PROTEINS!1!!1!1!!!!!
Protein Structure & Function
Proteins are complex macromolecules that are made up of ==long chains of amino acids!==
Proteins are chains of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds! (Polypeptide chain)
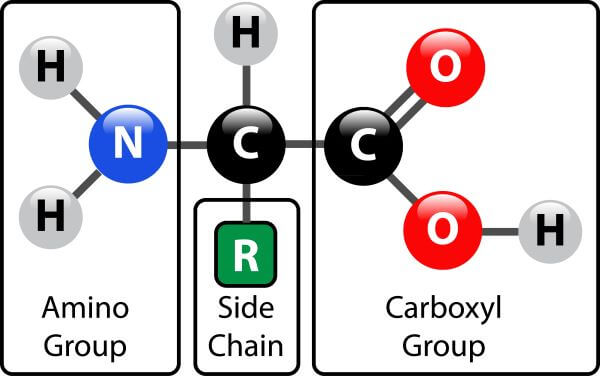 Every amino acid has the same structure except for the “R" group, each different R group gives the amino acid different properties, such as polarity and charge!
Every amino acid has the same structure except for the “R" group, each different R group gives the amino acid different properties, such as polarity and charge!
In order to form peptide bonds, the carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another. This creates a bond and releases water. Known as ==dehydration synthesis== OR condensation.
A chain of bonded amino acids is called a polypeptide.
Primary Structure
A chain of polypeptides is the primary structure.
Secondary Structure
The polypeptide chain folds due to ==hydrogen bonds==. These bonds create alpha helices and beta sheets.
The helices and sheets made by hydrogen bonds are the secondary structure.
Tertiary Structure
Interactions in the R groups of the helices and sheets cause ==disulfide bonds==. This results in the helices and sheets being twisted together.
Quaternary Structure
Some polypeptide chains are functional on their own (tertiary structure) Others form bonds with other polypeptides chains, this makes a quaternary structure.
Enzymes
A specific example of proteins is an enzyme!
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms.
Enzymes are highly specific, and can only work with certain substrates.
Enzyme activity is affected by:
-Temperature (high temps can break hydrogen bonds)
-pH (pH can alter the charges on the side chains)
Protein Stuff
Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
- Used to separate proteins based on size/mass (similar to Gel Electrophoresis).
- Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS detergent) binds to the proteins to make them uniformly negatively charged.
Western Blots
- Used to determine whether a protein band on a gel is actually the protein of interest with the help of a specific antibody.
- Protein samples are ran on a PAGE gel then transferred to a blotting membrane.
ELISA
- Uses antibodies to recognize specific proteins.
- Used to detect and measure the presence and concentration of a specific protein in a mixture.
- A colorimetric scale or spectrophotometer can be used to determine the concentration.
X-ray Crystallography
- ==Determines the 3-dimensional structure.==
- An x-ray beam shines on a pure protein crystal.
- As the beam hits the protein atoms, the x-ray light is diffracted.
- A detector records the pattern of diffracted light.
- A computer interprets the diffraction data and generates a 3-D image of a protein molecule.
Spectrophotometry
- Measures the protein concentration in a solution using the transmittance of light and the absorption of light in a protein sample.
- Reagents are added to the samples to visualize the protein.
- The maximum wavelength absorbance (lambdamax) in a sample is used to calculate the protein concentration.
Mass Spectrometry
- Measures the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of one or more molecules present in a sample.
- These measurements can be used to calculate the exact molecular weight.
- Mass spectrometers can be used to identify unknown compounds, to quantify known compounds, and to determine structure/chemical properties of molecules.