First Trimester Ultrasound Review
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for reviewing key concepts in first trimester ultrasound.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
What happens during ovulation?
Ovary releases mature ovum.
What happens if fertilization occurs after ovulation?
The corpus luteum cyst remains and the endometrium continues to grow.
What happens if fertilization does NOT occur after ovulation?
Estrogen and progesterone levels drop, and menstruation begins.
Where does fertilization most often occur?
In the ampulla of the fallopian tube.
What is the name of the outer layer of the ovum?
Zona pellucida
What happens during penetration of the ovum?
The sperm loses its tail and the genetic content of ovum combines with sperm.
What is created when the genetic content of the ovum and sperm merge?
A zygote with 46 chromosomes.
What are the stages of zygote development?
Zygote, Morula, and Blastocyst.
What is the outermost layer of cells in the blastocyst?
Trophoblast.
What are the two layers of the trophoblast?
Cytotrophoblast (inner) and syncytiotrophoblast (outer).
What hormone does the trophoblast produce?
HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin).
What is the function of HCG?
Causes the corpus luteum to remain.
What is the fluid-filled cavity within the blastocyst called?
Blastocele.
What happens during implantation?
Blastocyst burrows into the endometrium.
How is the opening sealed after blastocyst burrows into the endometrium?
Blood clot.
What is the decidua?
Thickened endometrium.
What are the three layers of the decidualized endometrium?
Decidua basalis, decidua capsularis, and decidua parietalis (vera).
What is the decidua basalis?
Develops at the point of attachment and is involved in forming the maternal portion of the placenta.
What is the decidua capsularis?
Decidual portion superficial to the blastocyst projecting into the uterine lumen.
What is the decidua parietalis (vera)?
Decidual lining of the uterus.
What are the embryonic membranes?
Amnion, yolk sac, allantois, and chorion.
What is the amnion?
Membrane surrounding the cavity containing the embryo.
What is the yolk sac?
Small cavity developing from the embryonic disc.
What is the allantois?
Projection of the hindgut
What is the chorion?
Develops from the trophoblast and forms the fetal portion of the placenta.
What are chorionic villi?
Finger-like projections that develop from the chorion and project into the decidua.
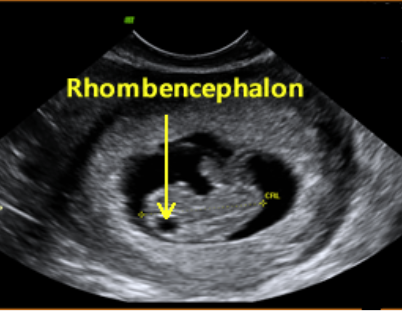
What is the first ultrasound appearance in the first trimester?
Lush echogenic endometrial echo and arcuate arteries.
What is the first definite ultrasound appearance of IUP?
Gestational sac.
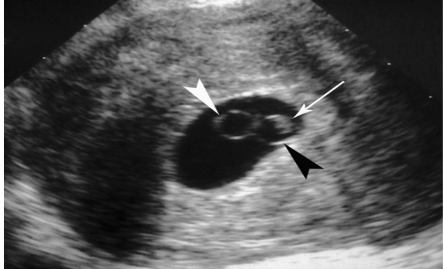
What is the first structure visualized in the gestational sac?
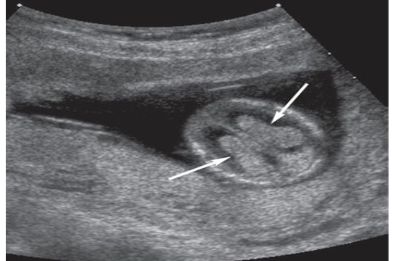
Secondary yolk sac.
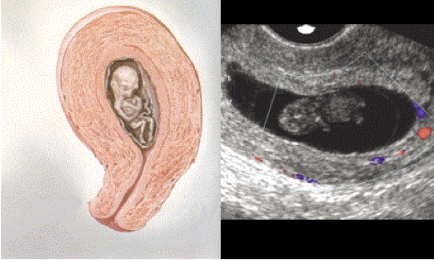
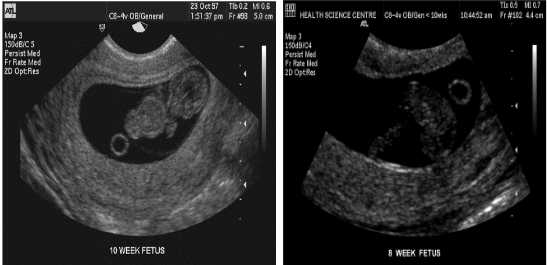
What are the normal sonographic features of a gestational sac?
Round or oval shape, fundal position, eccentrically placed, smooth contours, decidual wall thickness >3 mm.
What does the 'double decidual sac sign' describe?
Decidua capsularis and decidua parietalis before fusion.
Transvaginally, when should the gestational sac be seen when HCG reaches?
1000 mIU/ml (IRP) or 500 mIU/ml (2nd IS) and 4 1/2 weeks from LMP.
Transabdominally, when should the gestational sac be seen when HCG reaches?
1800 mIU/ml (2nd IS) and 6 weeks from LMP.
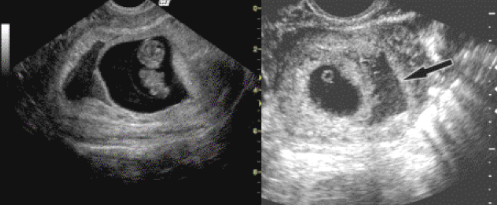
What is the yolk sac?
The first structure visualized in the gestational sac.
What is the appearance of the yolk sac on ultrasound?
Round sonolucent structure with echogenic rim.
What is the normal diameter of the yolk sac?
Should not exceed 6 mm.
When is the yolk sac seen transvaginally?
About 5 weeks from LMP.
When is the yolk sac seen transabdominally?
About 6-7 weeks from LMP.
Transvaginally, non-visualization of the yolk sac is abnormal when what?
MSD is greater than 8 mm.
Transabdominally, non-visualization of the yolk sac is abnormal when what?
MSD is greater than 20 mm.
What is the vitelline duct?
Connection between midgut and yolk sac.
When does the vitelline duct usually involute?
7th - 9th weeks.
How many days after conception do endothelial heart tubes start pulsating?
21 days after conception.
When should cardiac pulsations be seen when embryo measures?
5 mm or larger.
How fast does the embryo grow?
1-2 mm/day
During which weeks may herniation of the gut be seen?
7-8 weeks
By which weeks does the gut return to the body?
9-10 weeks
Transabdominally, when should the embryonic pole be visualized when MSD is?
MSD is 25 mm or greater.
Transvaginally, when should the embryonic pole be visualized when MSD is?
MSD is 16 mm or greater.
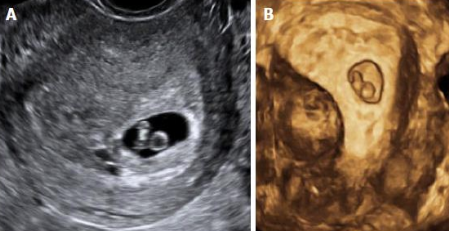
corpus luteum cyst - 7wk fetus
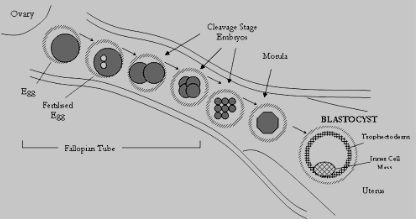
TRAVEL THROUGH
THE TUBE
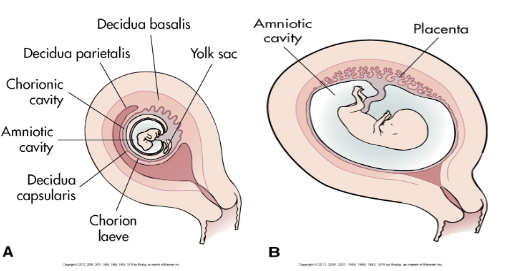
DECIDUA
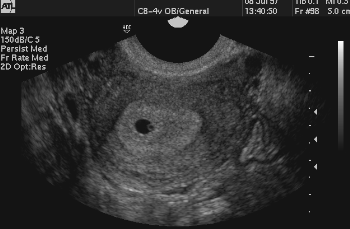
DOUBLE DECIDUAL SIGN EARLY IUP
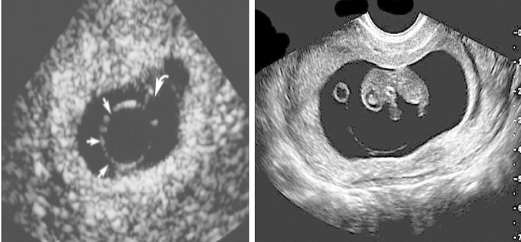
YOLK SAC
Double bleb sign
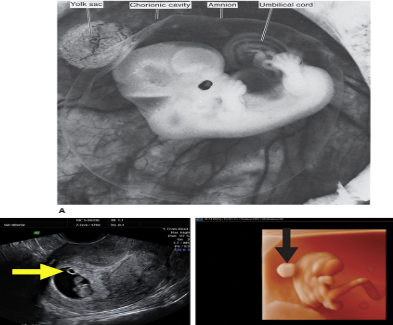
ULTRASOUND APPEARANCE
FIRST TRIMESTER
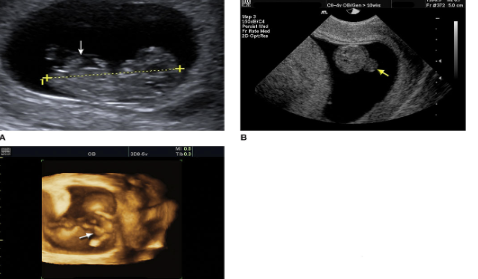
Normal Physiologic Herniation of Gut
Choroid plexus within the lateral ventricles. Choroid plexus (arrows) is seen within the lateral ventricle of this 13-week gestation fetus.
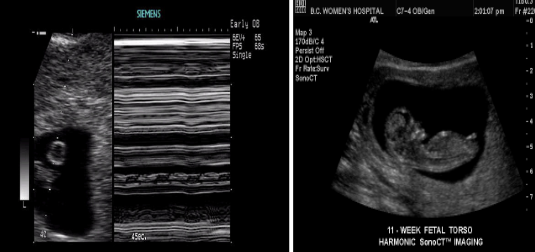
What is the definition of embryo during pregnancy?
From the first day of LMP through week ten.
What is the definition of fetus during pregnancy?
From week 10 until birth.
What does MSD stand for?
Mean Sac Diameter (MSD).
What does CRL stand for?
Crown Rump Length (CRL).
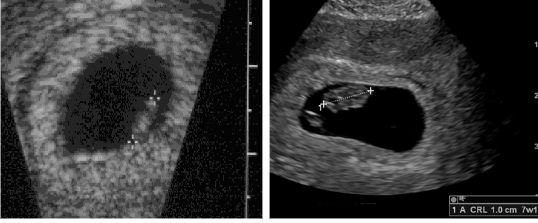
How is CRL measured?
Measure embryo in longest axis from head to rump.
What is CRL used for in dating during pregnancy?
Most accurate measurement for dating throughout pregnancy.
What are the indications for ultrasound in the first trimester?
Vaginal bleeding, size/dates discrepancy, ectopic pregnancy, hydatiform mole, coexisting masses.
What is the most important purpose of ultrasound in the first trimester?
Predicting viability and gestational age.
What is the definition of abortion?
Termination of pregnancy prior to 20 weeks of gestation.
What defines a complete abortion?
All products of conception expelled out of the uterus.
What defines an incomplete abortion?
Retained products of conception still within the uterus.
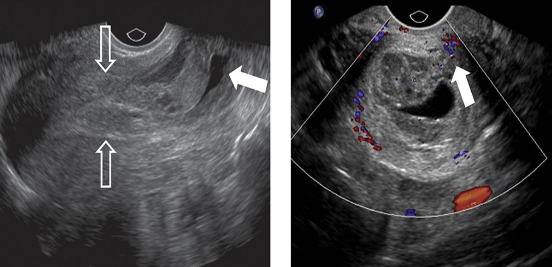
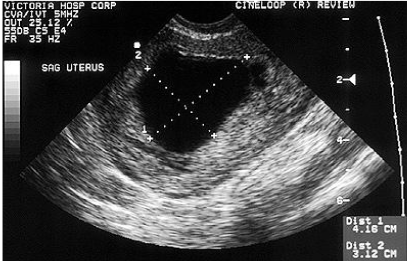
What defines a threatened abortion?
Vaginal bleeding with closed cervix prior to 20 weeks.
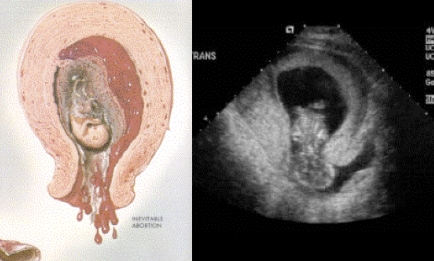
What defines an inevitable abortion?
Profuse bleeding with cervix beginning to dilate.
What defines a missed abortion?
A dead embryo which has not been expelled.
Clearly identifiable fetal pole with no FHM (fetal heart motion) and has not been expelled
What defines fetal demise?
what is the termination of the pregnancy by D & C or other surgical means?
therapeutic abortion
what may non-sterile instruments and infection result in?
septic abortion
what is diagonosed when there is no evidence of a fetal pole or yolk sac with in the gestational sac?
anembryonic gestation
what are the clinical findings of anembryonic gestation?
vag bleeding, reduction of preg symptoms, low hcg
what are the sonographic findings of an anembryonic gestation?
large and irregular gestational sac w/o embryo or yolk sac, absent-minimal sac growth, poor decidual reaction