Positive Psychology: Potency of Positive Emotions
The Potency of Positive Emotions
Dr. Alice Isen
- in experiencing mild positive emotions, we are more likely to
- help other people
- be flexible in our thinking
- come up with solutions to our problems
Dr. Barbara Fredrickson
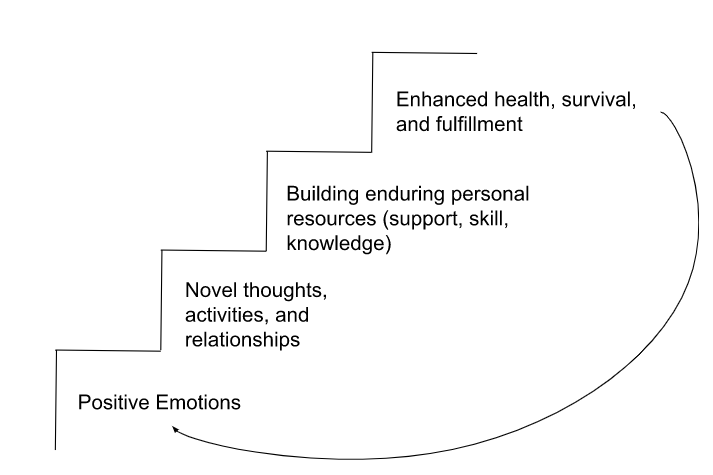
^^Broaden and Build Model^^
explain the social-cognitive effects of positive emotional experiences
- Negative Emotions: physical reactions (fight/flight)
- Positive Emotions: cognitive reactions
The experience of joy expands to the realm of what a person feels like doing at the time
- the person who is happy listed more possibilities than a person who is in a negative state
joy (positive emotions) appears to open up to many new thought and behaviors
Theories of Happiness
Need-Goal Satisfaction Theories
- Reduction of tension leads to happiness (psychoanalytic, humanist theories)
- ^^We are happy because we have reached our goals^^
- Happiness as a target of our psychological pursuits
Process-Activity Theory
- ^^Engaging in particular life activities generate happiness^^
- People who engage in FLOW in daily life tend to be happy
- Flow: engagement in interesting activities that match or challenge task related skills
- Engagement in activity produce happiness
- Process of pursuing goals generate energy and happiness
Genetic-Personality Predisposition
- Costa and McRae (1988)
- ^^biologically determined happiness^^
- genetic-factors contribute to positive emotionality (40%) and negative emotionality (55%)
- happiness dependent on temperament since individuals may vary in the type of adaptation to positive or negative external experiences
- more research is needed to strengthen the connection between happiness and personality
Emotional Experiences
Emotion-Focused Coping
- intense emotions were seen dysfunctional and opposed to rationality
- linking with maladaptive outcomes in life
- Stanton (1994) posits the potential of emotion-focused coping
- Emotional approach involves active moving towards, rather than away, from a stressful encounter
- Emotional Processing
- ^^attempts to understand emotions^^
- Examples
- I realize that my feelings are valid and important.
- I take time to figure out what I am feeling.
- I acknowledge my emotions.
- Emotional Expression
- ^^free and intentional displays of feeling^^
- Examples
- I feel free to express my emotions.
- I take time to express my emotions.
- I let my feelings come out freely.
- Benefits
- most people benefit (short term) from ^^expressing their emotions^^ in a meaningful way
- Emotional processing seem to be more adaptive as people learn more about what they feel and how they feel it
Emotional Intelligence
- array of non-cognitive capabilities, competencies and skills that help us deal with the demands of the environment
- measures personality and mood variables such as
- self-regard, empathy, tolerance, happiness
- ^^“higher form of intelligence”^^
- the ability to perceive and express emotions
- to use emotions and emotional understanding to facilitate thinking
- to understanding complex emotions, relationships among emotions and behavioral consequences
- to manage emotions
Socioemotional Selectivity Theory
- older adults are more able to
- focus less on negative emotions
- engage more deeply with emotional content
- savor the positive in life
Emotional Storytelling
- written disclosure of emotional upheaval
- useful means to process intense negative emotions
Positive Cognitive States and Processes
Positive Thinking and Management
- The positive thinking that usually comes with optimism is a key part of effective stress management and effective stress management is associated with many health benefits
Advantages of Positive Thinking
- Research shows that people who feel confident in themselves can ^^problem solve and make better decisions, take more risks, assert themselves and strive to meet their personal goals^^
- Advantages of positive thinking include ^^less stress, better overall physical and emotional health, longer life span, and better coping skills^^
Self-Efficacy
- ^^the belief that one’s skills and capabilities are enough^^ to accomplish one’s desired goals in a specific situation
- what I believe I can do with my skills under certain conditions
- Learned Human Pattern
- Social Cognition Theory: humans actively shape their lives rather than passively reacting to situations
- S-E Components
- performance accomplishment, vicarious learning, verbal encouragement, and emotional states
- Performance Appraisal: previous successes in similar situations
- Vicarious Learning: modeling on others in the same situations
- Verbal Encouragement: undergoing verbal persuasion by a powerful, trustworthy expert (or an attractive person)
- Emotional States: how level of arousal and state of emotion can be attached with the activity
Neurobiology of Self-Efficacy
- Frontal and Pre-Frontal Lobes: facilitate prioritization of goals and the strategic thinking that is crucial for self-efficacy
- Problem Solving: the ^^right hemisphere^^ reacts to the ^^dilemmas^^ as related by the linguistic left hemisphere
- Realistic self-efficacy can lessen ^^cardiac reactivity and lower blood pressure^^ -- which facilitates coping
Measures of Self-Efficacy
- Occupational Questionnaire (Teresa, 1991)
- Career Counseling Self-Efficacy Scale (O’Brien & Heppner, 1997)
- Hurricane Coping Self-Efficacy Survey
- Cultural Self-Efficacy Scale (Briones et.al., 2009)
Influence of Self-Efficacy
- building on successes through goal-setting and the incremental meeting of these goals
- allowing the person to imagine himself/herself behaving effectively
- teaching techniques for lowering arousal and to increase the likelihood of a more adaptive self-efficacious thinking