3.2 photosynthesis
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
write the equation for photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H20 → C6H12O6 + 6O2
why are chloroplasts known as transducers?
they convert energy in the photons of light into chemical energy
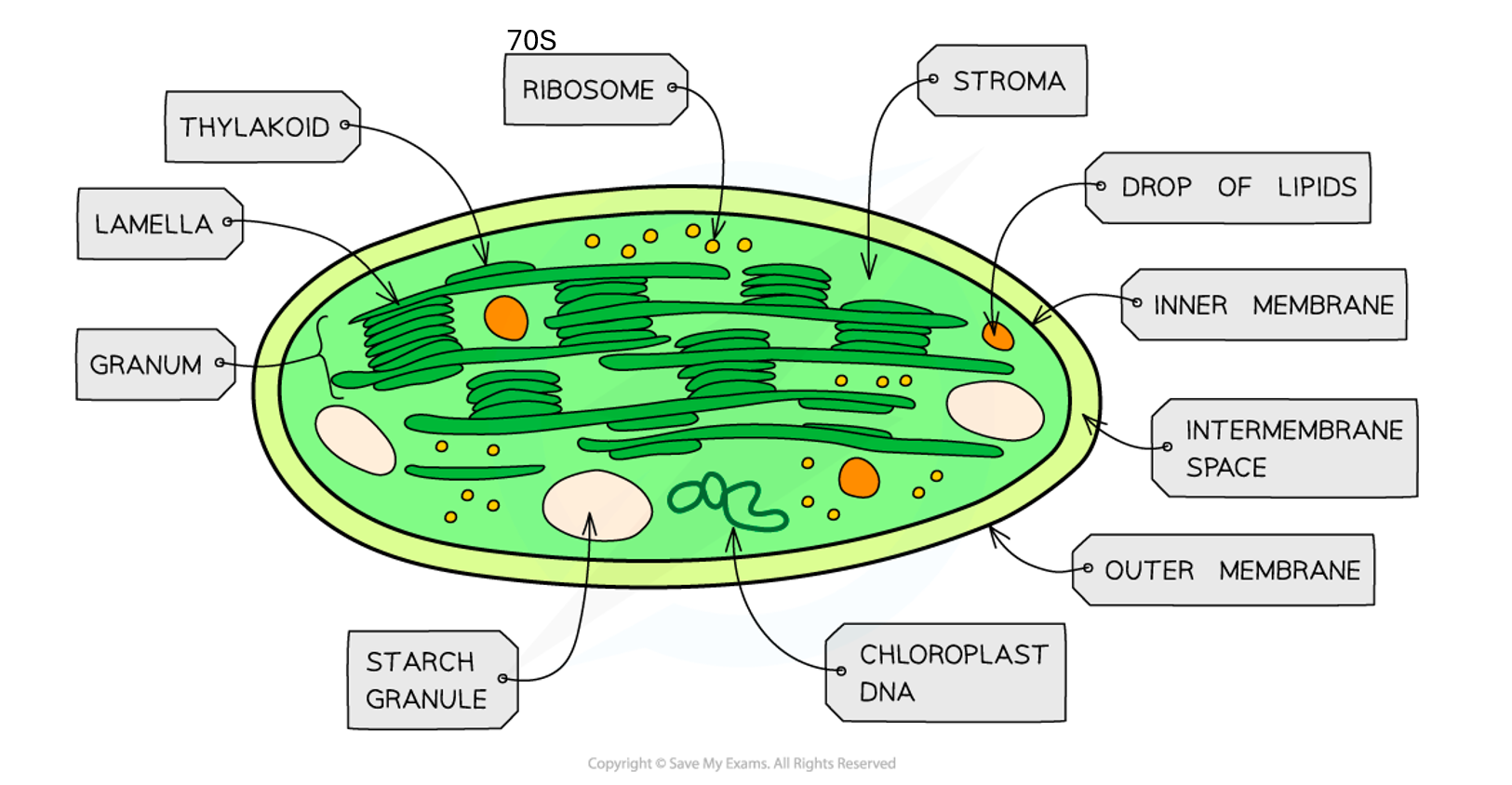
label the chloroplast
where is the main site of photosynthesis in the leaf?
palisade mesophyll cells
how is the feature of the leaf efficient for gas exchange: large surface area?
larger sa = more stomata
how is the feature of the leaf efficient for gas exchange: thin?
short diffusion pathway for gases entering/leaving the leaf
how is the feature of the leaf efficient for gas exchange: air spaces in spongy mesophyll tissue?
allows O2 and CO2 to diffuse more easily between stomata and cells
how is the feature of the leaf efficient for gas exchange: stomatal pores?
gas exchange in and out of leaf
in englemann’s experiment why did the bacteria cluster in the red and blue regions of the spectrum?
wavelengths of light absorbed the most
higher rate of light dependent stage
more photolysis of water to release O2
bacteria need O2 for aerobic respiration
in englemann’s experiment why are there no bacteria present on the green regions?
very little green light absorbed/it is reflected
what is a suitable control for englemann’s experiment?
use white light only
bacteria would distribute evenly across the tube
shows different wavelengths of light are causing the distribution seen in the experiment
what is a pigment?
a coloured substance that absorbs specific wavelengths of light
what are the 2 main classes of photosynthetic pigments?
chlorophylls
carotenoids
what are the different types of chlorophylls?
chlorophyll a - primary pigment
chlorophyll b/c - accessory pigments
what are the different types of carotenoids?
carotenes and xanthophylls - both accessory pigments
how would a lack of Mg result in poor growth in a plant?
lack of Mg so lack of chlorophyll
plant cannot absorb as much light energy
less light dependent stage
less ATP and NADPH for light independent stage
rate of photosynthesis decreases
less glucose for respiration
less ATP for protein synthesis/cell division
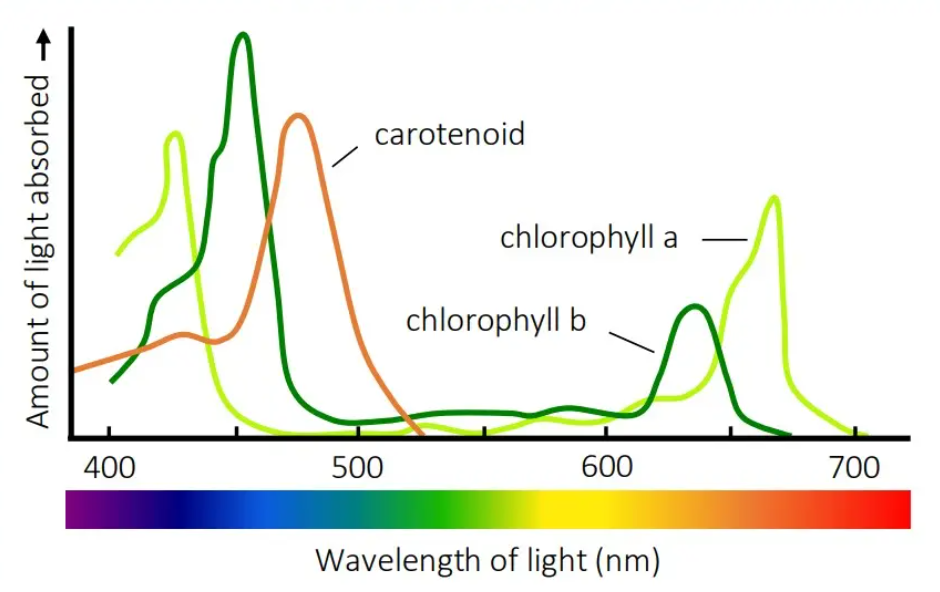
what graph is this?
absorption spectrum
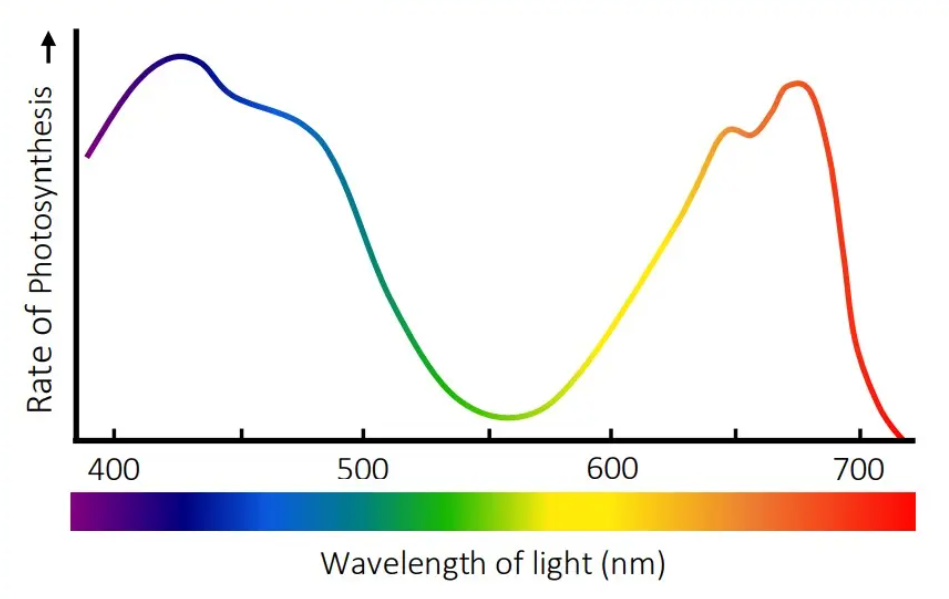
what graph is this?
action spectrum
what does an absorption spectrum show?
how much light energy a particular pigment absorbs at each wavelength
what are the advantages of having multiple pigments?
can absorb a wider range of wavelengths
more light dependent stage
more ATP and NADPH for light independent stage
rate of photosynthesis increases
what does an action spectrum show?
rate of photosynthesis at different wavelengths of light
what does the correlation between action and absorption spectrum suggest?
close correlation
photosynthetic pigments responsible for absorbing light energy in photosynthesis
where are the photosystems located?
thylakoid membranes
what is each photosystem made up of?
antenna complex
reaction centre
what is the antenna complex?
clusters of up to 400 photosynthetic pigments
anchored into phospholipids of thylakoid membrane
allows range of wavelengths to be absorbed
what is the reaction centre?
at base of antenna complex
2 molecules of primary pigment cha
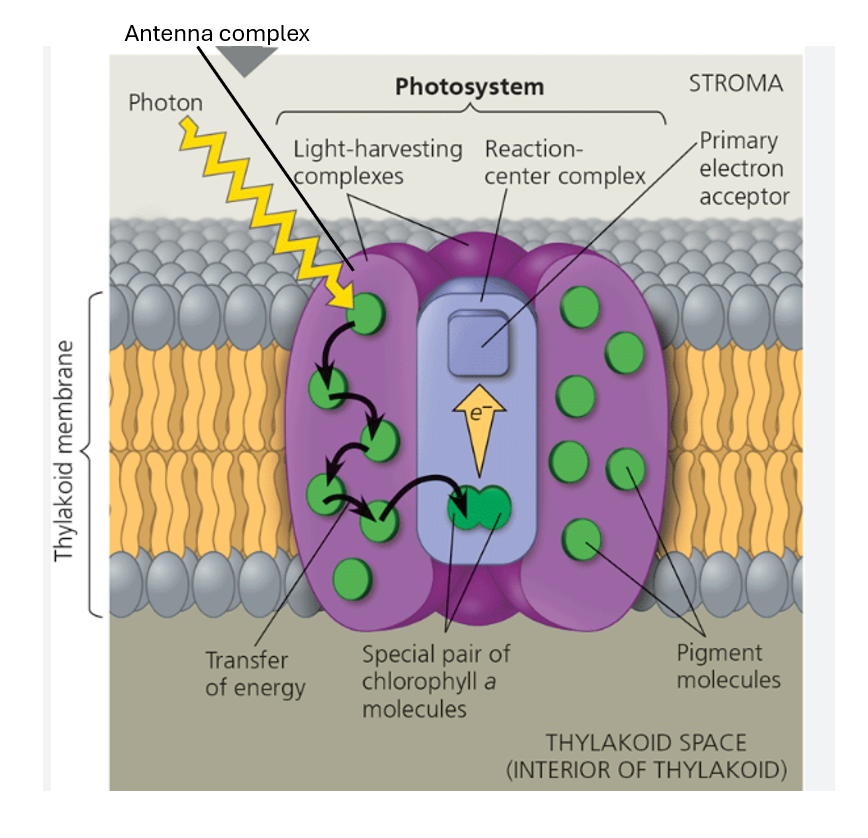
label the photosystem
photosystem I (PSI)?
absorption peak of 700nm
P700
richer in chlorophyll a than b
photosystem II (PSII)?
absorption peak of 680nm
P680
richer in chlorophyll b than a
what are the 2 stages of photosynthesis?
light dependent stage
light independent stage
what is the light dependent stage split into?
non-cyclic photophosphorylation
cyclic photophosphorylation
talk through non-cyclic photophosphorylation
The chlorophyll a in the reaction centre of photosystem II absorbs light energy, which causes 2 high energy electrons to be emitted to a higher energy level
The electrons are received by an electron acceptor
The photolysis of water occurs (H2O -> 2H+ + 2e- + 1/2O2) and the 2 electrons reduce the chlorophyll a in the reaction centre of PSII so it becomes stable
The high energy electrons move along the etc from one electron carrier to another, losing energy to fuel the 1 proton pump so it can pump protons from the stroma into the thylakoid space, setting up an electrochemical gradient
The protons diffuse down an electrochemical gradient through the stalked particle and ATP synthase, releasing energy which is used for ADP + Pi -> ATP by photophosphorylation
The chlorophyll a in the reaction centre of PSI absorbs light energy and emits 2 high energy electrons to a higher energy level
PSI is reduced by the 2 electrons from chlorophyll a in the reaction centre of PSII
2H+ + 2e- + NADP -> NADPH2 (NADP acts as the final electron acceptor)
The NADPH2 is used in the Calvin cycle