Unit 10 & 11: Imperialism, WW1, and the Russian Revolution Review
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
March 1917 Russian Revolution
Starts with riots for food, strikes, and protests against the war. The Soviets (local councils) form, and Czar Nicholas steps down from the throne, and Lenin returns to Russia to lead the Bolsheviks.

Linen's New Economic Policy
Allowed for some characteristic's of capitalism in the midst of a communist government, such as private land ownership.
New Imperialism
The late-nineteenth-century drive to create vast political empires abroad.

Imperialism
The conquering of foreign territories by powerful countries for natural resources.

Five Causes of the New Imperialism
1. Industrialization - Capitalism/New Technology
2. Racism - Thinking one race or people group is better than others.
3. Nationalism - "Our country is better than yours"
4. Humanitarianism - Helping new territories after conquering them. "thanks?"
5. Circumstance
"White Mans Burden"
European and Americans believed it was their responsibility to spread Christianity, civilize and educate other nations, and end the slave trade. Overall, the critique that white men are better and should make everything better according to them.

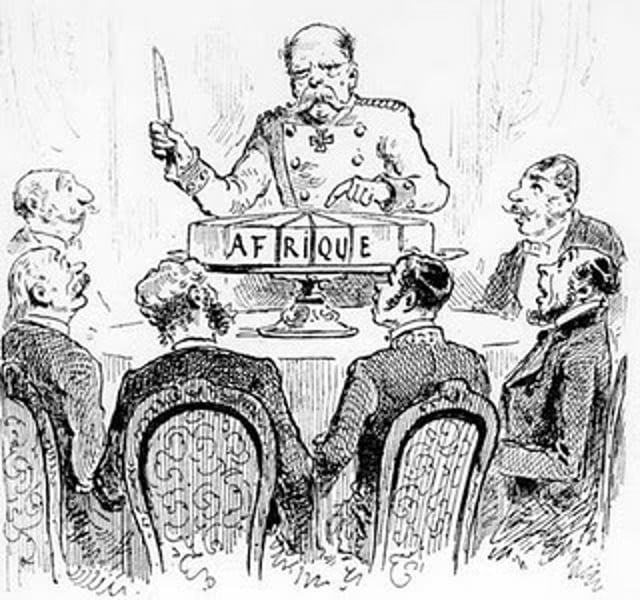
Berlin Conference (1884-1885)
A meeting at which representatives of European nations agreed upon rules for the European colonization of Africa. However, there were no representatives or natives of Africa.

"Social Darwinism"
The idea of survival of the fittest should be applied to societies and empires as well.

The Congo Free State
A large area in Central Africa that was privately controlled by Leopold II of Belgium. It was exploited from forces labor to gain ivory, rubber (for tires), and copper.

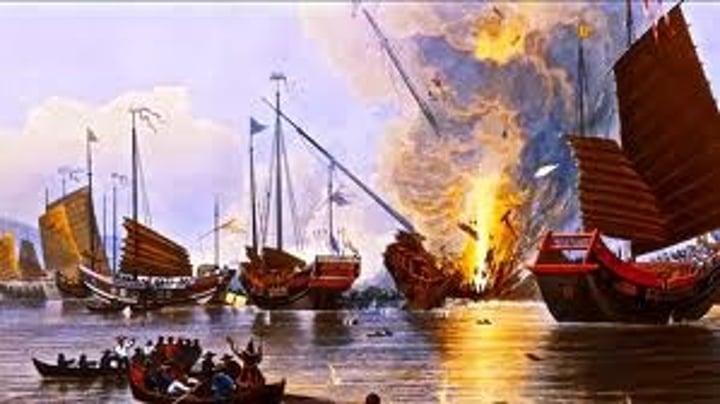
Opium Wars (impact on China)
China fights and loses these wars against Britain over the British Opium Trade. This weakened the Qing Dynasty which resulted in western nations forcing China to trade with the world.

Meiji Period of Japan
Japan has its own civil war, and it leads to the Meji restoration. This is where they commit to civilize and industrialize.

Sepoy Mutiny
The revolt of Hindu and Muslims over their mistreatment by the British.
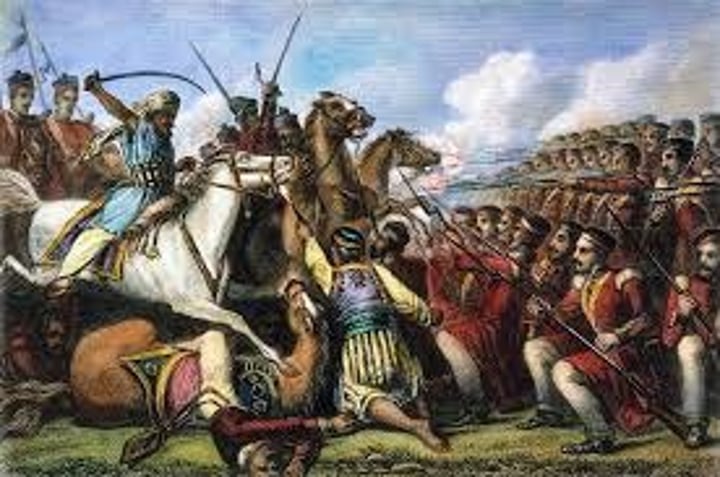

British Raj in India
After the Sepoys rebel, the British take direct control over India and introduce many reforms.

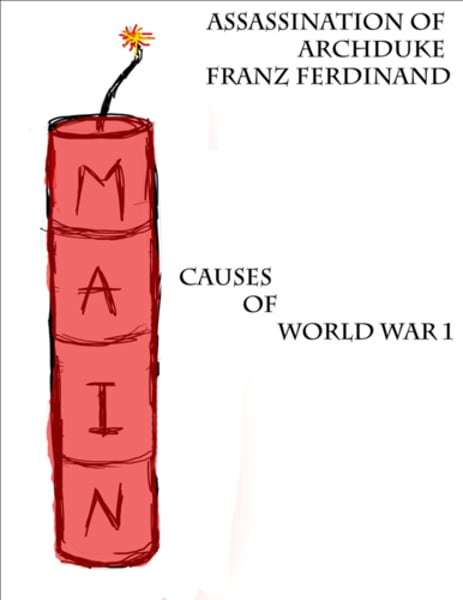
Causes of WW1 (M.A.I.N.)
Militarism - New military technologies & glorification of war.
Alliances - Most nations sign secret alliances. Allies and central powers mainly.
Imperialism - Competition and smaller wars over territory.
Nationalism - French-German boarder conflicts & ethnic nationalism.
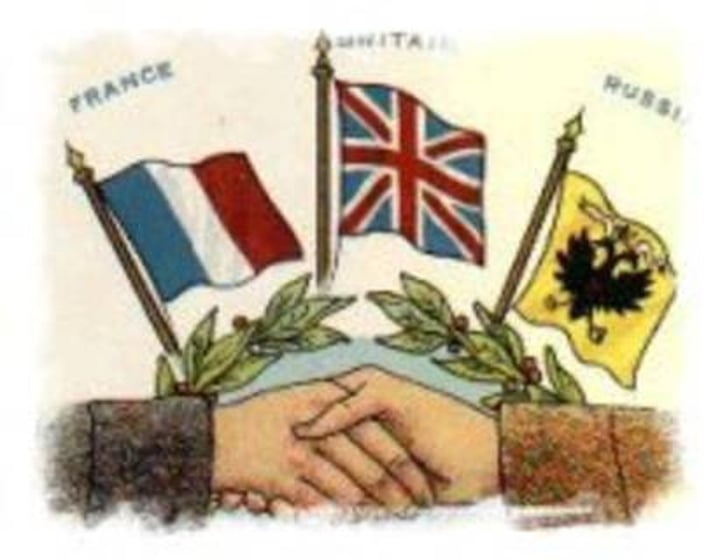
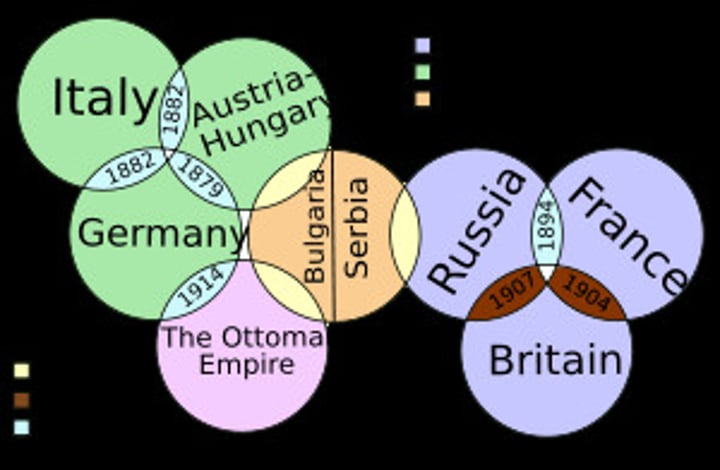
Triple Entende
Alliance between France, Russia, and Great Britain

Triple Alliance
Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy.
Franz Ferdinand
Assassination of this heir to Austria-Hungarys throne. June 28th 1914.
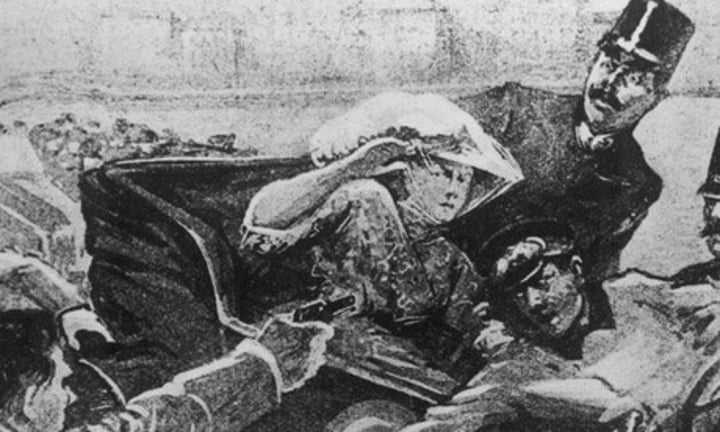
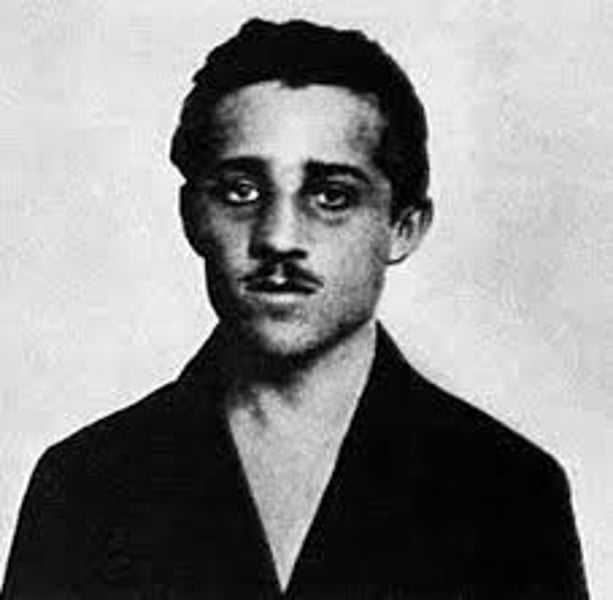
Gavrilo Princip
University student and member of the Serbian "Black Hand" terrorist group (motivated by Serbian Nationalism) who assassinates Franz Ferdinand.

Czar Nicholas II
This leader of Russia is overthrown for his poor war efforts in March 1917 during the Russian Revolution.

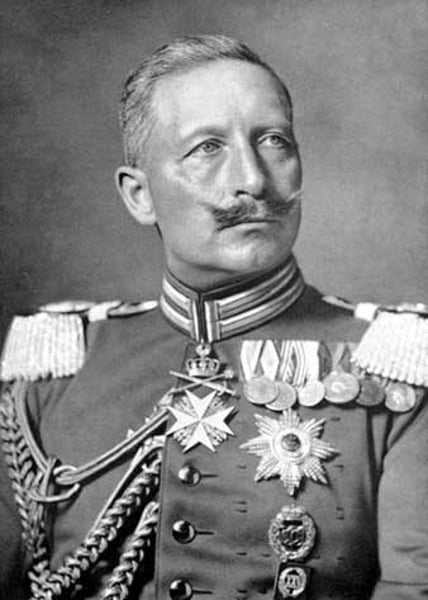
Kaiser Wilhelm II
Was the Kaiser of Germany at the time of the First World War reigning from 1888-1918. He pushed for a more aggressive foreign policy by means of colonies and a strong navy to compete with Britain. His actions added to the growing tensions in pre-1914 Europe.

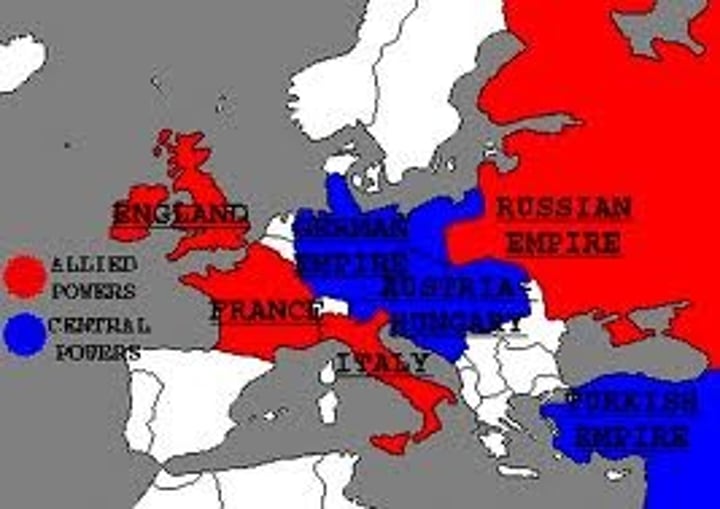
Allied Forces
Britain, France, and Russia - Later joined by Italy.

Central Powers
Austria-Hungary, Germany, Ottoman Empire.
Schlieffen Plan
A strategy drawn up by Germany to avoid fighting a war on two fronts by taking out France first and then dealing with Russia. Includes battle such as the Marne, Verdune, and the Somme.
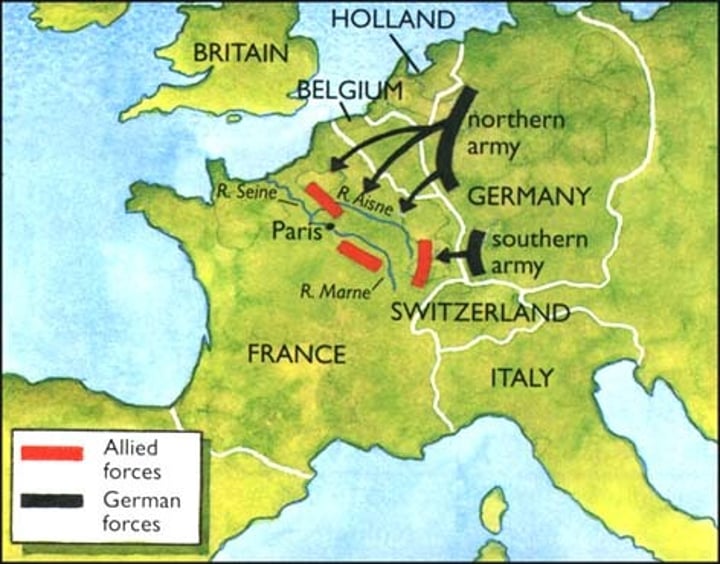
First Battle of Marne (Sept. 1914)
A costly Allied victory that stopped the Schlieffen plan.

Battle of Verdun
Long, deadly battle throughout 1916.

Battle of the Somme
Over 1 million casualties from July-November 1916.
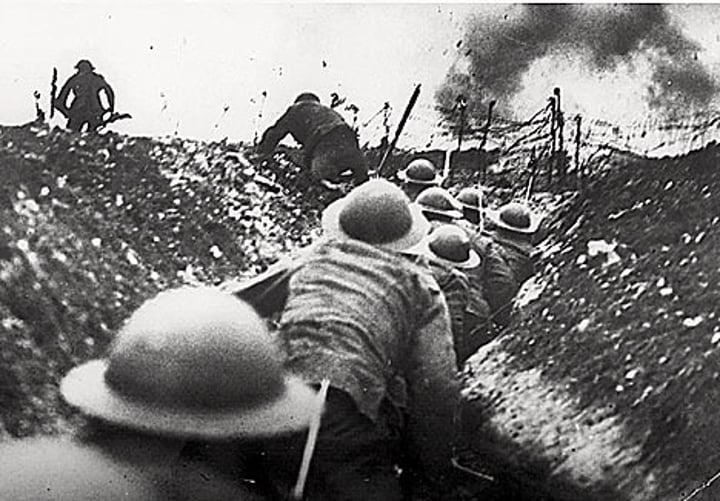

Trench Warfare
A form of warfare in which opposing armies fight each other from trenches dug in the battlefield.
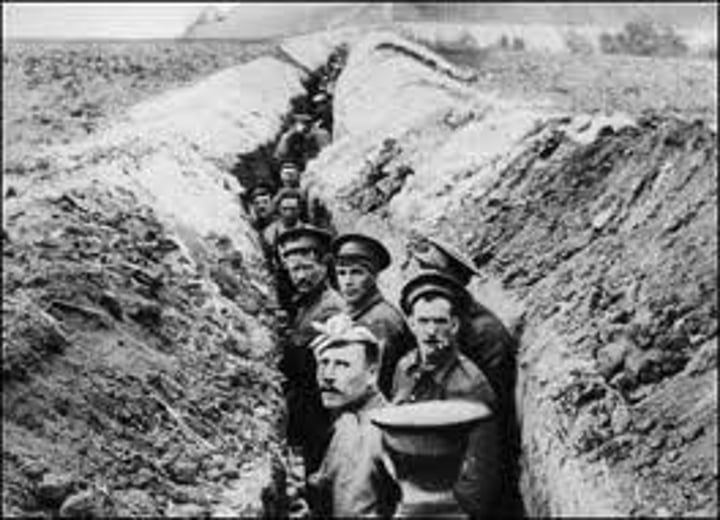

New Technologies (Weapons) of War
Machine guns, tanks, zeplines, grenades, planes, artillery.

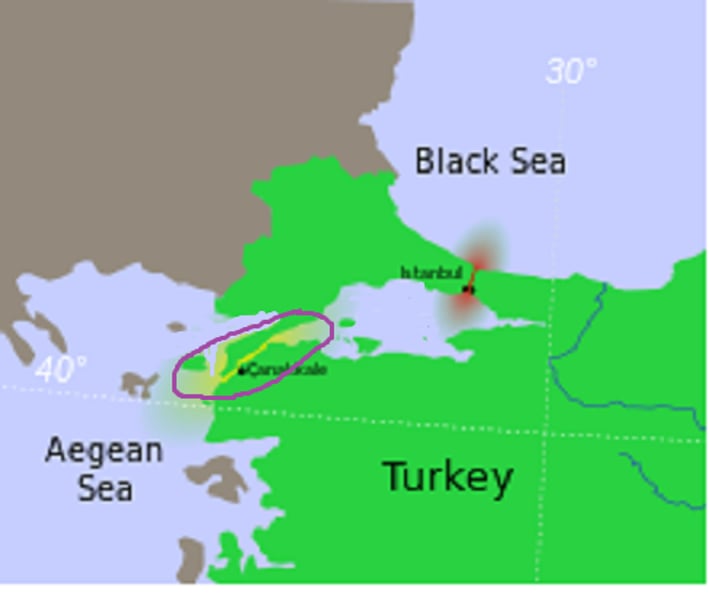
Gallipoli Campaign
From February 1915 to January 1916, the allies aim to weaken the Ottoman Empire by capturing Dardanelles to resupply the Eastern Front. However, the allies lose 250k+ soldiers and retreat.
British Naval Blockade of Germany
This blockade restricts Germanys ability to get supplies and food.

Battle of Jutland
Only real naval battle of WWI. German battleships and submarines attempt to defeat the British Naval Blockade on May 31st, 1916 but ultimately fail.

Battles on the Eastern front
Includes the Battle of Tannenberg which was a major defeat for Russia. Very high casualties (2mil+). Russias revolution forces them to back out of the war.
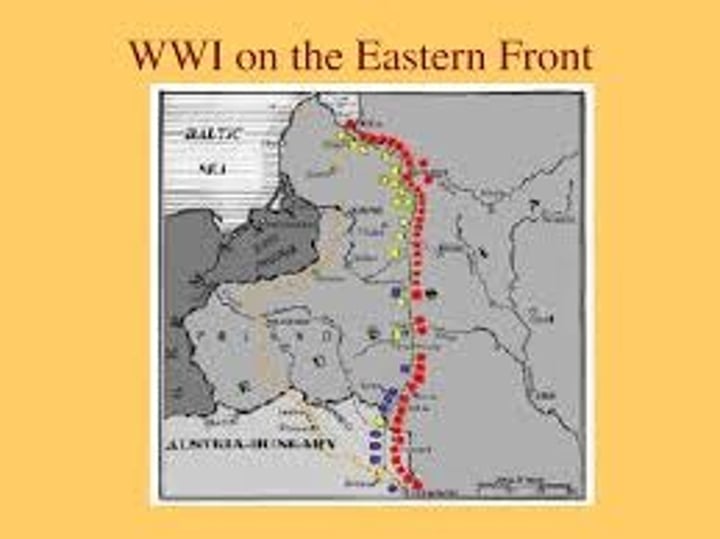
Role of the Russian Revolution during the War
The Russians overthrow Czar Nicholas II. Then, Vladmir Linen leads the communist Bolsheviks where they sign the Treaty of Brest-Litausk with Germany.
American Isolation
President Wilson campaigns on keeping America out of the war.

Unrestricted Submarine Warfare
Germany declares this to defeat the naval blockade of Britain.
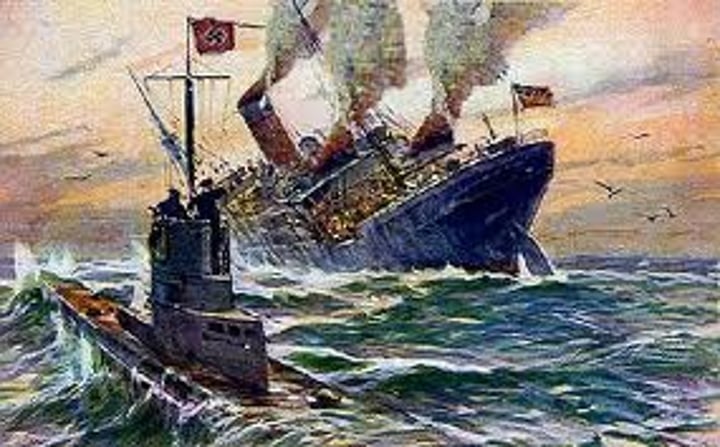

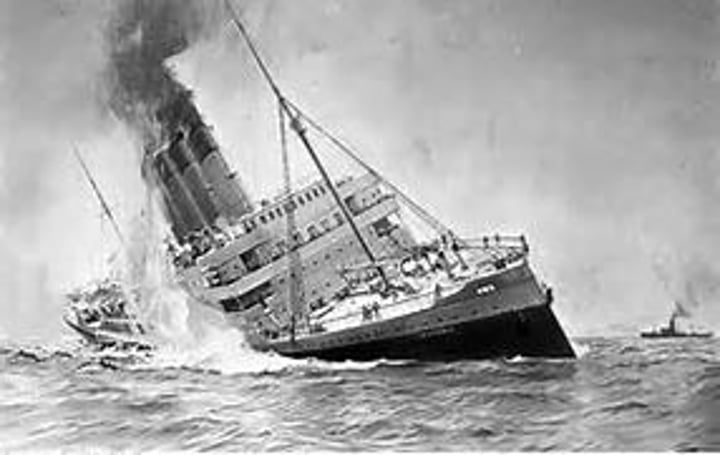
Sinking of the Lusitania
Sunk by German U-Boats (Submarines) in 195. Killing 1,198 people, including 128 Americans. Germany must apologize and stop targeting peaceful ships for America to stay nuetral.

The Zimmerman Telegraph
The secret message from Germany to Mexico that proposes an alliance against the US. Mexico declares war on America and gets lost territory after their victory.

American Declaration of War on Germany
After the press outrage from the Zimmerman Telegraph, congress officially declares war on Germany on April 6th, 1917.

The Draft in the USA
2.8 Millions "doughboys" are drafted into the armed forces.

Armistice Signed
November 11th, 1918 @ 11am an armistice is signed, ending the war. (Veterans day)

Total War
Military conflict in which contenders are willing to make any sacrifices in lives and other resources to obtain complete victory.

Effects of Total War on Women
Women replace men in factories, shops etc. They also serve in military auxiliary forces, especially as nurses and ambulance drivers. However, after the war women lose these jobs to returning veterans.

Rationing
Especially in Europe, food was limited because of major shortages.

Propaganda
One-sided information designed to persuade, to keep up morale, and support the war.

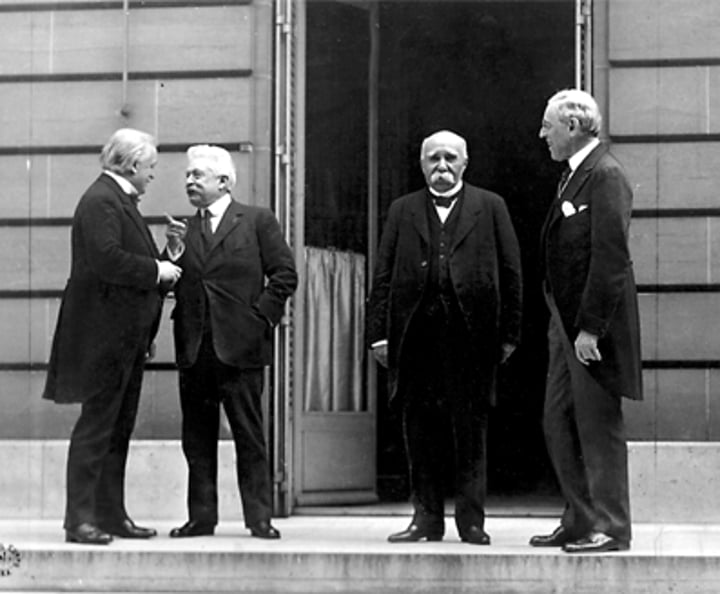
Paris Peace Conference - "The Big Four" (And who they represent)
David Lloyd George (Britain), Vittorio Orlando (Italy), George Clemenceau (France), Woodrow Wilson (USA)

Wilsons Fourteen Points
This presidents plan for lasting peace. However, conflicts with European desire to punish Germany.

Self-Determination
The notion that peoples should be able to choose their own national governments through democratic majority-rule elections and live free from outside interference in nation-states with clearly defined borders.

Treaty of Versailles
Treaty that forces Germany to accept full responsibility for war. (The War Guilt Clause). Germany then loses all territories and must pay reparations to allies as well as keep only a limited army.

League of Nations
A world organization established in 1920 to promote international cooperation and peace. It was first proposed in 1918 by President Woodrow Wilson, although the United States never joined the League. Essentially powerless, it was officially dissolved in 1946.

New Nations in Europe
Turkey, Hungary, Austria, Yugoslavia, Czechoslovakia, Estonia, Lithuania, Latvia, Poland, East-Prussia (German).
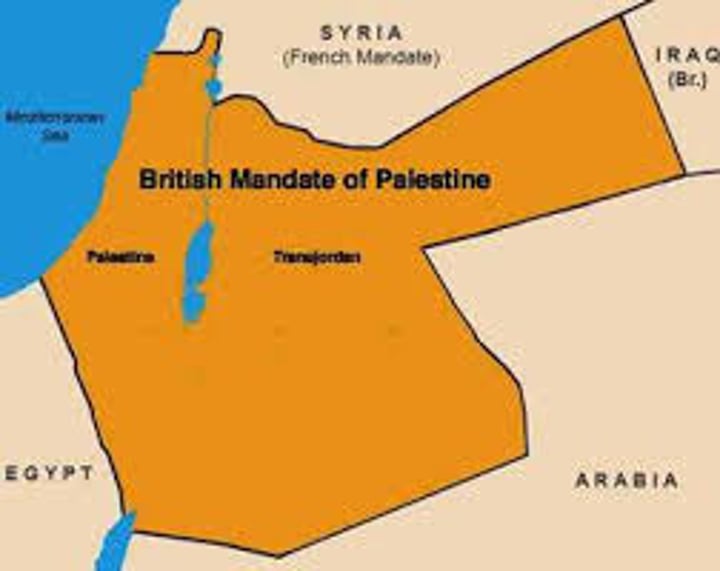
The Mandate System
The plan to allow France and Britain to administer former Ottoman Empire Territories. Britain takes Iraq, Jordan, and Palestine. France takes Syria and Lebanon.
Romanavs
Czarist royal family who ruled Russia for 3 centuries.
Bolsheviks
Communist majority faction of the Russian Social Democratic Workers Party.

Soviet
Elected councils formed during the Revolution.

Totalitarianism
Absolute unlimited power by a ruler and control over every phase of life.
Russian Revolution of 1905
Thousands of urban workers and poor workers peacefully protest for better working conditions and suffrage. However, czars guards fire into the crowd that sparks uprisings and strikes.
Results: The Duma (The Russian Congress) is given more power, but is later dissolved by Nicholas II.

Czarina Alexandria
Ran the Russian government while Nicholas II was at the Eastern Front for the war. She was heavily influenced by Rasputin.

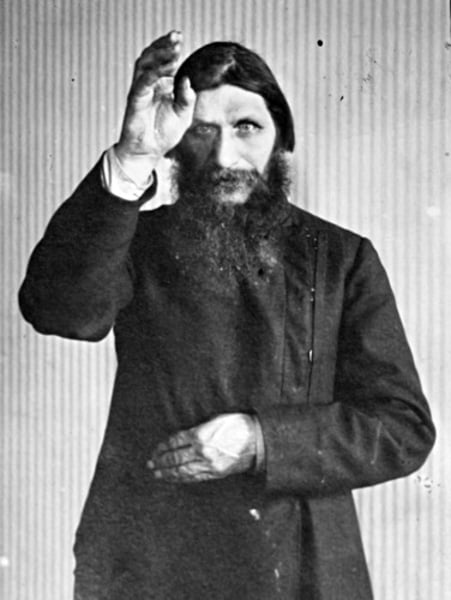
Rasputin
A mystical "holy man" who had healed Alexei, their son and heir. Scandals surrounding him served to discredit the monarchy.

Vladimir Linen
Leading Marxist who was revolutionary in Russia, committed to the struggle and revolution. This leader was exiled to Serbia, but returns to take the lead and implement communist reforms.

Leon Trotsky
Russian revolutionary and Communist theorist who helped Lenin and built up the Red army.

Russian Civil War
Fought between 1917-1920: The "reds" and "whites" battle.
Reds: Bolsheviks; Communist Party
Whites: Army officers, bourgeoisie, Cossacks, and moderate revolutionaries. Received support from US, France, England, and Japan.
Reds are ultimately victorious.

Execution of the Romanovs
After being placed under house arrest Czar Nicholas, Alexandra, and their 5 children were executed in July 1917.
