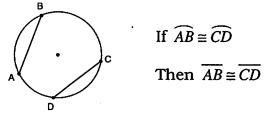Geometry Circles
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
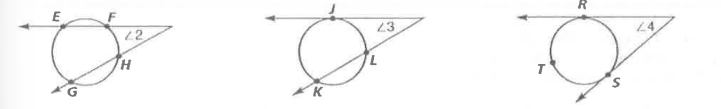
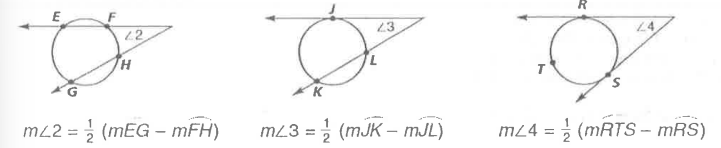
What happens if two secants, a secant and a tangent, or two tangents intersect outside a circle?
The measure of the angle formed is equal to half the measure of the difference of the intercepted arcs.
What is the measure of an inscribed angle equal to?
Half the measure of its intercepted arc.
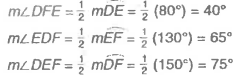
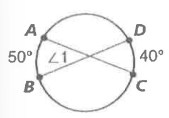
What happens if two chords intersect inside a circle?
The measure of each angle is equal to half the measure of the sum of the intercepted arcs.
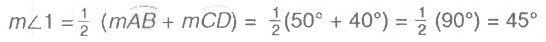
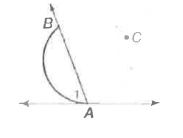
What happens if a secant and a tangent intersect at the point of tangency?
The measure of each angle formed is one half the measure of its intercepted arc.
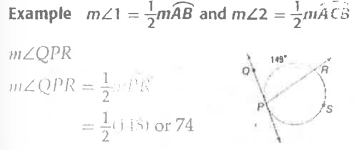
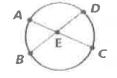
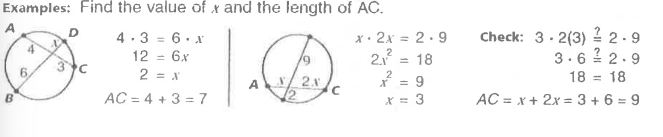
If two chords intersect, the product of the segment lengths along one chord is equal to what?
The product of the segment lengths along the other chord.
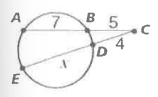
If two secant segments share the same point outside a circle, what is the product of the length of one secant and its external segment length equal to?
The product of the length of the other secant and its external segment length.
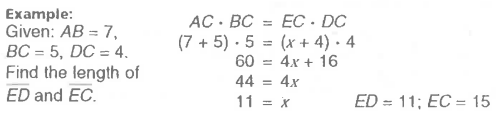
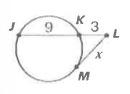
What happens if a secant segment and a tangent segment share the same external point?
The product of the length of the external segment is multiplied by itself and is congruent to the product of the length of the other secant and its external segment length.

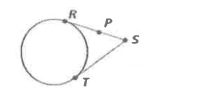
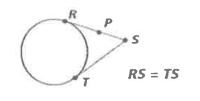
What happens if two tangent segments share the same external point?
The segments are congruent.
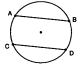
What happens if lines are parallel in a circle?
The arcs they intercept are congruent
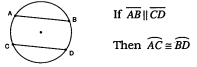

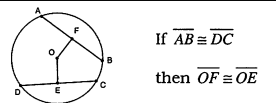
What happens if a radius (or diameter) is perpendicular to a chord?
The radius (or diameter) bisects the chord and the intercepted arc.
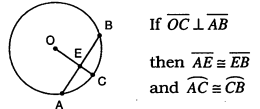
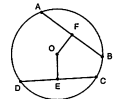
What happens if chords are congruent?
They are equidistant from the center.
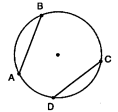
What happens if chords intercept congruent arcs?
The chords are congruent.