Hip Joint Complex
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
The Coxofemoral joint is what type of joint
Ball and socket
What DOF does the coxofemoral joint have
3 degrees of freedoms
Sagittal plane: Flexion/Extension
Frontal plane: abduction/adduction
Transverse plane: medial/lateral rotation
What is the acetabulum
The socket of the hip joint
The acetabulum is covered with
Articular cartilage that thickens peripherally
The acetabulum faces which ways?
Anteriorly, laterally, and inferiorly
The Acetabulum is thickened by what?
Labrum
What is the femur
Ball side of the joint
The neck of the femur angulates which ways
Superiorly, anteriorly, and medially
Nutation is caused by
Lumber extension
Counternutation is caused by
Lumbar Flexion
What is strain
Amount of deformation with respect to the structure
What is stress
Distribution of force within a body quantified as force divided by the area over which the force acts
What is bending
asymmetric loading that produces tension on one side of a body’s longitudinal axis and compression on the other side
What is a common injury with bending
Greenstick fracture
What is Wolff’s Law
Adaption to stress over time
How do bones adapt to loads
Mediated via cellular activity
Osteocytes detect strain damaged bone direct bone remodeling activity
Osteoblast deposits new bone
Osteoclast resorb bone
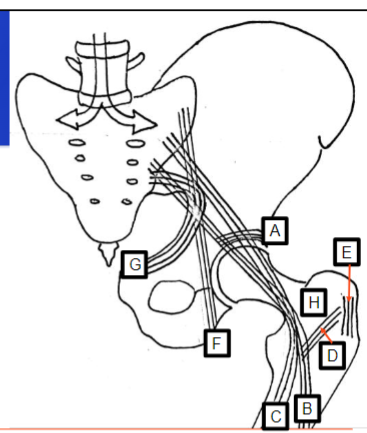
What does A represent
Internal structure on the superior aspect of the acetabulum
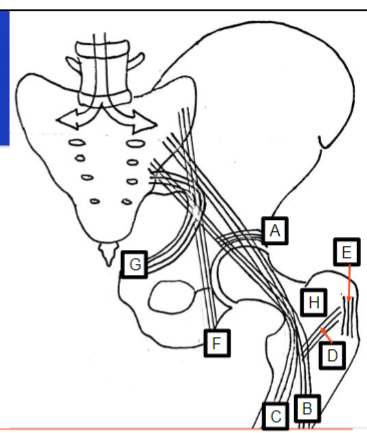
What does F represent
Refers to vertical lines passing through the ischium
Example being sitting
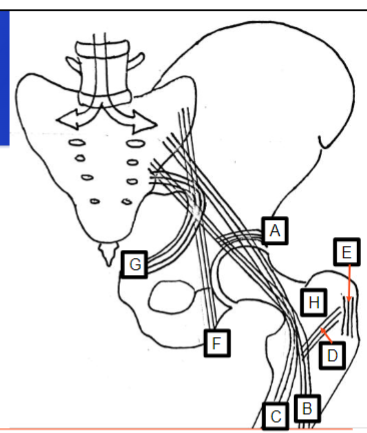
What does G represent
Refers to the curved lines along the pubic ramus
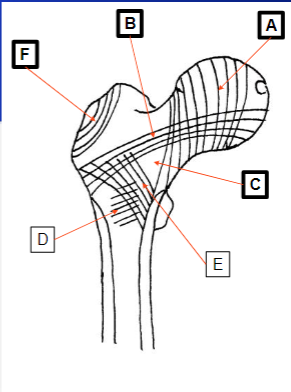
What does A represent
Medial compressive system
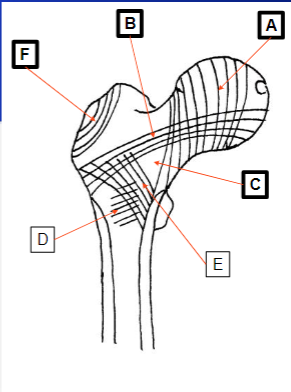
What does B represent
Lateral tensile system
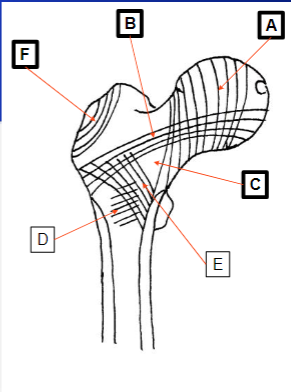
What does C represent
Zone of weakness
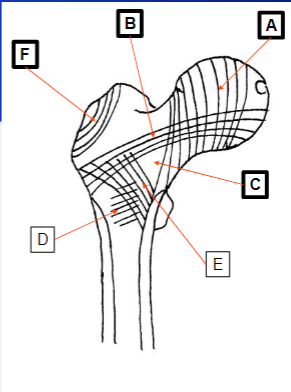
What does F represent
Trochanter System
What is stability
Ability to resist dislocation
What are factors that influence stability
Shape and congruence of bones
Supporting structures
What is the hip joint capsule
Strong dense and therefore a significant contributor of the hip joint
What are the attachments of the hip joint capsule
Periphery of acetabulum
Base of femoral neck
What are the fibers of the joint capsule
Circular (zone orbicularis)
Retinacular Fibers (carry blood Vessels)
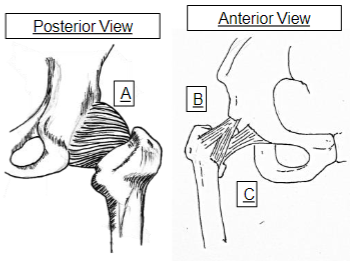
What does A represent
Ischiofemoral
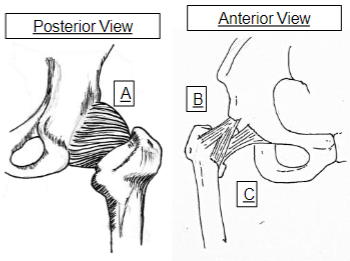
What does B represent
Illiofemoral
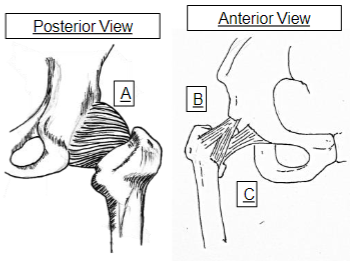
What does C represent
Pubofemoral
What is special about ischiofemoral ligament
taught in hip extension
What is special about iliofemoral ligament
fan shaped ligament, resembles inverted Y, strongest ligament at the hip. Checks hyperextension
What is special about pubofemoral ligament
taught in hip abduction and in extension. With the iliofemoral ligament it forms a Z on the anterior capsule
What are the functions of the Ligamentum teres
Secondary stabilizer preventing dislocation
Conduit for blood supply
Contains innervation for pain sensation
What movements cause max bony congruence
Flexion, abduction, and external rotation (frog legged position)
Not position of highest stability
What movements cause for most stable position
Extension, slight abduction, internal rotation
In most stable position how does extension affect ligaments
Further tightens, capsular ligaments
What movements cause for the least stable position
Flexion with adduction
Explain the Center edge angle
Also called Angle of Wiberg
Is the angle between vertical and a line drawn from center of femoral head to bony edge of the acetabulum
What is inclination angle
Neck to shaft angle- Superior inferior inclination
What is angle of anteversion
Anterior posterior angulation
Anteversion is often observed with
Coxa Valga
Where is the toe in gait if a person has retroversion
toe out gait
What is closed chain exercise
where the distal end of the limb is fixed to an immovable surface (ex squat or pushup)
What is open chain exercise
involve movement of the distal end of the limb (leg extension or bicep curl)
What is motion of posterior tilt
brings pubis up; leads to hip extension and lumbar flexion
What is motion of anterior tilt
brings anterior superior iliac spine anterior and inferior; leads to hip flexion and lumbar extension
If the right side of the pelvis drops (right hip drop) what are the motions of the right and left hip as well as the spine.
Right hip- abducts
Left hip- adducts
Spine- left lateral flexion
What is pelvifemoral rhythm
To maximize the apparent range of motion of the distal segment multiple joints are used in concert.
Explain lateral trunk lean
Lean toward the side of pain or weakness will reduce the moment arm of the gravitational force. Brings Center of mass closer to hip joint, so less counter torque needed by abductor muscles
When a cane is used contralaterally what are the benefits
Reduces weight of HAT, but also provides a counter torque to the torque of gravity thus reducing need for abductor muscle force
Canes considered to relieve hip of up to 60% of its load in stance
When is used ipsilaterally what is the benefit
Some benefit from alleviating some of the body weight through the cane
Define osteokinematics
Refers to bone movements of the joint about axes of rotation
Define arthrokinematics
Refers to the movement at the articulating surfaces of the joint
In flexion at hip what is the primary muscle
Iliopsosas
In flexion at the hip what are the secondary muscles used
Rectus femoris
Tensor fascia Latae
Sartorius
In extension at the hip what is the primary muscle
Gluteus maximus
In extension at the hip what are the secondary muscles
Semitendinosus
Semimembranosus
Biceps femoris, long head
abduction at 45-50 degrees is limited by what muscle
Gracilis
Adduction at 20-30 degrees is limited by what muscle
Tensor fascia Latae
What are the arthrokinematics during adduction
Inferior roll and superior gliding
What are the arthrokinematics during abduction
superior roll and inferior gliding
What is the primary muscle use when the hip is abducting
Gluteus Medius
What are the secondary muscles used when the hip is abducting
Gluteus Minimus and Tensor fascia latae
When the hip is adducting what is the primary muscle
Adductor magnus
When the hip is adducting what are the secondary muscles
Pectineus
adductor longus
Adductor brevis
Gracilis
Obturator externus
What are the arthrokinematics during medial rotation
Anterior roll and posterior gliding
What are the arthrokinematics during lateral rotation
posterior roll and anterior gliding
During lateral rotation at the hip what are the primary muscles
Gluteus maximus
Piriformis
During lateral rotation what are the secondary muscles
quadratus femoris
Obturator internus and externus
Gemellus superior and inferior
sartorius
What are the short external rotators of the hip
Piriformis
Quadratus femoris
Obturator Internus and externus
Gemellus superior and inferior
During medial rotation is what are the primary muscles
There is not
During medial rotation what are the secondary muscles
Tensor fascia Latae
Gluteus minimus
Gluteus Medius