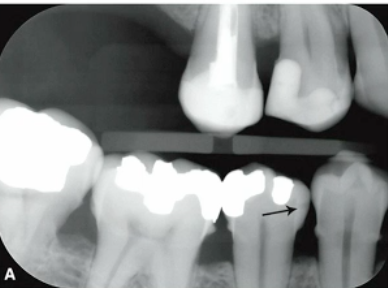
#29 M E1
caries classification?
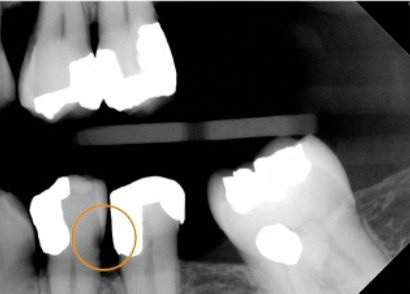
cavitation, D2, or high risk
what justifies surgical management of caries
at contact
susceptible zone for interproximal caries
caries (bone loss and irregular shape)
what is this lesion
incipient
caries that DO NOT extend into DEJ (E1 and E2)
root caries
what is this lesion
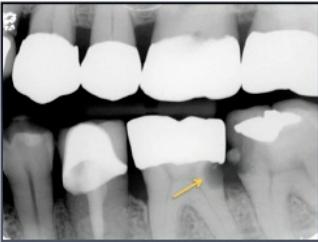
rampant caries
caries with rapid progression and severe widespread involvement
recurrent caries
caries that occur at margins of existing restorations
residual caries
areas of demineralization that remain after incomplete removal of caries
recurrent caries
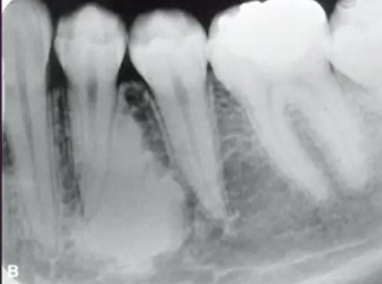
what are these lesions
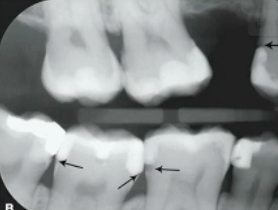
recurrent caries
what is the dark shadow the arrow is pointing at
cervical burnout
most common cause of false positive caries diagnosis
cervical burnout
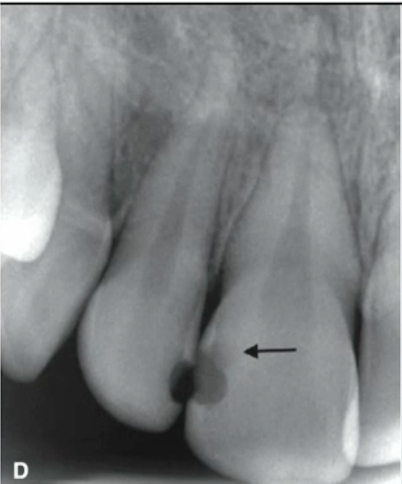
what are these lesions
caries
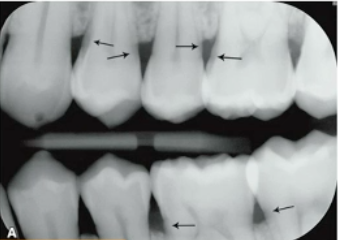
what are these lesions?
mach band effect
An optical illusion that creates the perception of increased contrast at the boundaries of two different shades
false
T/F demineralization on xray can determine if caries are active
extent in buccolingual plane (how wide the caries are)
what determines the degree of radiolucency of caries
superimposition
why might caries depth relative to the pulp be inaccurate?
greater
true depth of lesion is often ___ than visible on image
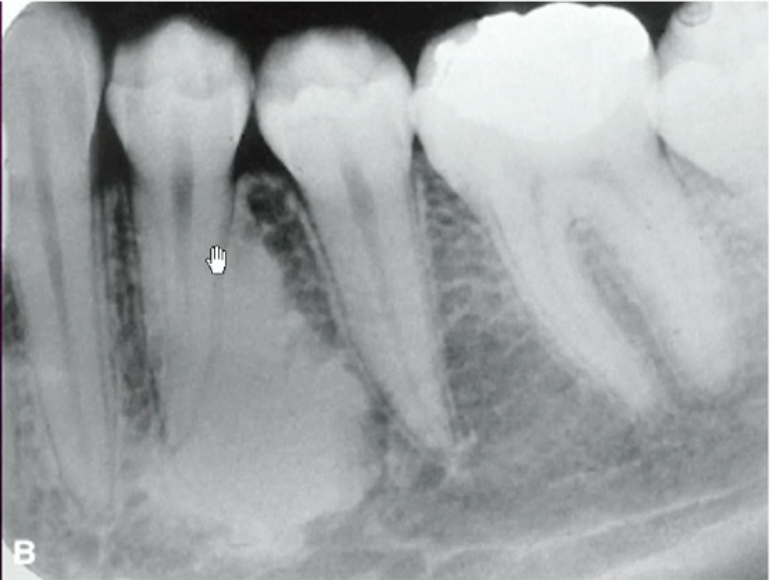
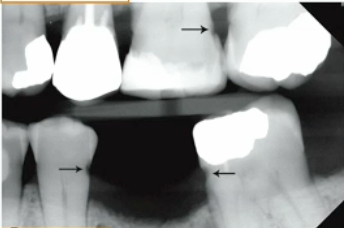
angulation (restoration superimposition)
why can recurrent caries be seen on image A but not image B
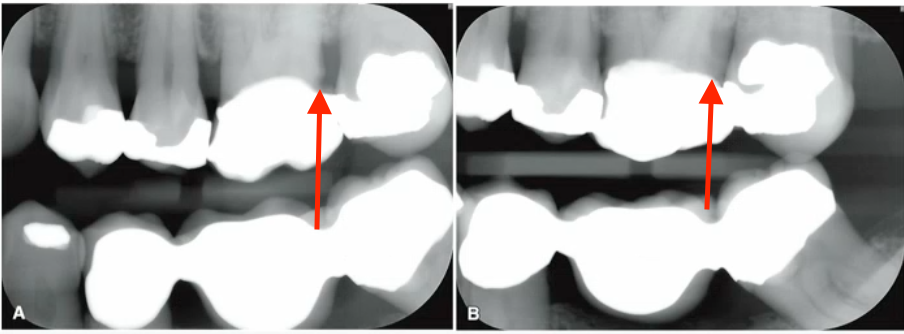
vertical angulation
why are PAs NOT ideal for visualizing caries?
pulp necrosis
most common cause of periapical inflammatory lesions
abscess
collection of pus
granuloma
formed when body attempts to isolate and eliminate inflammatory responsee
cyst
entrapped epithelial cell rest of malassez stimulated to proliferate
true
T/F abscess, granuloma, and cyst CANNOT be differentiated on xray
apical periodontitis
inflammation of apical periodontium of PULPAL origin
rarefying osteitis
inflammatory bone resorption at tooth apex, localized radiolucency
sclerosing osteitis
inflammatory bone deposition around tooth apex, localized radiopacity
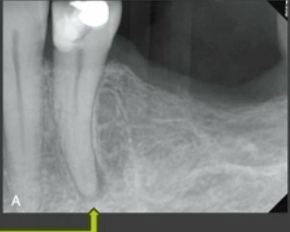
rarefying osteitis
what type of lesion is shown here
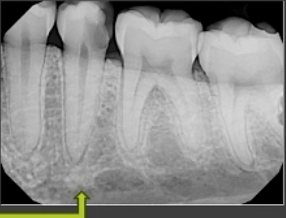
sclerosing osteitis
what type of lesion is shown here
periapical radiolucency
how would you describe this lesion
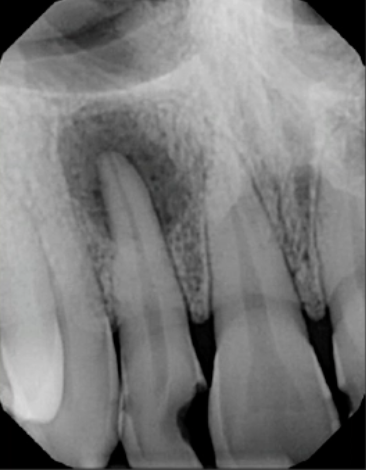
fully radiolucent (no internal mineralization)
how would you describe the internal structure of this lesion
can lead to osteonecrosis (due to decreased blood supply)
what is the danger of sclerosis over time
periosteal reaction
enlarged or extended bone border due to periapical inflammation
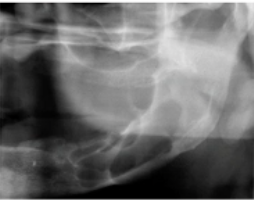
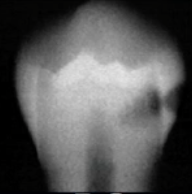
onion skin pattern (due to periosteal reaction)
how would you describe the appearance of this lesion on the ramus
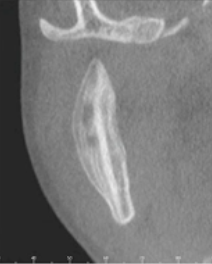
odontogenic mucositis
thickening of mucosal lining stimulated by periapical inflammatory disease
odontogenic mucositis
what is this lesion
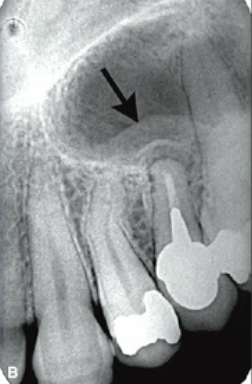
external resorption
outer layer of a tooth root is destroyed, often due to periapical inflammation from adjacent teeth.
hypercementosis
bulbous roots due to excess cementum, associated with periapical disease
periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia
periapical radiolucency of VITAL tooth
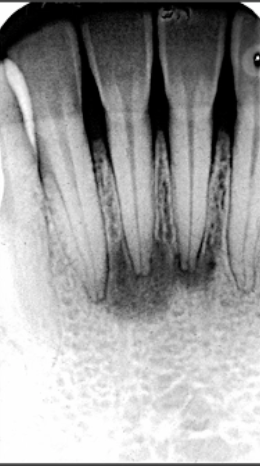
dense bone island
periapical radiopacity of VITAL tooth
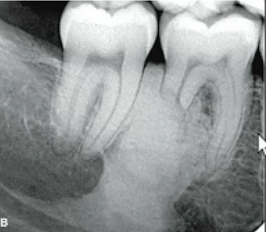
malignancy
periapical lesion with irregular PDL widening and variable sized regions of bone destruction
biopsy (cyst epithelial lining)
needed to distinguish cyst vs. granuloma
periapical scar
radiolucent lesion due to fibrous healing defect
periodontitis
inflammatory disease affecting the supporting structures of the teeth, leading to gum recession and bone loss