Physics: Atomic Structure
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
How big is the atom?
1×10-10nm
Do energy levels further from the nucleus have higher or lower energy?
Higher energy
What happens when an electron absorbs EM radiation?
Can move from lower to higher (outer) energy level
What happens when an electron releases EM radiation?
Electron returns back down to original energy level
What is in the nucleus?
Protons - Positive
Neutrons - Neutral
What is the atomic number?
Number of protons (equal to no. of electrons)
Bottom number
What is the atomic mass number?
Top number
No. of protons + Neutrons
What is an isotope?
Atoms of the same element with different number of neutrons.
What is an ion?
An atom with an overall charge
Atom loses one electron = 1+ charge
Gains one electron = 1- charge
What is the alpha scattering experiment?
To investigate the plum pudding model
Firing alpha particles (positively charged) at gold foil
Most particles went through - atom is mostly empty space
Some particles were deflected - Centre of atom must have positive charge which repelled alpha particles
Sometimes particle went straight back - Mass of atom is concentrated in centre (nucleus)
What was the first (Ancient Greek) belief of atoms?
Small solids spheres which made everything
What was the first scientific theory about the atom?
Plum pudding model
Ball of positive charge
With negative electrons in
What atom model did the alpha scattering experiment prove?
Nuclear model
What did Niels Bohr decide?
Electrons orbit the nucleus at specific distances
(Energy levels / shells)
Who discovered Neutrons? When?
James Chadwick
20 years after nuclear model
What is radio active decay?
Some isotopes have unstable nucleus
Nucleus gives out radiation to become stable
How is radioactive decay like popcorn?
Can’t predict which atom will decay next (random process)
What is the activity?
The rate a source of unstable nuclei decay
Measured in Becquerel (Bq)
1 Bq = 1 decay per second
How to measure activity of radioactive source?
What is the count rate?
Geiger-muller tube
Count rate no. of decays recorded per second by detector
Alpha particles
a
Alpha particle is same as a helium nucleus
2 protons
2 Neutrons
Beta particle
β
Electron ejected from nucleus at high speed
Formed inside nucleus when a neutron changes into a proton and electron
Gamma ray
Electromagnetic radiation from nucleus
Alpha properties
Travel 5 cm in air
Stopped by paper
Strongly ionising
Beta Properties
Travel 15cm in air
Stopped by few mm of aluminium
Strongly ionising not as powerful as alpha
Gamma Properties
Travel metres in air
`stopped by several cm of lead
Weakly ionising
What is the Half Life?
Time taken for number of nuclei in sample to halve (for half to decay)
Time taken for count rate / activity to reach half
radioactive isotopes
Radioactive isotopes decay and emit radiation from their nuclei
The radiation can form charged atoms (ionising Radiation)
This can increase cancer risk in humans
What is irradiation?
Why is it used?
Why is the object not made radioactive?
Exposing an object to nuclear radiation
alpha
beta
gamma
Gamma radiation kills bacteria to sterilise needles etc
The object isn’t radioactive because it is in contact with the nuclear radiation, not the radioactive isotope.
Precautions for radiation
Alpha - Gloves
Beta & gamma - lead apron / lead walls
Radiation monitor - stop working in too dangerous radiation levels
Radioactive contamination
unwanted radioactive isotopes end up on other materials,
This is hazardous as the radioactive atoms decay and emit
ionising radiation.
Alpha radiation contamination
Strongly ionising
Stopped by dead skin cells
Dangerous in inhaled /swallowed
Beta radiation contamination
Quite ionising
Penetrate skin into body
Can get out again
Gamma radiation contamination
Weakly ionising
Penetrate body
Pass through
What is peer review?
Scientists share their findings about the effects of radiation on humans. The findings can be checked
Background radiation
Natural
Rocks (granite)
Cosmic rays from space (exploding stars)
Man-made
Nuclear weapon testing
Nuclear accidents
Radiation dose
Sv Sieverts
How is iodine used to explore internal organs?
Drink a solution of radioactive iodine
Emits gamma radiation which passes through the body
Scan shows amount of iodine absorbed by thyroid (too high/low) to diagnose condition
Using tracers in exploring internal organs 4 rules
The tracer must emit radiation that can pass out of the body and be detected (gamma or beta radiation).
The tracer must not be strongly ionising to minimise damage to body tissue.
The tracer must not decay into another radioactive isotope.
The tracer must have a short half-life so it is not present in the body for a long period.
Controlling or destroying unwanted tissue
Gamma rays pass into body and destroy tumour
Healthy tissue may be damaged as radiation passes through
Use radioactive rod to target tumour procisesly
Nuclear Fission
In some elements, nucleus is large and unstable
Nucleus splits when absorbing a neutron
Daughter nuclei formed when split
Emit 2/3 neutrons and gamma radiation
Chain reaction
Controlled: in nuclear reactor
Uncontrolled: in nuclear explosions in weapons
Nuclear fusion
Two lighter nuclei join to form heavier nuclei
Some of the mass is converted to energy
Not chain reaction
Name a nuclear fuel
Uranium
What happens when an element releases alpha radiation (radioactive decay)
Mass (top) number decreases by 4
Atomic (bottom) number decreases by 2
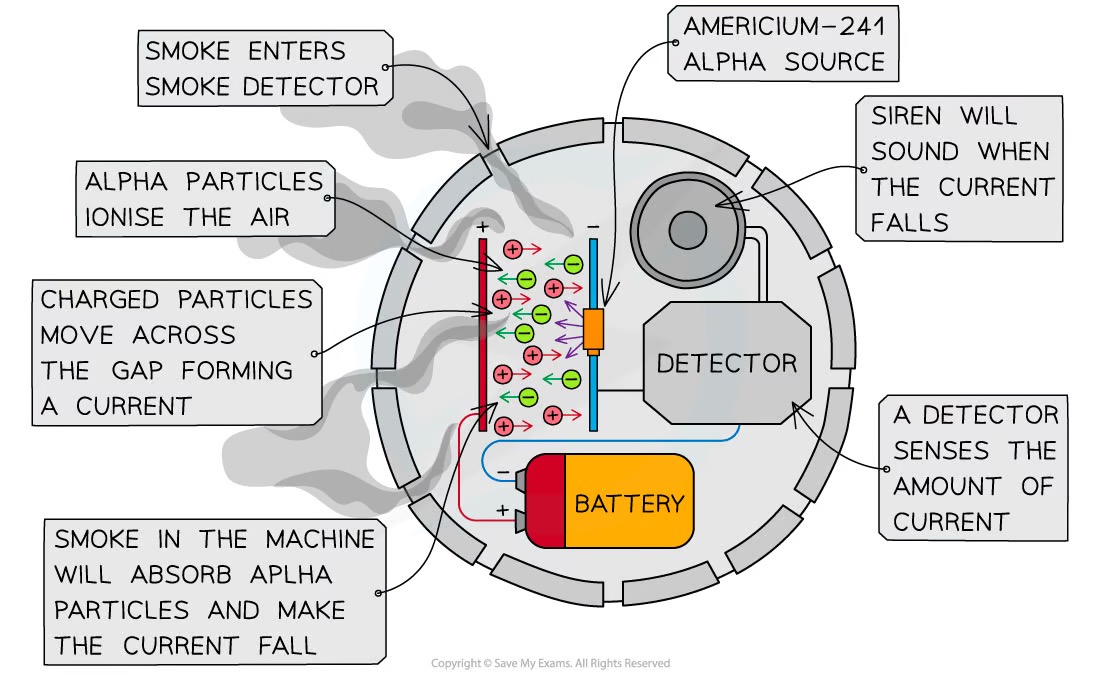
How does a smoke detector work?