ANSC 4050 Exam 2
1/239
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
240 Terms
Core
A vaccine of this type is for protection from endemic diseases, and has low enough risk that it can be given to the majority of patients
Risk-based
A vaccine of this type is given based on region and/or type of horse
Zoonotic
A disease that can be transferred between animals and humans
Noncommunicable
A disease that can’t be transmitted directly from host to host
Prophylaxis
An action taken to prevent disease
Encephalomyelitis/myeloencephalitis
Inflammation of the brain and spinal cord
Encephalitis
Inflammation of the brain
African Horse Sickness, CEM, EEE/WEE/VEE, WNV, EHVs, EIA, equine piroplasmosis, strangles, vesicular stomatitis
What are the priority reportable equine diseases in AL?
Reportable disease
A disease that a vet reports cases of to the state in order to document and prevent spread
Rabies, EEE/WEE, tetanus, WNV
List the core vaccinations we give to horses
Yes (communicable), virus, mammals, yes (inactivated), 100
Fill in the blanks for rabies:
Zoonotic: ___, Causative agent: ___, Vector: ___, Vaccine available & what type: ___, Mortality: ___%
Yes (noncommunicable), virus, mosquitos, yes (inactivated), 20-40 for WEE and 75-95 for EEE
Fill in the blanks for EEE/WEE:
Zoonotic: ___, Causative agent: ___, Vector: ___, Vaccine available & what type: ___, Mortality: ___%
Yes (noncommunicable), C. tetani neurotoxin, none, yes (inactivated), 100 if untreated and 75-80 if treated
Fill in the blanks for tetanus:
Zoonotic: ___, Causative agent: ___, Vector: ___, Vaccine available & what type: ___, Mortality: ___%
Yes (noncommunicable), virus, mosquitos, yes (inactivated, recombinant w/ adjuvant), 33
Fill in the blanks for West Nile Virus:
Zoonotic: ___, Causative agent: ___, Vector: ___, Vaccine available & what type: ___, Mortality: ___%
Yes (communicable), virus, mosquitos, yes (inactivated), 50-70
Fill in the blanks for VEE:
Zoonotic: ___, Causative agent: ___, Vector: ___, Vaccine available & what type: ___, Mortality: ___%
No (communicable), virus, respiratory and fomite, yes (inactivated, modified live), rare
Fill in the blanks for equine influenza:
Zoonotic: ___, Causative agent: ___, Transmission: _, Vaccine available & what type: ___, Mortality: ___
No (communicable), virus, respiratory secretions and fluids and fomites, yes (inactivated, modified live), 30-50 for 1
Fill in the blanks for EHV-1 and EHV-4:
Zoonotic: ___, Causative agent: ___, Transmission: ___, Vaccine available & what type: ___, Mortality: ___%
Yes (communicable), Strep. equi subsp. equi , respiratory secretions and fluids + fomites, yes (inactivated, modified live), 40% in complications
Fill in the blanks for strangles:
Zoonotic: ___, Causative agent: ___, Transmission: ___, Vaccine available & what type: ___, Mortality: ___%
No (communicable), equine arteritis virus, respiratory secretions + live cover + AI semen + fomite + in utero, yes, none unless in utero
Fill in the blanks for EVA:
Zoonotic: ___, Causative agent: ___, Transmission: ___, Vaccine available & what type: ___, Mortality: ___%
VEE, EHV-1 and -4, equine flu, strangles, scours, EVA
List the risk-based vaccinations we give to horses
Equine Infectious Anemia, Equine Protozoal Myeloencephalitis, vesicular stomatitis, Contagious Equine Metritis
List the diseases we do not have/give vaccines for
No (noncommunicable), virus, horseflies, no, euthanasia or quarantine required
Fill in the blanks for EIA:
Zoonotic: ___, Causative agent: ___, Transmission: ___, Vaccine available & what type: ___, Mortality: ___%
No (noncommunicable), Sarcocystis neurona and Neospora hughesi, spores in possum feces, no, 30% never recover
Fill in the blanks for EPM:
Zoonotic: ___, Causative agent: ___, Transmission: ___, Vaccine available & what type: ___, Mortality: ___%
Yes (communicable), virus, none approved, low
Fill in the blanks for strangles:
Zoonotic: ___, Causative agent: ___, Vaccine available & what type: ___, Mortality: ___%
No (communicable), Taylorella equigenitalis, live cover + contaminated equipment + AI semen, no, none
Fill in the blanks for CEM:
Zoonotic: ___, Causative agent: ___, Transmission: ___, Vaccine available & what type: ___, Mortality: ___%
0
At this grade on the AAEP lameness scale, lameness is not perceptible
1
At this grade on the AAEP lameness scale, lameness is difficult to observe or not consistent
2
At this grade on the AAEP lameness scale, lameness is difficult to observe but consistently apparent under other circumstances
3
At this grade on the AAEP lameness scale, lameness is consistently observable at a trot
4
At this grade on the AAEP lameness scale, there is obvious lameness
5
At this grade on the AAEP lameness scale, there is minimal weight bearing in motion or the horse is unable to move
3
Any AAEP ranking higher than a ___ disqualifies a horse from shows
Doesn’t perform tasks as well, no longer walks in an outline/frame, change in behavior, saddle slip
Stiff before or after work
List some of the signs of discomfort in a horse
soft
Soft tissue problems tend to be worse on ___ surfaces
hard
Bone issues tend to be worse on ___ surfaces
inside
When walking in a circle, horses apply more pressure to the hooves on the side ___ the circle
scintigraphy
During this procedure to test for lameness, radio isotopes are IV’d into a horse and concentrate at the area the lameness is at
acepromazine
What is the short-acting sedative used for lameness?
reserpine
What is the long-acting sedative used for lameness?
liniment
Liniment or poultice?
Alcohol component, used w/ a bracer, directions are very important
Poultice
Liniment or poultice?
Soft and often includes clay, premixed or homemade
stereotypic behavior
A repetitive, unvarying behavior w/ no obvious goal or function
10-20
Stereotypic behaviors affect about ___% of the global equid population
cribbing, wood chewing, flank biting, teeth grinding, tongue rolling, lip smacking
List the oral stereotypies we discussed
does
Unlike wind sucking, cribbing ___ involve a horse hooking onto the object first
gastric ulceration
What is cribbing associated w/ in foals?
lower gastric pH
What is cribbing associated w/ in adult horses?
displacement
Cribbing is associated w/ ___ colic
shoulder, chest
Besides the flank, where else do horses usually bite themselves during flank biting?
equine self-mutilation syndrome
Flank biting is also known as what?
Response to pain, misplaced male social behavior, presentation of behavior w/o above
List the three categories of flank biting
mouth/GI tract injuries, wooden enteroliths → colic/impactions, ingesting toxic chemicals
List the consequences of wood chewing
crib rings, cribbing collars/muzzles, crib rollers, modified Forssell’s procedure, metal bars
List some of the ways we manage cribbing
Continual access to quality forage, adequate diet, access to pasture, express their natural behavior
List some of the ways we manage wood chewing
Identify the underlying cause and eliminate it, castration, medication to help calm, enrichment and socialization
List some of the ways we manage flank biting
fiber
Wood chewing can be caused by a ___ deficiency
Keep groups together, ample forage
List some of the ways we manage fence pacing
hormone
For stallions specifically, fence pacing is ___-driven
anxiety
For horses in general, fence pacing is ___-driven
weaving, pawing/kicking, stall walking, fence pacing, head nodding
List the locomotor stereotypies we discussed
Keep groups together, ample forage, larger area for exercise/more exercise
List some of the ways we manage stall walking and weaving
stall walking
When horses are following a repetitious circuit around their stall
weaving
When horses are shifting weight from the left feet to the right feet repeatedly
grain/energy
A high ___ content in the diet can cause stall walking and weaving
Low levels of social interaction, high degree of stalling, especially w/ solid walls, little turn-out, high concentrate-low forage diet, evidence of genetic relationship, stressful competitive life, stressful weaning
List the risk factors for stereotypic behaviors
As much turn out and grazing time as possible, social interaction opportunities, low stress weaning, maximize forage, visual horizons, horse toys
List the ways we can prevent stereotypic behaviors
fertility, performance
Bulls are chosen for ___, while stallions are chosen for ___
12-24, 4-5
A male horse reaches puberty at ___ months of age, and sexual maturity at ___ years of age
temp, pressure, lubrication
What three factors can we change in an AV?
volume, concentration
Total sperm # = ___ x ___
30-50
An extended sample is usually about ___ million sperm/ml
defect
Stallion sperm morphology is categorized by ___
testes
Defects in sperm heads and midpieces, and coiled tails, are often the result of a problem in the ___
ampulla
Detached sperm heads are often the result of a problem w/ sperm storage, usually in the ___
stain
Bent sperm tails are often the result of a problem w/ the ___
long
Droplets on the sperm are often the result of an animal waiting too ___ to ejaculate
48, 6
Live cover breeding should be done ___ hours before or ___ after ovulation
24, 6
AI using cooled semen should be done ___ hours before or ___ after ovulation
12, 6
AI using frozen semen should be done ___ hours before or ___ after ovulation
48, 12
Sperm last for ___ hours cooled and ___ hours frozen
500
A standard insemination dose has ___ mil PM sperm
25-50, 5-20
Extended semen should have ___ mil sperm/ml and be ___% seminal plasma
500
A shipment of semen should have at least ___ mil PM sperm
30, 6-12
Frozen semen is >___% PM, but has a short lifespan of ___ hours
low libido
What is the most common reproductive problem in stallions?
azoospermia
Incomplete ejaculation caused by a blockage in the ampulla or accessory sex glands, which leads to testicular degeneration and congenital abnormalities
urospermia
Urine in the semen = ___
hemospermia
Blood in the semen = ___
oligospermia
Low total sperm # = ___
cow, horse, small ruminants
In which animals can we do ET in?
more
Cows are ___ resistant to damage during ET embryo handling than horses
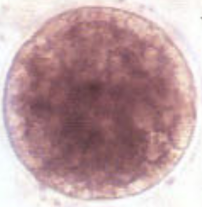
1
Grade that embryo!
I am spherical and have uniform size, color, and texture
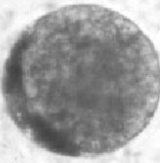
2
Grade that embryo!
I have few extruded blastomeres, irregular shape, and slight separation of my trophoblast
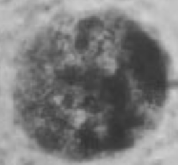
3
Grade that embryo!
I have a collapsed blastocoele, extruded blastomeres, and degenerate cells
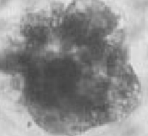
4
Grade that embryo!
I have a collapsed blastocoele, many extruded blastomeres, and degenerate cells. However, I am still somewhat viable
5
Grade that embryo!
I am either unfertilized or dead
cow
Cow or mare?
I get a uterine horn flush during ET along with FSH injections over several days. I can perform superovulation, and you can cryopreserve my embryos
mare
Cow or mare?
I get a uterine flush during ET and have 1-2 embryos implanted. You can vitrify my embryos
1
Put the embryo in a donor mare ___ day(s) behind where the embryo is in development
oocyte aspiration/TVA/OPU
During this ART, we can recover an oocyte from the ovary while bypassing the uterus