let's get an a in this bitch
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
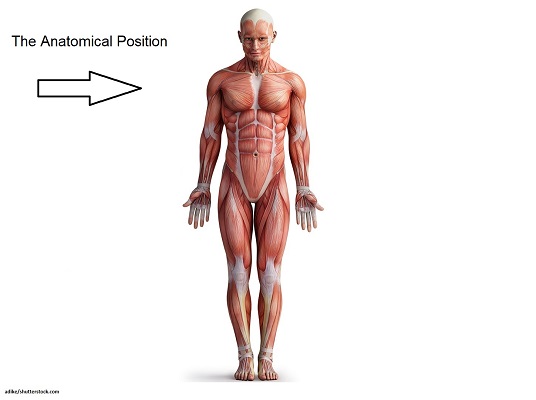
What is the anatomical position?
the universal position;
hands at sides, palms upward… face forward, feet forward
What is proximal?
near the body
What is distal?
away from the body
The elbow is _______ from the shoulder?
distal
The elbow is _______ to the waist?
proximal
The foot is ______ to the knee?
distal
What is lateral?
away from the midline
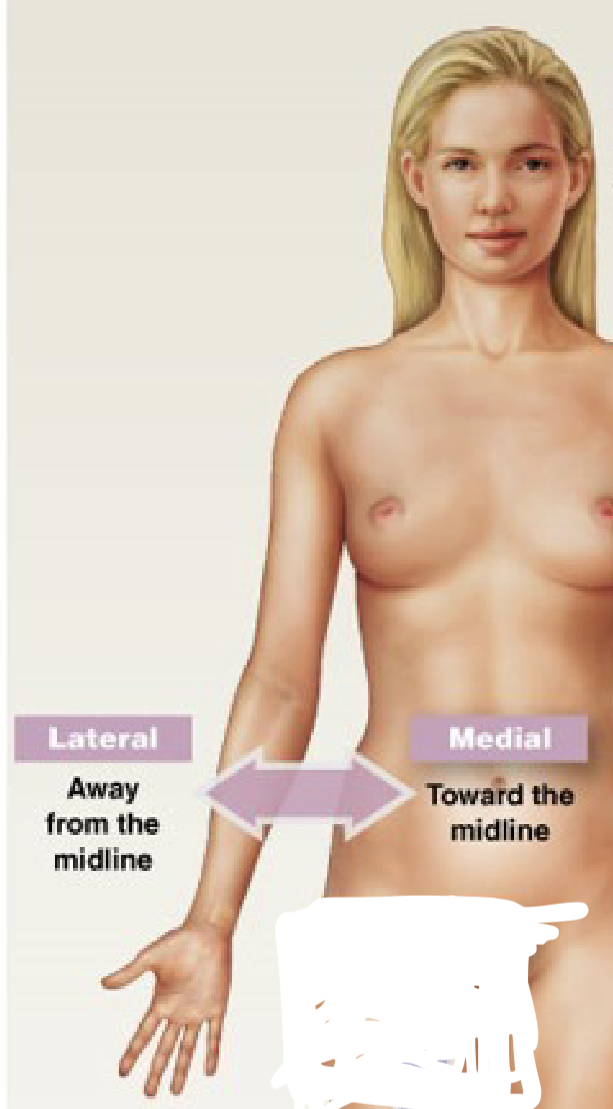
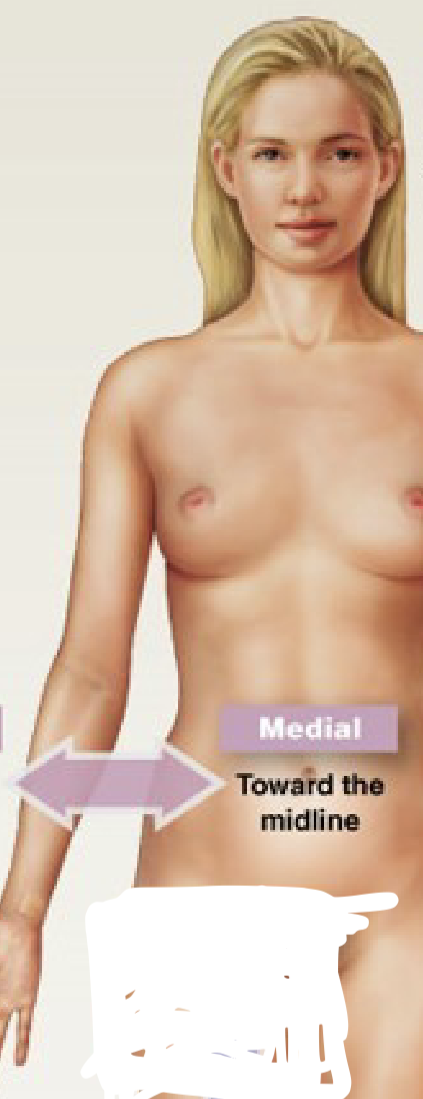
What is medial?
towards the midline
The thumb is ________ to the pinkie
lateral
The arms are _____ to the chest*
lateral
The eyes are _______ to the ears*
medial
What is anterior/ventral?
The front of the body
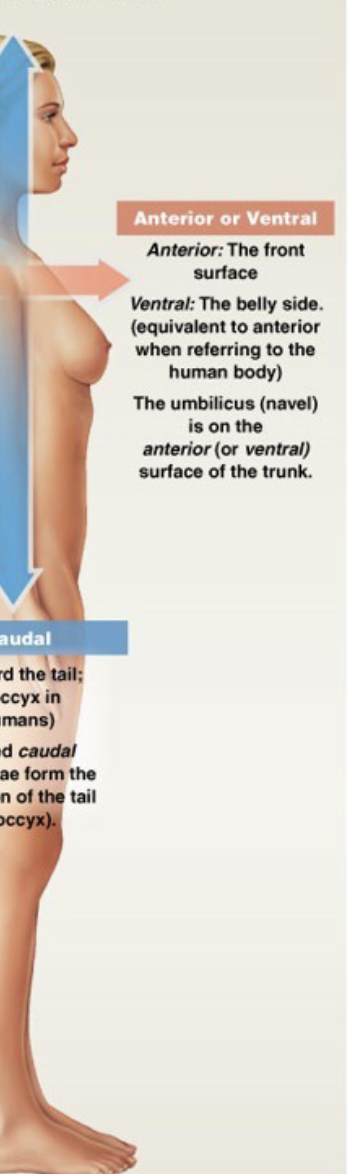
What is posterior/dorsal?
The back of the body
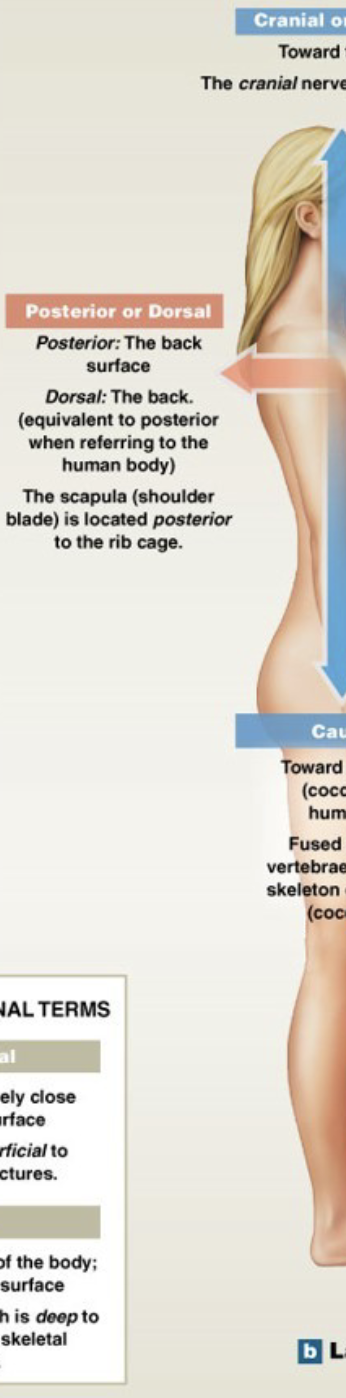
The shoulder blades are ______ to the ribcage*
posterior/dorsal
The navel is on the _______ surface of the body*
anterior/ventral
What is cranial/cephalic?
Toward the head
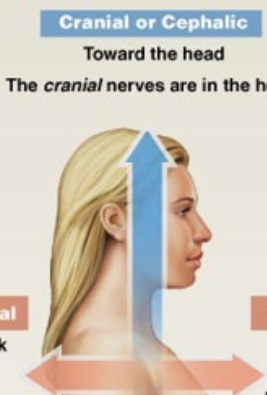
What is caudal?
Toward the “tail”; coccyx in humans

What is superficial?
near the surface of the body
What is deep?
farther from the surface of the body
The skin is __________ to underlying structures*
superficial
The bone of the thigh is ________ to the surrounding skeletal muscles*
deep
What is the sectional plane?
A single view along a two-dimensional flat surface
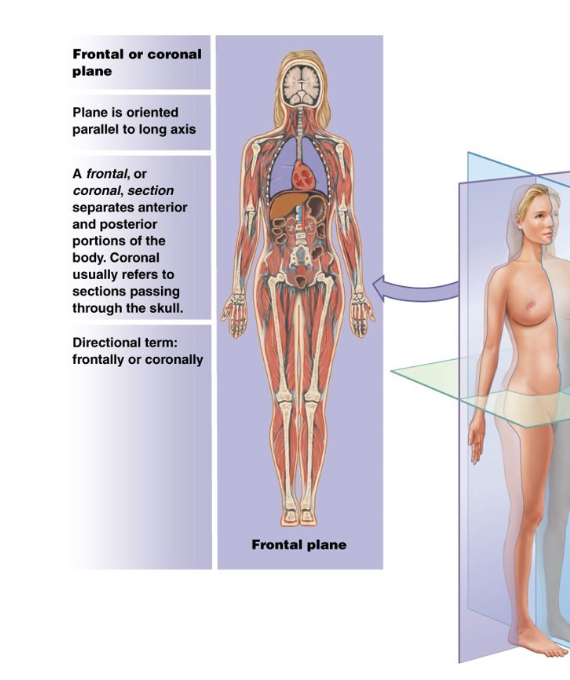
What is the frontal (coronal) plane?
A vertical plane that divides body into anterior and posterior portions
(a cut into this plane is called a frontal (coronal section))
What is the sagittal plane?
A vertical plane dividing body into left and right portions
(A cut in this plane is a sagittal section)
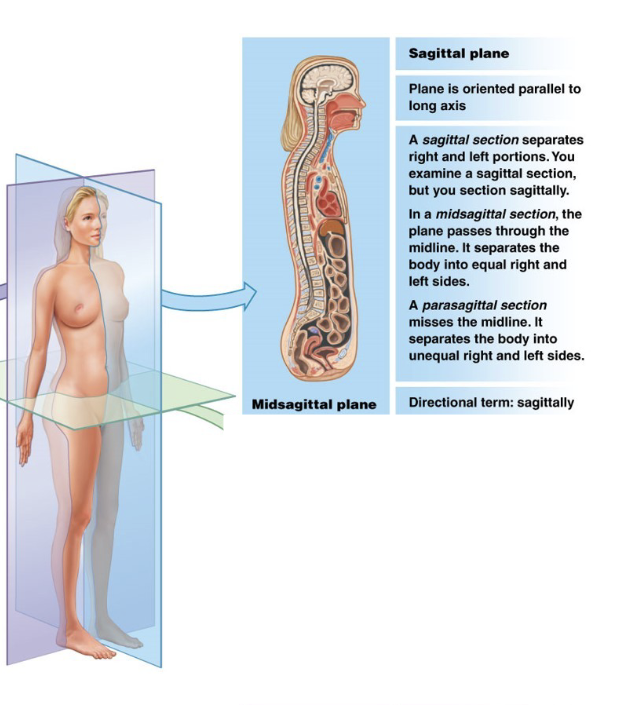
What is a midsagittal plane?
A plane that lies in the middle; it separates the body into equal left and right sides.
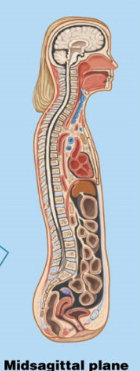
What is a parasagittal plane?
A plane that is offset from the middle; it separates the body into unequal right and left sides)
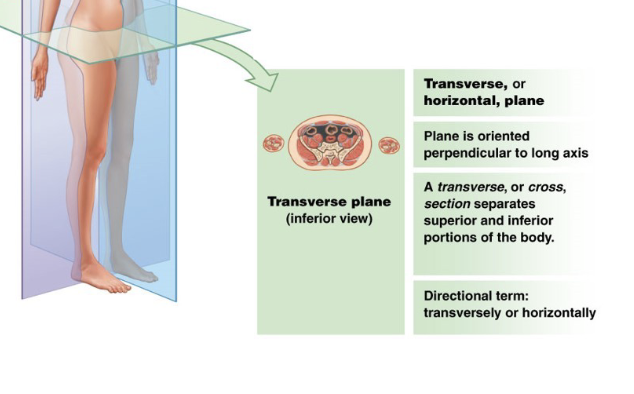
What is the transverse plane?
divides the body into superior and inferior portions
(a cut in this plane is called a transverse section)
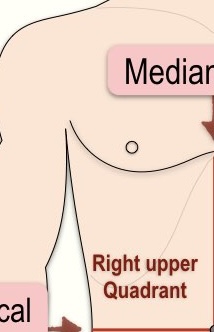
What quadrant is this?
Right upper quadrant
What organs are located in the RUQ (Right Upper Quadrant)?**
Liver
Gallbladder
Head of pancreas
Right kidney
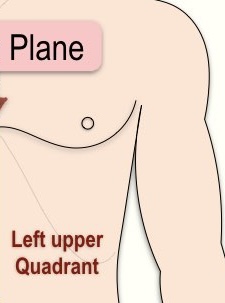
What quadrant is this?
Left upper quadrant
What organs are located in the LUQ (Left Upper Quadrant)?**
Left kidney
A lot of the stomach
Spleen
Tail of pancreas
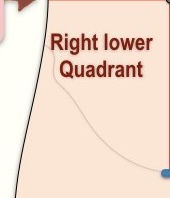
What quadrant is this?
Right lower quadrant
What organs are located in the RLQ (Right Lower Quadrant)?**
Portions of the large and small intestine
Right side of the reproductive organs
Appendix
Right ureter
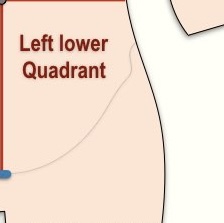
What quadrant is this?
Left Lower Quadrant
What organs are located in the LLQ (Left Lower Quadrant)? **
Left Ureter
More portions of the small and large intestine
Descending colon
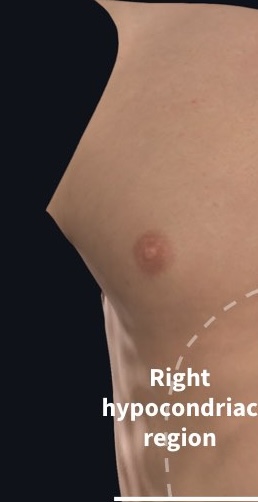
What region is this?
Right hypochondriac region
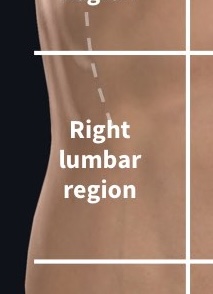
What region is this?
Right lumbar region

What region is this?
Right inguinal region
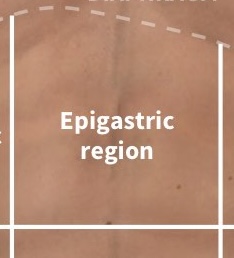
What region is this?
Epigastric region
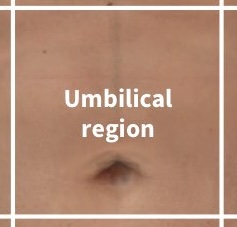
What region is this?
Umbilical region

What region is this?
Hypogastric (pubic) region
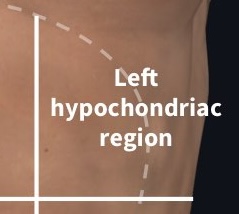
What region is this?
Left hypochondriac region
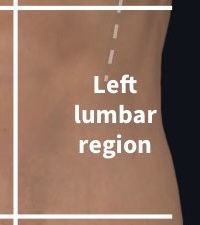
What region is this?
Left lumbar region
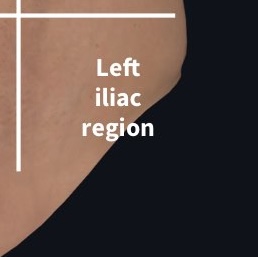
What region is this?
Left inguinal region
What region is above the lower side (umbilical region)?
Epigastric region
What region is below the umbilical region?
Hypogastric region
What is the name of the membrane that covers the heart?
Visceral pericardium
What is the name of the membrane that lines the heart?
Parietal pericardium
What is the name of the membrane that covers the lung?**
visceral pleura
What is the name of the membrane that lines the lung? **
parietal pleura
What is the name of the membrane that covers organs?
visceral peritoneum
What is the name of the membrane that lines organs?
parietal peritoneum
Which organ is considered retroperitoneal?
The kidneys
The three mechanisms of homeostasis are:
Receptor
-Receives the stimulus
Control Center
- Processes the signal and sends instructions
Effector
-Carries out instructions
What is a cation?
A positively charged ion; occurs when an atom loses one or more electrons
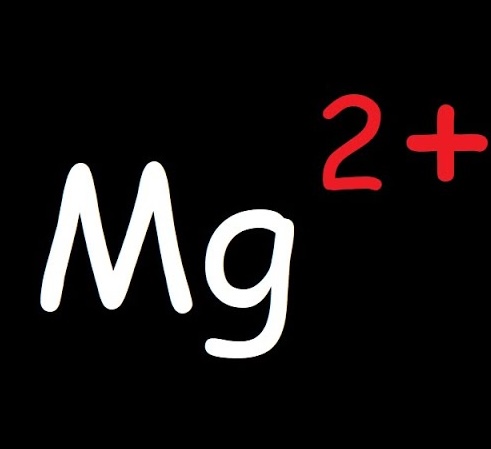
What is an anion?
A negatively charged ion; occurs when an atom gains one or more electrons
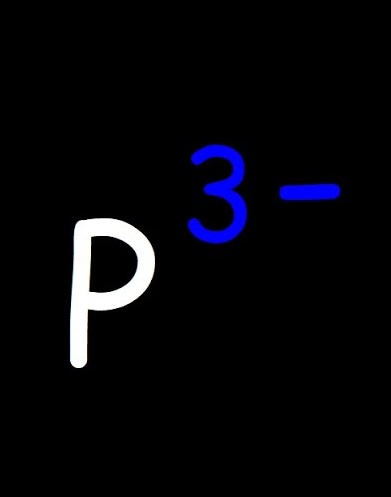
What is decomposition? (catabolism)
Breaks chemical bonds

What is synthesis? (anabolism)
Forms chemical bonds

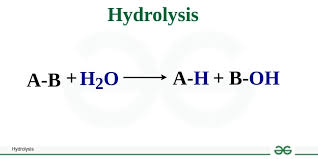
What is hydrolysis?
Adding water to a reaction to break it down
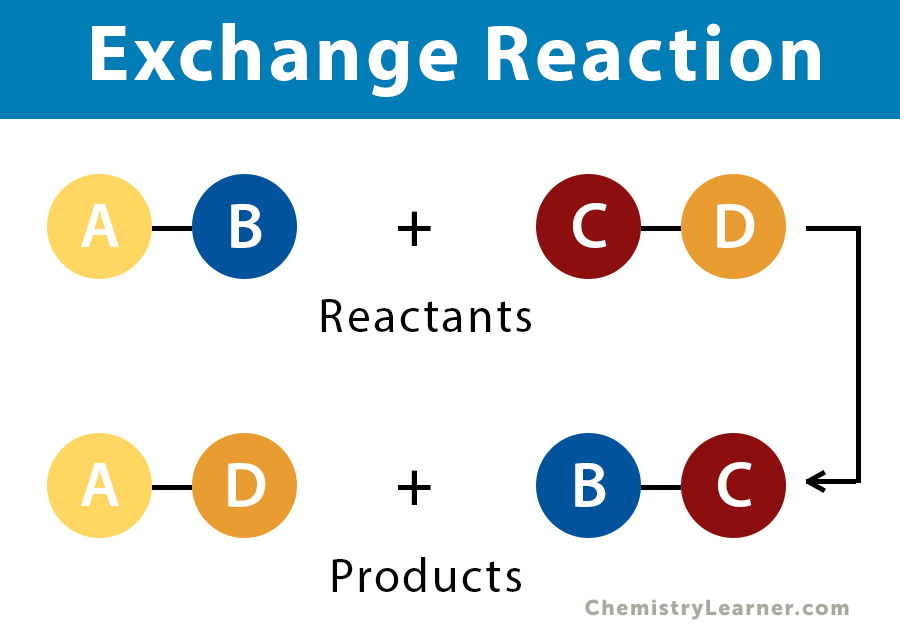
What is an exchange reaction?
when reactants exchange and combine
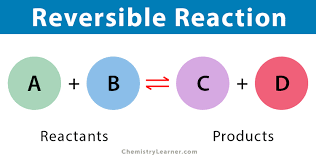
What is reversible?
At equilibrium, the amounts of chemicals do not change even though the reactions are still occurring
What is dehydration synthesis? (condensation)
the reverse reaction of Hydrolysis; loss of water to form chemical bonds
What is anabolism
builds up/creates
What is catabolism?
Breakdown
(think CANNIBALISM)
The ending for most enzyme names is “________”
-ase
What is the purpose of an enzyme?
Speeds up chemical reaction
Lowes the activation energy
What is diffusion?
The passive movement of substances from a higher to lower concentration
(requires no energy)
What is osmosis?
The diffusion of water
What is pinocytosis?
Cellula drinking; cells taking in fluids
What is active transport?
Requires energy; substances go from a lower to a higher concentration
If the solution is hypertonic, the red blood cell shrivels——
crenation
If the solution is hypotonic, the red blood cell swells up—-
hemolysis
What is crenation?
when the red blood cell loses water and shrinks; occurs in a hypertonic solution
What is hemolysis?
when the red blood cell swells up with water and ruptures; occurs in a hypotonic solution
What is hydrophilic in simple terms?
likes water
(Includes ions and polar molecules)
What is hydrophobic in simple terms?
scared of water
(Includes nonpolar molecules, fats, and oils)
The normal pH of blood ________?
ranges from 7.35 to 7.45
The acidic pH range is ______?
lower than 7.0
High H+ concentration
Low OH− concentration
The neutral pH is _______?
7
The basic (or alkaline) pH range is ______?
higher than 7.0
Low H+ concentration
High OH− concentration
Protein consists of ________?
20 amino acids
Amino acids are connected by ________?
peptide bonds
Protein synthesis occurs in the rough endoplasmic reticulum (E.R) because ___________
it has ribosomes
The plasma membrane consists of a __________
phospholipid bilayer
What is cytoplasm?
stuff inside the cell
What is cytosol?
solution inside of the cell
What is phosphorylation?
The process of adding a phosphate group to another molecule
The phosphorylation of AMP gives you _______
ADP
The phosphorylation of ADP gives you ______
ATP
What is the enzyme that catalyzes ATP to ADP?
Adenosine triphosphatase (AT Pase)
What do exergonic reactions do?
release energy
What do endergonic reactions do?
absorb energy
What is endocytosis?
the importation of extracellular materials packaged within vesicles, which require ATP
(remember, endo means inside)
What is exocytosis?
Granules or droplets are released from the cell as a vesicle fuses to the plasma membrane
(remember, exo means outside )
What is the order of mitosis?
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis
What is the difference between rough ER and smooth ER?
Rough ER has ribosomes
What is DNA?
Genetic material
What is RNA?
helpful for protein synthesis