Chapter 13
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What are the main components of the Central Nervous System (CNS)?
Brain and Spinal cord
What do the directional terms "Rostral" and "Caudal" mean in the CNS?
Rostral: Toward the nose (front)
Caudal: Toward the tail (back)
Used to describe anatomical locations, especially in four-limbed animals.
What basic functions does the brain control?
Vital body functions: heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure
Regulates: Autonomic Nervous System (ANS), Controls Endocrine System (hormone secretion)
Involved in peripheral innervation via cranial nerves (12 pairs) and spinal nerves (31 pairs), which are part of the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
What are some higher-level neural functions of the brain?
Intelligence, consciousness, memory, sensory-motor integration, emotion, behavior, socialization
What is cephalization?
The formation and growth of the head and brain during embryonic development, starting from the rostral part of the neural tube.
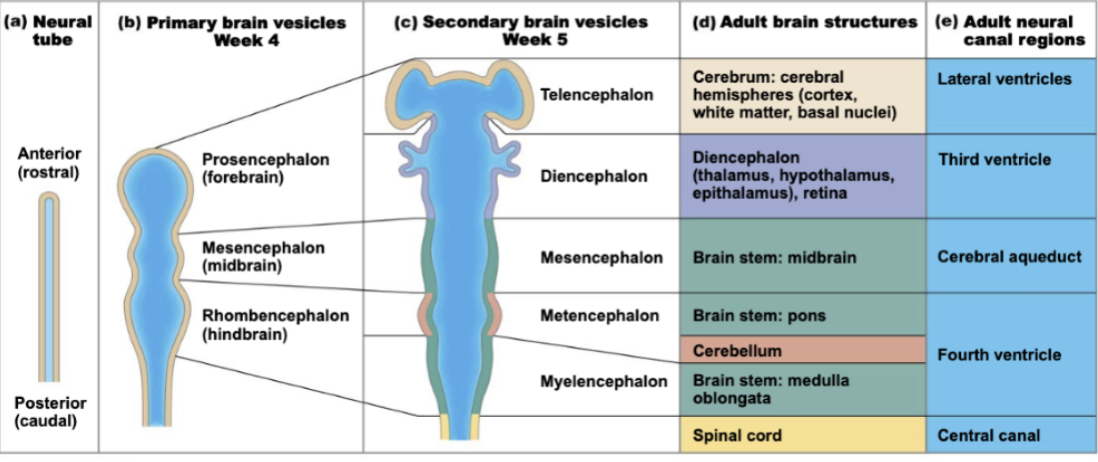
What are the primary brain vesicles and what do they develop into?
Prosencephalon (Forebrain): divides into Telencephalon and Diencephalon
Mesencephalon (Midbrain): remains undivided
Rhombencephalon (Hindbrain): divides into Metencephalon and Myelencephalon
What is convolutions, gyri and sulci, and why are they important?
Convolutions: folds of the brain that increase surface area and neural communication
Gyri: raised ridges
Sulci: grooves between gyri
They increase the brain’s surface area, allowing more neurons and improved neural communication.
Match these secondary brain vesicles to their adult brain structures:
Telencephalon
Diencephalon
Mesencephalon
Metencephalon
Myelencephalon
Telencephalon → Cerebral hemispheres (Cerebrum)
Diencephalon → Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Epithalamus
Mesencephalon → Midbrain
Metencephalon → Pons and Cerebellum
Myelencephalon → Medulla Oblongata
What are the major functions of the Telencephalon (Cerebrum)?
Largest brain region; responsible for complex thought, cognition, consciousness, and empathy.
Where is Diencephalon located and their functions?
Thalamus: sensory relay
Hypothalamus: homeostasis and endocrine regulation
Epithalamus: contains pineal gland (melatonin production and circadian rhythms)
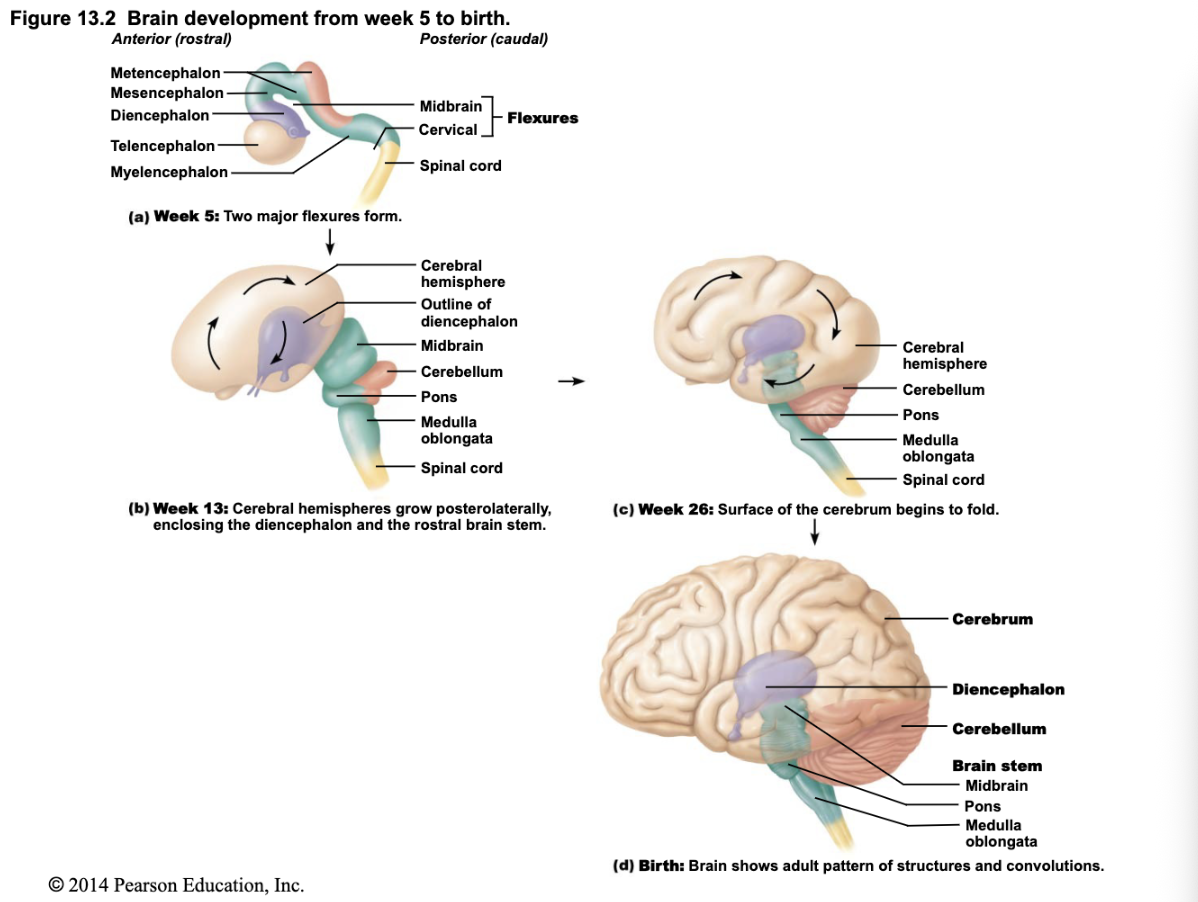
What are the main functions of the Mesencephalon (Midbrain)?
Part of brainstem; involved in visual and auditory reflexes, and motor pathways.
What are the functions of the Metencephalon (Pons and Cerebellum)?
Pons: communication bridge between brain regions
Cerebellum: coordination, balance, and motor control; second largest brain region.
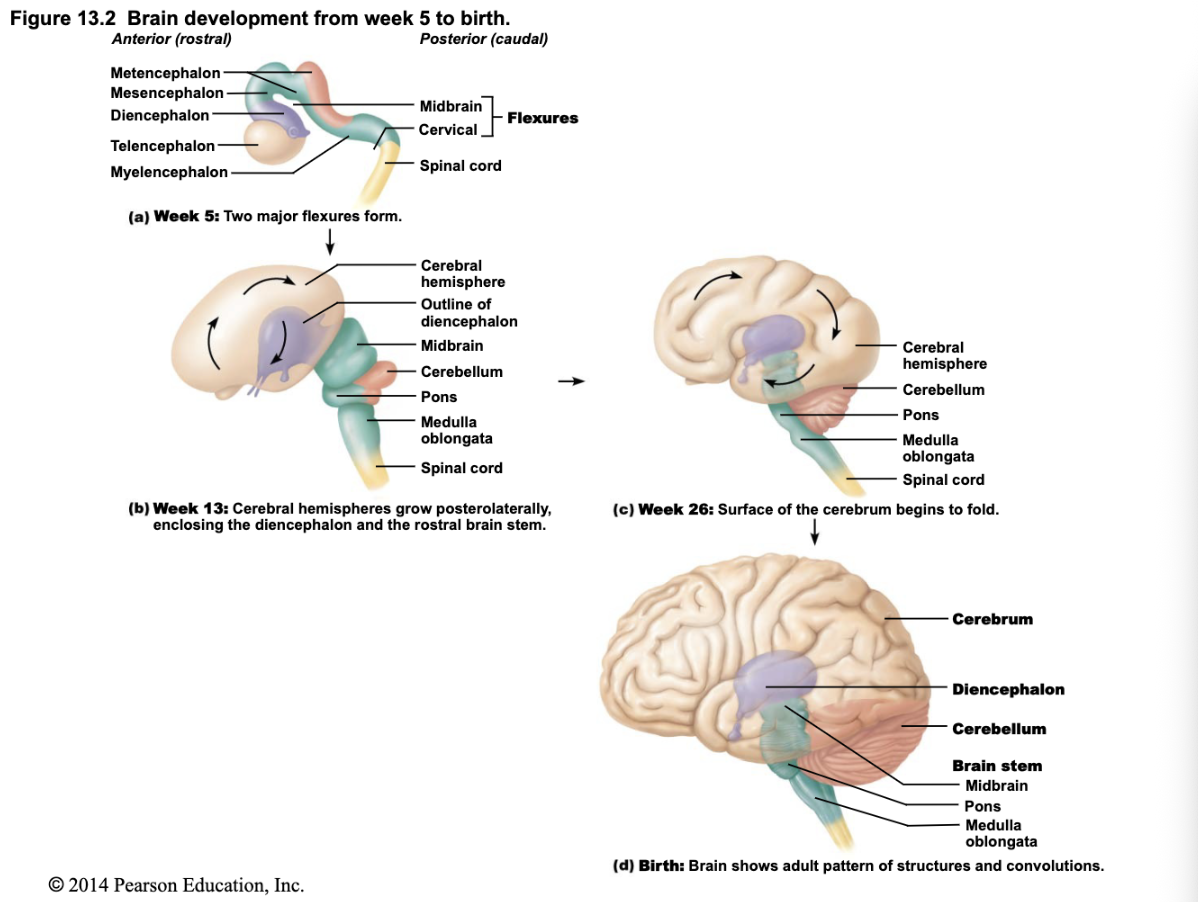
What autonomic functions does the Myelencephalon (Medulla Oblongata) control?
Breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
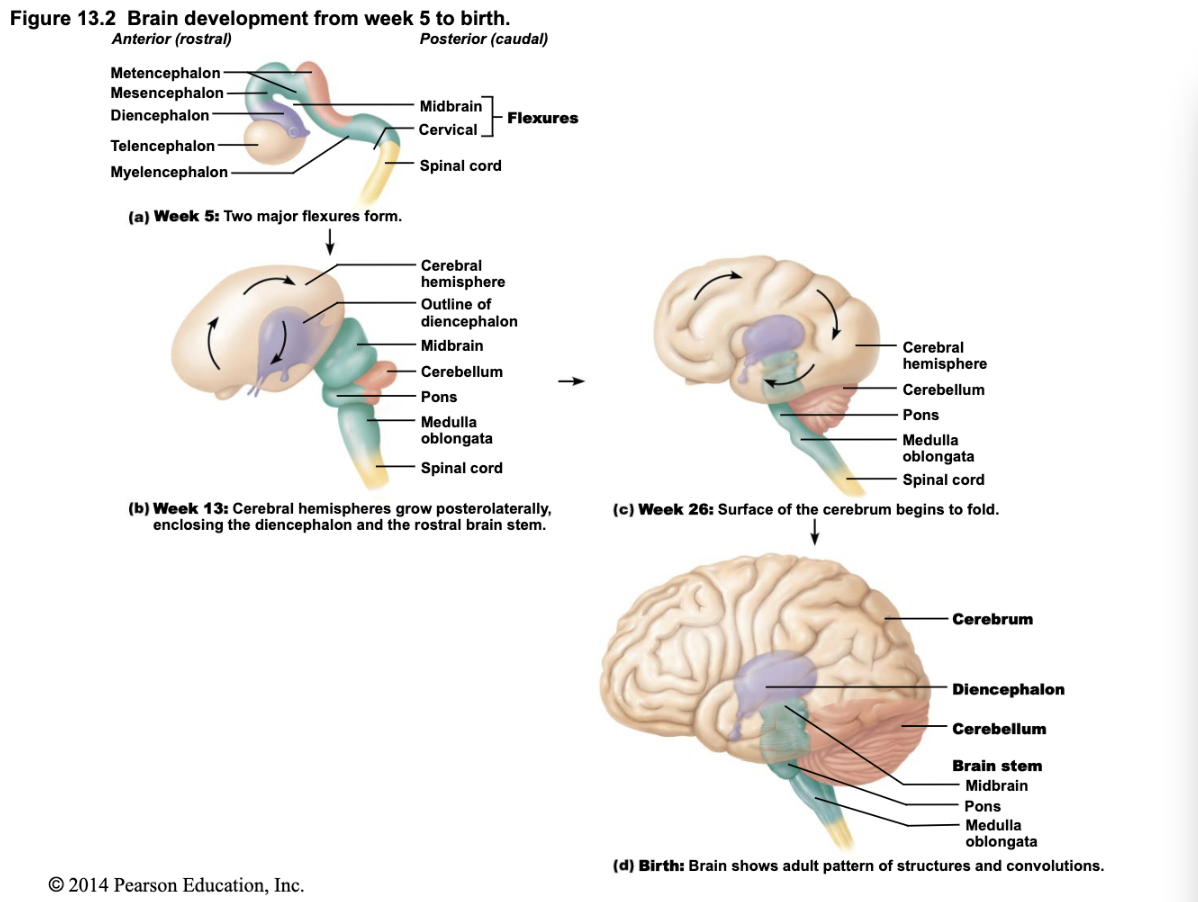
Summary of Development Pathway
Neural tube (Week 4, embryonic structure)
2. → Three primary brain vesicles
3. → Five secondary brain vesicles .
→ Adult brain structures
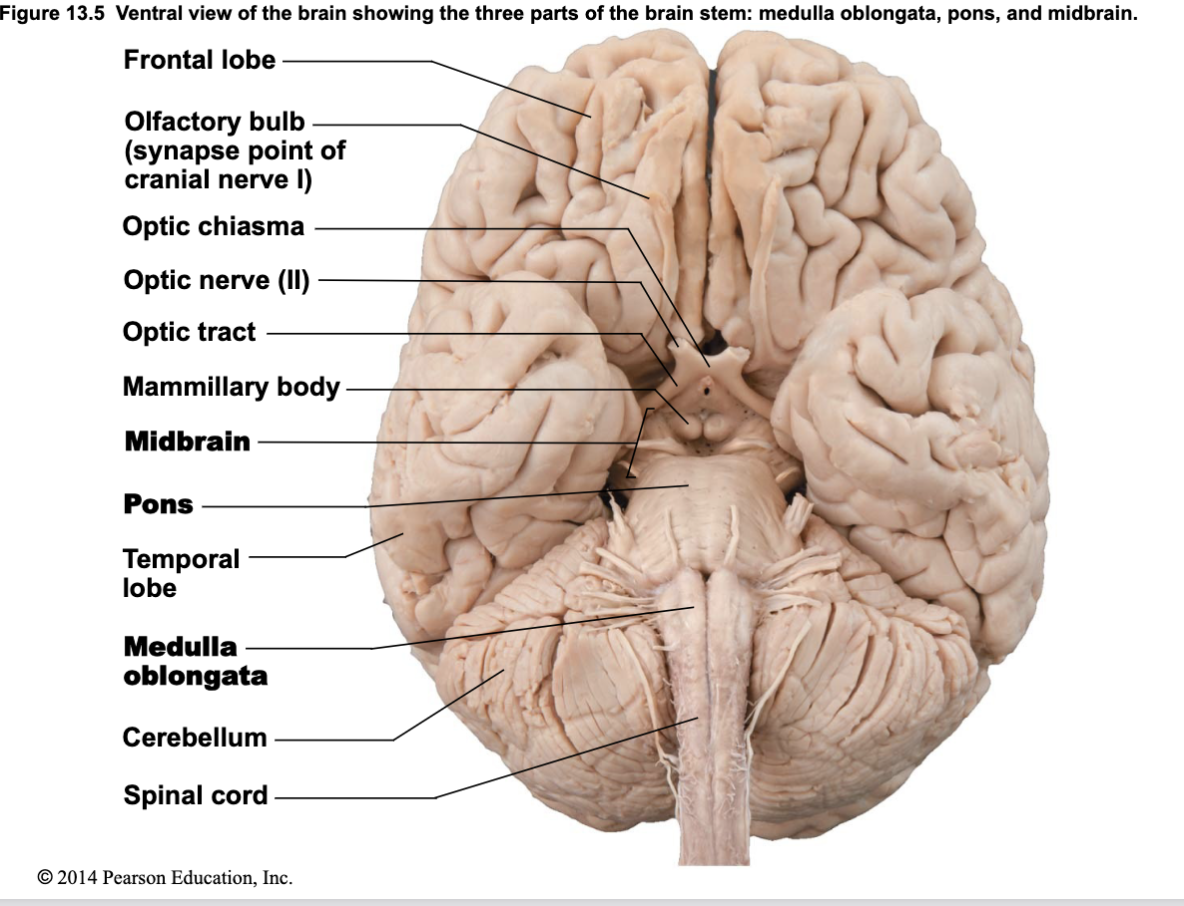
What structures make up the brainstem, and what are its general functions?
Midbrain, Pons, Medulla Oblongata
Passageway for fiber tracts between cerebrum and spinal cord
Innervates face and head (motor and sensory)
Houses 10 of the 12 cranial nerves
Controls automatic survival behaviors: breathing, heart rate, digestion
Integrates visual and auditory reflexes (especially midbrain)
What are brain ventricles and what do they contain?
Fluid-filled spaces derived from the neural tube’s central cavity, containing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) which protects, nourishes, removes waste, and maintains intracranial pressure.
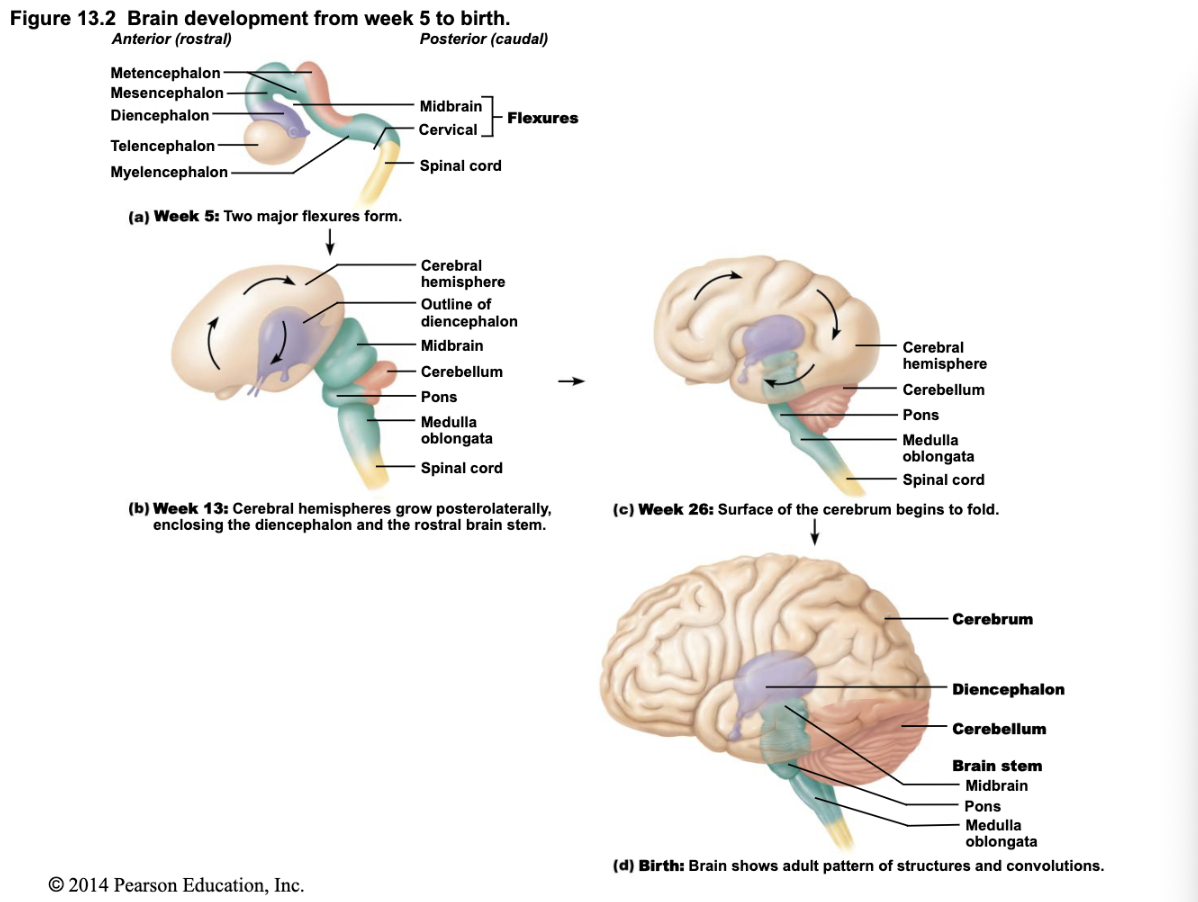
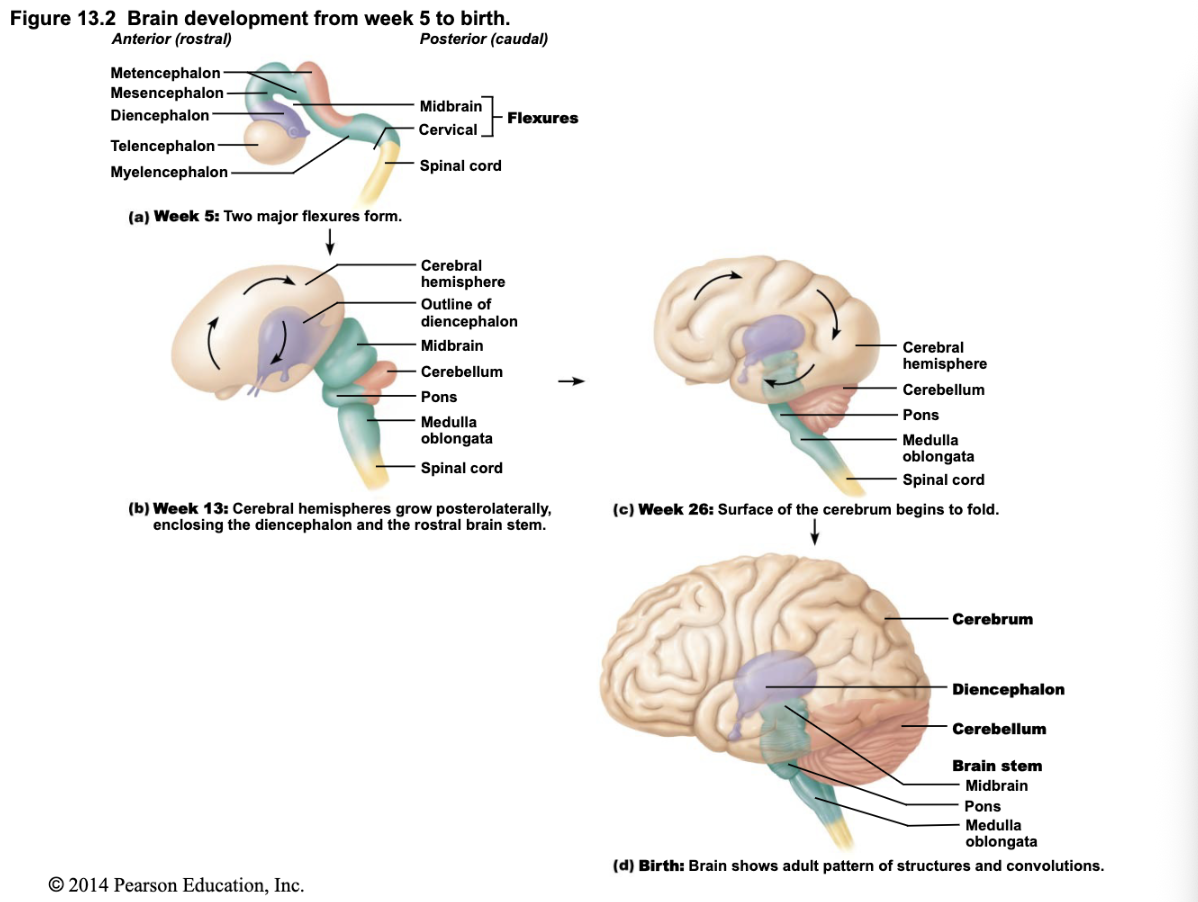
What happens during rapid brain growth in embryonic development?
The brain grows quickly; different regions develop and expand at varying rates.
What are the roles of gray and white matter in the brain?
Gray Matter: Neuronal cell bodies; involved in processing & integration
White Matter: Myelinated axons; provides communication pathways
How do brain structures shift during development?
Cerebral hemispheres grow larger and eventually surround the diencephalon and midbrain, making them mostly hidden in the adult brain.
What are the four major brain regions?
Brainstem – midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
Cerebellum – coordination, balance, motor control
Diencephalon – thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus
Cerebral Hemispheres (Cerebrum) – higher cognitive functions
Where is gray matter found in the brain?
Deep regions (central core)
Outer layer (cortex) of the cerebrum and cerebellum
Where is white matter found, and what is its function?
Surrounds deep gray matter; allows communication between brain regions through nerve tracts.
What is the cortex in brain tissue?
The outer layer of gray matter found in the cerebrum and cerebellum, formed by neuron migration during development.
What is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and what are its functions?
Filtered from blood by choroid plexuses
Functions: Shock absorption, Nutrient delivery, Waste removal
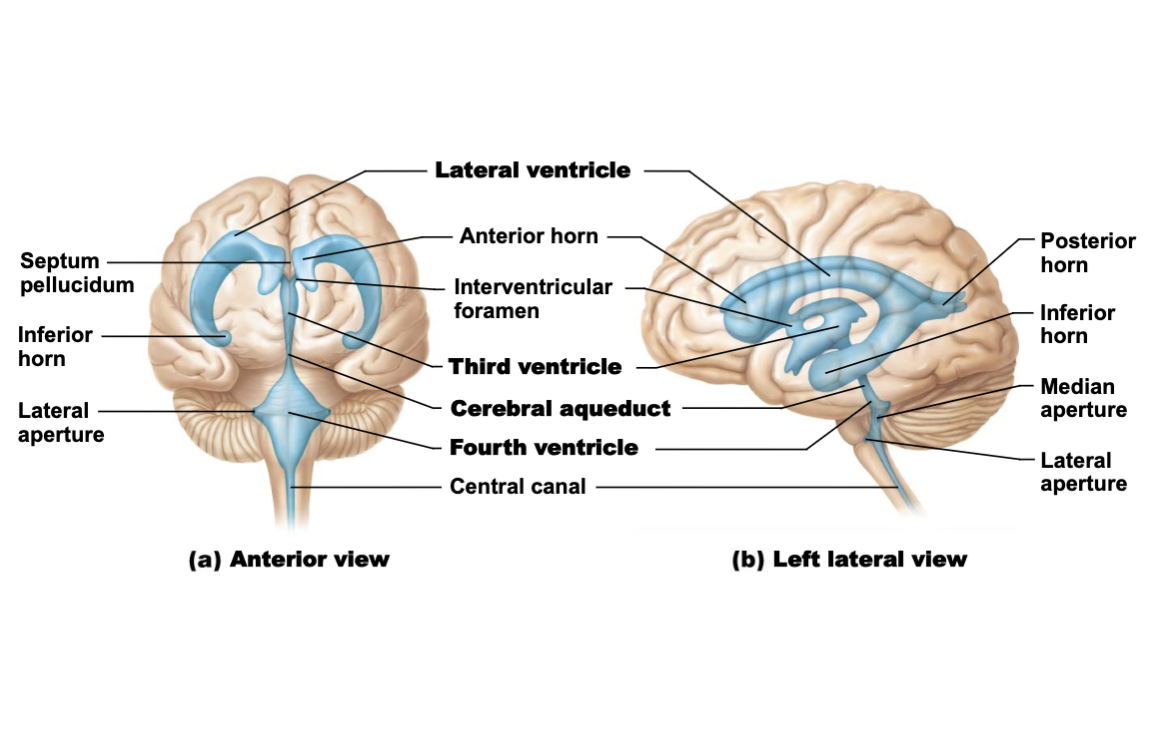
What are the ventricles of the brain and their locations?
Lateral Ventricles: In cerebral hemispheres (horseshoe-shaped)
Third Ventricle: In diencephalon
Fourth Ventricle: In hindbrain (between pons and cerebellum)
Cerebral Aqueduct: Narrow channel through midbrain connecting 3rd and 4th ventricles
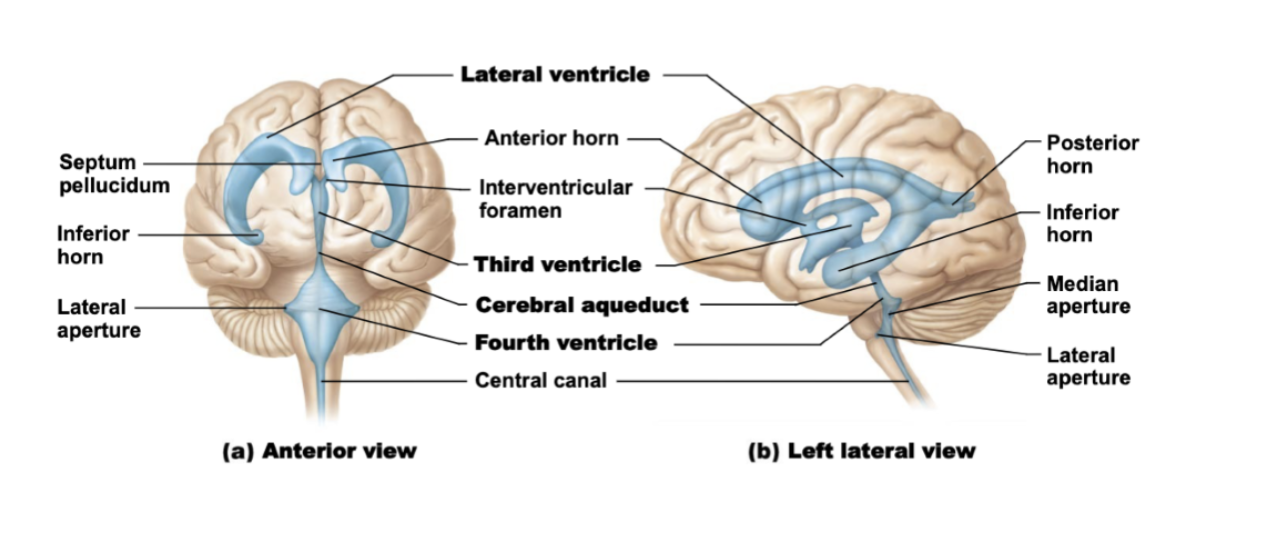
How does CSF flow through the ventricular system?
Lateral ventricles
→ Interventricular foramina
→ Third ventricle
→ Cerebral aqueduct
→ Fourth ventricle
→ Central canal of spinal cord & subarachnoid space
What is Midbrain (mesencephalon)
Develops from the mesencephalon (embryonic brain vesicle)
Functions: Controls eye motor movement, Processes visual and auditory information
Part of brainstem, located between forebrain and hindbrain