Metabolism FINAL
1/750
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
751 Terms
What are the two main processes involving proteins in living organisms?
Protein synthesis and proteolysis.
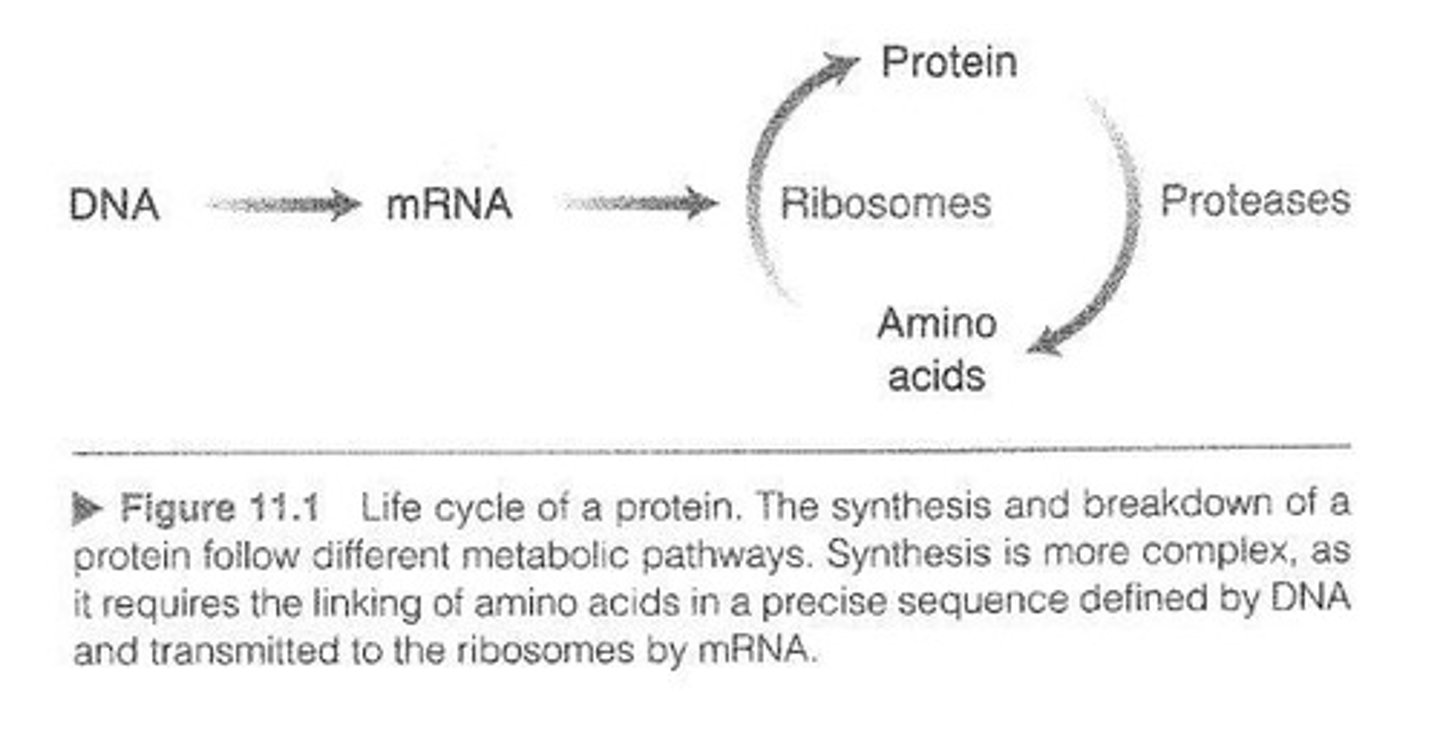
Where does protein synthesis take place?
In the ribosomes.
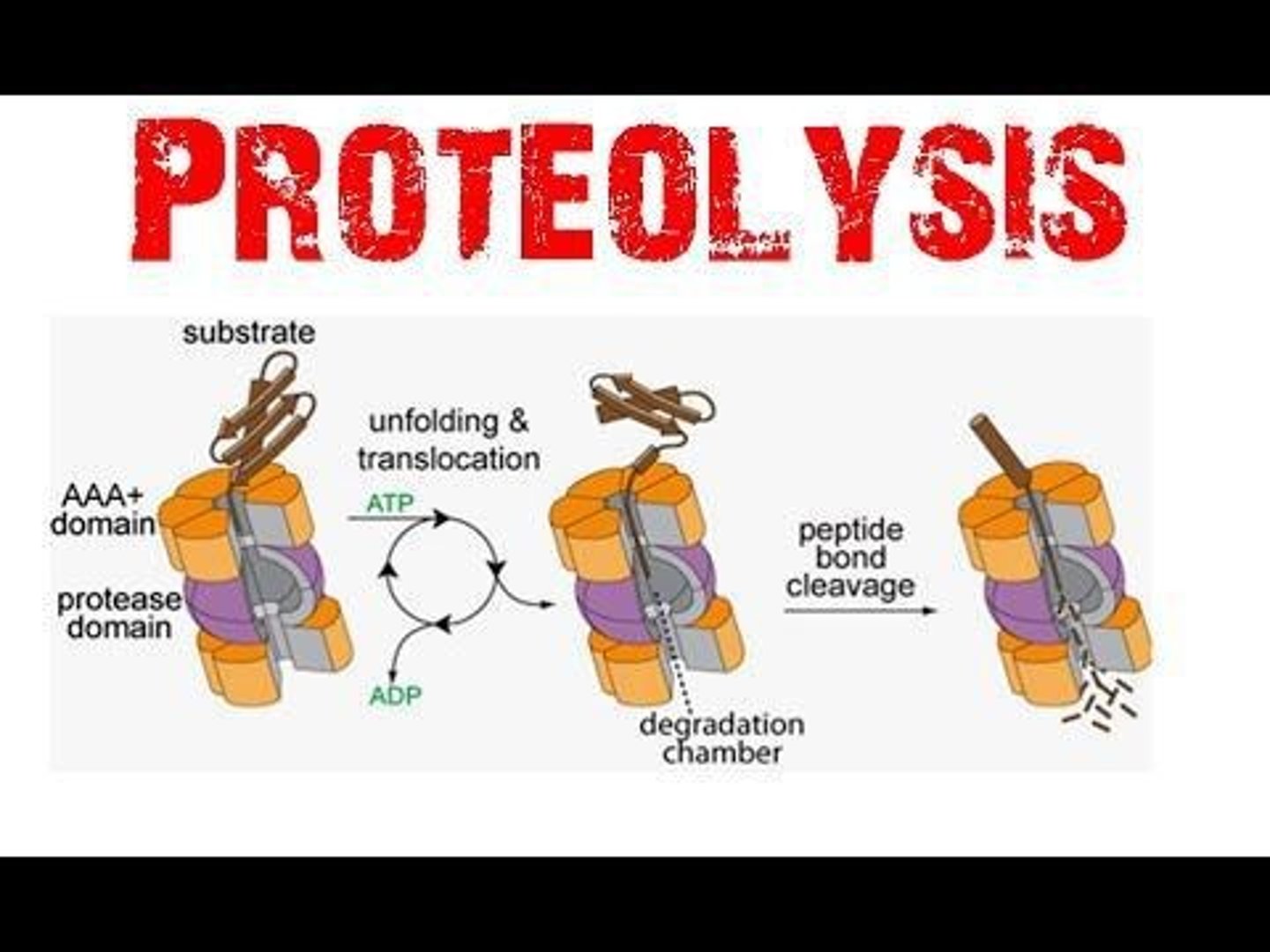
What is the role of proteases in proteolysis?
They catalyze the hydrolysis of proteins to their constituent amino acids.
What marks a protein for degradation in the proteolysis process?
The attachment of ubiquitin chains.
What is the function of the proteasome in protein metabolism?
It hydrolyzes proteins into small peptides.
What powers the attachment of ubiquitin and the operation of the proteasome?
ATP hydrolysis.
What is the average rate of protein synthesis and proteolysis in a healthy adult?
They are approximately equal, resulting in a constant protein mass.
What is the primary source of amino acids for the body?
Dietary proteins.
Why must dietary proteins be broken down in the digestive tract?
Because protein molecules are too large to cross the intestinal wall.
Which protease works in the stomach?
Pepsin.

Name two proteases that work in the small intestine.
Aminopeptidase and chymotrypsin.
What happens to dietary proteins in the small intestine?
They are converted to amino acids by the action of proteases.
How are amino acids absorbed after digestion?
They are absorbed by the epithelial cells lining the small intestine and enter the capillaries.
What effect does acute endurance exercise have on leucine?
It results in increased leucine oxidation, implying higher dietary protein requirements.

How do dietary protein requirements for endurance athletes compare to sedentary individuals?
They are higher for endurance athletes.

What happens to glutamate and BCAA uptake during exercise?
Their uptake from the blood is increased.
What occurs to the concentrations of glutamate and glutamine at exercise intensities above 70% max?
There is a sharp decrease in their concentrations in muscle.
What is the role of glutamine and alanine released by muscles during intense exercise?
They help remove ammonia from the muscle and transport it to the liver for conversion to urea.
What happens to protein balance during prolonged or high-intensity exercise?
The net negative protein balance that is normally observed after eating is increased.
What accumulates in the muscle during prolonged or high-intensity exercise?
Amino acids that are not metabolized increase.
What is unclear regarding the changes in protein metabolism during intense exercise?
It is unclear if the changes are due to increased proteolysis or decreased protein synthesis.
How does muscle protein turnover change after resistance exercise?
Muscle protein turnover increases due to an acceleration of both protein synthesis and degradation.

How does muscle protein breakdown compare to synthesis after resistance training?
Muscle protein breakdown is increased but to a smaller degree than muscle protein synthesis.
How long do elevations in protein degradation and synthesis remain after exercise?
They are transient but still present at 3 hours and 24 hours after exercise, returning to baseline after 48 hours.
What type of exercise does not seem to affect muscle protein turnover like resistance exercise?
Low-intensity to moderate intensity dynamic endurance exercise.
What effect does prolonged endurance exercise have on protein oxidation?
Endurance exercise may result in increased protein oxidation, especially during later stages and glycogen depletion.
What percentage does protein contribute to energy expenditure in resting conditions?
About 5-15%.
How does the contribution of protein to energy expenditure change during exercise?
It likely decreases as carbohydrate and fat become more important as fuels.
What happens to protein's contribution to energy expenditure during very prolonged exercise?
It may increase up to about 10% of total energy expenditure when carbohydrate availability is limited.
What is the relative contribution of protein to energy expenditure during endurance exercise?
Total protein oxidation increases, but the relative contribution remains small.
What is the controversy regarding protein requirements for endurance athletes?
There is debate over whether endurance athletes need to consume more protein than less active individuals.
What effect does training have on protein breakdown and oxidation during exercise?
Training seems to have a protein-sparing effect, resulting in lower protein breakdown and oxidation.
What is the recommended protein intake for endurance athletes?
1.2 g/kgbw to 1.8 g/kgbw, compared to 0.8 g/kgbw for the average population.
Do endurance athletes typically have trouble meeting their protein needs?
No, if energy intake matches energy expenditure, they do not need to supplement their diets with protein.
How does resistance exercise affect leucine oxidation?
Resistance exercise does not significantly increase the rate of leucine oxidation.
What is the suggested protein intake for strength athletes?
1.6 g/kgbw/day to 1.8 g/kgbw/day.
Can strength athletes meet their protein requirements with a normal diet?
Yes, this requirement can be easily met without extra protein intake.
Are protein supplements necessary for meeting recommended protein intake?
No, protein supplements are often used but are not necessary to meet the recommended protein intake.
What is the reported range of protein intake for athletes?
Studies have reported protein intakes of athletes between 1.0 g/kgbw/day to 3 g/kgbw/day.
How does the protein intake of athletes compare to the RDA?
Athletes consume far more than the RDA for protein, which is 0.8 g/kgbw/day.
What can result from protein deficiency in individuals?
Protein deficiency can compromise function and lead to a loss of body protein (atrophy).
Which groups of athletes are recognized as being at risk for protein and energy deficiency?
Ammenorrheic female runners, male wrestlers, male and female gymnasts, and female dancers.
Why might vegetarian athletes be at risk for protein deficiency?
Vegetarian athletes may be at risk due to lower quality proteins from plant sources and potential low digestibility.
What is the effect of strength training on muscle?
Strength training results in muscle hypertrophy and increased muscle mass.
How does endurance training affect muscle mass?
Endurance training has limited effect on muscle mass but dramatically increases mitochondrial density inside muscle fibers.
What is the relationship between protein synthesis and strength training?
Hypertrophy from strength training must be caused by increased protein synthesis occurring in the recovery phase between training sessions.
How does training affect protein turnover?
The body adapts to training by becoming more efficient with protein, resulting in decreased protein turnover and less net protein degradation.
What happens to protein synthesis in the hours after exercise?
Protein synthesis may exceed protein degradation after feeding, but if feeding is delayed by 24-48 hours, net protein balance remains negative.
What role does a mixed diet play in protein synthesis?
Feeding a mixed diet provides substrates and creates a favorable hormonal environment for protein synthesis.
How do higher amino acid concentrations in plasma affect protein synthesis?
Higher amino acid concentrations in plasma have a stimulatory effect on protein synthesis.
What effect does increased availability of glucose and amino acids have on plasma insulin?
Increased availability results in higher plasma insulin concentrations, which may reduce protein breakdown and slightly increase protein synthesis.
What is the effect of amino acids on protein synthesis immediately after exercise?
Increased availability of amino acids immediately after exercise has a larger effect on protein synthesis compared to resting conditions.
What effect do carbohydrates have when ingested with protein after exercise?
Carbohydrates may not directly affect protein synthesis but elevate plasma insulin, reducing protein breakdown.
How do carbohydrates and protein work together after exercise?
Protein delivers amino acids while carbohydrates increase the anabolic environment for net protein synthesis.
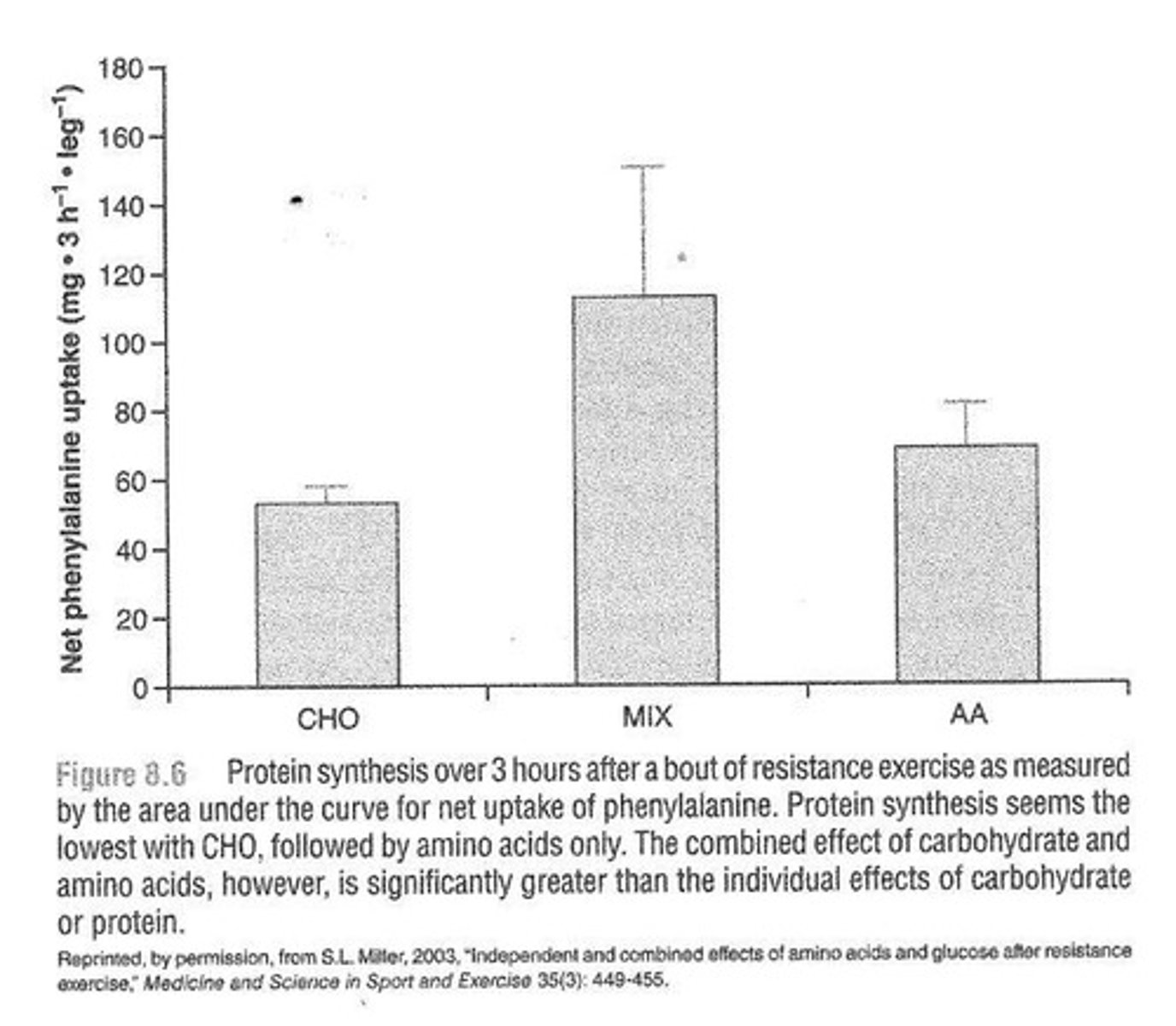
What is the significance of ingesting amino acids after exercise?
Studies have found that ingestion of amino acids after exercise can enhance net protein synthesis.
What is the potential impact of delaying feeding after exercise?
Delaying feeding by 24-48 hours can result in a negative net protein balance and prevent muscle hypertrophy.
What is the relationship between exercise and amino acids on protein synthesis?
Amino acids and exercise have an additive effect on net protein synthesis.
What is the primary reason dehydration is a concern for athletes?
Dehydration impairs exercise performance.
How does the body determine hydration status?
It is determined by the balance between water intake and water loss.
What percentage of body mass does water typically account for in most people?
50-60%.
How does lean body tissue compare to adipose tissue in terms of water content?
Lean body tissues contain about 75% water by mass, while adipose tissue contains only about 5%.
What factors influence the normal body-water content?
The fat content of the body largely determines the normal body-water content.
Why is the water content of the female body generally less than that of the male body?
The female body is lighter and contains a higher proportion of fat.
What is the recommended hydration strategy for athletes before training or competition?
Athletes must be fully hydrated before they train or compete.
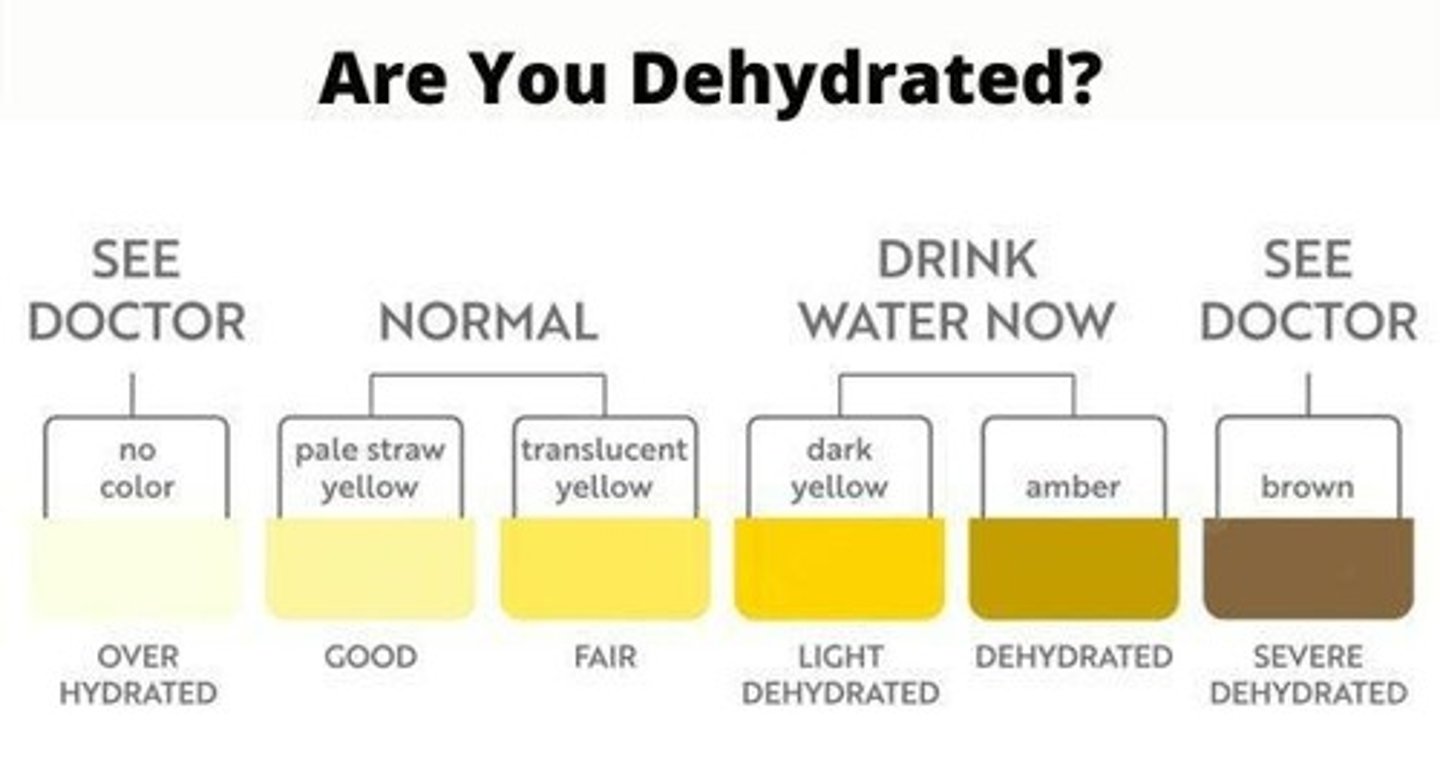
What is a simple method to check hydration status before exercise?
Observing the color of urine; it should be pale.
What does a sudden drop in body mass indicate in athletes?
It likely indicates dehydration.
What is the recommended fluid intake before prolonged exercise?
Approximately 500 ml of fluid should be consumed every 2 hours before exertion and another 500 ml about 15 minutes before exercise.
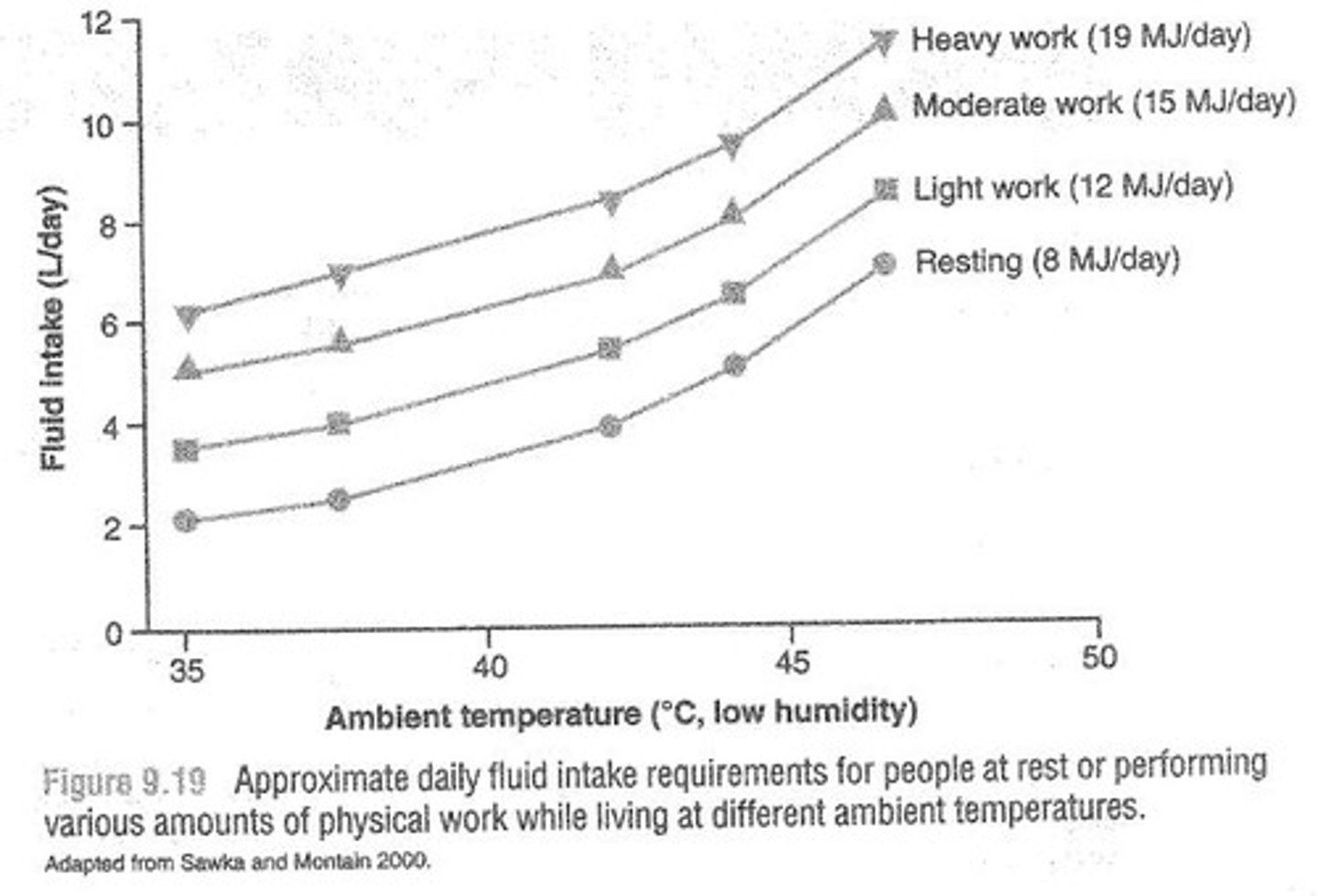
What is the recommended fluid intake during exercise in hot humid environments?
Frequent consumption of 120-180 ml of fluid every 15-20 minutes.
What role do sports drinks play during exercise?
They supply exogenous fuel substrate, help maintain plasma volume, and prevent dehydration.
How does carbohydrate addition affect gastric emptying of fluids?
It slows gastric emptying due to increased osmolarity.
What is the ideal composition of a rehydration solution during exercise?
It should contain carbohydrates (20-60 g/L) and sodium (20-60 mmol/L) and not exceed isotonicity (290 mOsmol/L).
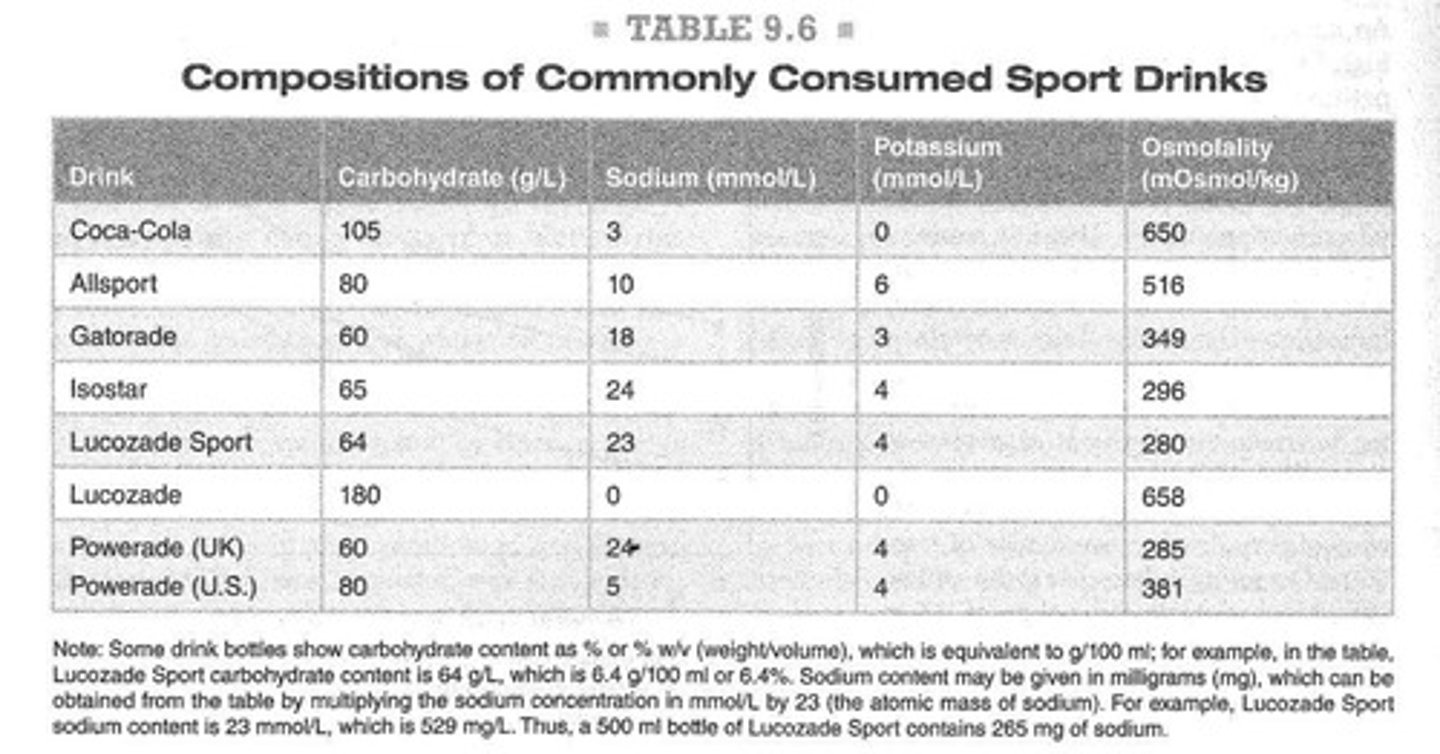
What is the typical carbohydrate concentration in commercially available sports drinks?
60-80 g/L of carbohydrate, predominantly as glucose or glucose polymers.

What is the recommended glucose polymer concentration in cool environments for endurance performance?
100-150 g/L of glucose polymers.
What is the ideal drink for fluid replacement during exercise?
One that tastes good, does not cause gastrointestinal discomfort, promotes rapid gastric emptying, and provides energy in the form of carbohydrates.
What is crucial for rehydration after exercise?
Replacement of water and electrolytes, especially sodium.
Why is plain water not ideal for rehydration after exercise?
It can cause a rapid fall in plasma sodium concentration and osmolarity, delaying rehydration.
What sodium concentration is recommended to add to water for effective rehydration?
77 mmol/L or 0.45 g/L.
What is the effect of sodium chloride on plasma volume restoration?
It promotes rapid and complete restoration of plasma volume.
How does carbohydrate presence in rehydration drinks affect fluid absorption?
It stimulates fluid absorption in the gut and improves beverage taste.
What fluid intake strategy is recommended for post-exercise recovery?
Ingesting 150% or more of weight loss to achieve normal hydration within 6 hours.
What is the effect of caffeine and alcohol on post-exercise recovery?
Their intake is generally discouraged due to diuretic actions.
What is the role of food intake in rehydration after exercise?
It helps restore sodium and chloride losses, especially when sweat losses are high.
What is a challenge with high-sodium drinks for rehydration?
They can be unpalatable, leading to reduced consumption.
Lipid
A substance that is soluble in organic solvents but not in water.
Esterification
The making of triglycerides, involving attachment of a fatty acid to glycerol by means of an oxygen atom.
Hydrolysis
The process of triglyceride hydrolysis, also known as lipolysis.
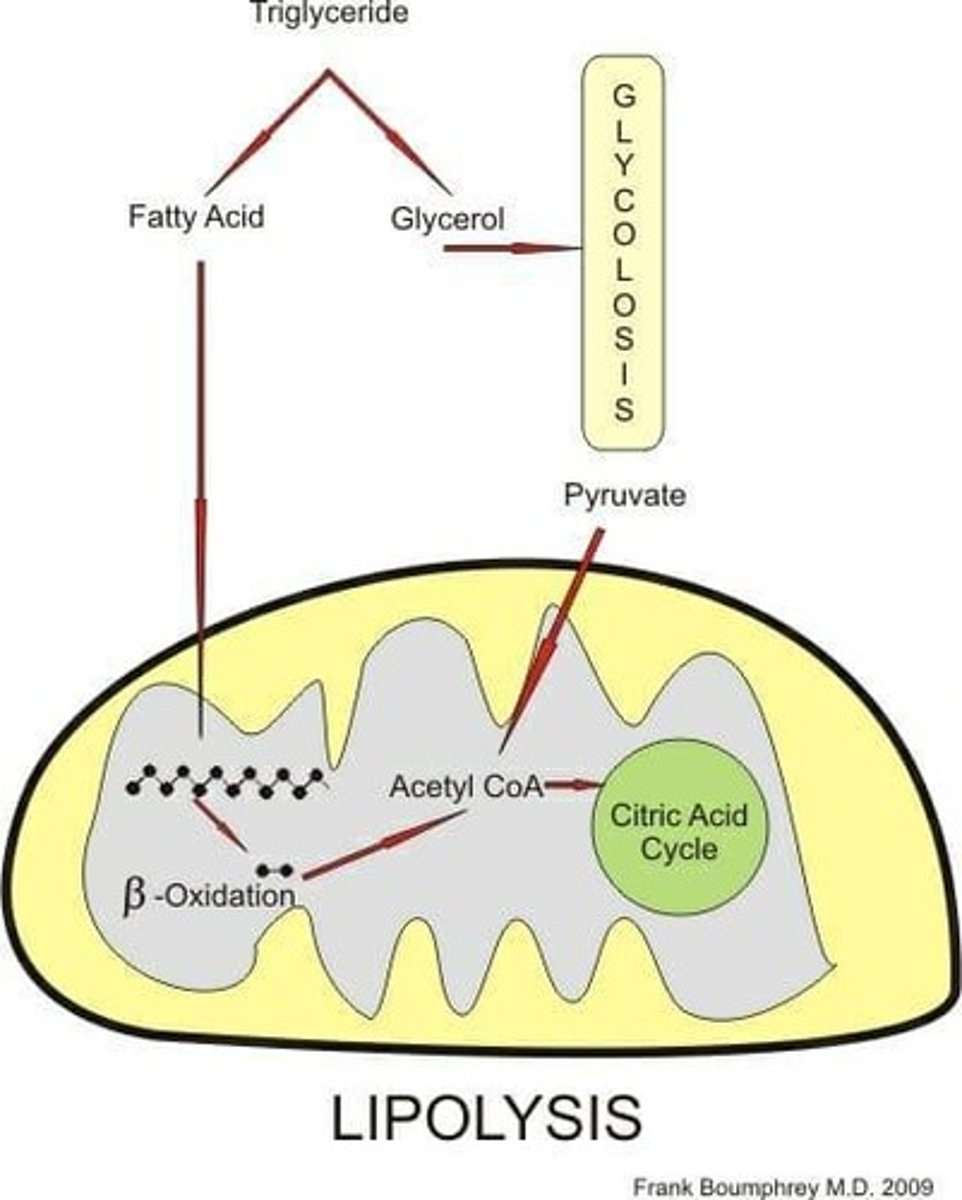
Triglycerides
The vast majority of the lipid consumed in the diet and stored within the body.
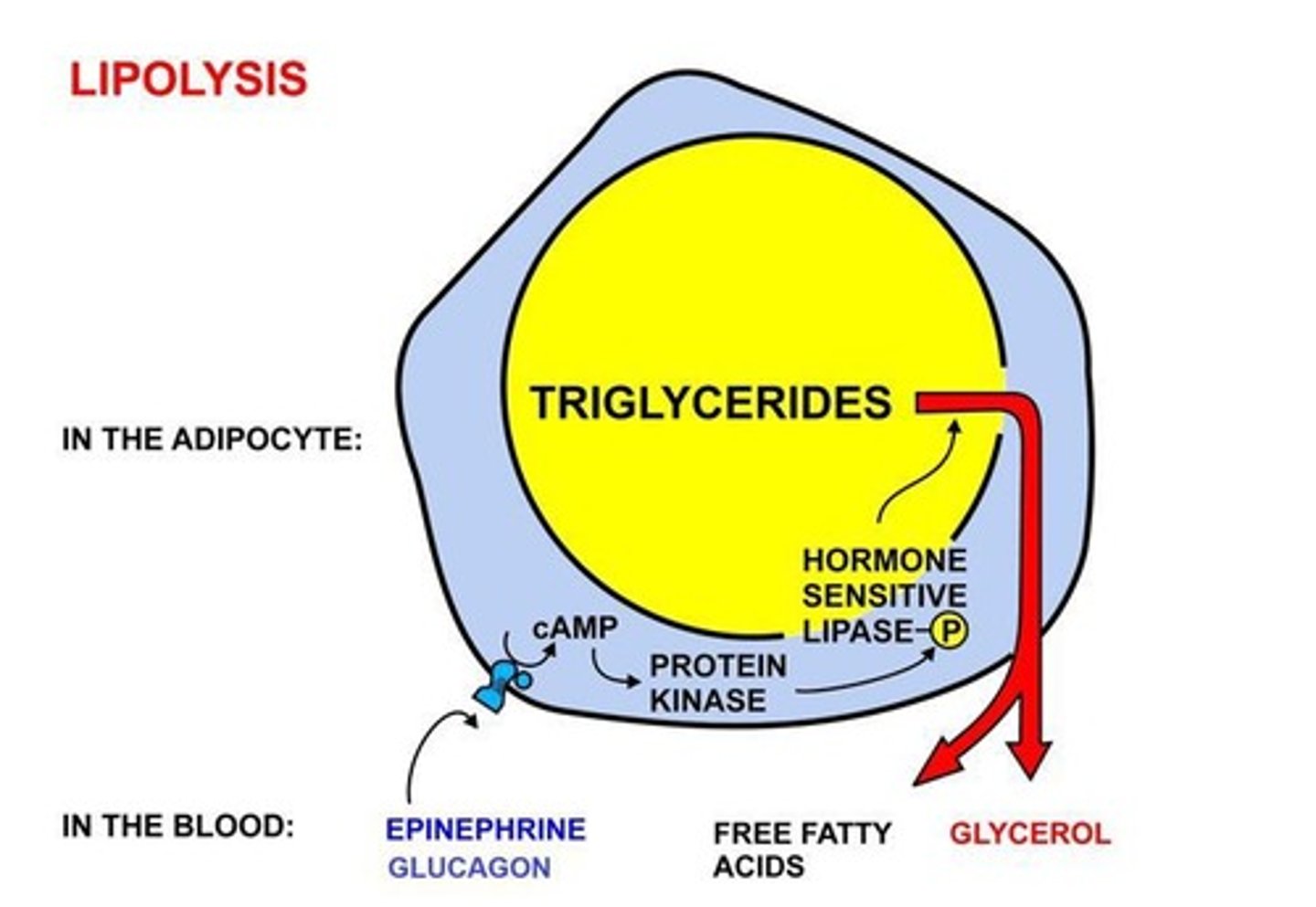
Lipolysis
The process of triglyceride hydrolysis.
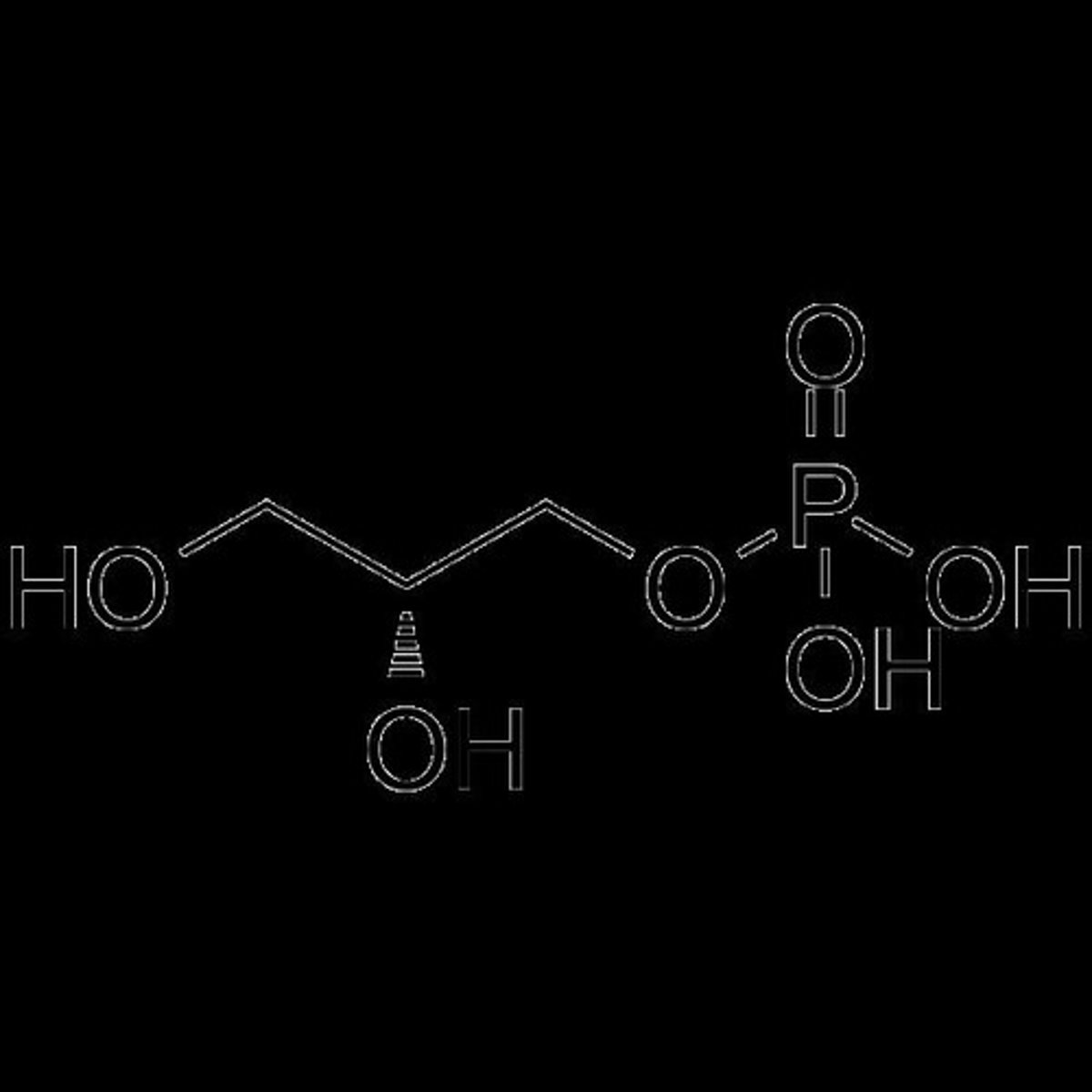
α-glycerolphosphate
The backbone substrate for triglyceride synthesis derived from glycolysis.
Re-esterification
The process of reattaching fatty acids to glycerol to form triglycerides, primarily occurring in the liver.
Fatty Acids
Can combine with glycerol to form mono-, di-, or triglycerides.
Dietary Fat
The preferred energy storage form, with carbohydrate oxidation providing more energy for a given amount of oxygen.
Fat Utilization
The process of using fat as fuel during rest and exercise.
Fat Oxidation
The process of breaking down fat for energy, influenced by exercise duration, intensity, and aerobic capacity.
Mobilization of Triglycerides
The process involving lipolysis to release stored triglycerides from adipose tissue.
Effects of Diet on Fat Metabolism
The impact of dietary choices on fat metabolism and performance.
Short-term, High-fat Diet
A dietary approach that can affect fat metabolism and performance in the short term.
Long-term, High-fat Diet
A dietary approach that can affect fat metabolism and performance over an extended period.
Biological Role of Lipids
Energy storage forms held in reserve for use when carbohydrate energy availability is limited.
Aerobic Process
A process that requires oxygen, as seen in fat catabolism.