tuberculosis
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
how many people are estimated to have latent TB worldwide?
1.7 billion - 1 in 4
how many cases of active TB were there in 2019?
10 million
what are the risk factors for TB?
- immunosuppression
- homelessness
- birth in an endemic country
which countries to WHO list as the most endemic to TB?
- India
- China
- Indonesia
- The Philippines
- Pakistan
- Nigeria
- Bangladesh
- South Africa
what is given to babies who were born or whose parents were born abroad?
BCG vaccine
what are the 2 phases of tuberculosis?
- latent
- active
what is latent TB?
individuals who are infected with TB but have no active disease, no symptoms and are not infectious
what is active TB?
individuals who are symptomatic and have the progressive disease
what bacterium causes tuberculosis?
mycobacterium tuberculosis
what type of bacterium is mycobacterium tuberculosis?
gram positive bacillus
what happens when doing a gram stain with mycobacterium tuberculosis?
does not the hold stain well - acid-fast bacilli (afb)
what property do acid fast bacilli (AFB) have?
resistance to decolourisation of staining by acid
which stain should be used instead?
Ziehl-Neelsen stain
what colour will the Ziehl-Neelsen stain in the presence of TB?
bright red
what are the 4 types of mycobacterium are capable of causing TB in humans?
- mycobacterium tuberculosis - only humans can host
- mycobacterium bovis - cattle and other mammals
- mycobacterium africanum - seen in west Africa
- mycobacterium microti - other mammals
what are these 4 mycobacterium called?
mycobacterium complex (MTc)
do mycobacterium requre oxygen to grow?
yes
what is the technical name of requiring oxygen to grow?
obligate aerobes
where can mycobacterium grow?
can grow extracellularly, but advantageous to grow intracellularly - facultative intracellular
what can happen after the initial inhalation of mycobacterium tuberculosis?
- infection cleared straight away (breathed back out)
or
- primary TB
what is primary TB?
- infection present but suppressed by immune system
- asymptomatic
what can primary TB lead to ?
- progressive-primary TB
- latent TB
what is progressive-primary TB? (2)
- primary infection is not suppressed
- prolonged infection occurs
what can progress from latent TB?
post-primary TB
what is post-primary TB?
- also called reactivation
- usually due to immunocompromisation
what drug can cause post-primary TB?
infliximab - for rheumatoid arthritis and IBD
what happens when mycobacterium tuberculosis is inhaled at a microscopic level? (3)
- it can evade the mucociliary escalator
- through bronchioles and into alveoli
- usually into the middle and lower lobes first
what happens to the TB in the alveoli? (3)
- usually would be engulfed by alveolar macrophages (dust cells) and then digested by lysozymes
- but TB inhibits lysozymes and proliferates
- causing primary TB
what happens once a critical mass of TB is created in the lungs?
triggers cell-mediated immune response
what molecules on TB stimulated the macrophages?
CORD factor
is TB an exogenous or endogenous pathogen?
exogenous
which class of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins will be activated?
class II
which type of cells will be activated from class II MHCs?
CD4+ cells
what will CD4+ cells release?
interferon gamma
what does interferon gamma do?
stimulates macrophages to secrete (tissue/tumour necrosis factor) TNF-alpha
what do the macrophages then do? (4)
- encircle a group of TB
- the inside dies and becomes necrotic
- the outside stays alive
= small caseating granuloma
what is a small caseating granuloma also called?
Ghon focus
what does a Ghon focus look like?
cheese :D
what can happen if the TB spreads into the lymphatic system?
a network of ghon foci develops in the lungs and lymphatics = Ghon's complex
what is it called when the Ghon's complex gets calcified?
Ranke complex
what happens if the infected persons immune system is compromised?
TB can be reactivated, the ranke complexes can no longer be maintained
where can the TB go first?
upper lobes of the lungs
why does the TB go to the upper lobes first?
most oxygen concentrated
what does this cause in the upper lobes?
lesions
what are the 3 ways that TB can spread?
- bronchogenic
- lymphatic
- circulatory
what can bronchogenic spread cause?
bronchopneumonia
what can lymphatic spread cause?
swelling in cervical nodes = scrofula
what does miliary tuberculosis mean?
tuberculosis spreads through the blood
what can you see on x-ray with miliary TB?
millet seeds
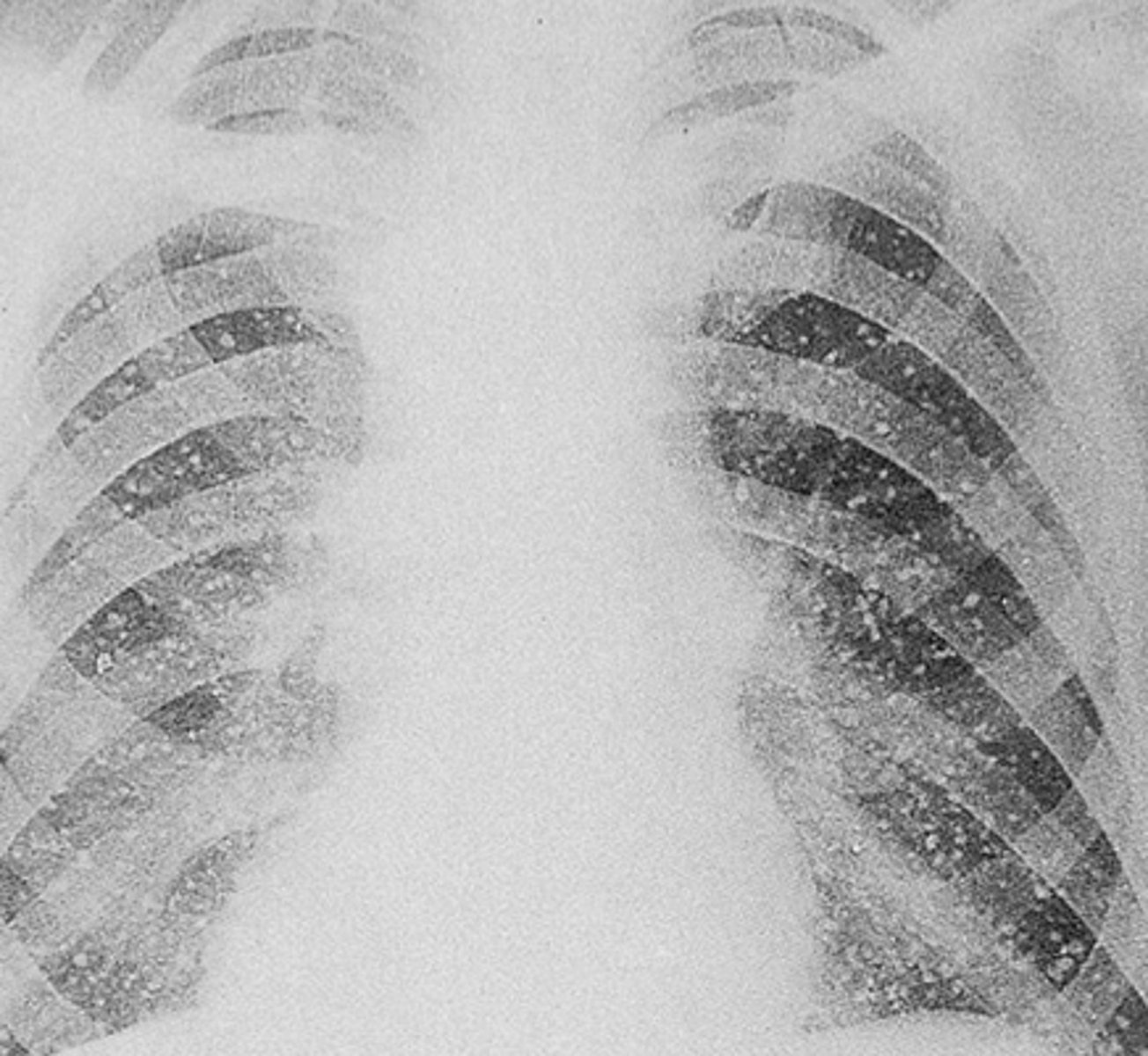
where are the 5 places that TB mainly spreads to via the blood?
- kidneys
- meninges
- lumbar vertebrae
- liver
- adrenal glands
what problems does TB cause for the kidneys? (3)
sterile pyuria:
- elevated WBC in urine
- cannot grow on culture (hence sterile)
what problems does TB cause for the meninges?
meningitis
what problems does TB cause for the lumbar vertebrae? (4)
Pott's disease:
- lower back pain
- microfractures
- inflammation
what problems does TB cause for the liver?
hepatitis
what problems does TB cause for the adrenal glands?
Addisons disease:
- effects sex steroids, catecholamines, mineralocorticoids
what are the symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis? (4)
- fever
- nightsweats
- haemoptysis
- unplanned weight loss
- could have SOB
how would you diagnose TB?
1) skin or blood test
2) chest X-ray
what is the main skin test used?
mantoux test
what does the mantoux test involve?
- intradermal injection of tuberculin (protein derivative of mycobacterium TB)
- if patient has had TB they will have a type 4 hypersensitivity reaction
what can interfere with the mantoux test?
- previous BCG vaccination (for TB)
- mantoux test should be used prior to BCG vaccination
what is the blood test used?
interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA)
what does IGRA test for?
- the bodies cellular immune response to TB
- so tests whether person currently has TB
what is taken along with a chest X-ray?
sputum samples
what would they be looking for in a chest X-ray?
lesions
what is the treatment for latent TB?
isoniazid for 9 months
what must someone do if they have active TB?
quarantine for 2-3 weeks
what is the mneumonic for the drugs used in active TB?
R
I
P
E
what does RIPE stand for?
Rifampicin
Isoniazid (+ pyridoxine)
Pyrazinamide
Ethambutol
what does rifampicin do?
inhibits RNA polymerase and hence bacterial RNA synthesis
what does isoniazid do?
inhibits mycolic acid synthesis
what are the side effects of isonaizid?
peripheral neuropathy (pin and needles)
what is taken along side isonaizid to prevent peripheral neuropathy?
pyridoxine
what does pyrazinamide do?
inhibits cell wall synthesis
what is a side effect of ethambutol?
red-green colour blindness
why do we give all these drugs at once?
giving just one of the drugs increases the chance of TB becoming resistant
what is the difference in diagnosing a typical from an atypical pneumonia?
typical - can give co-amoxiclav
atypical - by a pathogen that cannot be gram stained
what is the first line treatment for active TB?
- RIPE for 2 months
- RI for further 4 months
(4 for 2, 2 for 4)
what is the first line treatment for latent TB?
- isoniazide for 6 months
OR
- isoniazide + rifampicin for 3 months