Parasitology Exam 2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
1
New cards
In people, most species of trematodes occur in habitats other
than the intestine. Name three of these other habitats and (1)
list a trematode species that lives there. For each of the
species named, (2) explain how their eggs escape from the
human host, and (3) describe the consequences to the host of
the escape.
than the intestine. Name three of these other habitats and (1)
list a trematode species that lives there. For each of the
species named, (2) explain how their eggs escape from the
human host, and (3) describe the consequences to the host of
the escape.
Liver: Fasciola hepatica; eggs are released in feces; no consequence of eggs escaping
Blood vessels: Schistosoma mansoni; eggs burrow their way through tissue to the s. intestine to then be released in feces; granuloma forms around eggs and general tissue damage
Lungs: Paragonimus westermani; eggs are coughed up and either spit out or swallowed; fibrosis around egg (damage to lung tissues)
Blood vessels: Schistosoma mansoni; eggs burrow their way through tissue to the s. intestine to then be released in feces; granuloma forms around eggs and general tissue damage
Lungs: Paragonimus westermani; eggs are coughed up and either spit out or swallowed; fibrosis around egg (damage to lung tissues)
2
New cards
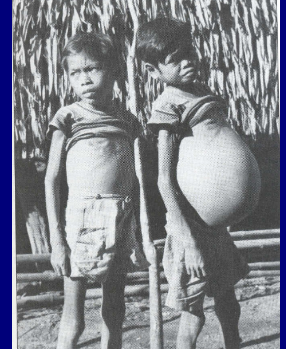
The photograph below shows two males one 13 and one 24
years old. One of them is infected with a species of parasite
and the other is not. The caption below (not shown) refers to
stunting of growth due to a parasitic disease.
years old. One of them is infected with a species of parasite
and the other is not. The caption below (not shown) refers to
stunting of growth due to a parasitic disease.
caused by Schistosoma japonicum
anterior mesentenic veins of small intestine
interfere with absorption
anterior mesentenic veins of small intestine
interfere with absorption
3
New cards
The cartoon below is amusing but biologically it is inaccurate
in several regards. From a parasitological point of view what
are at least three flaws?
in several regards. From a parasitological point of view what
are at least three flaws?
1. tapeworms are segmented
2. tapeworms generally stay in the small intestine
3. tapeworm offspring do not stay in the same individual, they are released as eggs in either proglottids or in the feces
2. tapeworms generally stay in the small intestine
3. tapeworm offspring do not stay in the same individual, they are released as eggs in either proglottids or in the feces

4
New cards
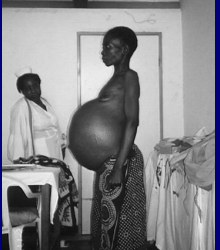
The photograph below represents a woman from Kenya infected
with a parasite. Based on her condition in the photograph, what are (1) two likely species of parasites and (2) their ontogenetic stages that she may be infected with? Second how would you (3) diagnose her infection for each of these parasites? Knowing that she is a Turkana woman from a dry part of Kenya (4) which species of the two
parasites might you assume she is infected with?
with a parasite. Based on her condition in the photograph, what are (1) two likely species of parasites and (2) their ontogenetic stages that she may be infected with? Second how would you (3) diagnose her infection for each of these parasites? Knowing that she is a Turkana woman from a dry part of Kenya (4) which species of the two
parasites might you assume she is infected with?
1. Schistosoma mansoni and Echinococcus granulosus
2. infected with adults laying eggs; hydatid cyst continuous growth
3. look for eggs in feces; physical imaging or serodiagonosis
4. Schistosoma mansoni
2. infected with adults laying eggs; hydatid cyst continuous growth
3. look for eggs in feces; physical imaging or serodiagonosis
4. Schistosoma mansoni
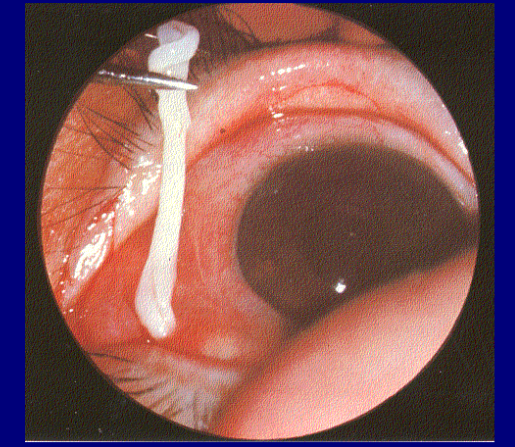
5
New cards
An ontogenetic stage of a cyclophyllidean tapeworm that would be found in an intermediate host
ooncosphere or hydatid cyst
6
New cards
An ontogenetic stage of a cyclophyllidean tapeworm that would be infective to a definitive host
hydatid cyst
7
New cards
A genus of the intermediate host for Schistosoma mansoni
Biomphalaria
8
New cards
An ontogenetic stage of a pseudophyllidean tapeworm that hatches from an egg
coracidium
9
New cards
An organism from which people could acquire the infective stage of Fasciola heatica
aquatic grasses (uncooked infected watercrest)
10
New cards
The ontogenetic stage of Paragonimus westermani infective to people
metacercaria
11
New cards
what is the larval stage and potential species?
Spirometra mansonoides, plerocercoid
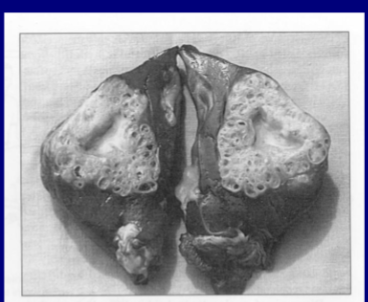
12
New cards
what is the larval stage and potential species?
Taenia solium, cysticercus
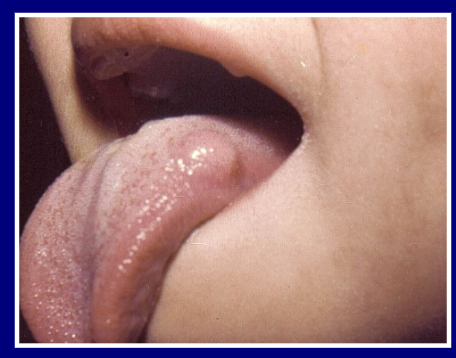
13
New cards
what is the larval stage and potential species?
Echinococcus granulosus, hydatid cyst
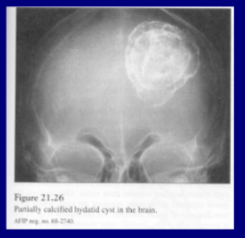
14
New cards
what is the larval stage and potential species?
Echinococcus multiocularis, alveolar hydatid cyst