Chapter 12: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/123
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
1
New cards
Spinal cord labelled
2
New cards
The spinal cord consists of:
- The foramen magnum to the 2nd lumbar vertebra
- Segments (cervical, thoracic, lumbar, & sacral)
- 31 pairs of spinal nerves
- Segments (cervical, thoracic, lumbar, & sacral)
- 31 pairs of spinal nerves
3
New cards
Cervical enlargement
the non-uniform diameter of the spinal cord that supplies nerves to the upper limbs
4
New cards
Lumbosacral enlargement
the non-uniform diameter of the spinal cord that supplies nerves to the lower limbs
5
New cards
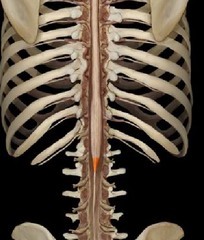
Conus medullaris
the tapered inferior end of the spinal cord
6
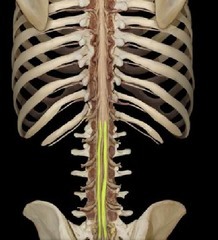
New cards
Cauda equina
origin of spinal nerves (includes lumbosacral enlargement and conus medullaris)
7
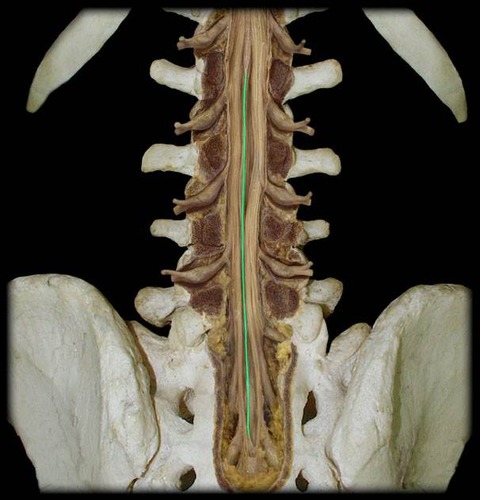
New cards
Filum terminale
anchors spinal cord to coccyx
8
New cards
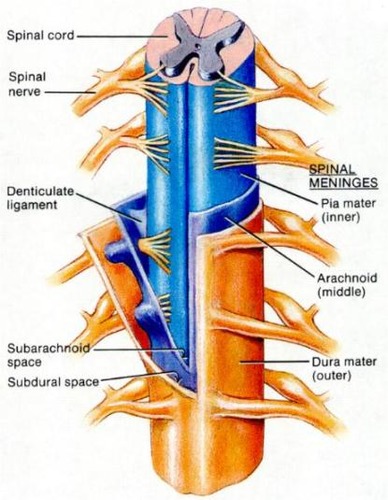
Meninges
connective tissue membranes
9
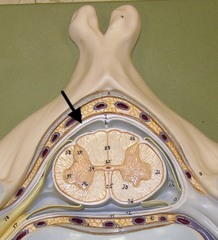
New cards
Dura mater
- The most superficial and thickest meninge that is continuous with dura mater around the brain and spinal nerves
- Forms a thecal sac that surrounds the spinal cord from the foramen magnum to the end of the 2nd sacral vertebra
- Forms a thecal sac that surrounds the spinal cord from the foramen magnum to the end of the 2nd sacral vertebra
10
New cards
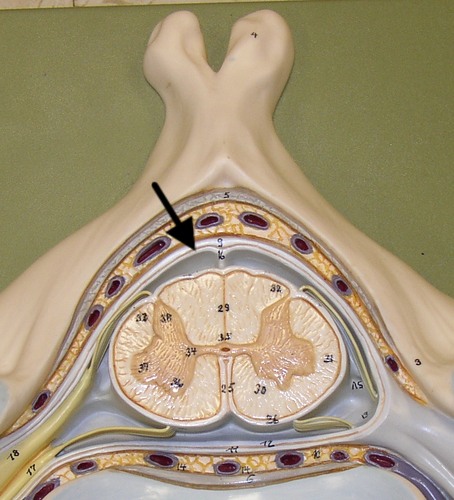
Arachnoid mater
A meninge that is thin and wispy, like a spiderweb
11
New cards
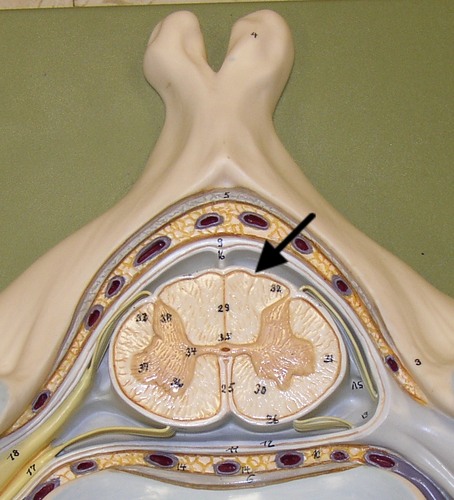
Pia mater
The deepest meninge, bound tightly to surface of the spinal cord.
12
New cards
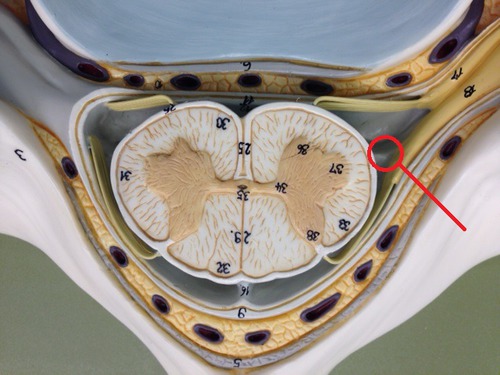
Denticulate ligaments
attach spinal cord to dura mater
13
New cards
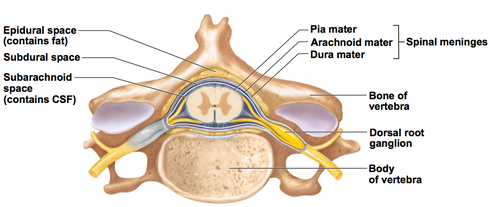
Epidural space
The space between the dura mater and periosteum that is filled with blood vessels, areolar C. T, adipose, spinal nerve roots
14
New cards
Which space in the spinal cord is anesthesia injected into?
epidural
15
New cards
Subarachnoid space
The spcae between the arachnoid mater and pia mater that contains CSF, blood vessels, and web-like strands of arachnoid
16
New cards
Subdural space
The space between the dura mater and arachnoid mater that contains serous fluid
17
New cards
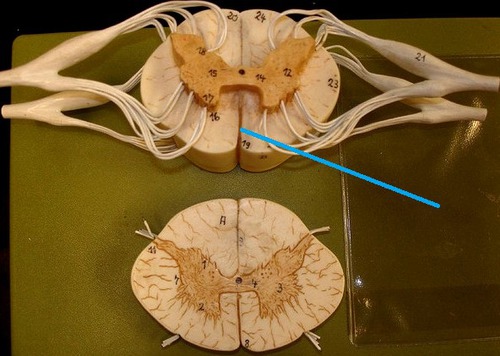
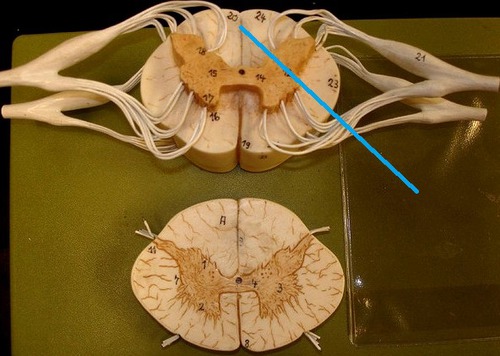
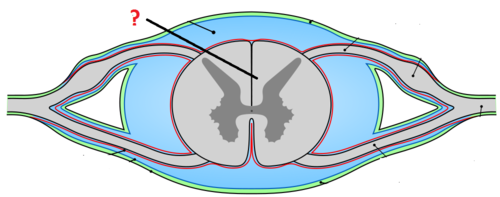
Cross section of the spinal cord
18
New cards
Anterior median fissure
a deep cleft on the anterior side of the spinal cord partially separating the left and right halves
19
New cards
Posterior median sulcus
a deep cleft on the posterior side of the spinal cord partially separating the left and right halves
20
New cards
White matter of spinal cord
myelinated axons that are divided into columns (funiculi - ventral, dorsal, lateral) that are divided into tracts (fasciculi)
21
New cards
Ventral column of white matter
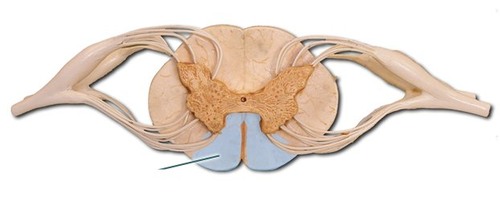
22
New cards
Lateral column of white matter
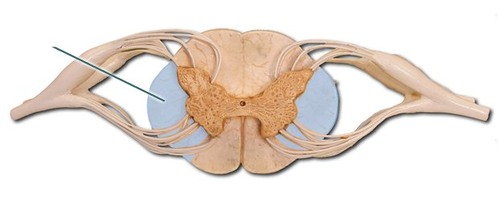
23
New cards
Dorsal column of white matter
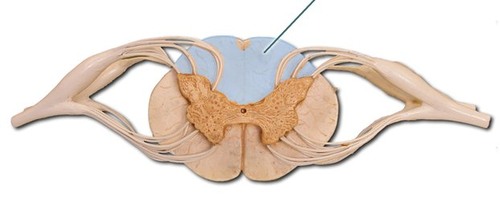
24
New cards
A collection of axons inside the CNS
a tract
25
New cards
A collection of axons outside the CNS
a nerve
26
New cards
Gray matter of spinal cord
neuron cell bodies, dendrites, axons that are divided into horns (posterior, anterior, and lateral)
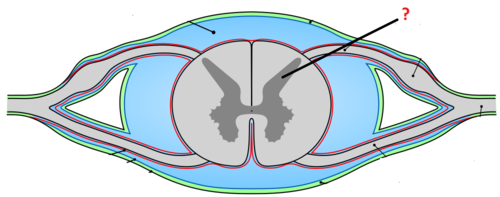
27
New cards
Posterior horn of gray matter
dorsal
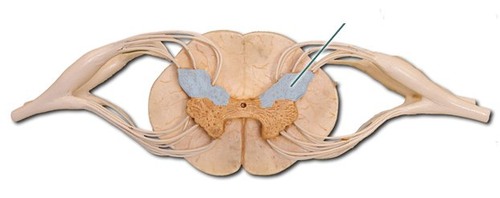
28
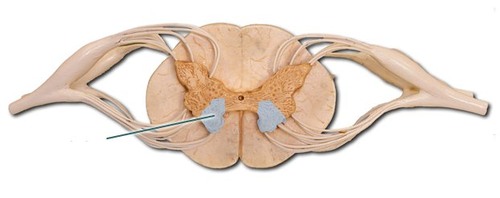
New cards
Anterior horn of gray matter
ventral
29
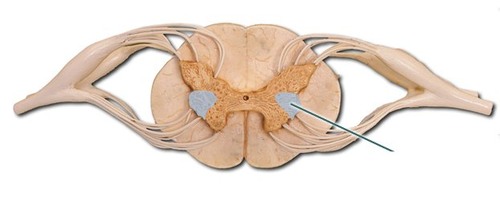
New cards
Lateral horn of gray matter
associated with ANS
30
New cards
Commissures
connections between halves
31
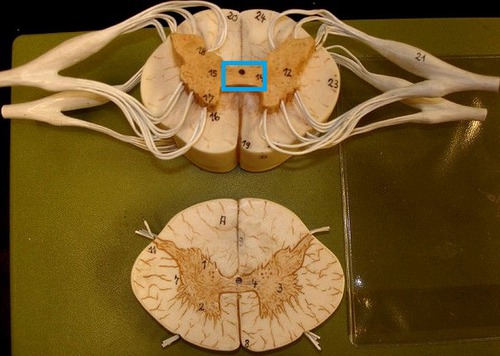
New cards
Gray commissure
central canal in center
32
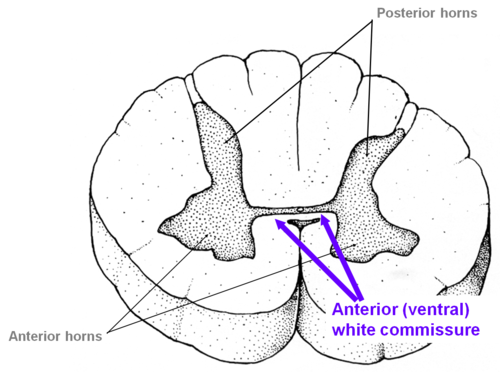
New cards
White commissure
33
New cards
Roots
the combined rootlets that arise from spinal nerves
34
New cards
Dorsal (posterior) root ganglion
collections of cell bodies of pseudo-unipolar sensory neurons
35
New cards
Ventral (anterior) root
36
New cards
Two roots merge laterally to form the
spinal nerve
37
New cards
Motor neuron cell bodies are in
anterior (motor) and lateral (autonomic) horns of gray matter
38
New cards
What do the motor neuron cell bodies innervate?
muscles/glands
39
New cards
Axons of motor neurons form
ventral roots and pass into spinal nerves
40
New cards
Cell bodies for spinal sensory neurons are located in the
A. anterior horn of spinal cord gray matter.
B. lateral horn of spinal cord gray matter.
C. dorsal root ganglia
D. posterior columns
A. anterior horn of spinal cord gray matter.
B. lateral horn of spinal cord gray matter.
C. dorsal root ganglia
D. posterior columns
C. dorsal root ganglia
41
New cards
The spinal cord extends from the
A. What's a spinal cord?
B. Level of the third cervical vertebra to the coccyx.
C. Level of the axis to the lowest lumbar vertebra.
D. Medulla oblongata to the level of the 2nd lumbar vertebra.
A. What's a spinal cord?
B. Level of the third cervical vertebra to the coccyx.
C. Level of the axis to the lowest lumbar vertebra.
D. Medulla oblongata to the level of the 2nd lumbar vertebra.
D. Medulla oblongata to the level of the 2nd lumbar vertebra.
42
New cards
Reflex
an automatic response to a stimulus produced by a reflex arc; it is the simplest portion capable of receiving a stimulus & producing response.
43
New cards
Automatic reflex
response to a stimulus without conscious thought (ex: BP, Blood CO2)
44
New cards
Somatic reflexes
remove the body from painful stimuli or keep the body from falling (etc.)
45
New cards
Reflex arc path
Action potentials produced in sensory receptors transmitted to -> sensory neuron -> interneuron -> motor neuron -> effector organ, which responds with a reflex
46
New cards
3 types of reflexes
1. Stretch Reflex
2. Golgi Tendon Reflex
3. Withdrawal Reflex
2. Golgi Tendon Reflex
3. Withdrawal Reflex
47
New cards
Stretch Reflex
when muscles contract due to a stretching force applied to them (example: knee jerk)
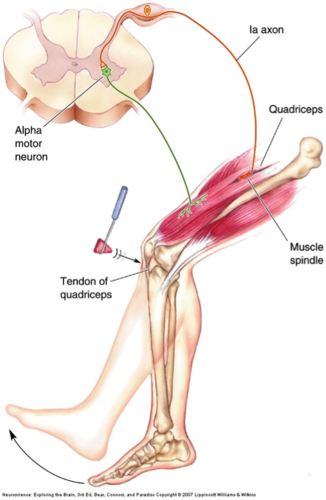
48
New cards
What is unique about the stretch reflex? And why?
there is no interneuron, because the sensory neurons synapse with alpha motor neurons
49
New cards
Alpha motor neurons
motor neurons in the spinal cord that innervate the muscle in which the muscle spindle is embedded
50
New cards
Muscle spindle
a sensory receptor made of specialized skeletal muscle fibers that respond to stretch
51
New cards
What is muscle spindle innervated by?
specific motor neurons (like gamma motor neurons) that control sensitivity of muscle spindle
52
New cards
Where are muscle spindle cells innervated?
the noncontractile centers
53
New cards
Golgi Tendon Reflex
prevents contracting muscles from applying excessive tension to tendons so they aren't damaged by excess tension
54
New cards
Golgi tendon organ
a sensory receptor that is an encapsulated nerve ending located near the muscle tendon junction
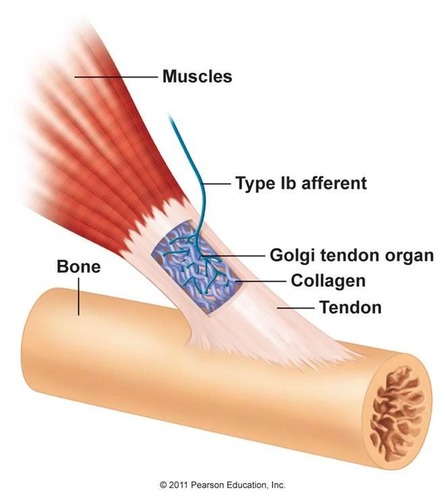
55
New cards
What produces sudden relaxation of the muscles, like a weightlifter suddenly dropping a heavy weight?
the Golgi tendon reflex
56
New cards
What do sudden movements like "clean and jerk" do?
put so much tension on tendons like the Achilles tendon, they could break
57
New cards
Withdrawal Reflex
Removes body limb from a pain sensation
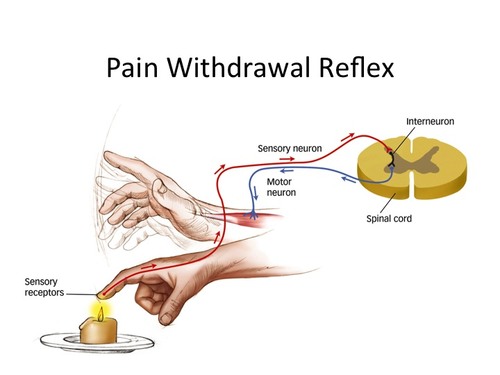
58
New cards
Reciprocal innervation
relaxation of extensor muscle when flexor contracts in withdrawal reflex, but is also involved in stretch reflex
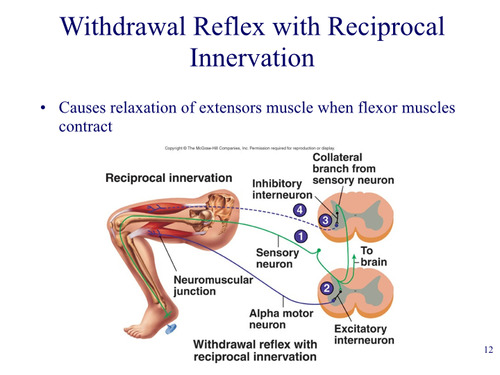
59
New cards
Crossed extensor reflex
when a withdrawal reflex is initiated in one lower limb, the crossed extensor reflex causes extension of opposite lower limb
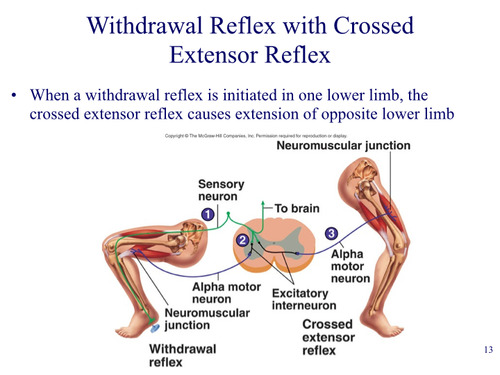
60
New cards
Relationship of Brain and Spinal Cord Reflexes
Sensory information (pain) goes to brain, then --> Descending tracts from brain carry info to reflexes
61
New cards
How do neurotransmitters affect the sensitivity of the reflex?
by either stimulating or inhibiting the motor neuron
62
New cards
Review:
1. Define reflex.
2. Name the three types of reflexes and their sensory receptors.
1. Define reflex.
2. Name the three types of reflexes and their sensory receptors.
1. An automatic response to a stimulus produced by a reflex arc.
2. Stretch reflex - muscle spindle, Golgi Tendon reflex - Golgi tendon organ, & Withdrawal reflex - pain receptor
2. Stretch reflex - muscle spindle, Golgi Tendon reflex - Golgi tendon organ, & Withdrawal reflex - pain receptor
63
New cards
What 3 things do peripheral nerves consist of?
1. Axon bundles
2. Schwann cells
3. Connective tissue surrounding the epineurium, perineurium, and endoneurium
2. Schwann cells
3. Connective tissue surrounding the epineurium, perineurium, and endoneurium
64
New cards
Epineurium
entire nerve (continuous with the Dura Mater of the CNS)
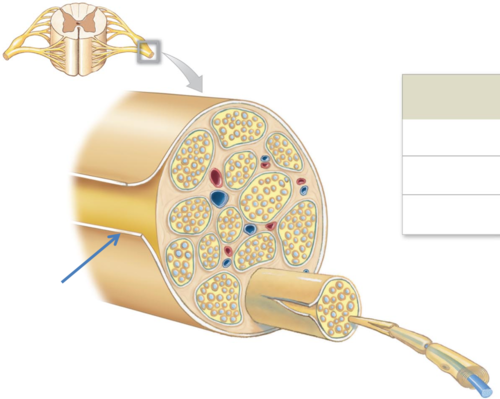
65
New cards
Perineurium
axon groups form fascicles
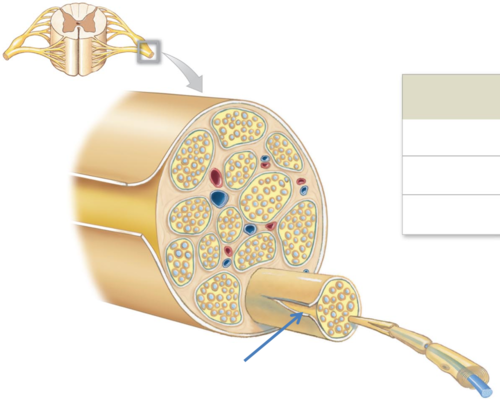
66
New cards
Endoneurium
individual neurons
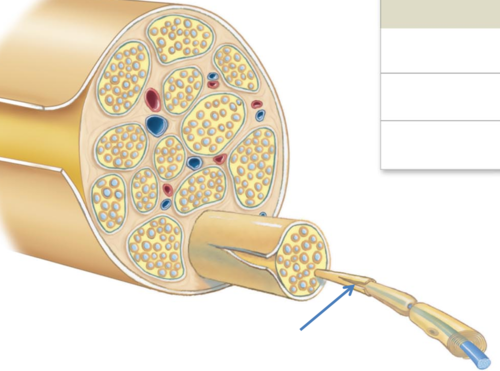
67
New cards
What is the name of the covering that covers axon groups to make up fascicles?
A. epineurium
B. endoneurium
C. perineurium
B. endoneurium
C. perineurium
68
New cards
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there?
31
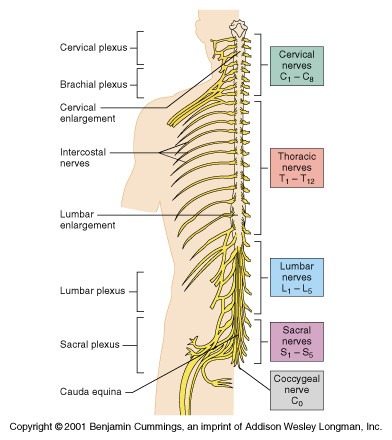
69
New cards
Where is the first pair of spinal nerves?
between skull and atlas
70
New cards
Where do nerves of the sacrum exit?
through the sacral foramina
71
New cards
Where do all other nerves (besides the ones of the sacrum) exit?
the intervertebral foramina
72
New cards
How many pairs of cervical nerves are there?
8
73
New cards
How many pairs of thoracic nerves are there?
12
74
New cards
How many pairs of lumbar nerves are there?
5
75
New cards
How many pairs of sacral nerves are there?
5
76
New cards
How many pairs of coccygeal nerves are there?
1
77
New cards
Dermatomal map
skin area supplied with sensory innervation by spinal nerves
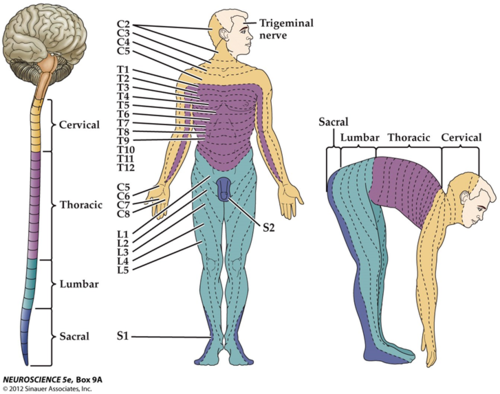
78
New cards
How many cervical vertebra are in the spine?
A. 12
B. 7
C. 5
D. The cervical vertebra number equal the cervical vertebra nerves.
A. 12
B. 7
C. 5
D. The cervical vertebra number equal the cervical vertebra nerves.
B. 7
79
New cards
A collection of spinal nerves that join together after leaving the spinal cord is called a
A. ganglion
B. nucleus
C. projection nerve
D. plexus
A. ganglion
B. nucleus
C. projection nerve
D. plexus
D. plexus
80
New cards
Branches of Spinal Nerves (3 things)
A. Dorsal Ramus
B. Ventral Ramus
C. Communicating Rami
B. Ventral Ramus
C. Communicating Rami
81
New cards
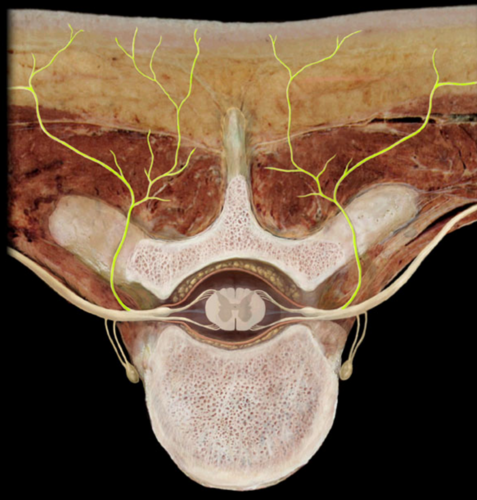
Dorsal Ramus
innervates deep muscles of trunk and functions in movements of the vertebral column and sensation of the skin near the middle of the back.
82
New cards
Ventral Ramus - 2 ways of distribution
1. intercostal nerves
2. plexuses
2. plexuses
83
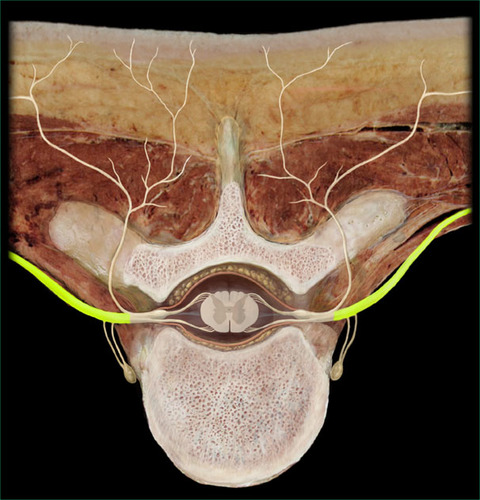
New cards
Ventral ramus intercostal nerves
intercostal nerves in the thoracic region that innervate intercostal muscles and skin over thorax
84
New cards
Ventral ramus plexuses (5 things)
1. Cervical plexus (C1-C4)
2. Brachial plexus (C5-T1)
3. Lumbar plexus (L1-L4)
4. Sacral plexus (L4-S4)
5. Coccygeal plexus (S5-CO)
2. Brachial plexus (C5-T1)
3. Lumbar plexus (L1-L4)
4. Sacral plexus (L4-S4)
5. Coccygeal plexus (S5-CO)
85
New cards
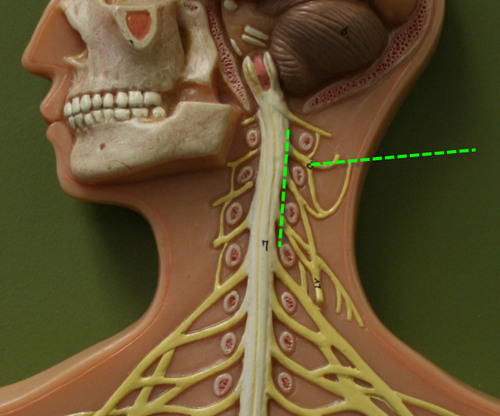
Cervical plexus
A. C1-C4
B. Innervates superficial neck structures, skin of the neck, the posterior portion of the head
B. Innervates superficial neck structures, skin of the neck, the posterior portion of the head
86
New cards
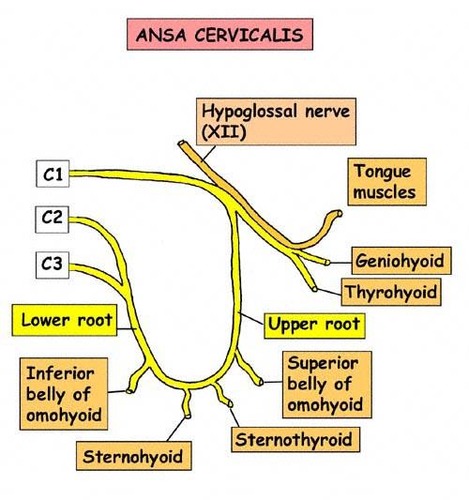
Ansa cervicalis
the loop between C2 and C3
87
New cards
Phrenic nerve
A. From C3-C5 (in the cervical and brachial plexuses)
B. Innervates diaphragm
B. Innervates diaphragm
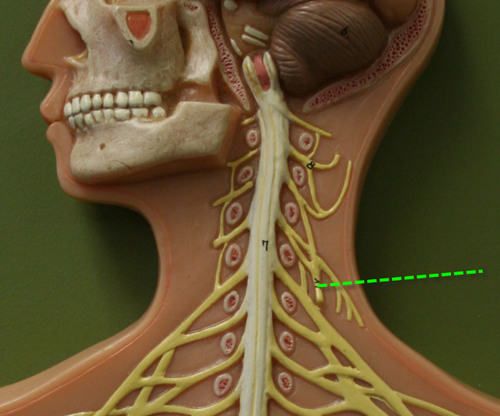
88
New cards
Brachial plexus
A. Originates from spinal n. C5-T1
B. Five ventral rami form three trunks, that separate into six divisions, then form cords that give rise to branches of smaller nerves (ARMUM)
B. Five ventral rami form three trunks, that separate into six divisions, then form cords that give rise to branches of smaller nerves (ARMUM)
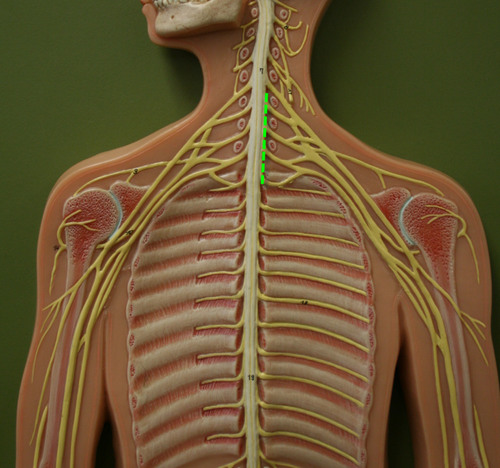
89
New cards
STOP slide 60
90
New cards
Axillary nerve
1. Laterally rotates arm - teres minor
2. Abducts arm - deltoid
3. Skin: inferior lateral shoulder
2. Abducts arm - deltoid
3. Skin: inferior lateral shoulder
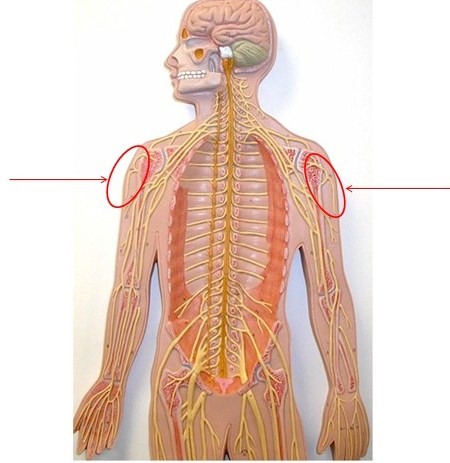
91
New cards
Radial nerve
1. Movements at elbow and wrist
2.. Thumb movements
3. Skin: posterior surface of arm and forearm & lateral 2/3 of dorsum of hand
2.. Thumb movements
3. Skin: posterior surface of arm and forearm & lateral 2/3 of dorsum of hand
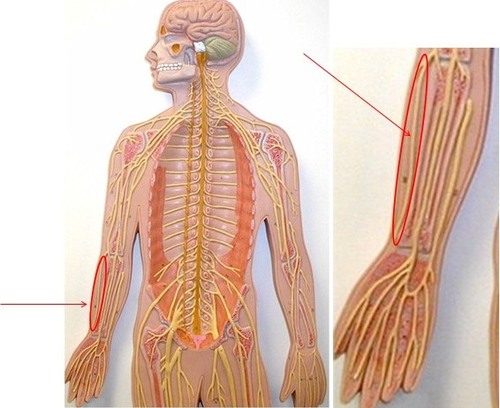
92
New cards
Musculocutaneous nerve
1. Movements of flexion at the shoulder, elbow and wrist
2. Supination of the forearm and hand
3. Skin: lateral surface of forearm
2. Supination of the forearm and hand
3. Skin: lateral surface of forearm
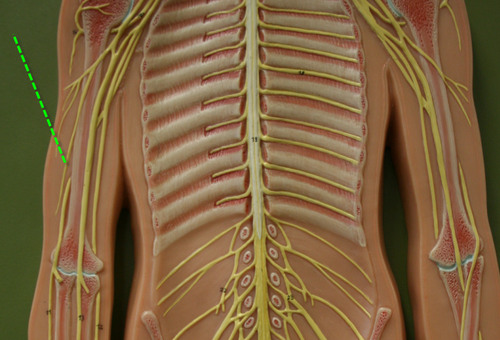
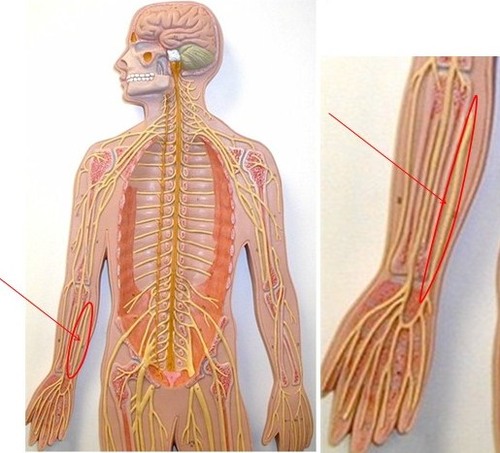
93
New cards
Ulnar nerve
1. Movements at wrist & fingers
2. Most of intrinsic hand m.
3. Skin: medial 1/3 of hand, little finger, and medial ½ of ring finger
2. Most of intrinsic hand m.
3. Skin: medial 1/3 of hand, little finger, and medial ½ of ring finger
94
New cards
Which nerve is the most easily damaged of all spinal nerves and why?
ulnar nerve - because ______.
95
New cards
Median nerve
1. Movement of hand, wrist, fingers, thumb
2. Skin: lateral 2/3 palm, thumb, index and middle fingers + lateral ½ of ring finger and dorsal tips of same fingers
2. Skin: lateral 2/3 palm, thumb, index and middle fingers + lateral ½ of ring finger and dorsal tips of same fingers
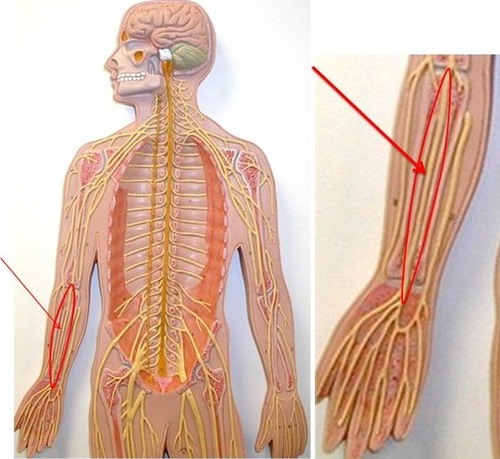
96
New cards
Carpal Tunnel syndrome
Tingling, burning, numbness in hand, especially the thumb and middle fingers, cause by damage to median nerve
97
New cards
Which nerve is involved when you hit your Funny bone?
A. Ulnar
B. Radial
C. Median
A. Ulnar
B. Radial
C. Median
A. Ulnar
98
New cards
Which nerve is compressed in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
A. Ulnar
B. Radial
C. Median
A. Ulnar
B. Radial
C. Median
C. Median
99
New cards
Smaller nerves in the brachial plexus that innervate muscles acting on scapula and arm and supply cutaneous innervation of arm and forearm: (3 things)
1. Pectoral nerve
2. Subscapular nerve
3. Suprascapular nerve
2. Subscapular nerve
3. Suprascapular nerve
100
New cards
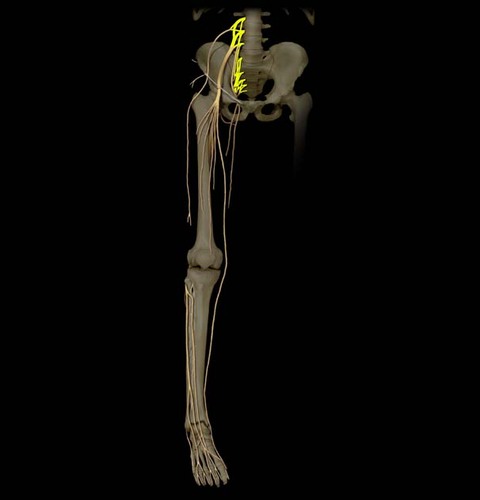
Lumbosacral plexus
A. Lumbar plexus: ventral rami of L1-L4
B. Sacral plexus: ventral rami of L4-S4
C. Usually considered together because of their close relationship
B. Sacral plexus: ventral rami of L4-S4
C. Usually considered together because of their close relationship