Exercise 28 - Gram Negative Bacteria
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
What is a characteristic feature of the cell wall structure in gram-negative bacteria?
Gram-negative bacteria possess a thin layer of peptidoglycan in their cell wall.
What additional structural feature is found in the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria?
Gram-negative bacteria have an outer phospholipid bilayer membrane containing lipopolysaccharides (LPS).
What is the role of Lipid A (Endotoxin A) in gram-negative bacteria?
Lipid A, a component of lipopolysaccharides (LPS), accounts for symptoms of endotoxic shock.
Where are gram-negative bacilli commonly found?
Gram-negative bacilli are found in soil, fresh water, salt water, and occur in abundance in the intestinal tracts of mammals.
Which are the three tests for hydrogen sulfide?
TSI
SIM
LIA
Any black color on any of these tests is positive for H2S, unlike the bile esculin slant, which needs to be at least ½ black to be positive.
MacConkey
True or false? MacConkey agar is both selective and differential.
True
MacConkey
What does MacConkey agar contain and what does it select for?
Bile salts and crystal violet
Selects for Gram-negative bacteria
MacConkey
What is MacConkey agar’s carbohydrate?
Lactose
MacConkey
What is MacConkey agar’s pH indicator?
Neutral red
MacConkey
Name one strong lactose fermenting Gram negative bacilli on MacConkey agar.
Escherichia coli
MacConkey
Name one weak lactose fermenting Gram negative bacilli on MacConkey agar.
Enterobacter aerogenes
MacConkey
Name one non-lactose fermenting gram negative bacilli on MacConkey agar.
Morganella morganii
Salmonella
MacConkey
Pink growth on the MacConkey agar means that the organism is able to ferment ______________.
Lactose
MacConkey
Growth on MacConkey agar means the organism is Gram -_____.
Gram-negative
MacConkey
Colorless growth on MacConkey agar means the organism is…?
Non-lactose fermenting
Urease Test
In the urease test, what is the main enzyme?
Urease
Urease Test
In the urease test, what is the substrate and the pH indicator?
Substrate - Urea
pH indicator - Phenol red
Urease Test
In the urease test, what is produced if the test is positive?
Ammonia, CO2, and water
Ammonia raises the pH and produces a hot pink color
Urease Test
In the urease test, is ammonia considered acidic or alkaline? What would be the approximate pH?
Alkaline, with a pH above 7.
Urease Test
Name three bacteria that produce urease.
Proteus vulgaris
Proteus mirabilis
Morganella morganii
Urease Test
The enzyme urease breaks down urea into which three components?
Ammonia, CO2, and H2O
Citrate Utilization
The citrate agar slant contains what enzyme?
Citrase
Citrate Utilization
What is the pH indicator in the citrate test?
Bromthymol blue
Citrate Utilization
Name two citrate positive bacteria.
Enterobacter aerogenes
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Citrate Utilization
What color is produced if the citrate utilization test is positive?
Prussian blue

Nitrate Reduction
In the nitrate reduction test, which enzyme allows bacteria to anaerobically reduce nitrate to nitrite?
Nitrate reductase
Some bacteria further reduce the nitrite to ammonia or completely to molecular nitrogen.
Nitrate Reduction
In the nitrate broth, do the enzymes require oxygen to function?
No, the nitrate reduction process is anaerobic.
Nitrate Reduction
What are the steps in nitrate reduction?
Nitrate → Nitrite → Ammonia → Molecular Nitrogen
NO3 ——> NH2 ——> NH3 ————> N2
Nitrate Reduction
What reagents are added to a nitrate broth?
Nitrate Reagent A
Nitrate Reagent B
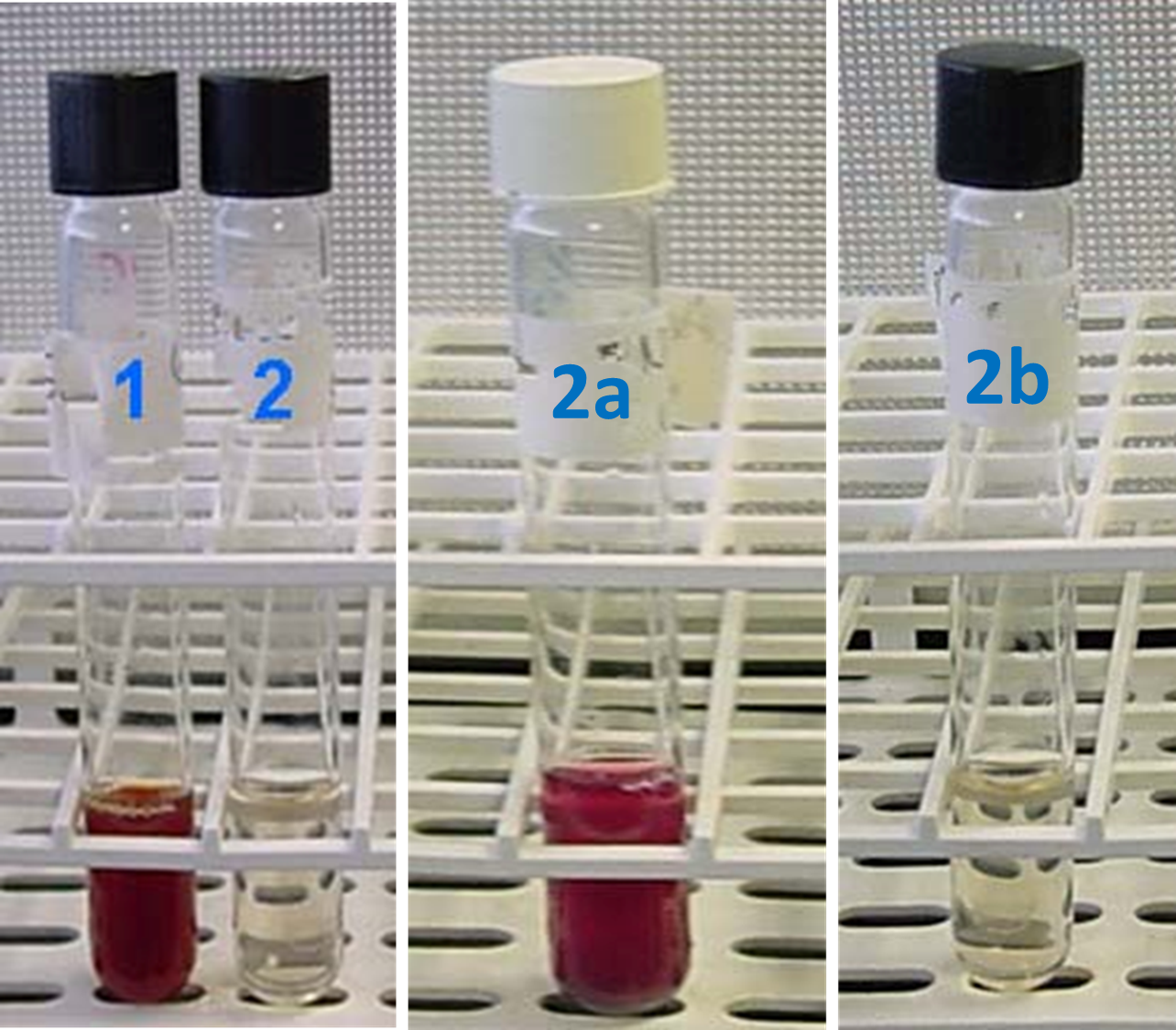
Nitrate Reduction
What are the results for each test? Positive or negative?
What is added to each test?
Test 1 (Positive)
Reagent A and B added
Nitrate has been reduced to nitrite
Test 2 (Negative)
Reagent A and B added
Bacteria did not reduce nitrate to nitrite
Next step is to add zinc (2a & 2b)
Test 2a (Negative)
Zinc is added
Zinc reduced the nitrate, not the bacteria
Test 2b (Positive)
Zinc is added but there is no color change
Bacteria is positive for nitrate reduction
Bacteria reduced nitrates beyond nitrites to ammonia or molecular nitrogen
SIM Test
How is the Sulfide Indole Motility (SIM) test done?
SIM agar deep with a needle stabbing the butt a single time
SIM Test
What three things does the SIM agar deep tube test for?
Indole production
Hydrogen sulfide production
Motility
SIM Test
What amino acid does the SIM agar tube contain?
Tryptophan
SIM Test
If an organism produces the enzyme tryptophanase in the SIM test, it will degrade tryptophan into what?
Indole, pyruvate, and ammonia
SIM Test
What is added to the SIM agar tube after incubation?
Kovac’s Reagent
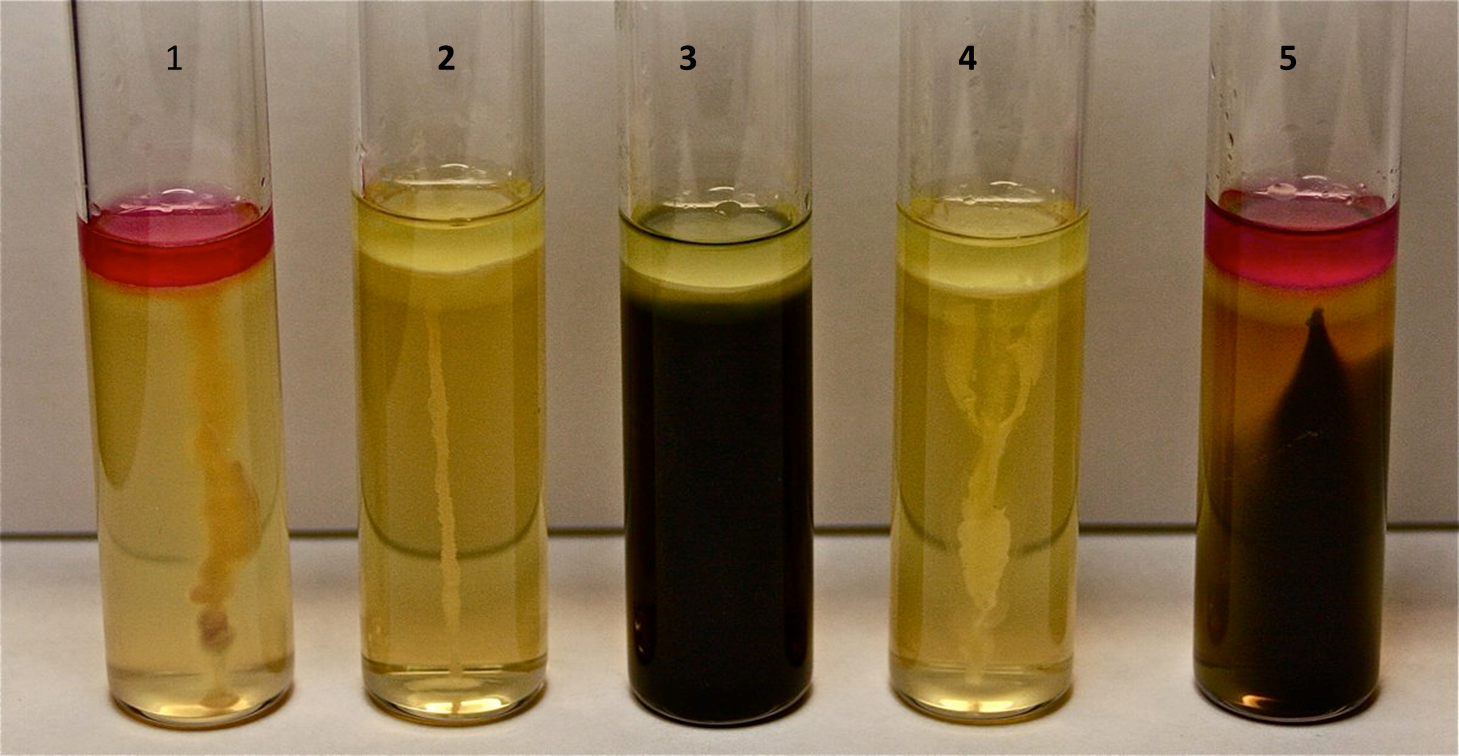

SIM Test
Which test tubes are considered motile?
Tubes 1,3,4,5
SIM Test
Which tube is positive and which is negative?
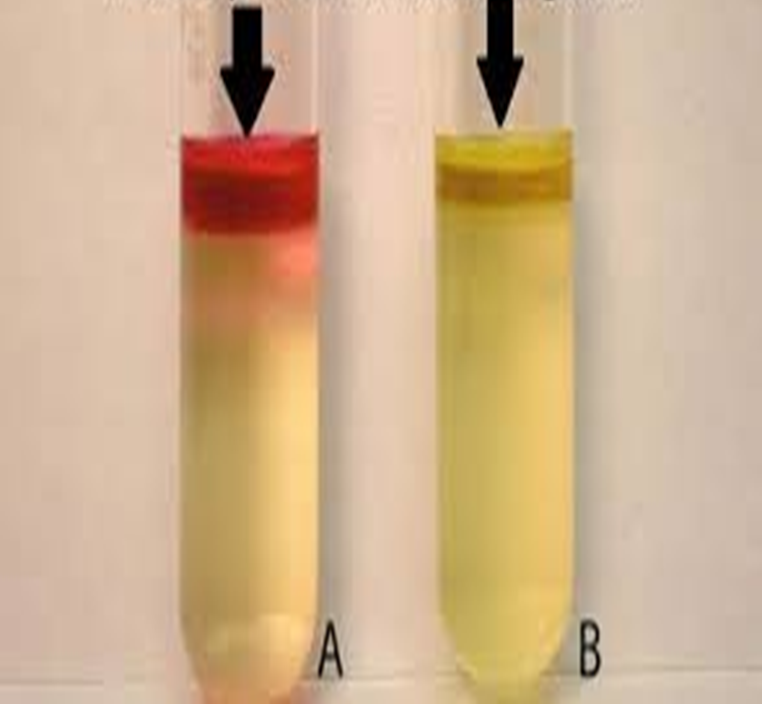
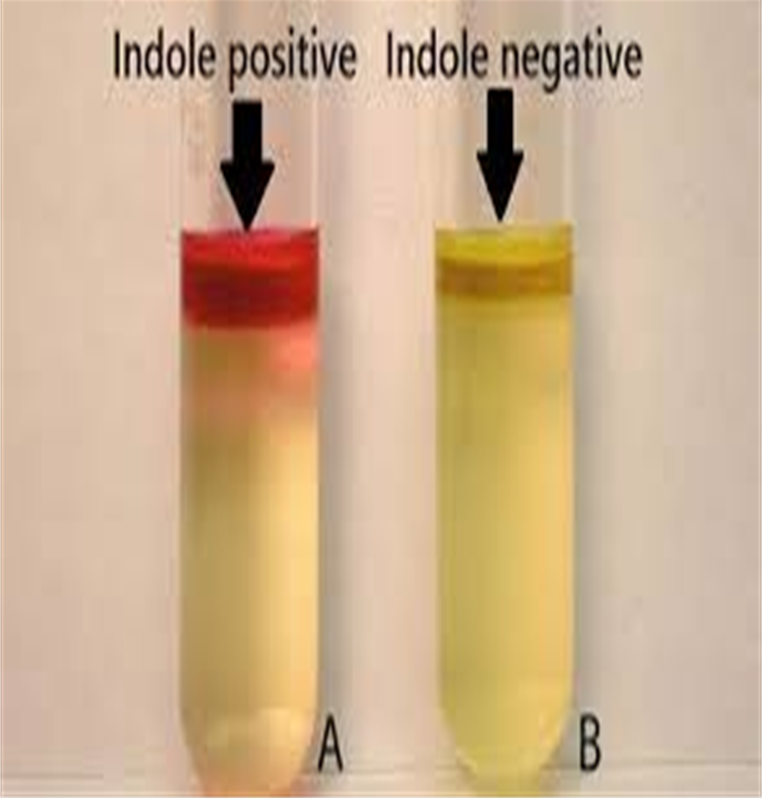
SIM Test
If the SIM agar test tube produces thiosulfate reductase, sulfur is reduced to what gas? What color will be produced?

Hydrogen sulfide gas is produced with a black precipitate.
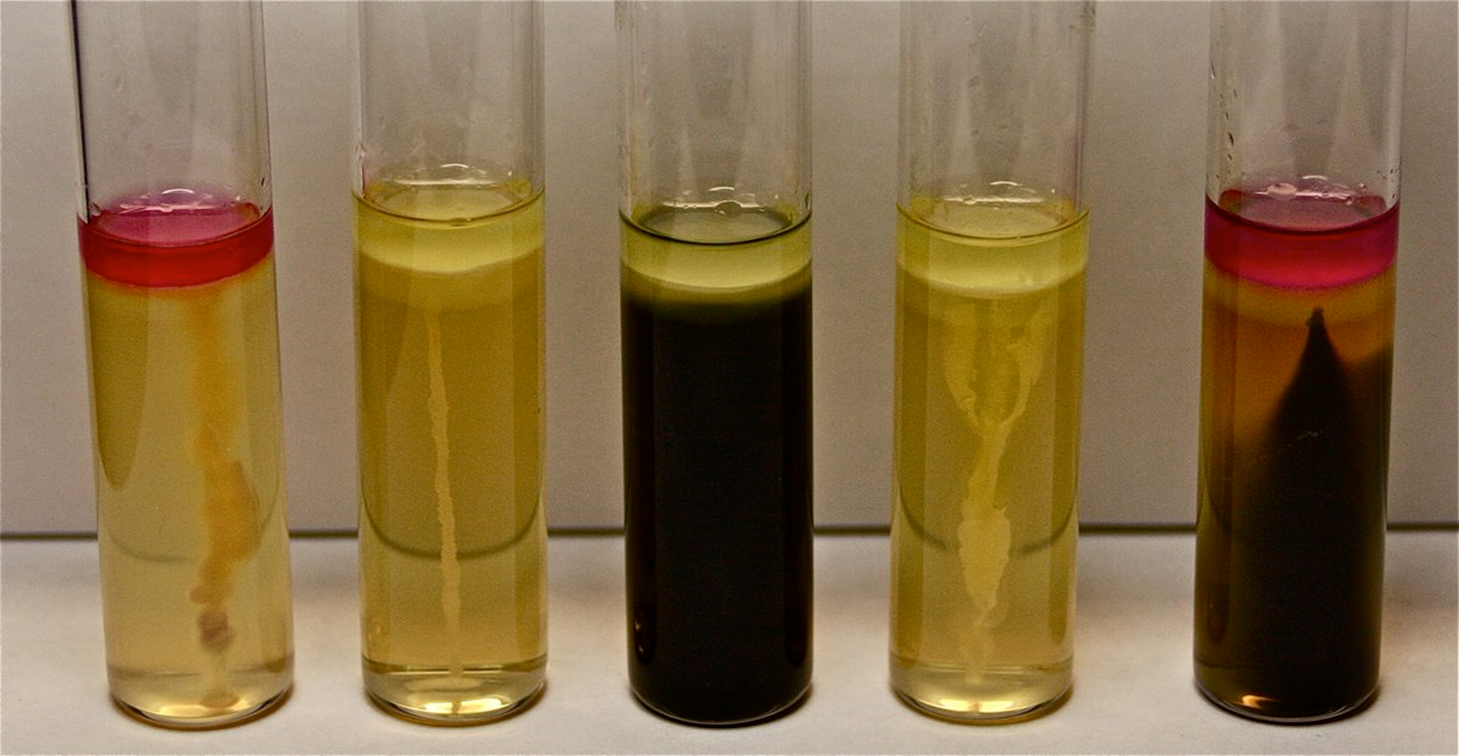

SIM Test
In this SIM test, indicate if there is a presence of:
Indole
Hydrogen sulfide
Motility
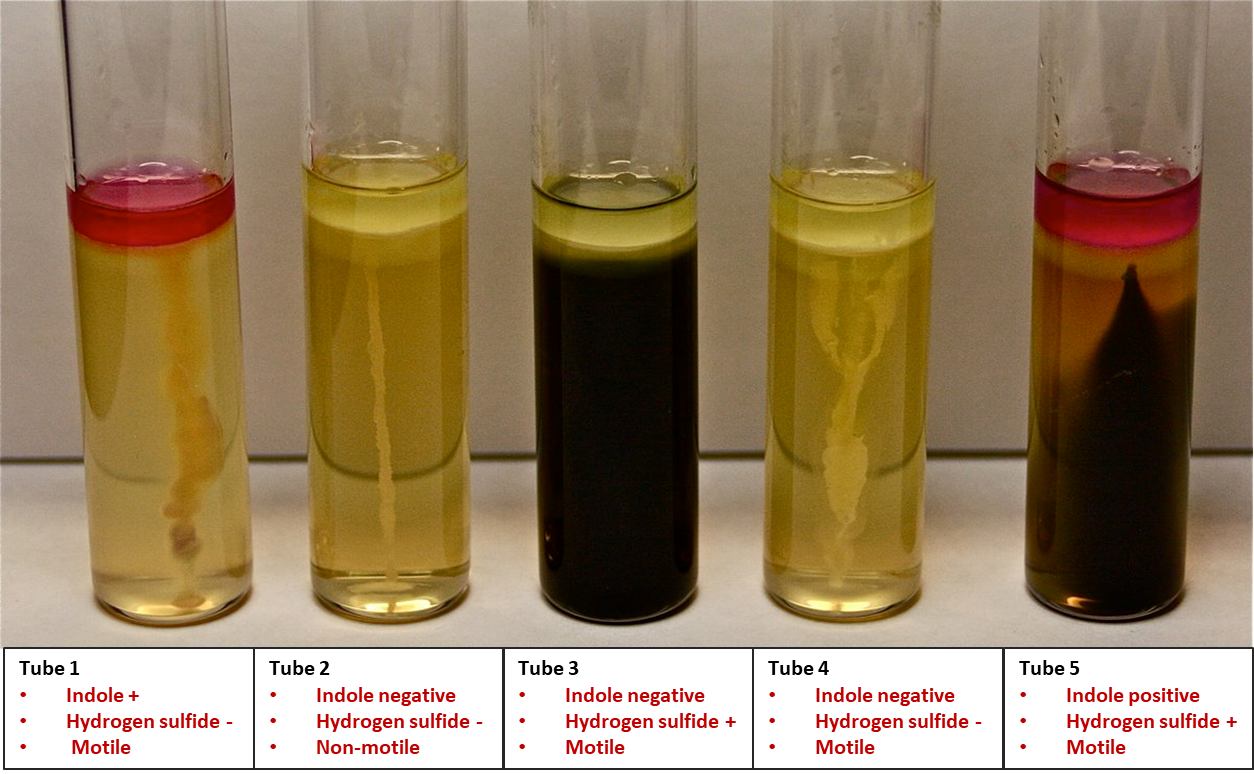
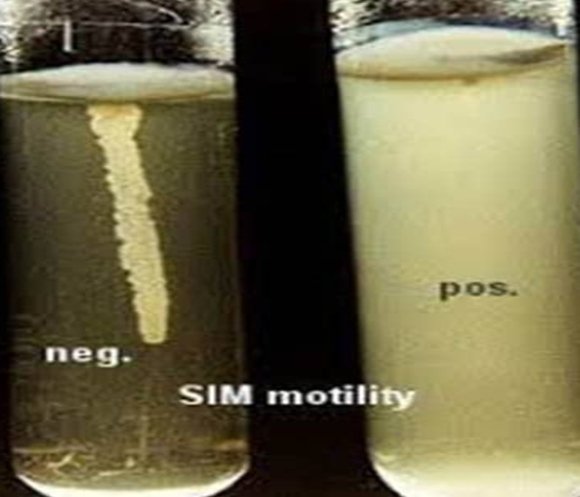


SIM Test
Diffuse growth throughout without seeing a stab line also shows motility.
LIA Test
In the LIA slant test, is lysine deamination an aerobic or anaerobic process? Where does it occur?
Aerobic process that occurs in the slant
LIA Test
In the LIA slant test, is lysine decarboxylation an aerobic or anaerobic process? Where does it occur?
Anaerobic process that occurs in the butt of the media
LIA Test
How is the lysine irone agar (LIA) test performed?
A sterile needle is used to stab the butt and streak the surface of the slant of the LIA medium with the organism.
LIA Test
What is the pH indicator of the LIA media?
Bromcresol purple
LIA Test
What are the colors of both positive deamination and decarboxylation?
Dark Red / Purple
LIA Test
What are the colors of both negative deamination and decarboxylation?
Purple / Yellow

LIA Test
In this tube, what is the result for deamination and decarboxylation?
Deamination - Positive (Dark red)
Decarboxylation - Negative (Yellow)

LIA Test
In this tube, what is the result for deamination and decarboxylation?
Deamination - Negative (Purple)
Decarboxylation - Positive (Purple)

LIA Test
In this tube, what is the result for deamination and decarboxylation?
Deamination - Negative (Purple)
Decarboxylation - ???

LIA Test
In this tube, what is the result for deamination and decarboxylation?
Deamination - Positive
Decarboxylation - Negative
LIA Test
What color is produced if the organism positively decarboxylates (butt) lysine?
Purple color of the butt
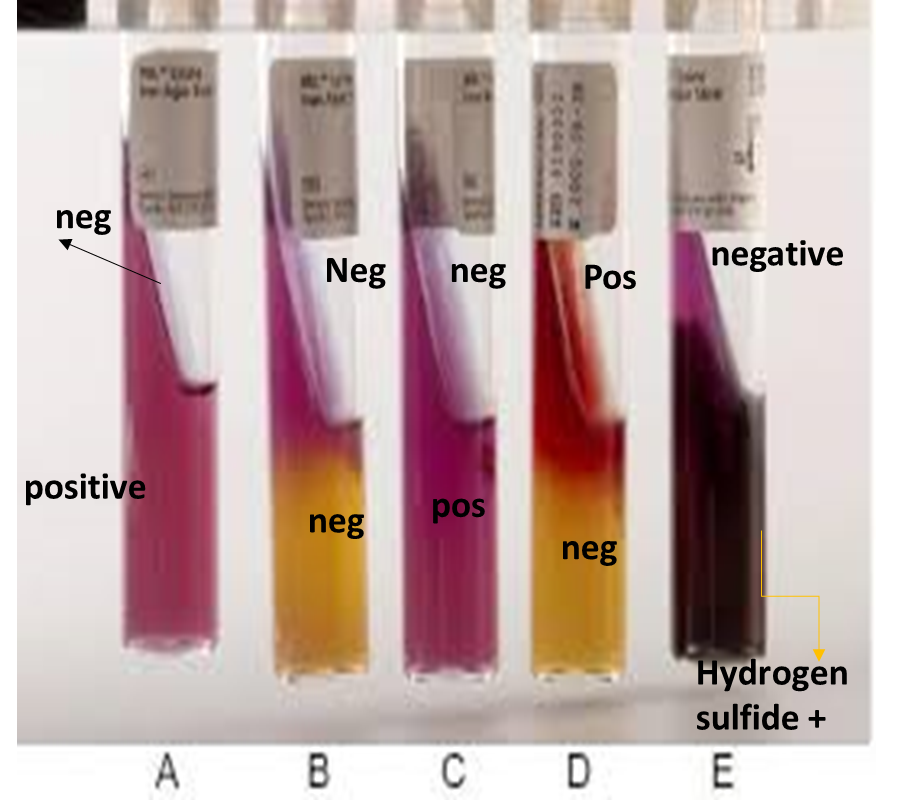

LIA Test
What color is produced if the organism does NOT decarboxylate (butt) lysine?
Yellow color of the butt
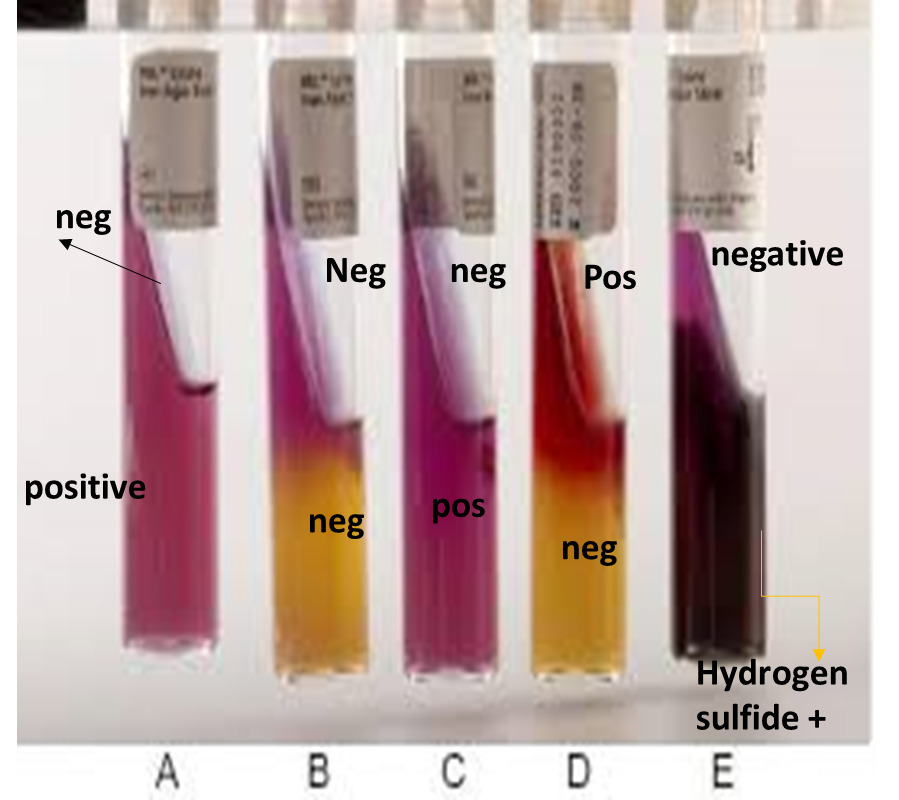

LIA Test
What color is produced if the organism positively deaminates (slant) lysine?
Dark red color of the slant
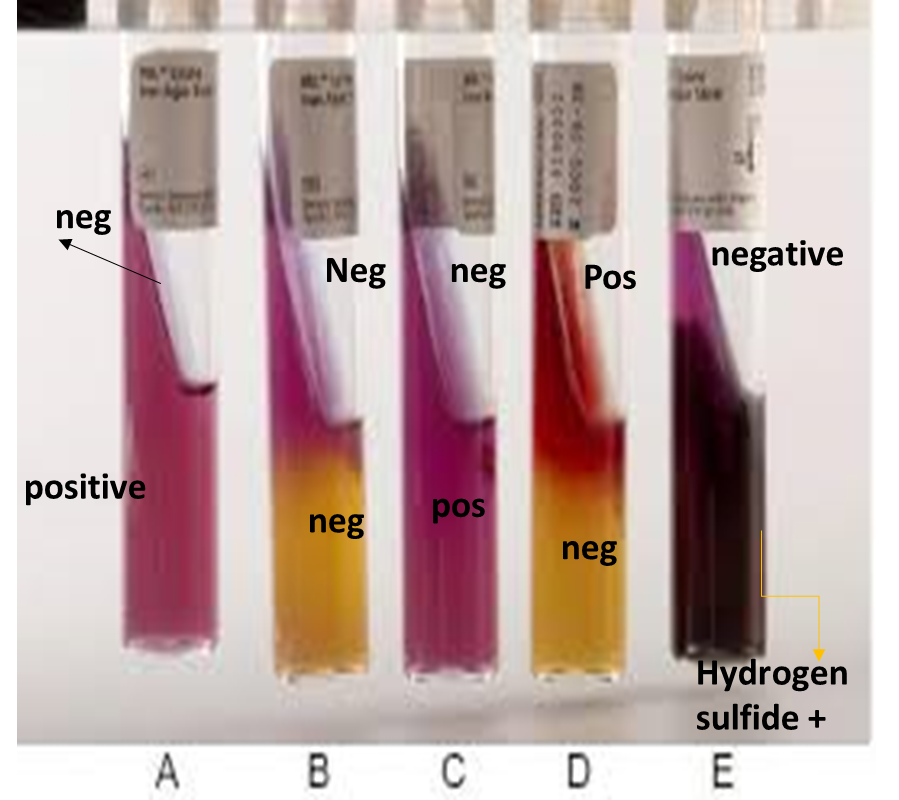

LIA Test
What color is produced if the organism does NOT deaminate (slant) lysine?
Purple color of the slant
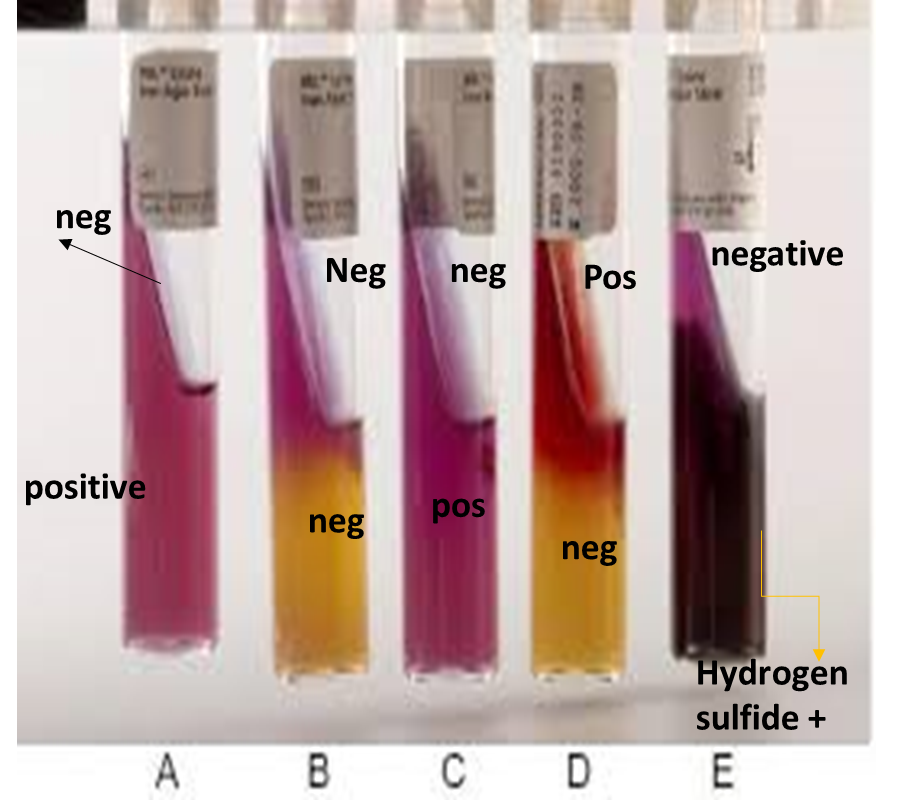

LIA Test
Hydrogen sulfide gas will produce what precipitate in the LIA test?
Black precipitate
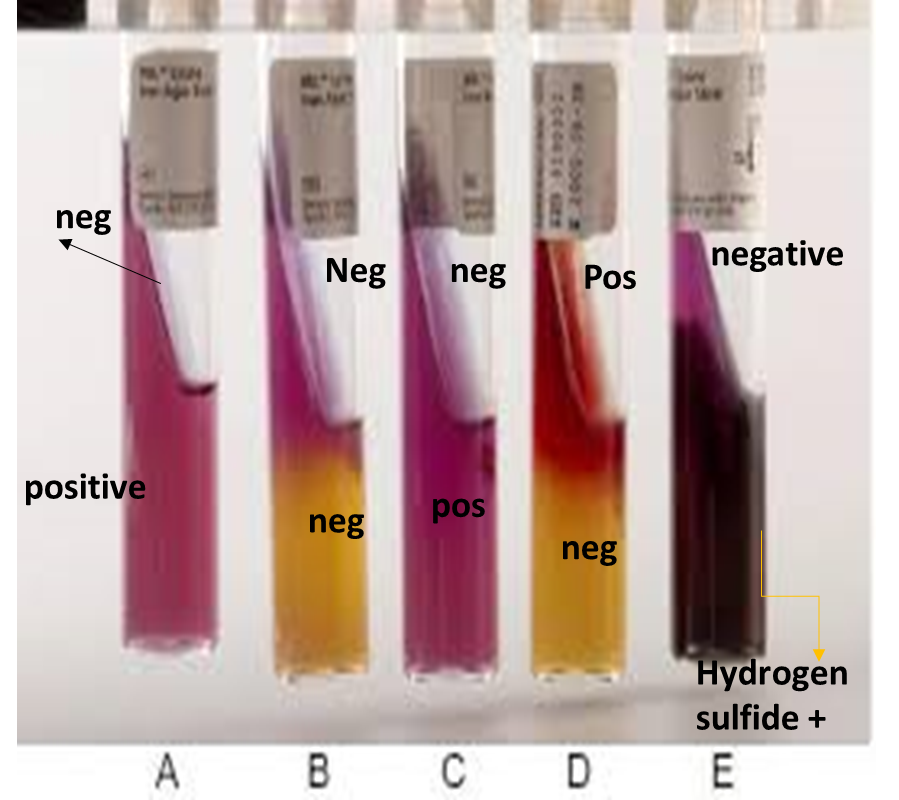

LIA Test
What components of the LIA media test for H2S production?
Sodium thiosulfate
Ferric ammonium citrate?
MRVP
What are the two components of the MRVP test?
MR-Methyl Red Test
VP-Voges Proskauer Test
MRVP
What is the purpose of the MRVP test?
To determine if the organism is able to ferment glucose and what types of fermentation acids are produced.
MRVP
The MRVP test was initially designed to distinguish between which two organisms?
Escherichia coli
Enterobacter aerogenes
MRVP
What would the results be for the MR and VP test for the following bacteria?
Escherichia coli
Enterobacter aerogenes
Escherichia coli
MR Positive (Red broth)
VP Negative
Enterobacter aerogenes
MR Negative
VP Positive (Red diffusing band)
MRVP
What reagent is added to the MR test?
Methyl red
MRVP
In the methyl red test, a positive E. coli test produces which three acids?
Lactic acid
Acetic acid
Formic acid
MRVP
In the methyl red test, Enterobacter aerogenes only produces which acid in the methyl red test?
Acetic acid
MRVP
In the methyl red test, the acids produced by E coli are strong enough to overcome the buffering capacity of the phosphate buffer. Does this increase or decrease the pH?
Decreases the pH
MRVP
MRVP broth contains which three components?
Peptones
Phosphate buffer
Glucose
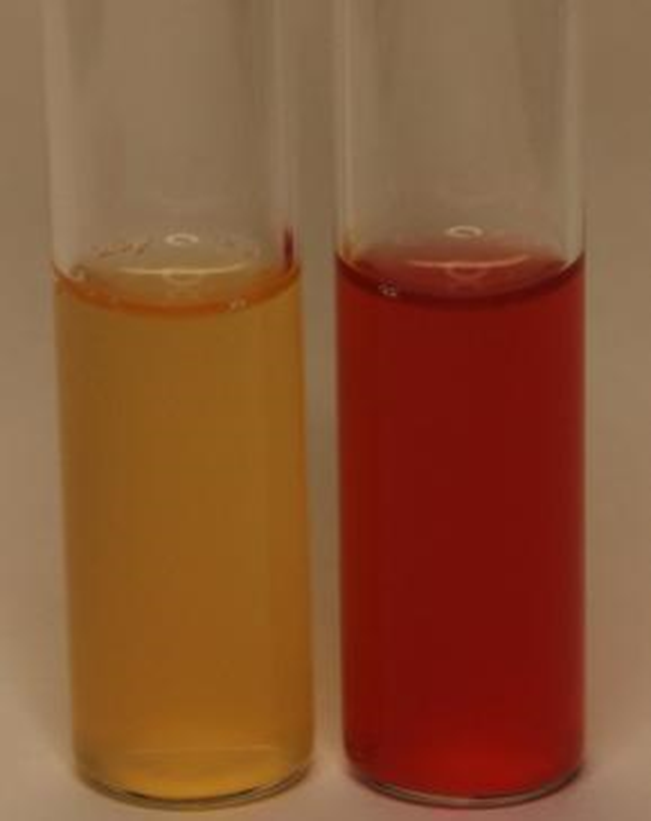

MRVP
In this methyl red test, which is positive and which is negative?
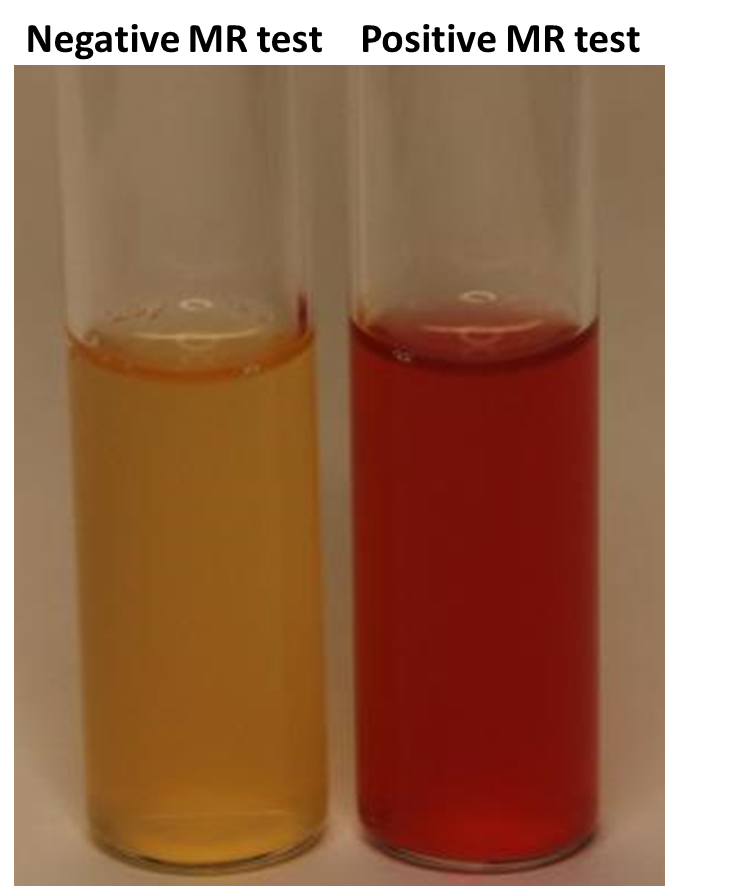

MRVP
In the methyl red test, a cherry red positive color indicates what pH?
pH of 4.4 or lower
MRVP
In the VP test, what is the pH of acetylmethylcarbinol?
pH 6.2
MRVP
In the methyl red test, an orange color indicates that the test is positive or negative?
Negative
MRVP
What is the end product of a positive MR test?
Lactic acid
Acetic acid
Formic acid
The bacteria produces a mixture of acids from the fermentation of glucose that is in the media.
MRVP
What is the end product of a positive VP test?
Only acetic acid
The bacteria is able to ferment the glucose but is only able to produce one acid end-product.
MRVP
In the VP test, acetic acid is converted to…?
Acetylmethylcarbinol
MRVP
In the VP test, what is added to the empty tube with the MRVP broth?
Barritt’s reagent A(alpha naphthol)
Barritt’s reagent B( 40% KOH)
MRVP
What characteristic is shown in a positive VP test after 20 minutes?
Dark red band at the top of the broth, which will diffuse over time. This means that the organism fermented glucose to produce acetic acid.
MRVP
Can an organism be positive for both the MR and VP test?
No
MRVP
Why can’t both tests be positive for a certain organism?
Different metabolic pathways: The MR-positive pathway favors strong acid production, whereas the VP-positive pathway converts acids to neutral products.
Bacteria typically specialize in one pathway, not both simultaneously, due to enzyme regulation and resource allocation.
If the organism produces enough stable acids to turn MR positive, it generally lacks the capacity to convert those acids into neutral products needed for a VP-positive result, and vice versa.
TSI
What are the ingredients in the TSI agar slant?
Glucose/Sucrose/Lactose
Phenol red
Peptones
Sodium thiosulfate
Ferrous sulfate
TSI
What are the carbohydrates and their concentrations in the TSI slant?
Glucose 0.1%
Sucrose 1.0%
Lactose 1.0%
TSI
What is the pH indicator of the TSI slant?
Phenol red
TSI
How is the triple-sugar iron agar test performed?
A sterile needle is used to stab the butt and a zig zag streak is made on the surface of the TSI agar slant.
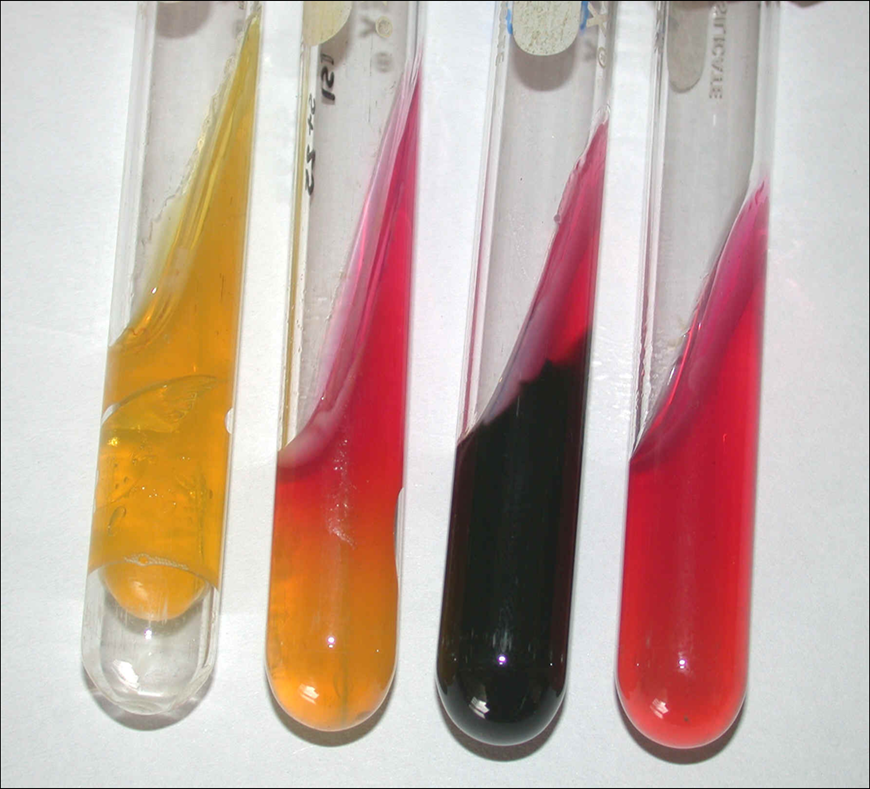

TSI
In this TSI agar test, indicate:
Is the slant/butt acidic or alkaline
Is there gas present
Is there hydrogen sulfide present
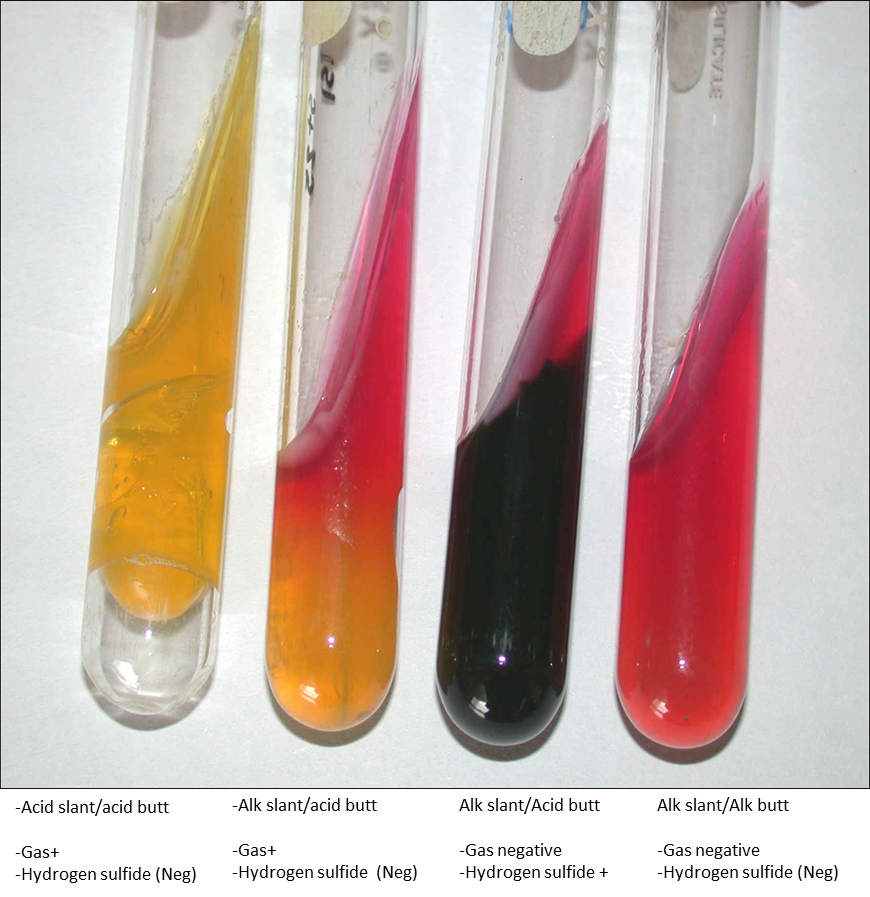


TSI
What carbohydrates are being fermented?
Glucose

TSI
What carbohydrates are being fermented?
Glucose

TSI
What carbohydrates are being fermented?
1st glucose, then sucrose and/or lactose

TSI
What carbohydrates are being fermented?
None, no carbohydrates are being fermented
TSI
In an alkaline slant/acid butt, what has occurred?
Only glucose fermentation has occured
TSI
In an acid slant/acid butt, what has occurred?
Glucose fermentation plus lactose and/or sucrose fermentation has occurred
TSI
In an alkaline slant/alkaline butt, what has occurred?
No carbohydrate fermentation has occurred
TSI
Is hydrogen sulfide production in the TSI test, acidic or alkaline?
Acidic. The black color of hydrogen sulfide will mask the yellow color of the pH indicator.
TSI
Which components of the media test for H2S production?
Sodium thiosulfate
Ferrous sulfate
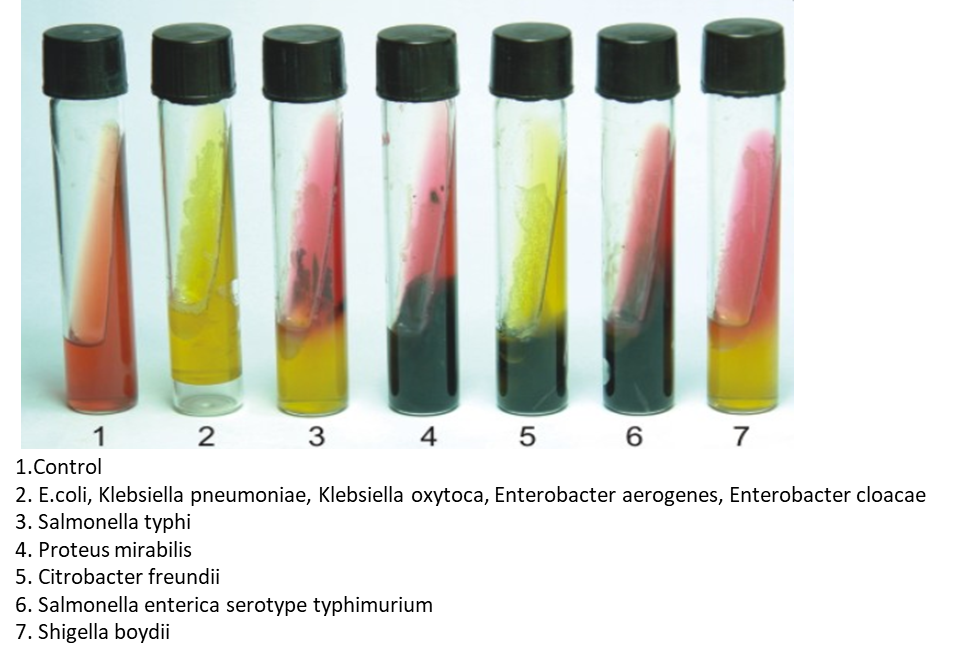

TSI
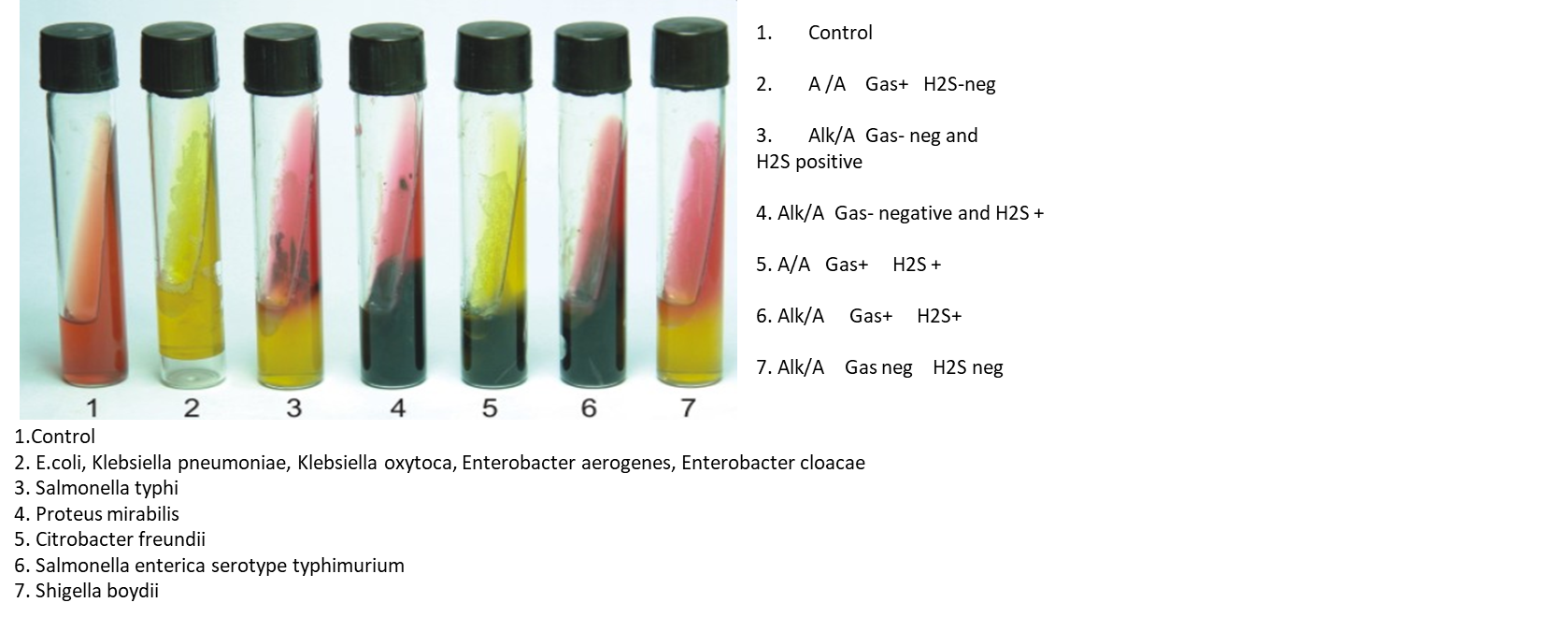


TSI
What are the following results for this tube?
Acidic or Alkaline?
Presence of gas?
Presence of hydrogen sulfide?
Acid/Acid
Gas +
H2S +
Lactose and/or sucrose fermentation has occurred.
Hydrogen sulfide production is always acidic, even though black coloration masks yellow color of pH indicator.

TSI
What are the following results for this tube?
Acidic or Alkaline?
Presence of gas?
Presence of hydrogen sulfide?
Alkaline/Acid
Gas (Negative)
H2S +
Only glucose fermentation has occurred

TSI
What are the following results for this tube?
Acidic or Alkaline?
Presence of gas?
Presence of hydrogen sulfide?
Alkaline/Alkaline
Gas (Negative)
H2S (Negative)
No carbohydrate fermentation has occurred. Instead, peptones are catabolized resulting in an alkaline pH due to the production of ammonia.
TSI
Fermentation of glucose, sucrose, and lactose will result in what color of the slant and/or butt of a TSI agar?
Yellow, as the acids will react with the phenol red
TSI
Production of ammonia will result in what color of the slant and/or butt of a TSI agar?
Red, as the ammonia, produced by peptones, will react with the phenol red.

TSI
What is being catabolized when a TSI agar is all alkaline with an all over orange/red color?
Peptones are being catabolized, not carbohydrates
Rise in pH due to ammonia production
Peptones react with phenol red
Color changes to a deeper red