Pharmacological strategies to reduce cardiovascular risk
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
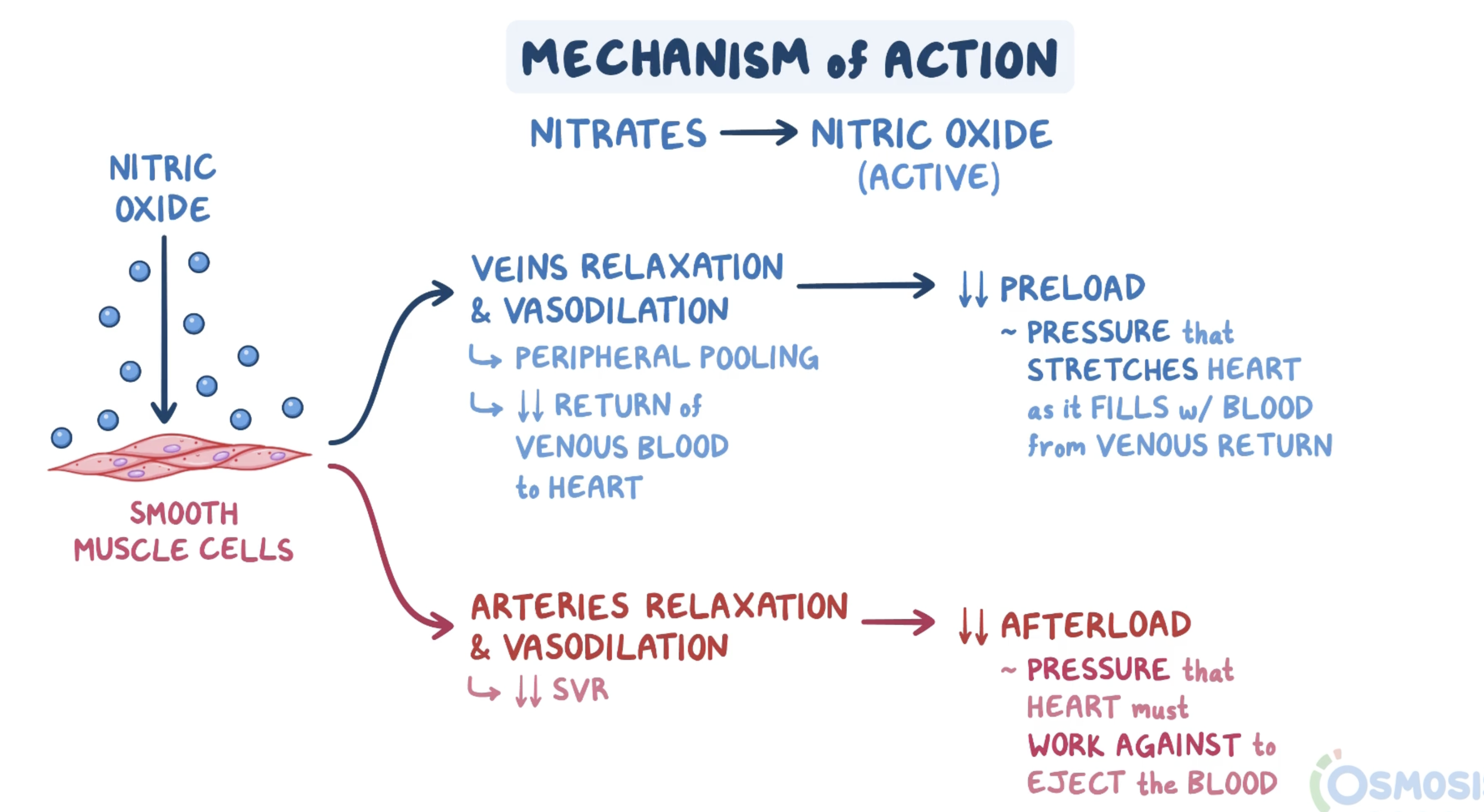
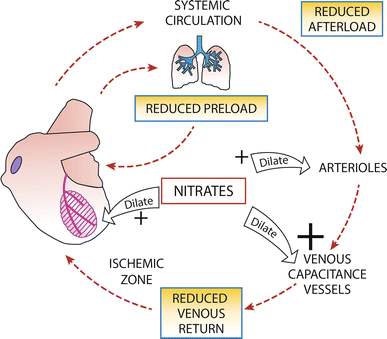
nitrates
Vasodilators (short lived but potent)
Induce release of nitric oxide (NO)
In Low dose
relax venous smooth muscle
via cGMP mediated activation of PKG
In High dose
relax arteriolar smooth muscle
via cGMP mediated activation of PKG
→ dilation of peripheral arteries & veins (reduces preload and afterload)
PKG
Protein Kinase G
activated by nitrates via cGMP
activates a variety of systems:
Activates K+ efflux channels by phosphorylation → hyperpolarisation
Activates pumps to sequester calcium
calcium inhibited from promoting muscle contraction
Inhibits rho kinase (ROCK) → stimulates myosin phosphatase
myosin inhibited from binding to actin, contracting muscle
Thereby promotes muscle relaxation
nitrate subgroups
Short acting
Glyceryl trinitrate (GTN)
Three Ns sourced per molecule (compared to one - this means faster and more intense onset)
Sublingual or IV (high first pass)
Acts in seconds to relieve pain of attack
Long acting
Isosorbide dinitrate, isosorbide mononitrate
One N sourced per molecule (mononitrate form)
Oral (sustained release) or transdermal patch
long term will cause problems
nitrate AEs
Vasodilation → lowered BP → can evoke reflex tachycardia
HR will increase in response to try and increase BP
→ ↑ cardiac oxygen demand
response: beta-blocker (targets SA node)
Headache (vasodilation of brain blood vessels ouch)
Flushing (duh)
Dizziness (postural hypotension)
Tolerance
Ensure 8-10h nitrate free interval per 24h
explain nitrate tolerance
Within 24 hours, vasodilation → BP drops → body compensates:
RAAS activation: kidneys retain sodium + water → ↑ plasma volume
(homeostasis: since venous return ↑ but heart isn’t able to pump faster, body holds onto water)
↑ catecholamines → vasoconstriction.
↑ vasopressin (ADH): more water retention → ↑ plasma volume
True tolerance: After about 48–72 hours of continuous exposure, body decreases NO production
aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibition (enzyme that converts nitrates to NO)
increased chemical mechanisms which scavenge/inactivate nitric oxide (since NO is a reactive chemical species → body has mechanisms in place to rapidly inactivate it)
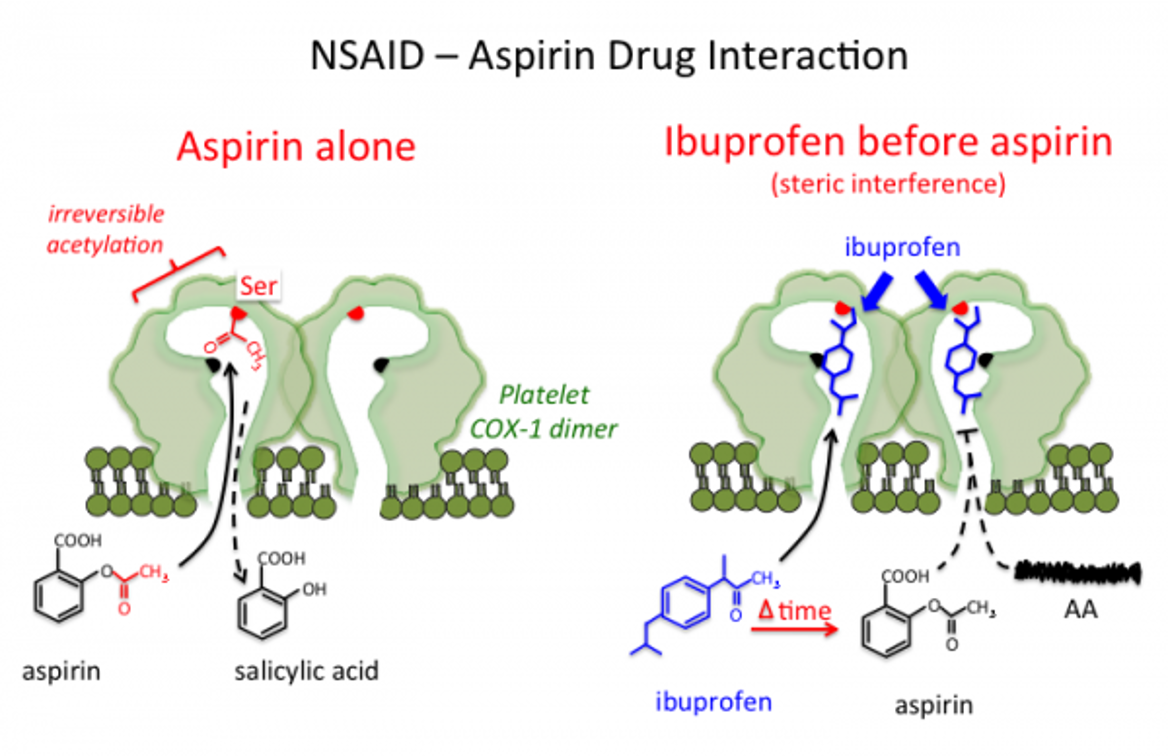
Aspirin mostly deactivates platelets in______
Aspirin mostly deactivates platelets in hepatic portal system (as aspirin is inactivated in the liver-> converted to salicylic acid)
Aspirin, when its bound to COX in a platelet, is active for_____
active for 7-10 days (platelet lifespan)
NSAID (ibuprofen) and aspirin drug interaction
Ibuprofen taken at the same time as aspirin-> ibuprofen blocks the access of aspirin (steric interference)
Shouldn't be taken at the same time
Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP) role in platelet formation
Released from platelet dense-granules & injured cells
binds to 2 platelet G-protein-coupled receptors:
P2Y1
initiates ADP-induced platelet aggregation
P2Y12
Mediates platelet activation:
inhibits adenylate cyclase-mediated signaling pathway
&
decreases intracellular cAMP levels.
→ decreased rate of phosphorylation of vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein
→ decreased activation of GPIIb/IIIa receptor & platelet aggregation
clopidogrel MOA
Active metabolite of clopidogrel (since clopidogrel is a prodrug) irreversibly inactivates P2Y12 receptor
→ prevents ADP binding to this receptor and activating glycoprotein IIb/IIIa
→ inhibits ADP-induced platelet aggregation and reduces platelet dense-granule secretion (which includes ADP)
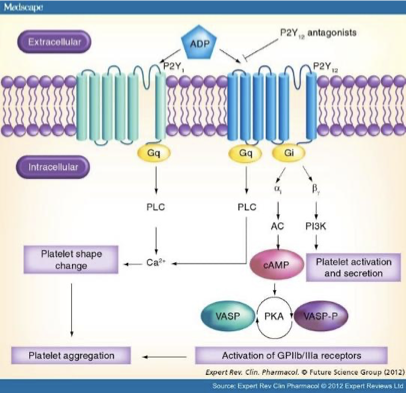
Clopidogrel vs Ticagrelor
Both are P2Y12 receptor blockers, but:
Clopidogrel has to be metabolised to its active metabolite before it exerts its action on the receptor, whereas Ticagrelor can directly act on the receptor
→ certain drugs can prevent the metabolism of clopidogrel into its active state
Ticagrelor is also reversible whereas clopidogrel is irreversible
statins
HmG CoA reductase inhibitor
Rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol synthesis
By decreasing the cellular production of cholesterol, statins force the cell to import (through diet rather than making) more of it, using the LDL-receptor. This reduces cholesterol circulating in plasma.
Always ends in -statin e.g. Rosuvastatin (this is literally a random one, idek if we need an example)
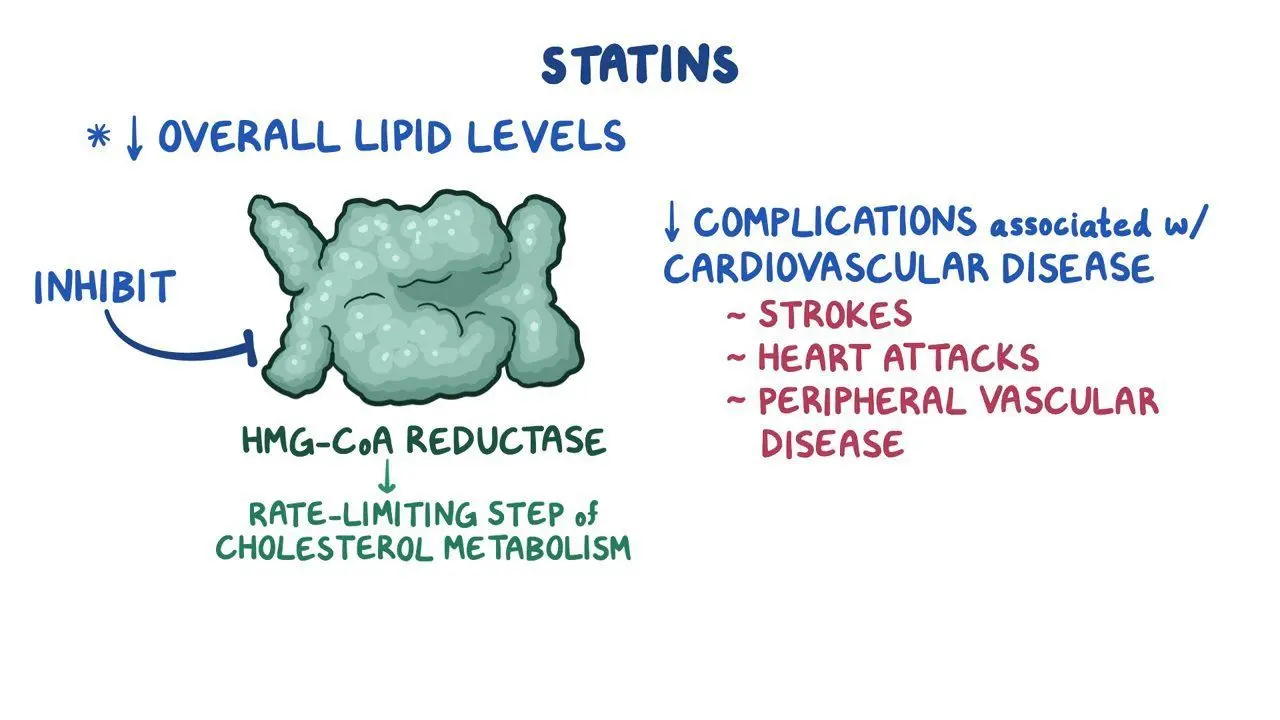
statins AEs
Myalgia/myopathy
Myalgia (aches & weakness) + increased creatine kinase (marker of muscle damage)
Super bads
Diabetes mellitus T2
Skin rashes
GIT
Drug interactions
warfarin ( bleeding risk)
Myopathy incidence significantly higher when statins taken with CYP inhibitors
(might just need to know myalgia)
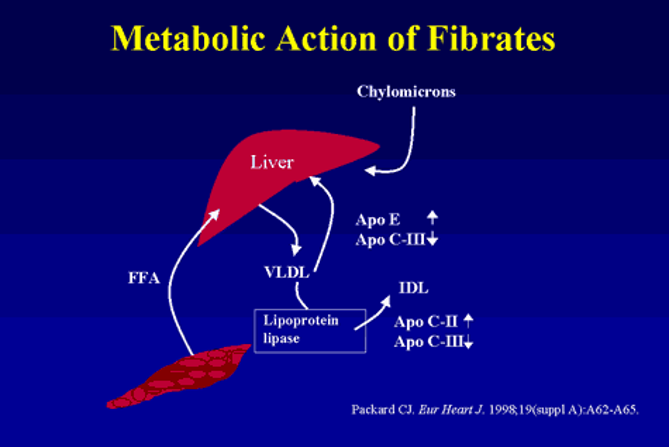
Fibrates
usually a statin works better, except for hypertriglyceridemia (isolated)
e.g. Gemfibrozil or Fenofibrate
Fibrates MOA
Activate PPAR (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors), esp PPARα:
Intracellular receptors modulate carbohydrate & fat metabolism
Induce transcription of a number of genes that facilitate lipid metabolism
increase activity of lipoprotein lipase & increase synthesis of apoC-III together enhance clearance of circulating TG-rich lipoproteins.
→ increased hepatic fatty acid oxidation → increased production of TG-rich lipoproteins
(might not need to know in detail)