Endocrine System
Endocrine System = Made of glands that secrete substances into the bloodstream
Exocrine glands secrete substances into ducts and onto body surfaces like skin or stomach (epithelial tissue) (exo = external)
Function:
Communication and Control
Same as nervous system but SLOWER
Hormones: Specific chemicals released in small quantities from one part of the body and carried through the bloodstream that affects another part of the body
Target cells receive specific hormones with their receptors
If hormones contact cells with no target cells and receptors = NO EFFECT
When contacting a target cell, hormones produces one or more changes within the cell:
Alter plasma/cell membrane permeability, potential or both
Stimulate protein synthesis
Activate/Deactivate enzymes
Induce a secretory activity
Stimulate mitosis
2 MAJOR TYPES OF HORMONES:

Water-soluble hormones (amino acid)
Not able to pass through cell membrane
Bind to receptors on outside of target cell which activate a 2nd messenger to mediate the response to the target cell
Molecular relay!
Lipid-soluble hormones (steroids)
Can pass directly through the target cell membrane, forming a hormone-receptor complex, which alters action of the cell
Glands are activated in 3 ways:
Hormonal Stimuli - Glands are encouraged by hormones secreted by other glands (Hypothalamus stimulates pituitary)
Humoral Stimuli - Levels of nutrients and ions in the blood can cause glands to secrete hormones (Blood calcium levels stimulate parathyroid glands)
Neural Stimuli - Nerve impulses cause glands to secrete hormones (Sympathetic nervous system during stress causes release of epinephrine from adrenal glands)
Endocrine glands
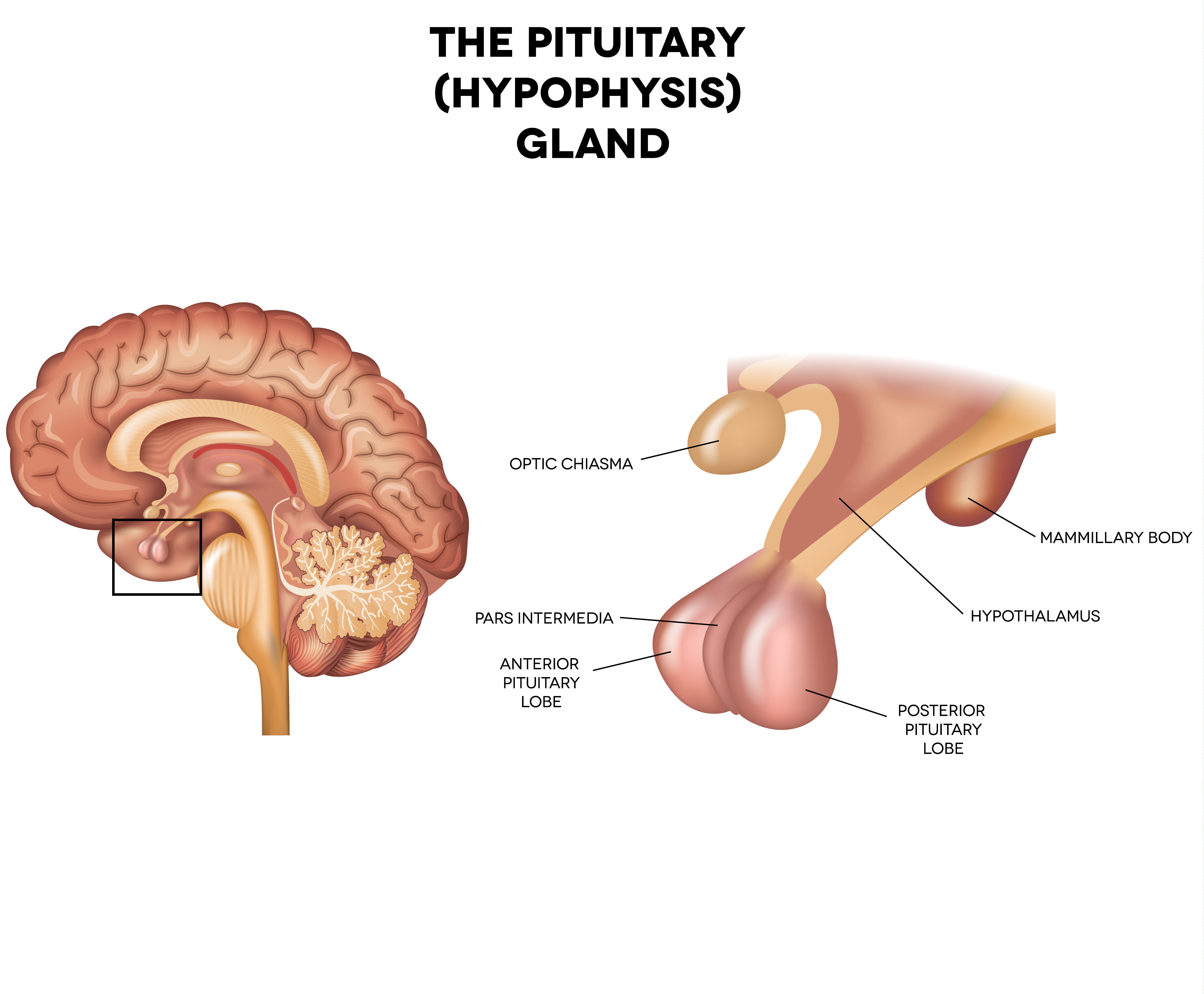
Pituitary Gland:
Small bulb on the underside of brain
2 lobes: anterior pituitary and posterior pituitary
“Master Gland” = controls many other glands in body
Anterior pituitary hormones:
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) = causes thyroid to produce thyroxine
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) = stimulates adrenal glands
Growth Hormone (GH) = Stimulates growth in bones and muscles
Melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH) = stimulates melanocytes to produce melanin
Prolactin (PRL) = stimulates production of breast milk
Gonadotropins
Luteinizing hormone - stimulates release of sex hormones
Follicle stimulating hormone - stimulates egg/sperm production
Posterior Pituitary hormones:
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or vasopressin = increases water retention in kidneys, decreasing urine production
Oxytocin (OT) = stimulates contraction of uterus during childbirth and promotes release of breast milk
Pineal Gland:
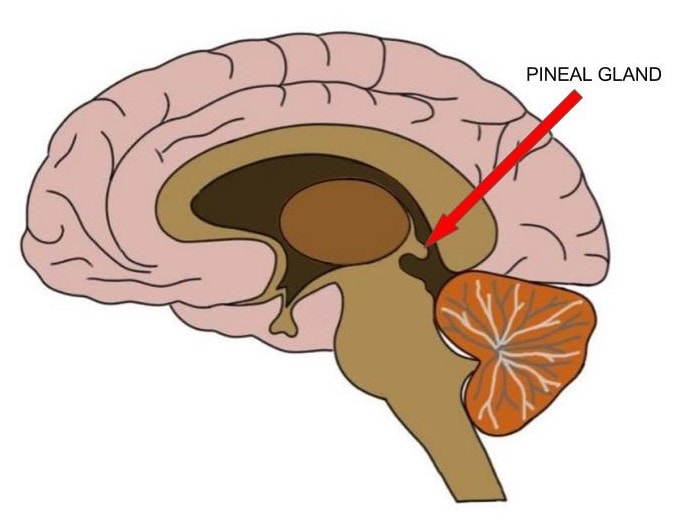
Tiny cone shaped gland near the cerebellum
Main secretion is melatonin = sleep and wake cycle
Thyroid Gland:
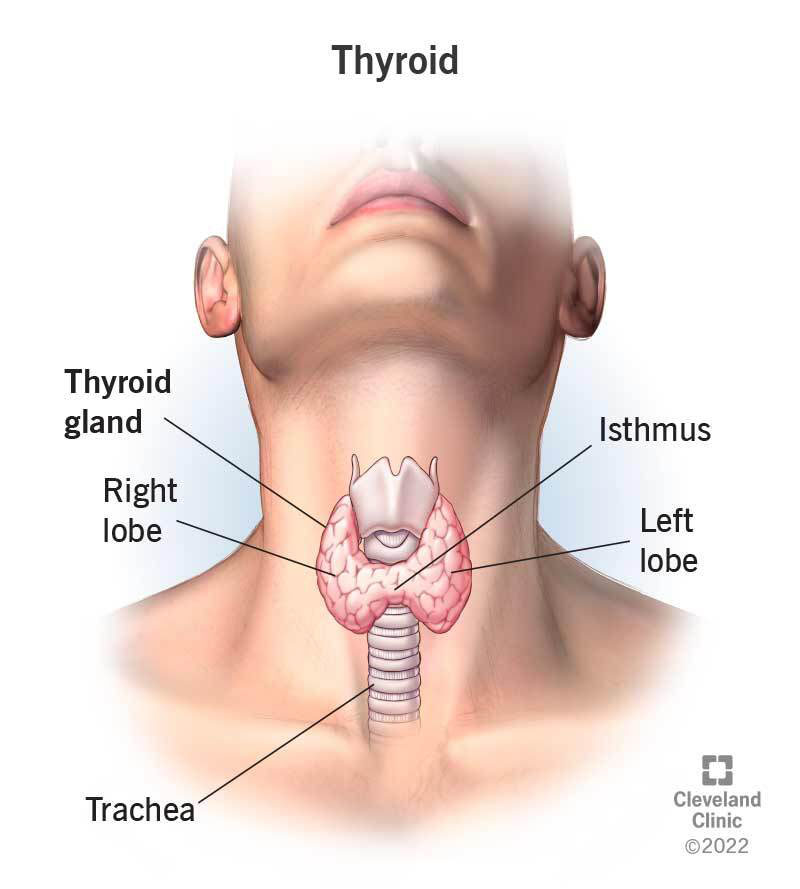
Located at base of neck
2 distinctive halve - butterfly shape
Hormones:
Calcitonin = reduces calcium levels in bloodThyroid Hormones (TH)
Thryoxine + Triiodothyronine = Regulates metabolism+body heat, controls oxygen usage, maintains blood pressure
Parathyroid Gland:
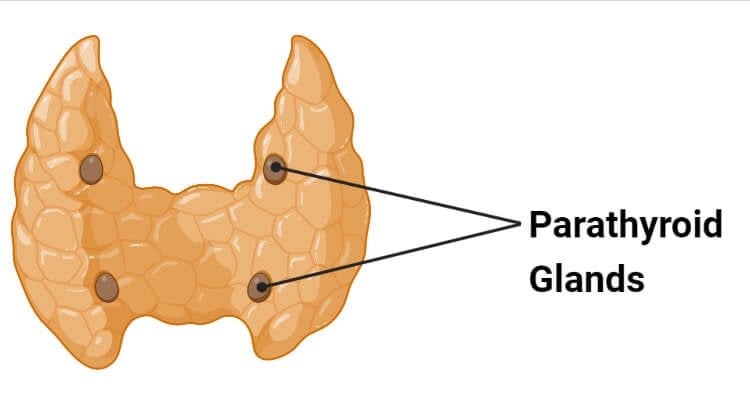
Attached to back of thyroid
Produces parathyroid hormone (PTH) = opposite of calcitonin; brings calcium out of bones into bloodstream to increase calcium levels

Adrenal Glands:
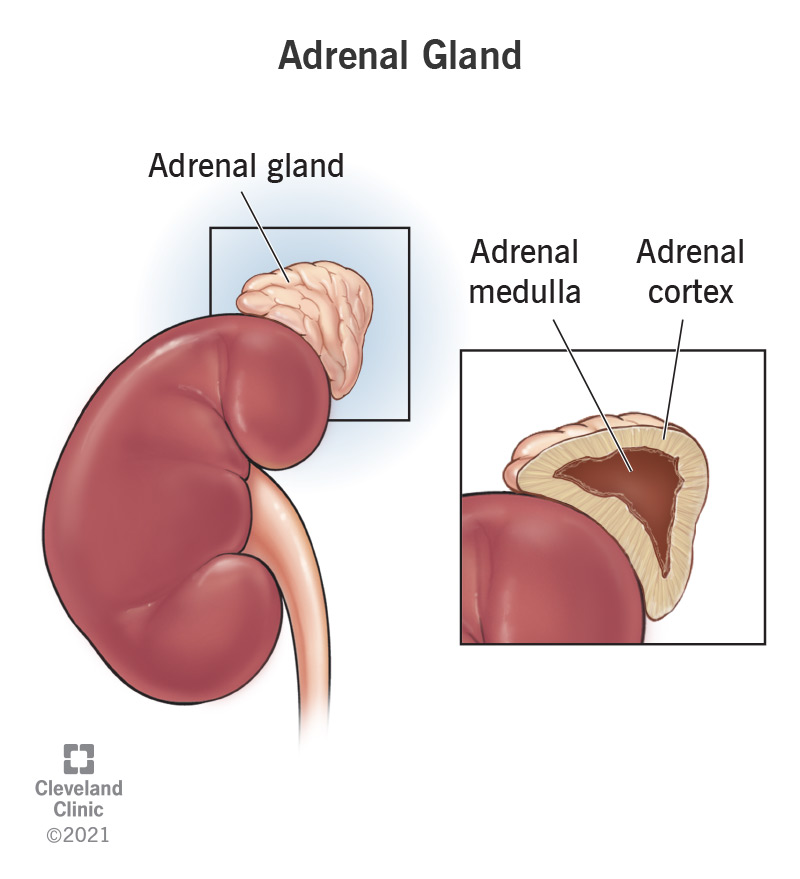
Sits on top of each kidney
Outer layer - Adrenal Cortex
Glucocorticoids (cortisol and aldosterone) = regulates ion levels for quick energy
Inner layer - Adrenal medulla
Epinephrine + Nonepinephrine = Fight or flight respones, increases heart rate, blood pressure and flow, intake of oxygen for immediate energy
Pancreas:

Both exocrine and endocrine glands!
Endocrine part is made up of islets of Langerhans which produce insulin and glucagon
Beta cells = insulin, lowers blood glucose levels
Alpha cells = glucagon, raise blood glucose levels
Thymus Gland:
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/human-thymus-anatomy-513000737-d60061aa3a334e67bc64f6177465698c.jpg)
Near Sternum
Produces thymopoietin, thymic factor, thymosin = immune system
Gonads:
Reproductive organs that produce sex cells and secrete sex hormones
Estrogen - Maturation of reproductive organs and secondary sex characteristics
Females = ovaries
Progesterone - breast development and menstrual cycle
Males = testes
Maturation of reproductive organs and secondary sex characteristics, sperm dev

Hormone regulation
Control of hormone secretion is required to regulate the amt of hormones released
Control thru feedback loops
EX: If calcium levels are too high, calcitonin is released. If calcium levels get too low, then PTH is released
Improper functioning:
Hyposecretion - not enough hormone released
Hypersecretion - too much hormone released
Disorders are either hyposecretions or hypersecretions of hormones