Cranium
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
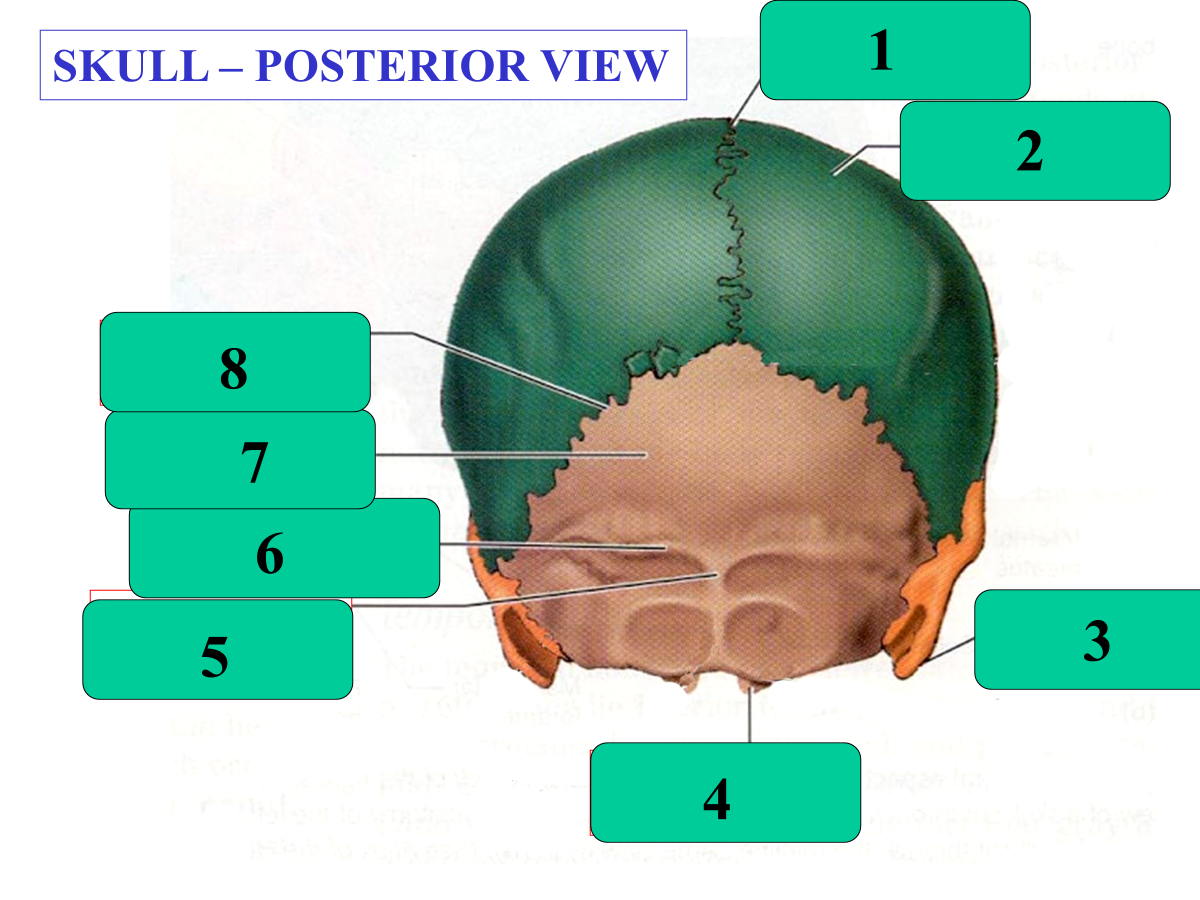
Sagittal Suture
Parietal Bone
Mastoid Process
Occipital Condyle
External Occipital Protuberance
Superior Nuchal Line
Occipital Bone
Lambdoid Suture
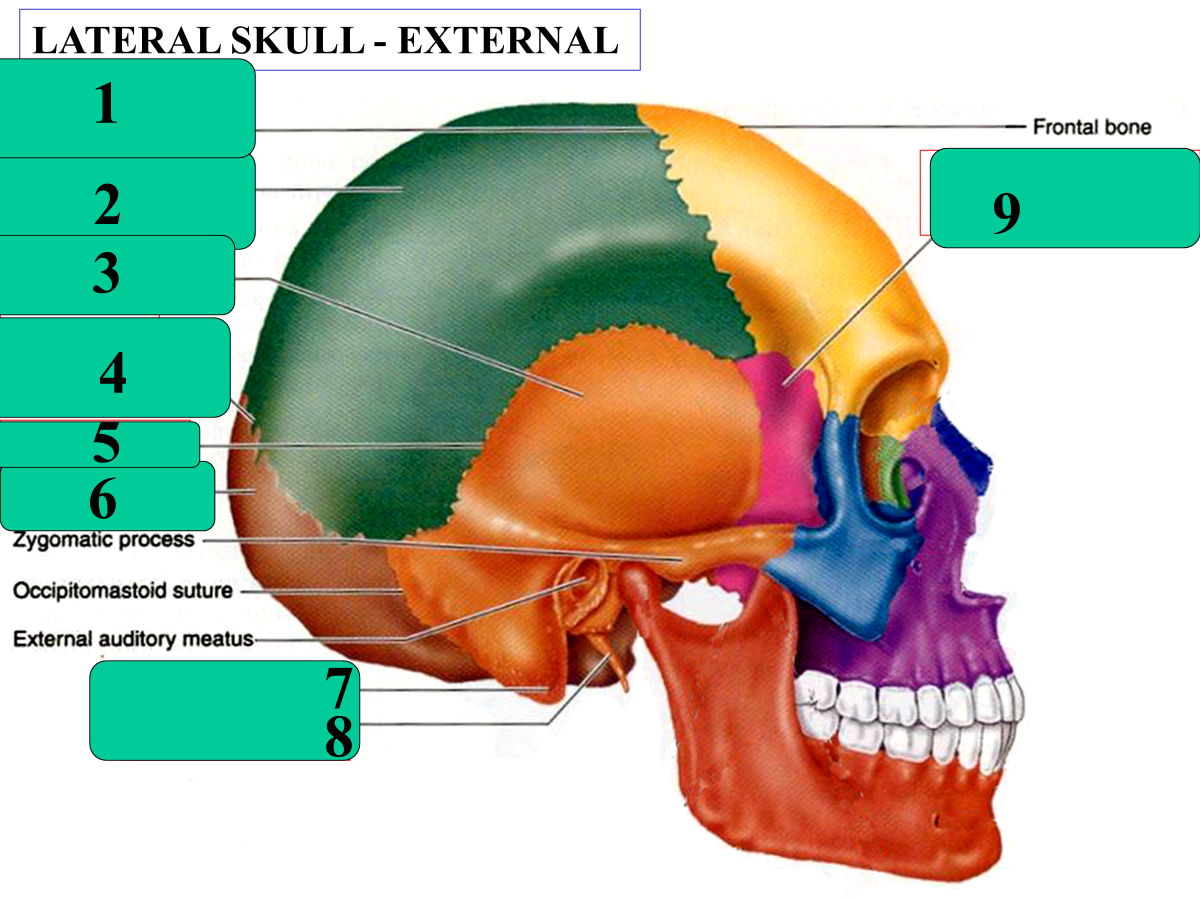
coronal suture
parietal bone
temporal bone
lambdoid suture
squamous suture
occipital bone
mastoid process
styloid process
sphenoid bone
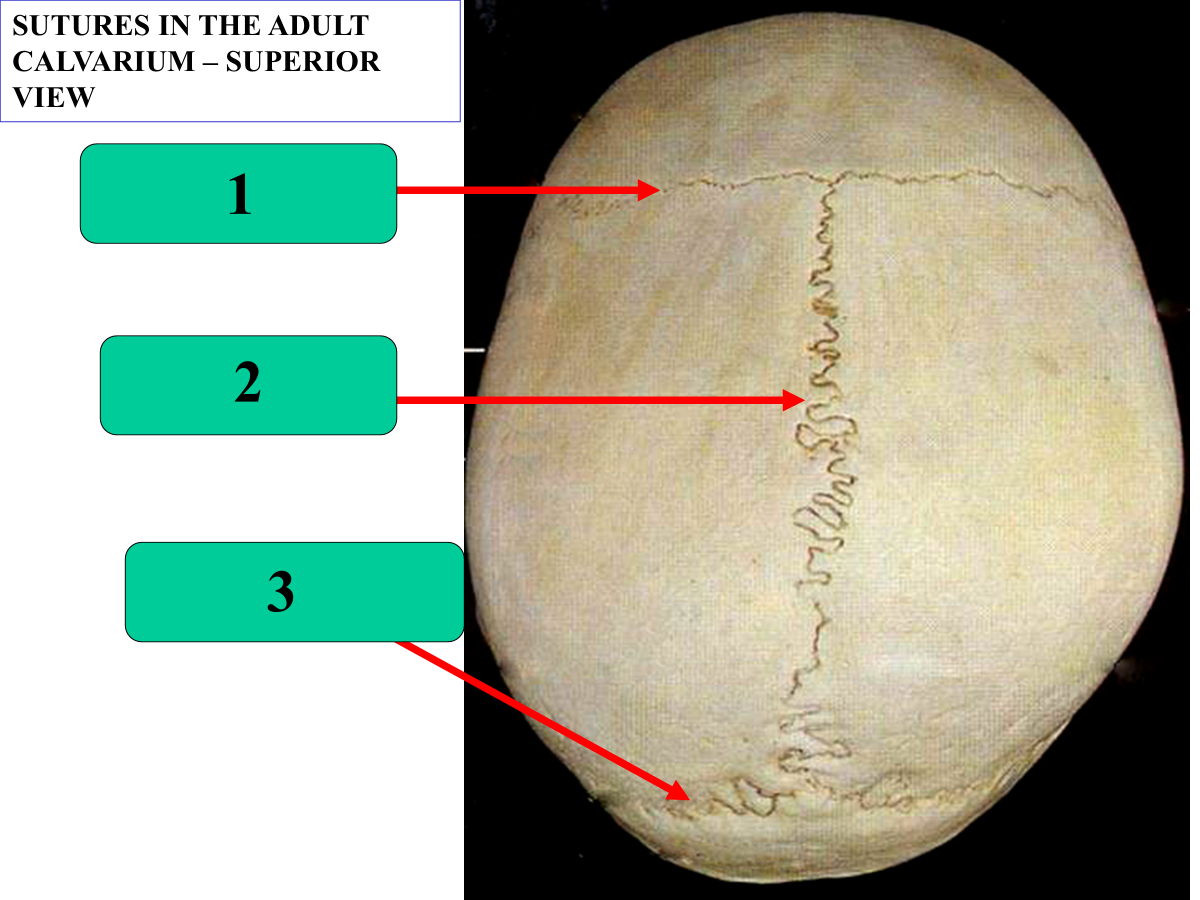
coronal suture
sagittal suture
lambdoid suture
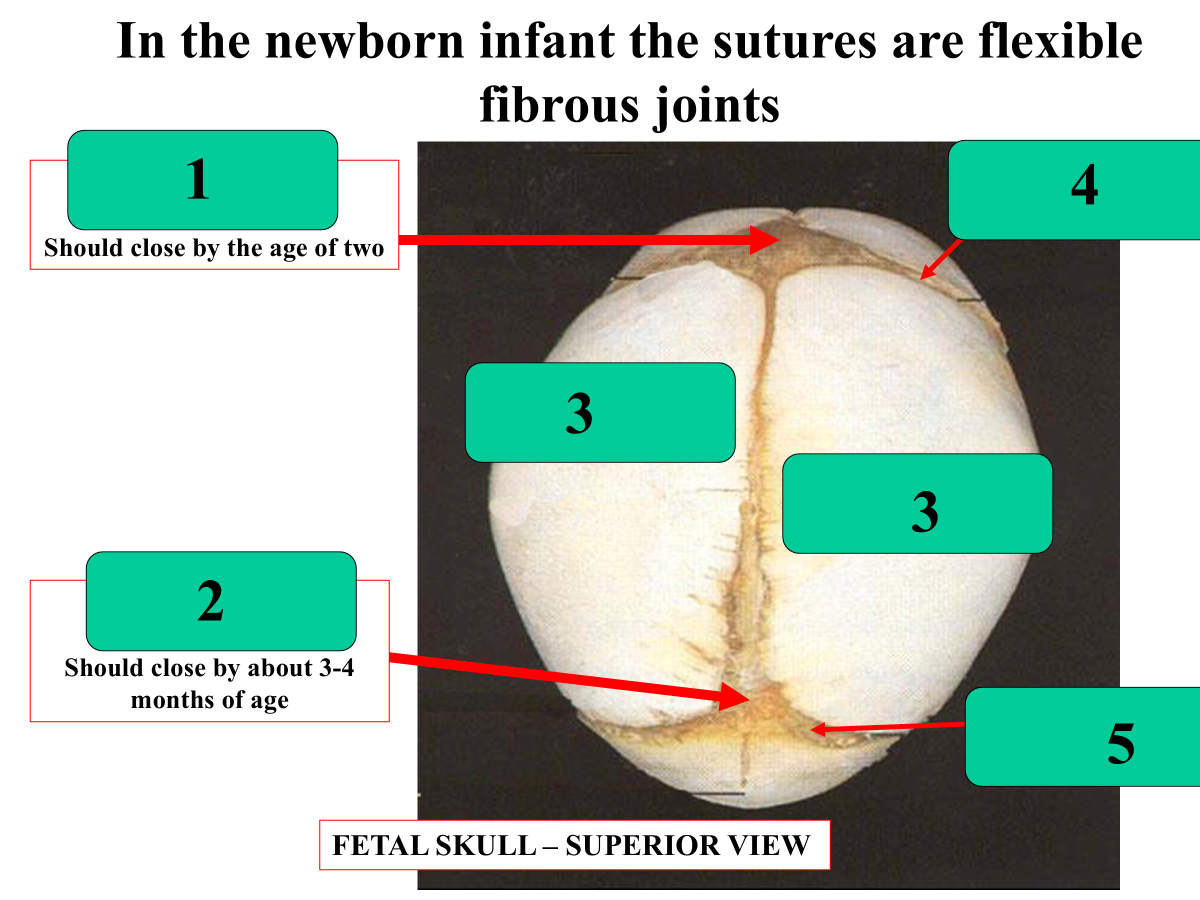
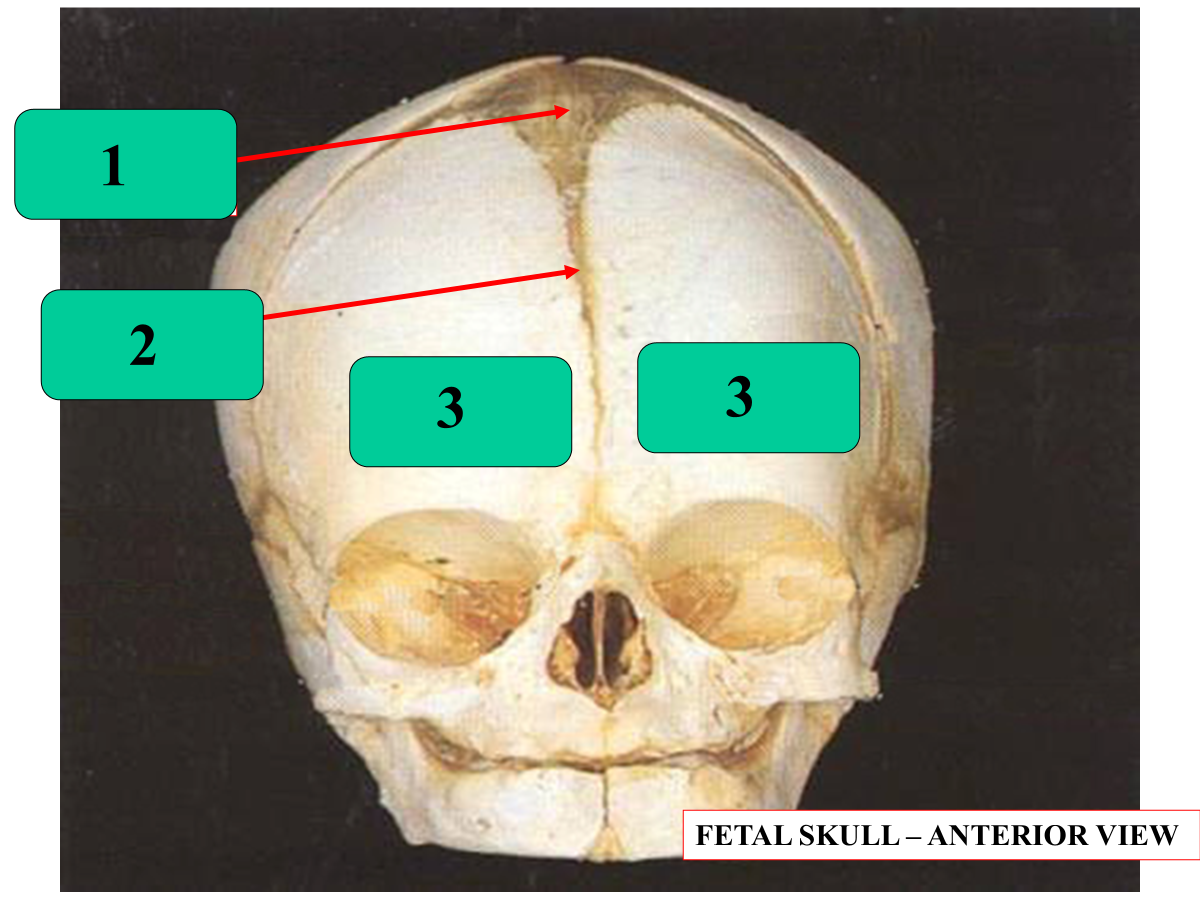
anterior fontanelle
posterior fontanelle
parietal
coronal suture
lambdoid suture
_______________ should close by the age of 2
anterior fontanelle should close by the age of 2
_____________ should close by about 3-4 months of age
posterior fontanelle should close by about 3-4 months of age
anterior fontanelle
metopic suture
frontal
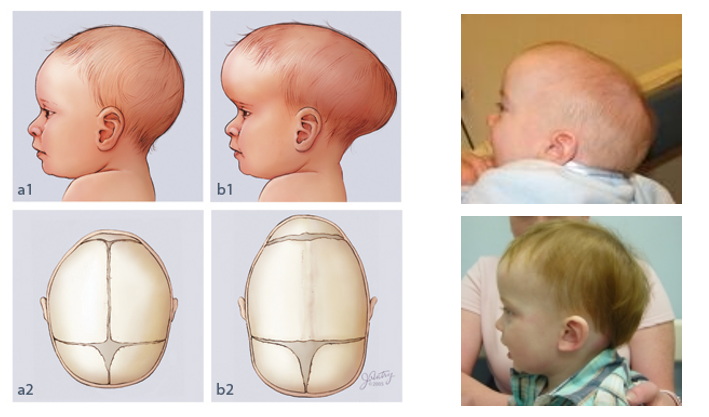
What is this condition called and what causes it?
Craniosynostosis → premature closure of cranial suture
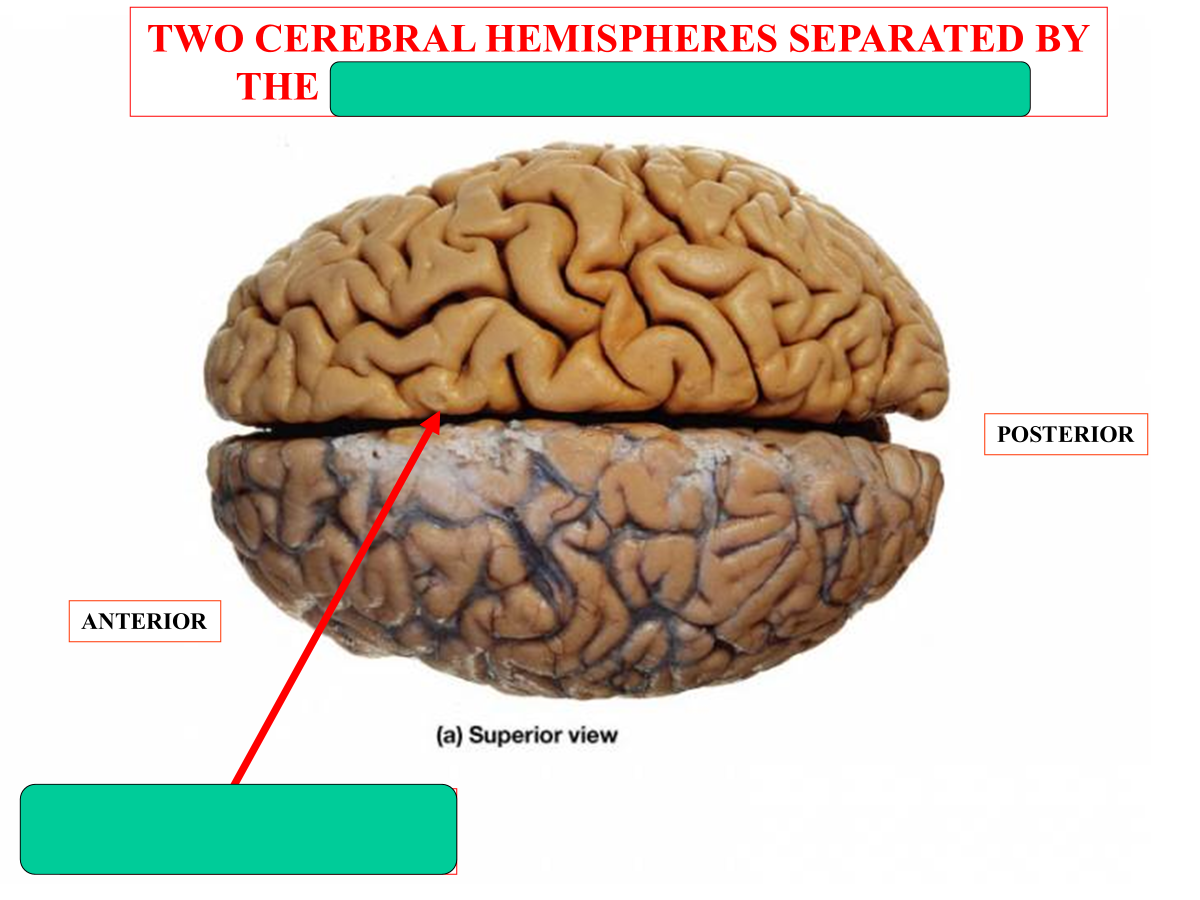
Median longitudinal fissure
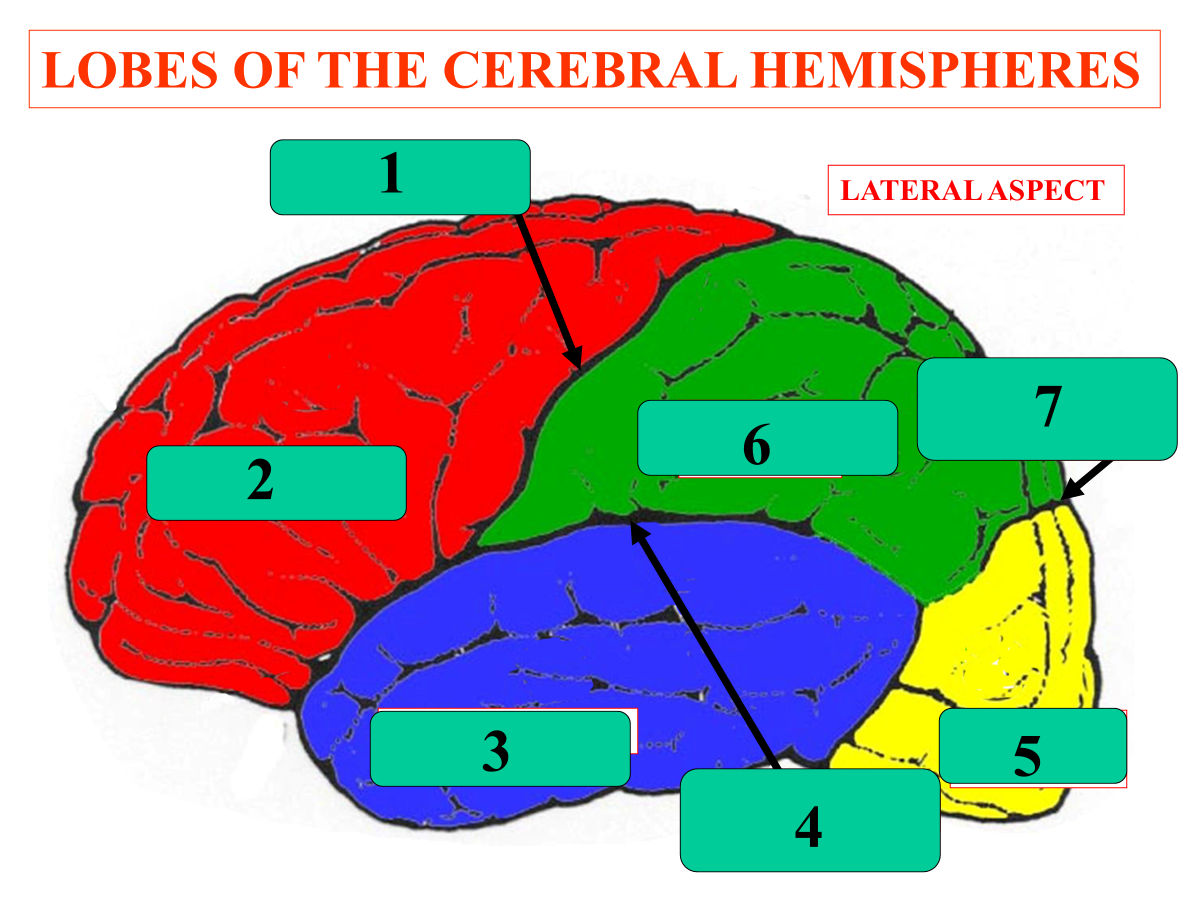
central sulcus
frontal lobe
temporal lobe
lateral sulcus
occipital lobe
parietal lobe
parieto-occipital notch
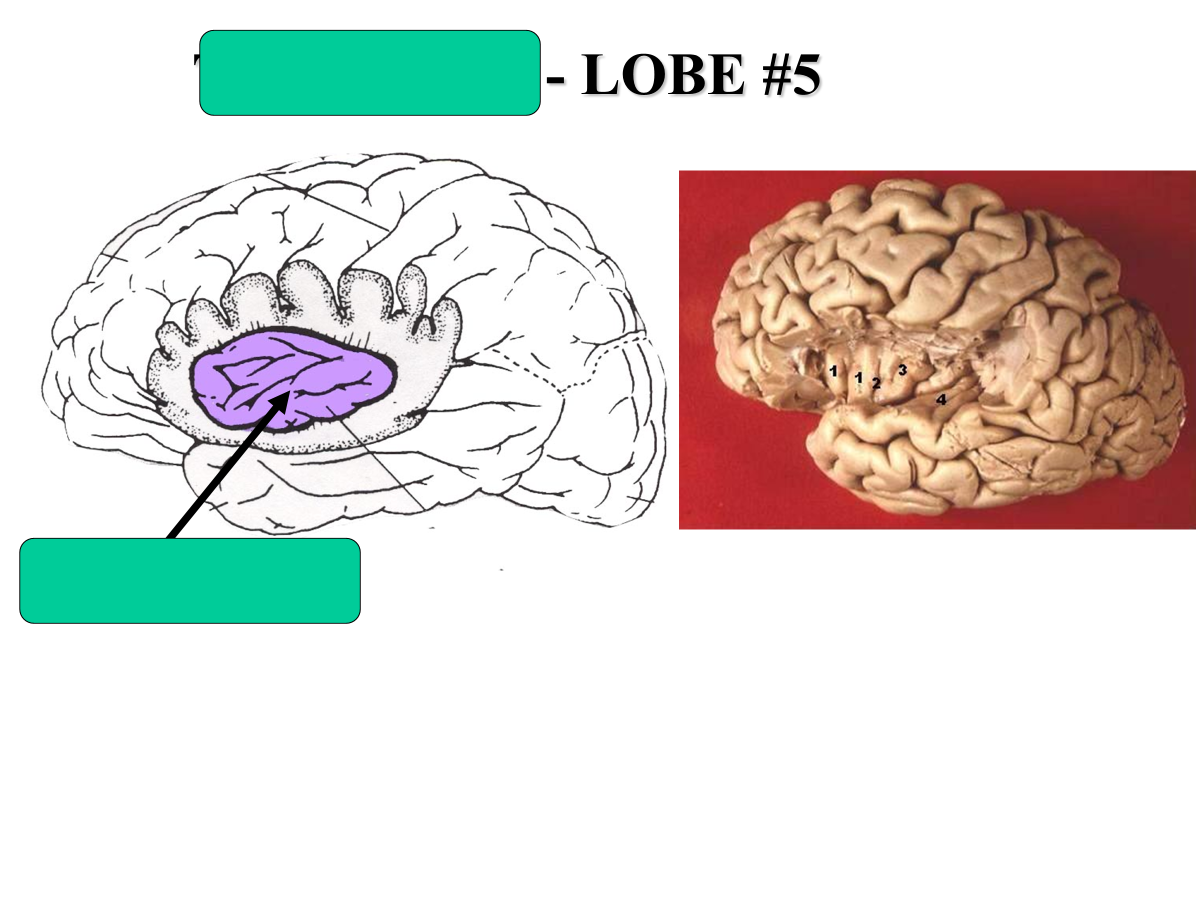
what is lobe #5 called?
insula
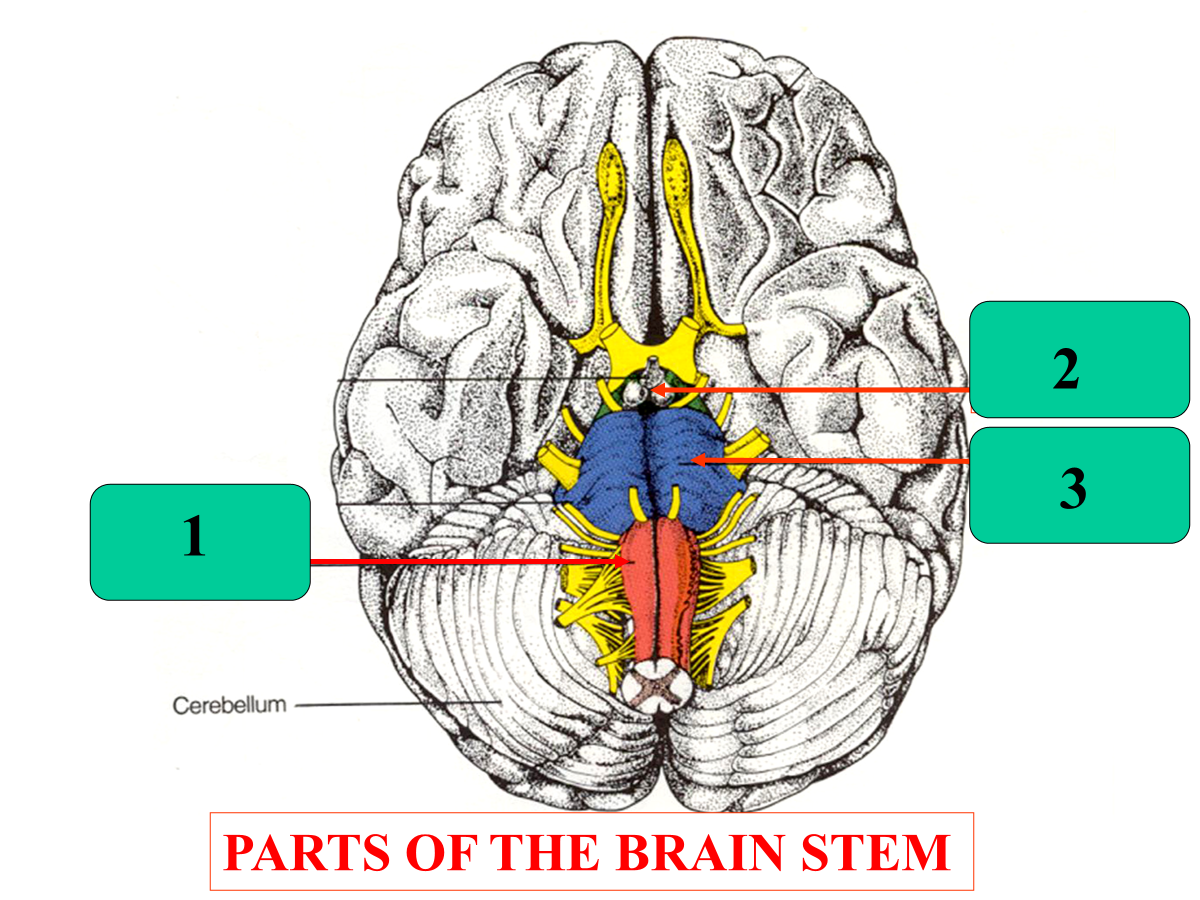
medulla
midbrain
pons
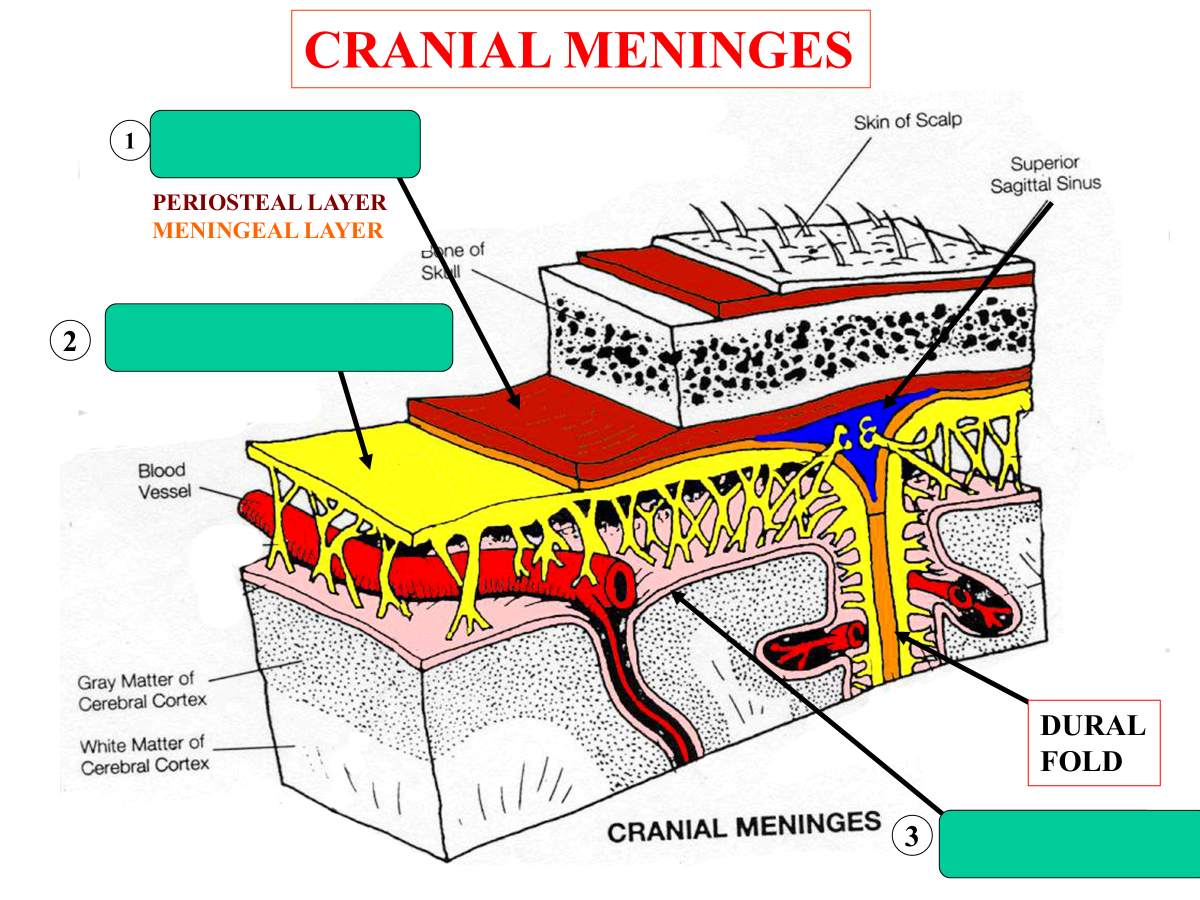
what are the three layers of protective connective tissue that cover and protect the brain
dura mater (tough outer layer)
periosteal layer
meningeal layer
arachnoid mater (middle layer)
pia mater (delicate inner layer)
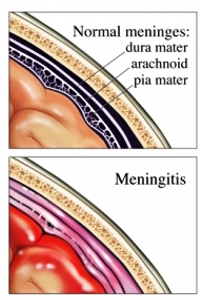
What is a bacterial infection of the meninges called?
bacterial meningitis
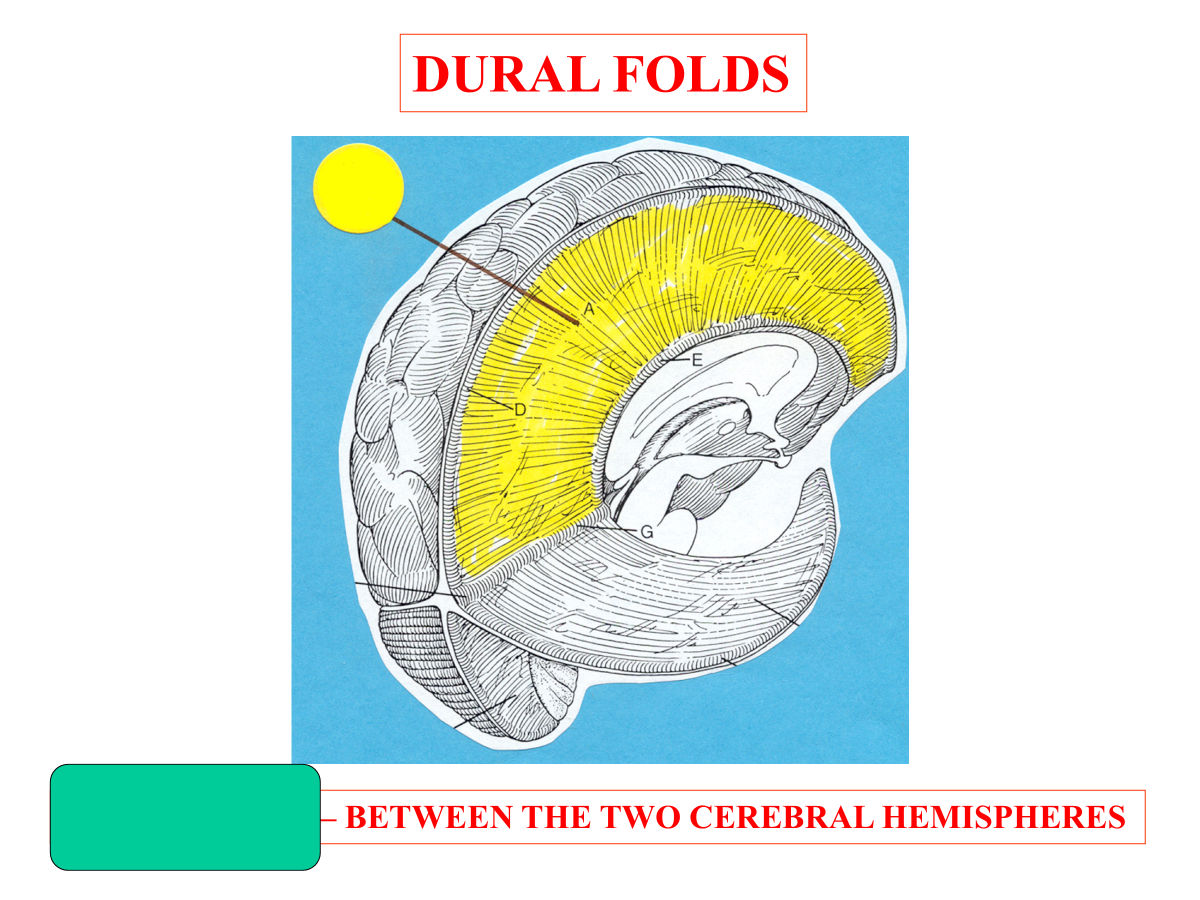
falx cerebri
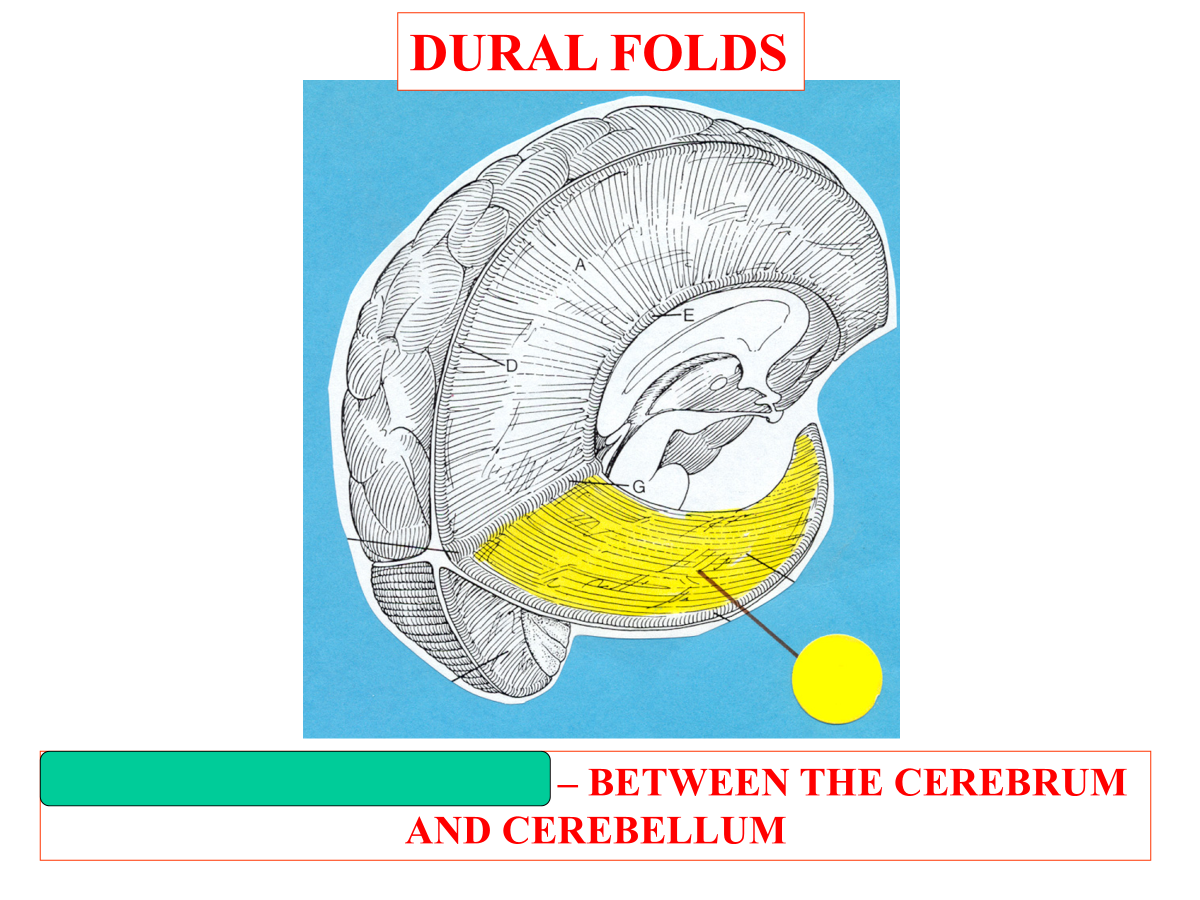
tentorium cerebelli
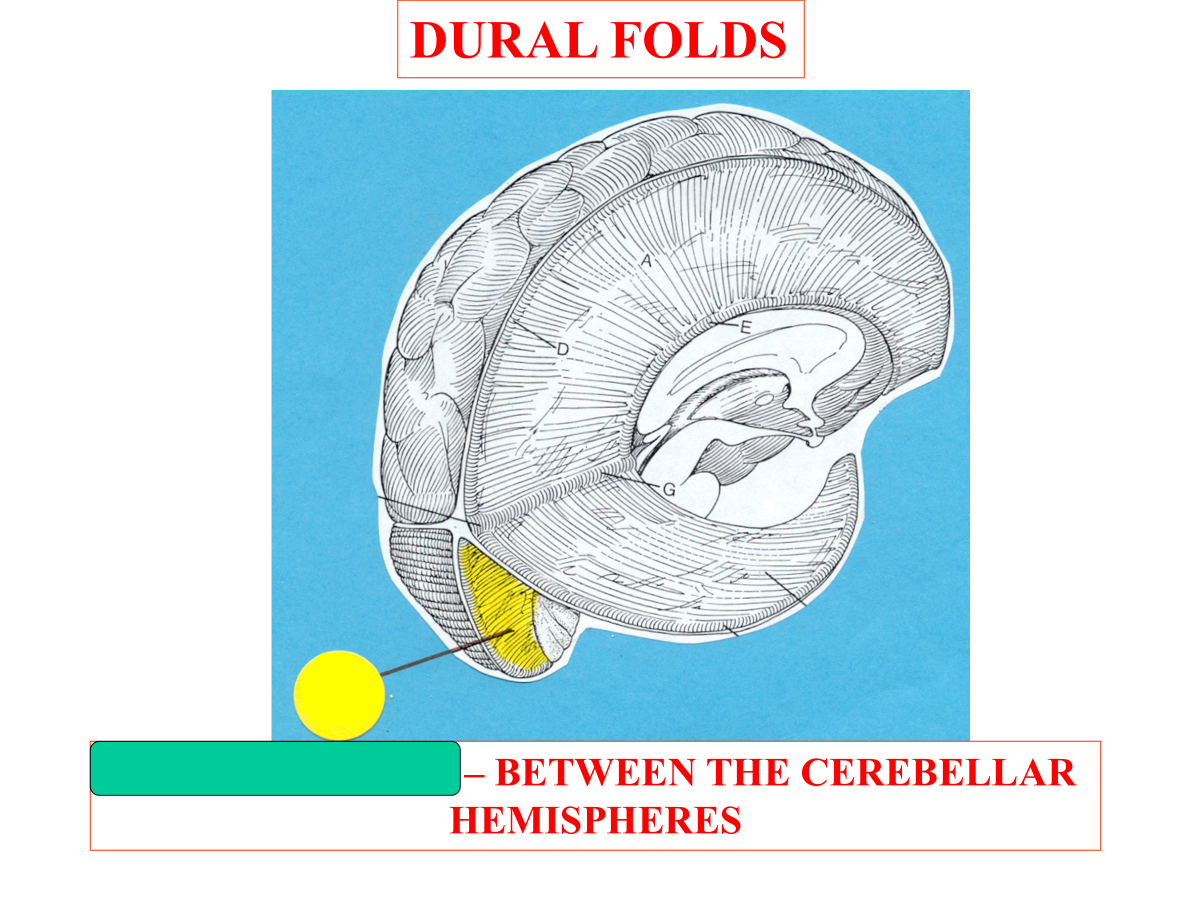
falx cerebelli
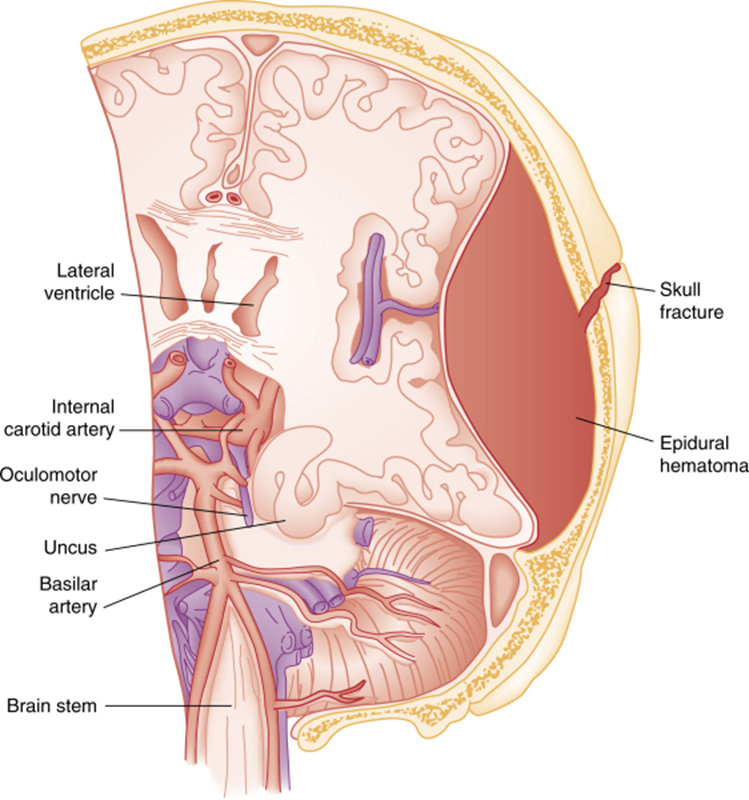
What is the accumulation of blood in epidural space?
Epidural hematoma
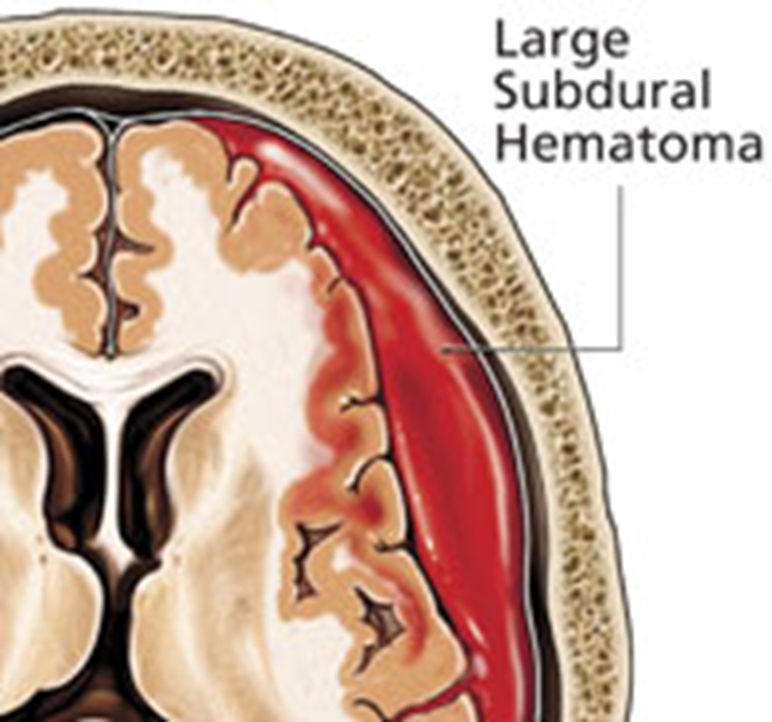
What is the accululation of blood in subdural space that frequently leads to brain damage?
subdural hematoma
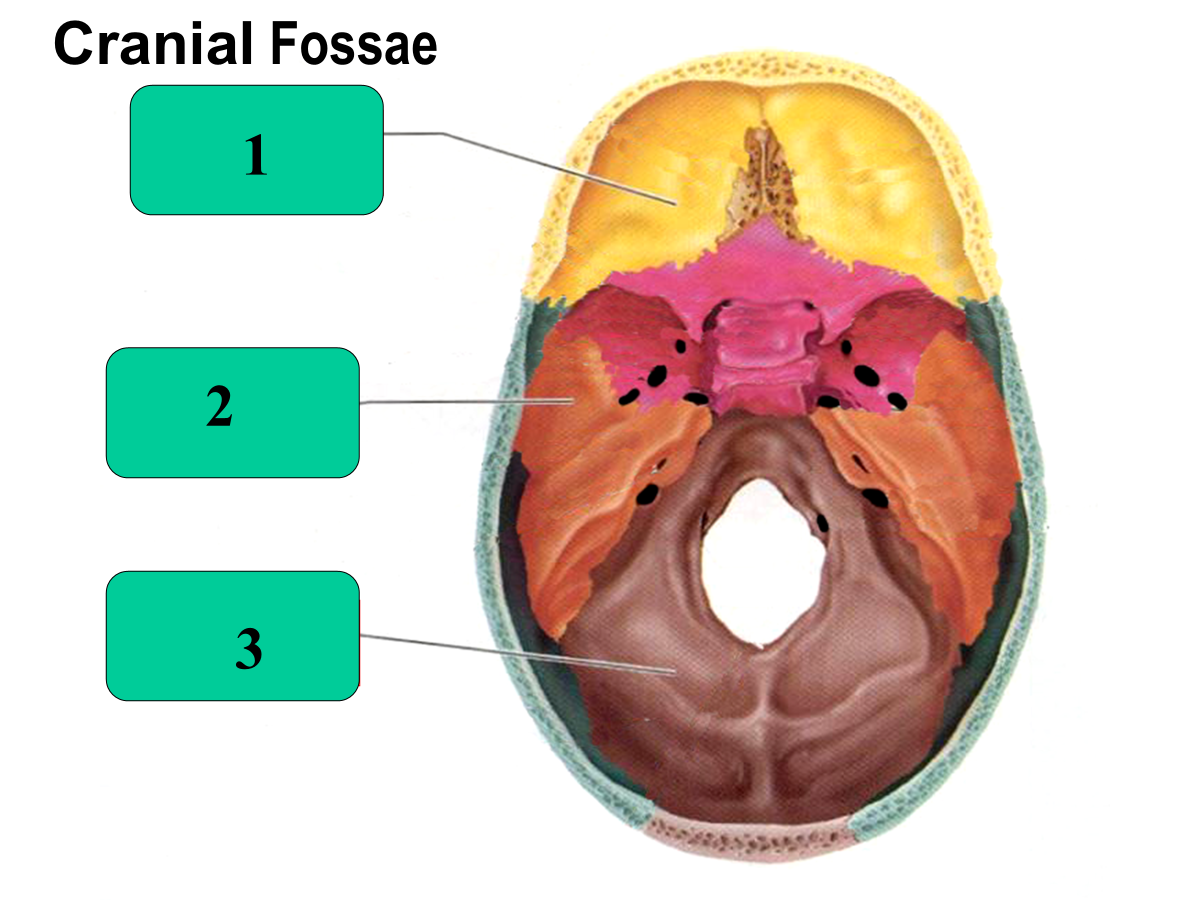
anterior cranial fossa
middle cranial fossa
posterior cranial fossa
What cranial nerves are in the anterior cranial fossa?
CN I and CN II
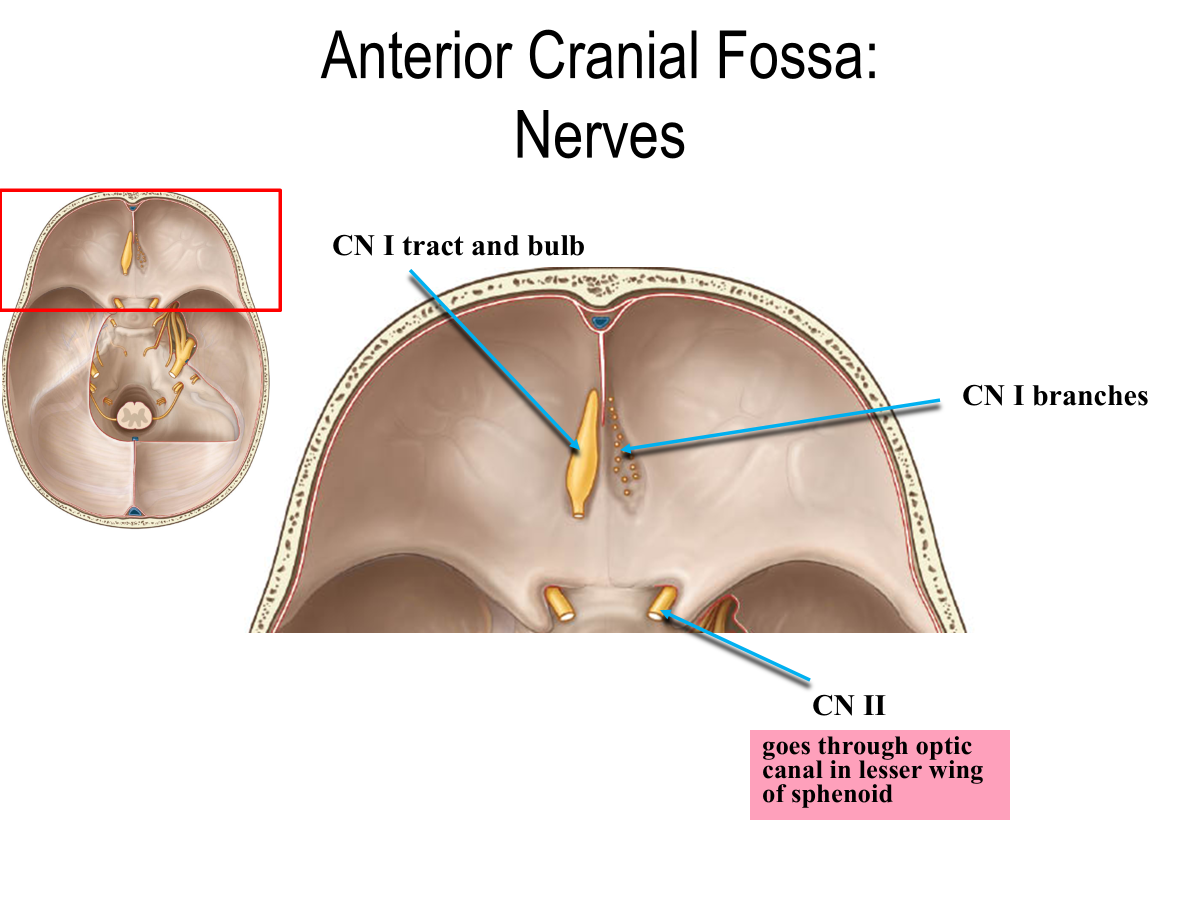
What space does CN II pass through?
Optic canal in lesser wing of sphenoid
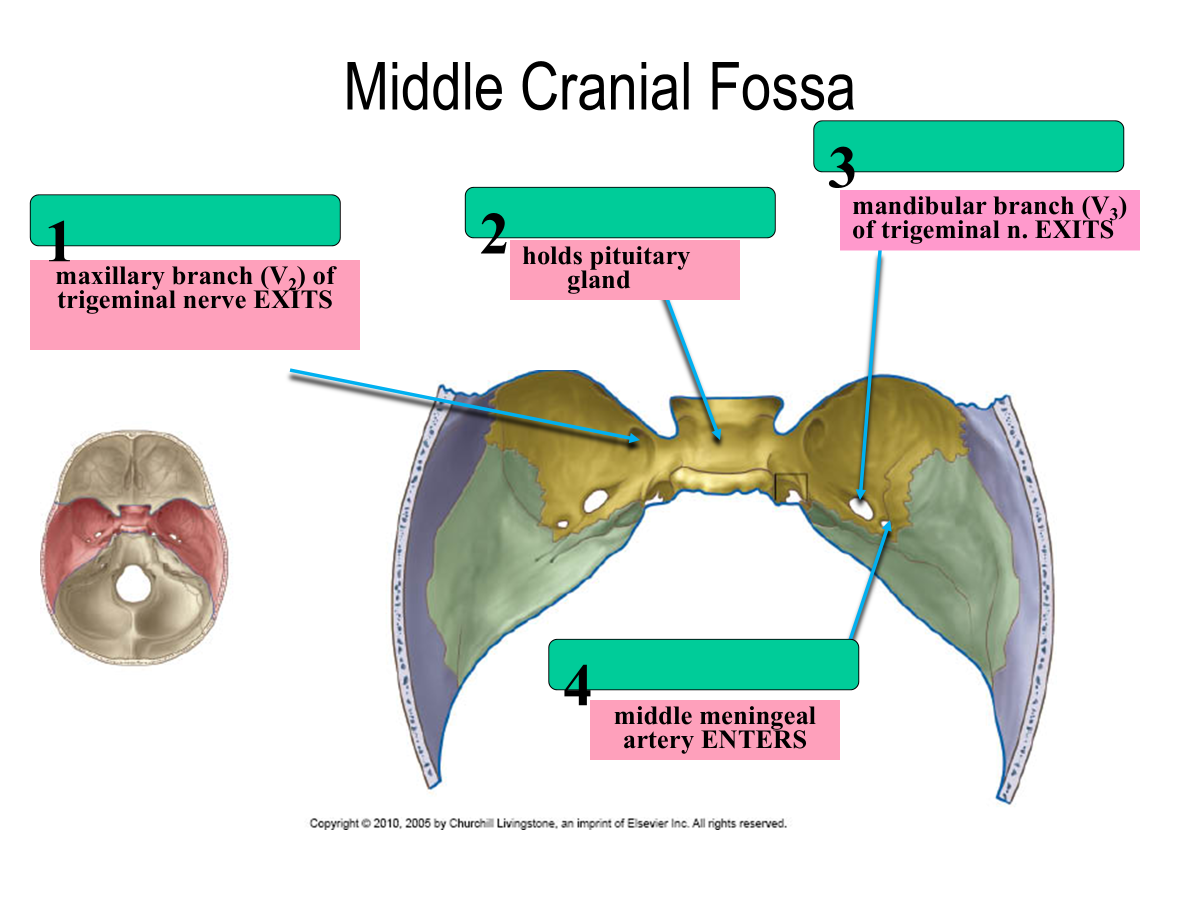
foramen rotundum
sella turcica
foramen ovale
foramen spinosum
What nerve exits the foramen rotundum?
maxillary branch (V2) of trigeminal nerve
What nerve exits the foramen ovale?
mandibular branch (V3) of trigeminal n. EXITS
What artery enters through the foramen spinosum?
middle meningeal artery
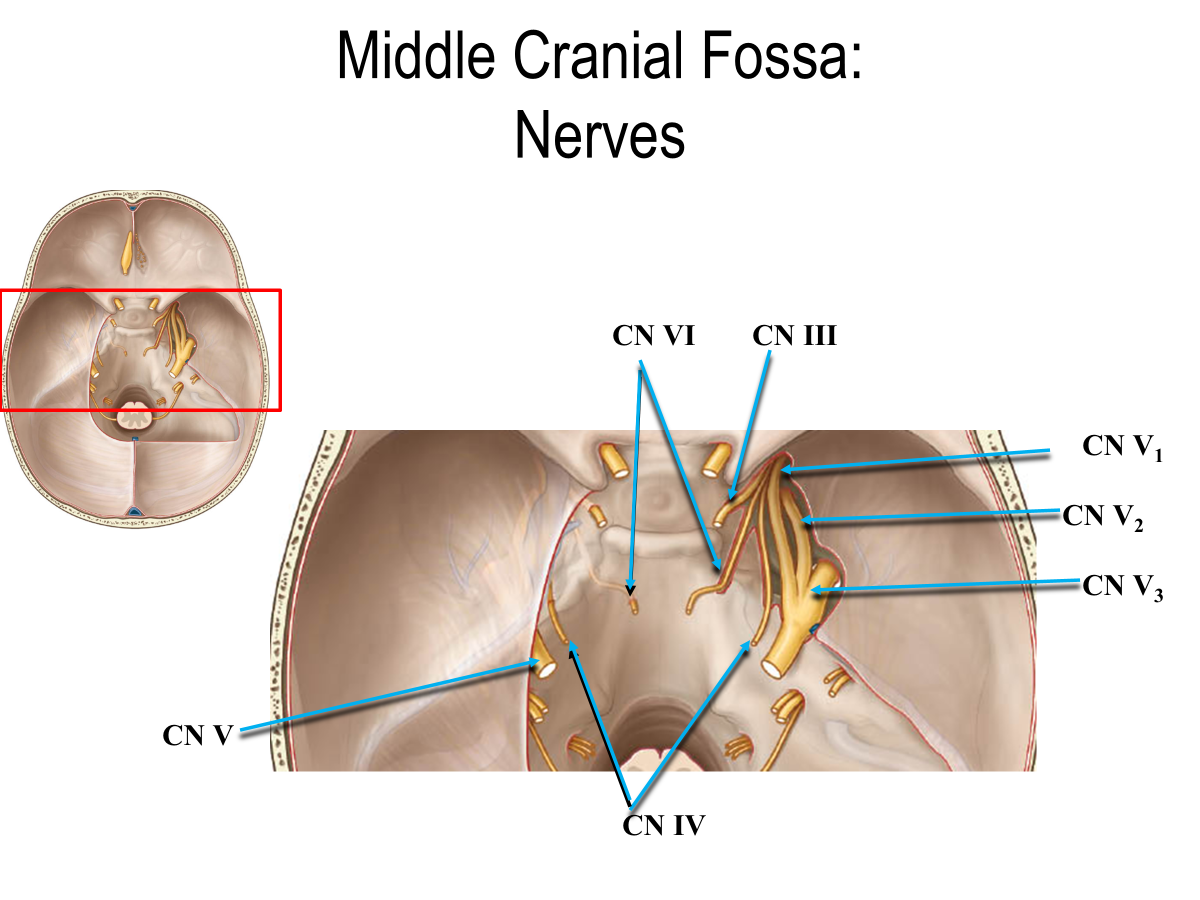
Which cranial nerves are in the middle cranial fossa?
CN III
CN IV
CN V → CN V1, CN V2, CN V3
CN VI
What is the space through which CN III, IV, V1, VI travel from middle cranial fossa into orbit?
Superior orbital fissure
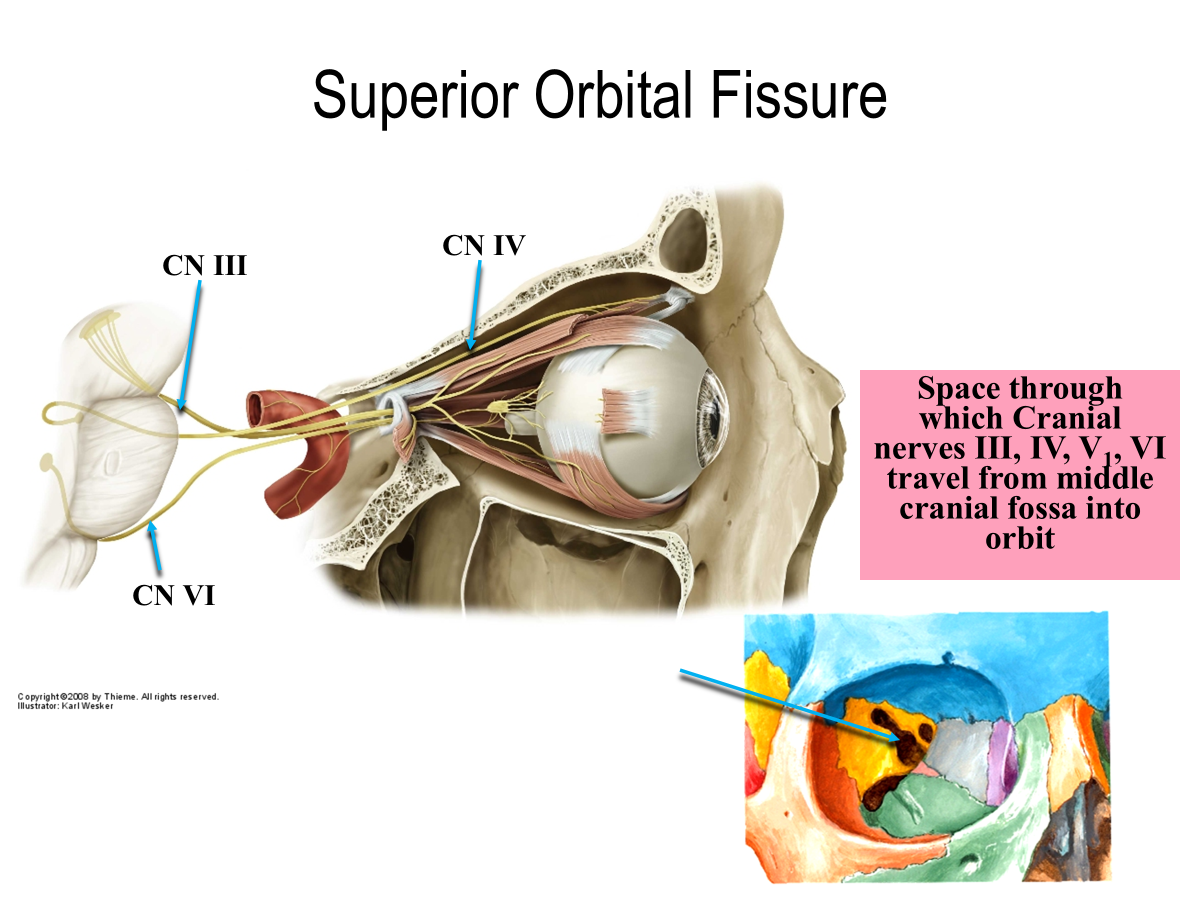

What is this space called?
Superior orbital fissure
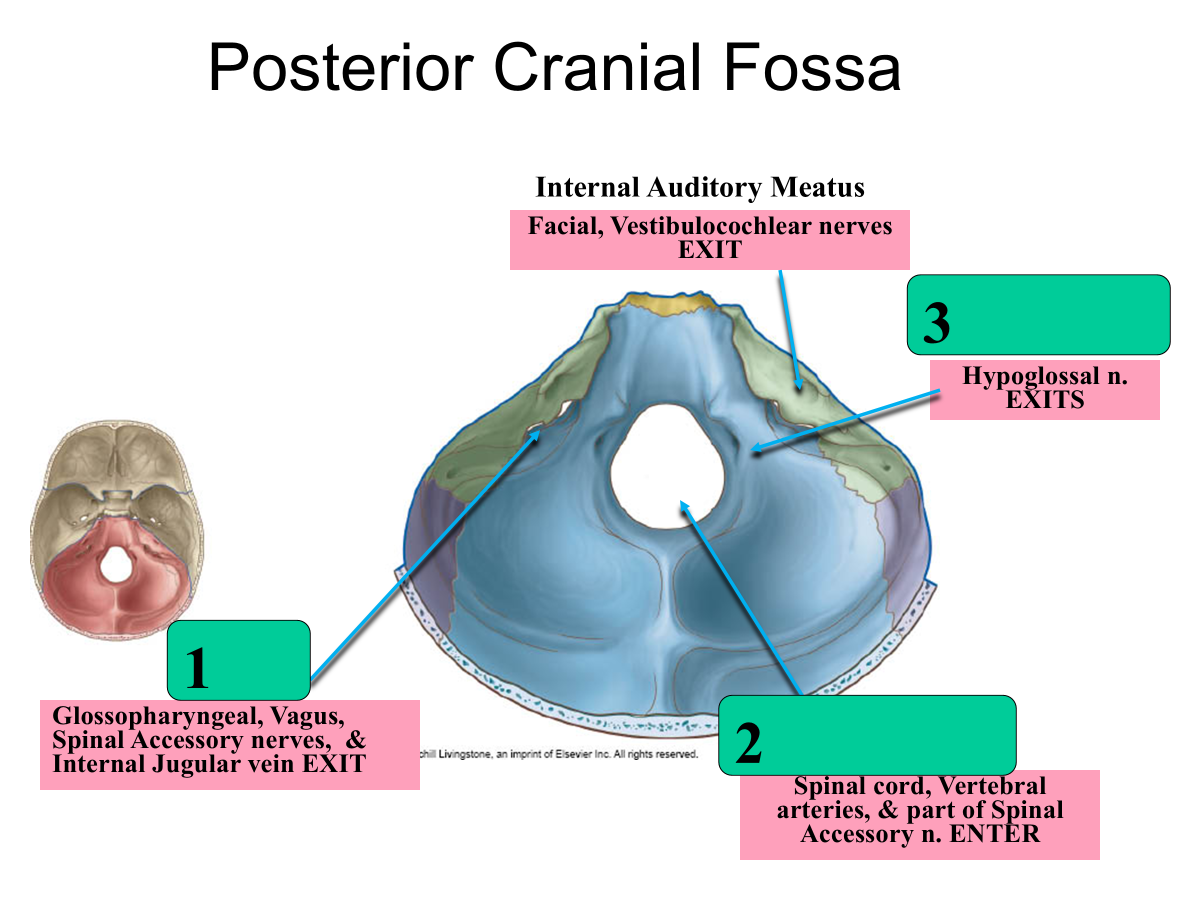
Jugular Foramen
Foramen Magnum
Hypoglossal Canal
What passes throuh the jugular foramen?
Glossopharyngeal, Vagus, Spinal Accessory nerves
Internal Jugular vein EXIT
What passes through the foramen magnum?
spinal cord
vertebral arteries
part of spinal accessory n. ENTER
What passes through the hypoglossal canal?
hypoglossal n. EXITS
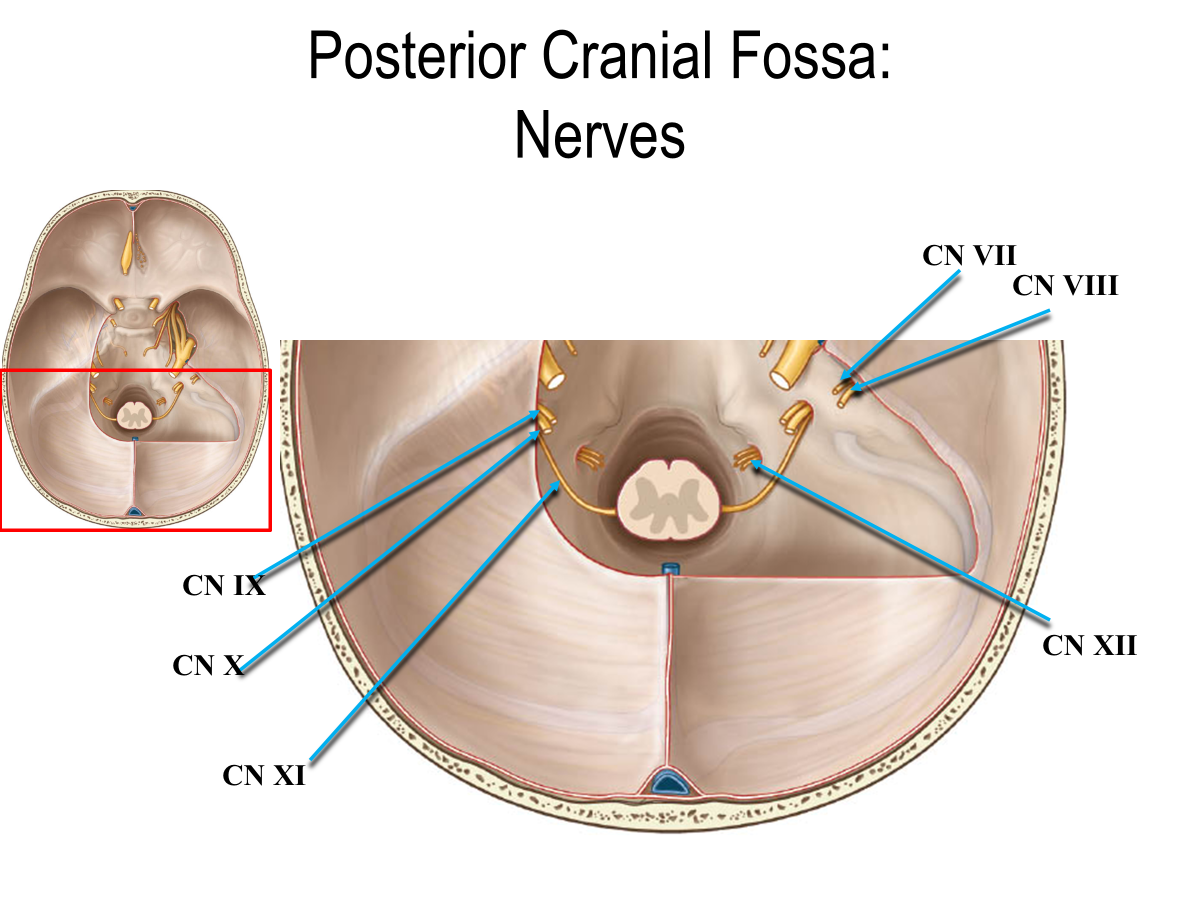
What cranial nerves are in the posterior cranial fossa?
CN VII
CN VIII
CN IX
CN X
CN XI
CN XII
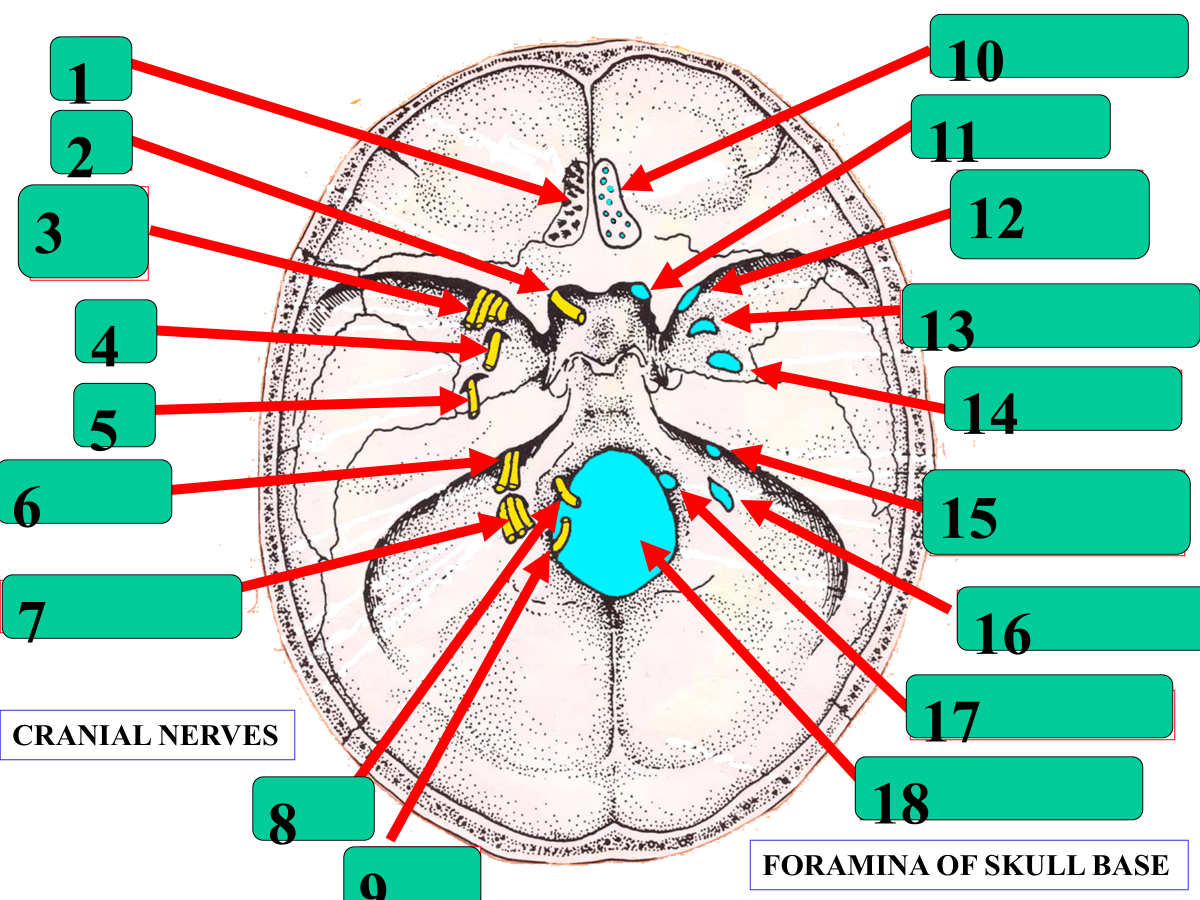
CN I
CN II
CN III, IV, VI, V1
V2
V3
CN VII, VIII
CN IX, X, XI (out)
CN XII
XI (in)
Cribriform plate
optic canal
superior orbital fissue
foramen rotundum
foramen ovale
internal auditory meatus
jugular foramen
hypoglossal canal
foramen magnum
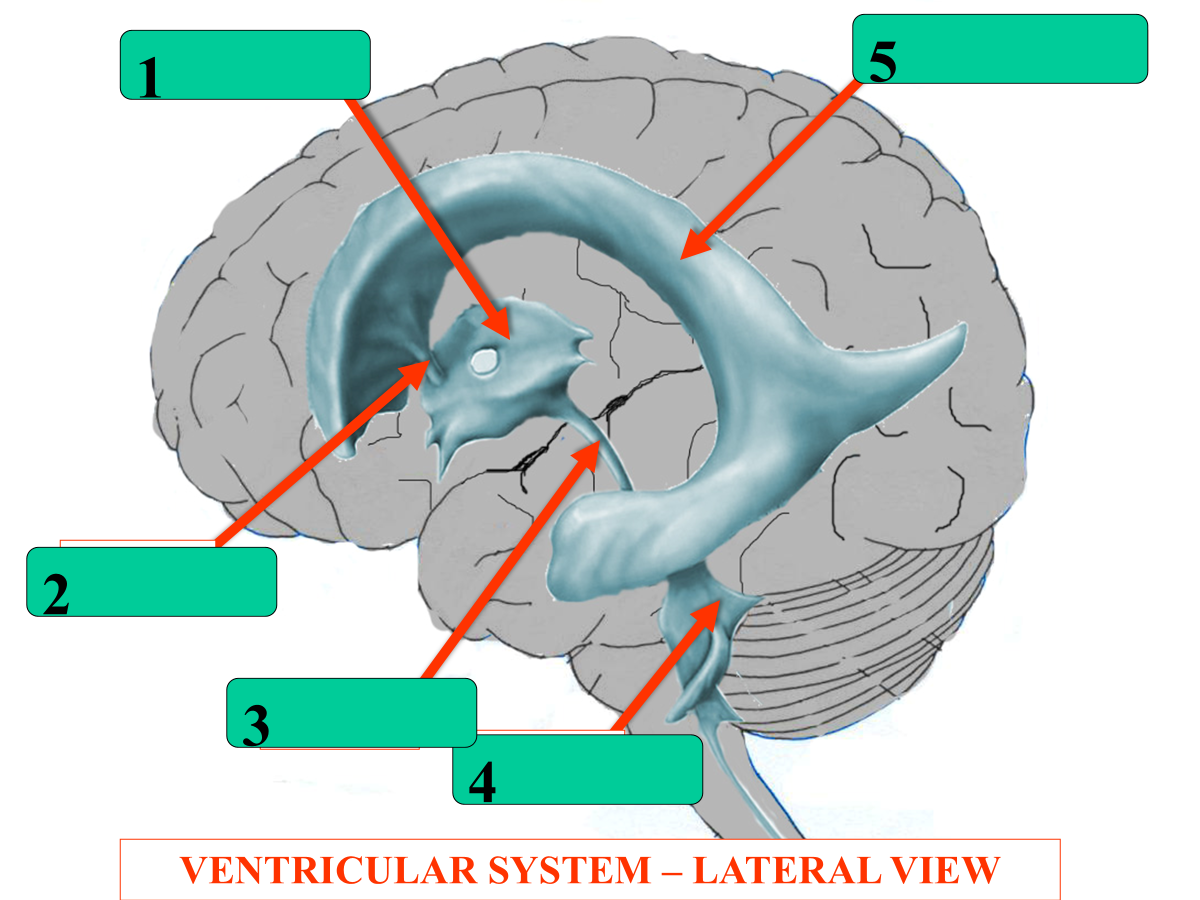
3rd ventricle
foramen of monro
cerebral aqueduct
4th ventricle
lateral ventricle
What does the choroid plexus secretes?
CSF
What is the flow of CSF through the ventricles?
Choroid Plexus (lateral)
interventricular foramen
3rd ventricle
aqueduct
4th ventricle
lateral aperture
central spinal canal
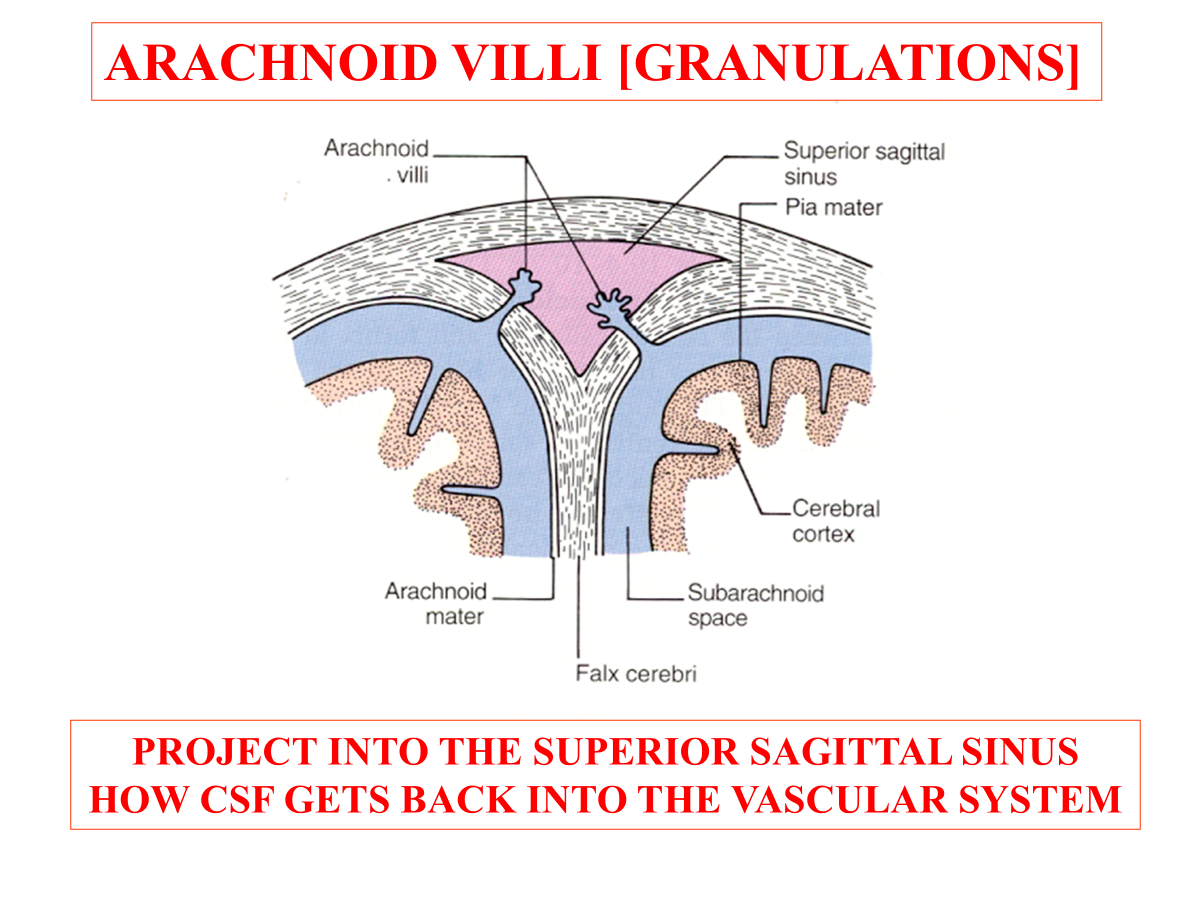
What structure is responsible for returning CSF from the brain back into the vascular system?
Arachnoid villi (granulations)
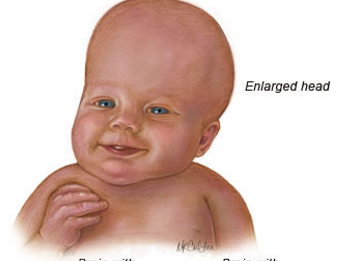
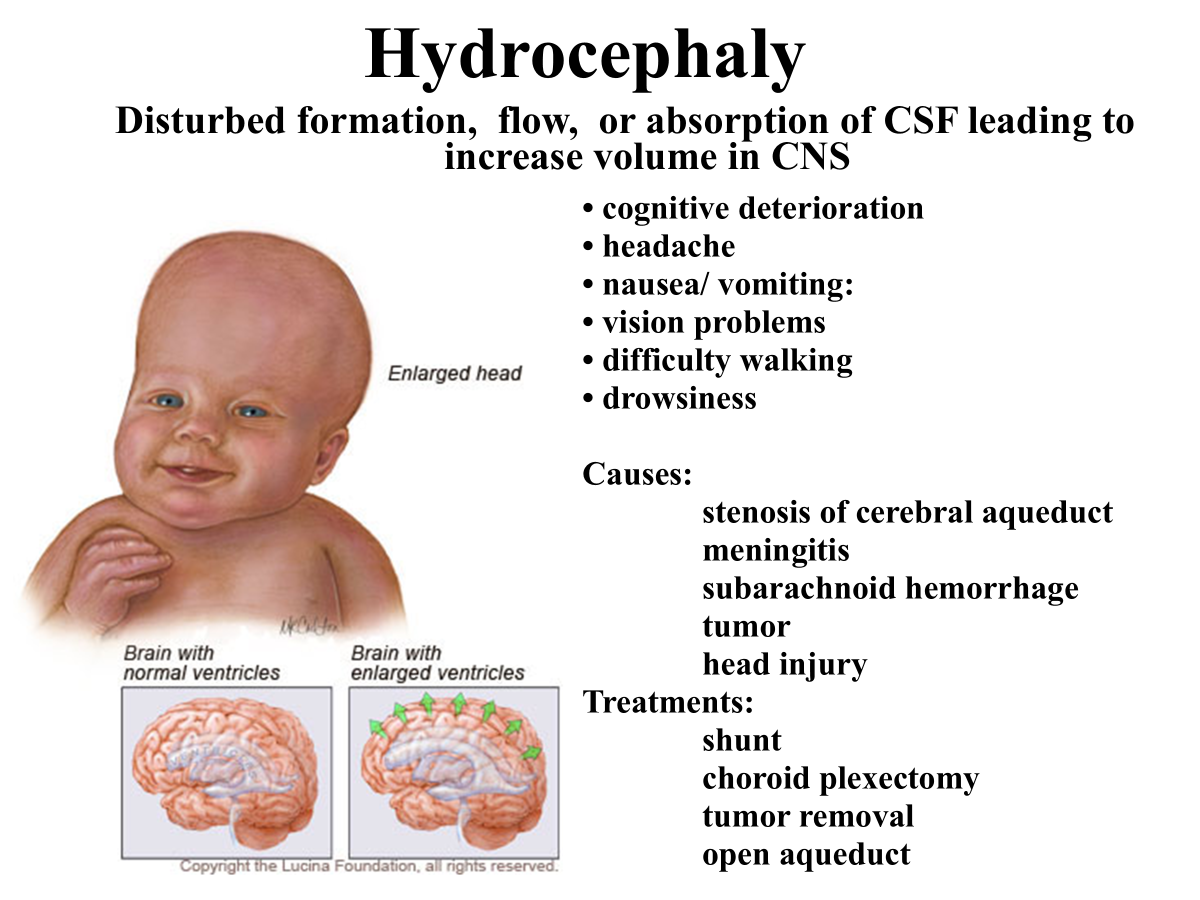
What is the condition called when there is disturbed formation, flow, or absorption of CSF leading to increase volume in CNS during childhood?
Hydrocephaly
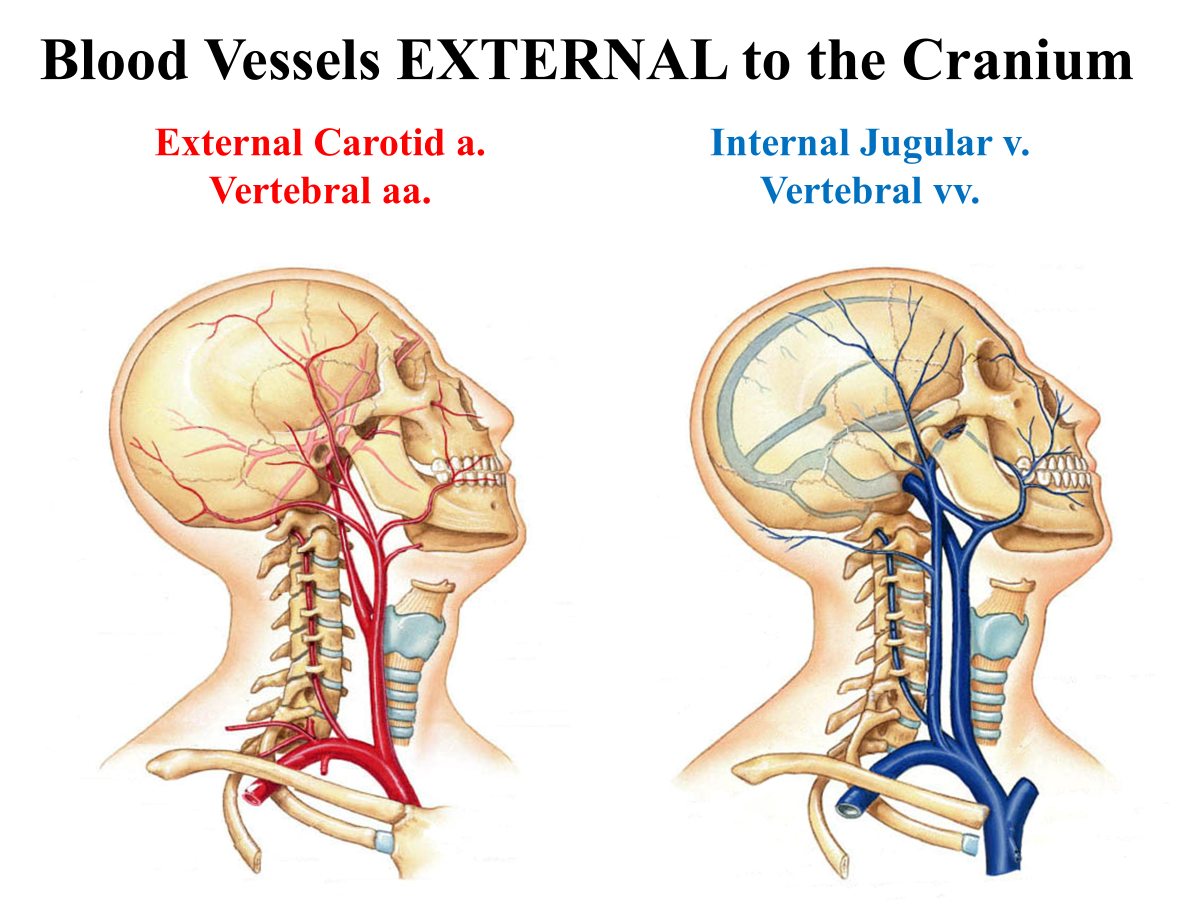
What blood vessels are external to the cranium?
External carotid a.
Vertebral aa.
Internal Jugular v.
Vetrebral vv.
What blood veseels are internal to the cranium?
internal carotid aa.
circle of willis
vertebral aa.
dural sinuses
What is a branch off the external carotid artery that supplies the dura and enters the cranium through the foramen spinosum?
middle meningeal artery
The circle of willis is an __________________, which is a circular connection of arteries located at the base of the brain
The circle of willis is an arterial anastomosis, which is a circular connection of arteries located at the base of the brain.
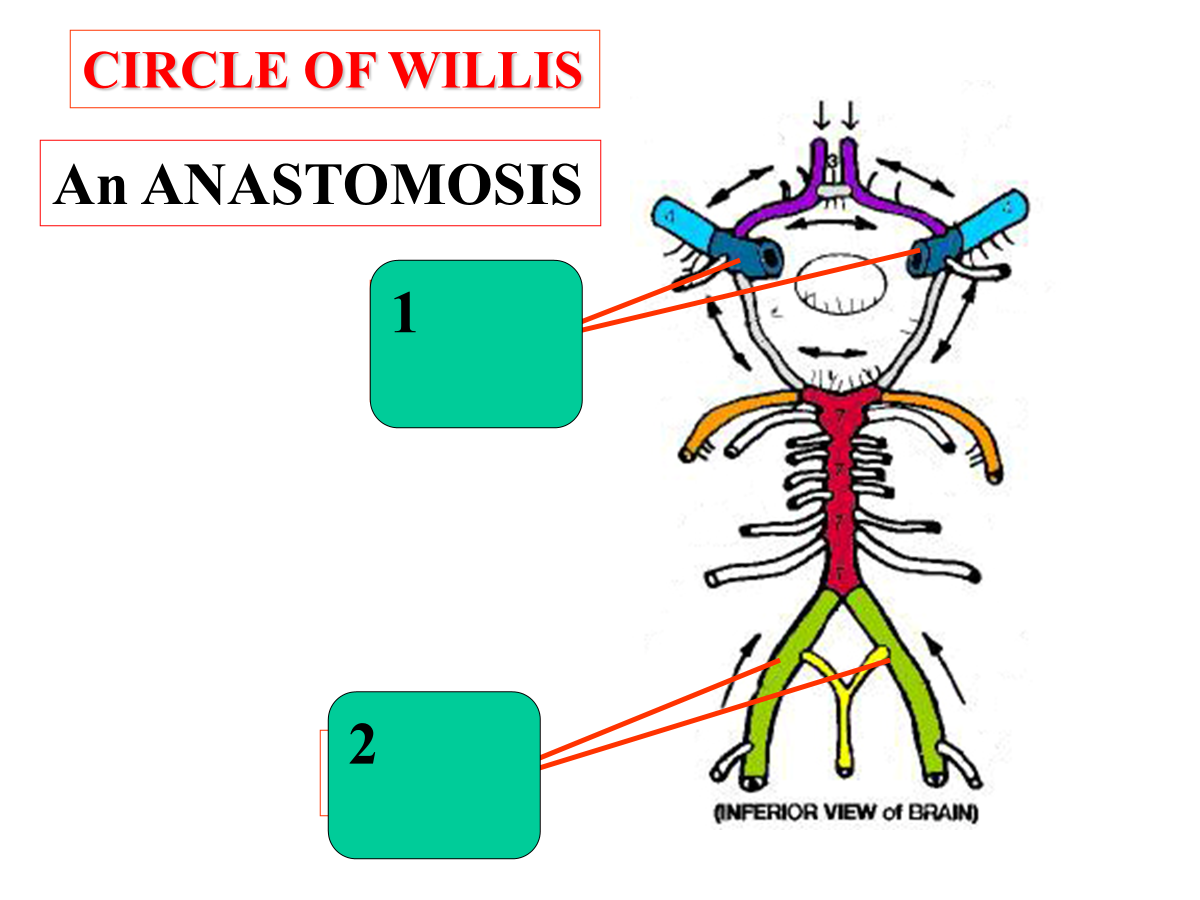
internal carotid arteries
vertebral arteries
Blood enters the circle of willis from two main pairs of arteries:
________________, which enter the skull from the front of the neck and supply most of the anterior brain
________________, which travel through cervical vertebrae, join to form the basilar artery, and supply the posterior brain
Blood enters the circle of willis from two main pairs of arteries:
Internal carotid arteries, which enter the skull from the front of the neck and supply most of the anterior brain
Vertebral Arteries, which travel through cervical vertebrae, join to form the basilar artery, and supply the posterior brain
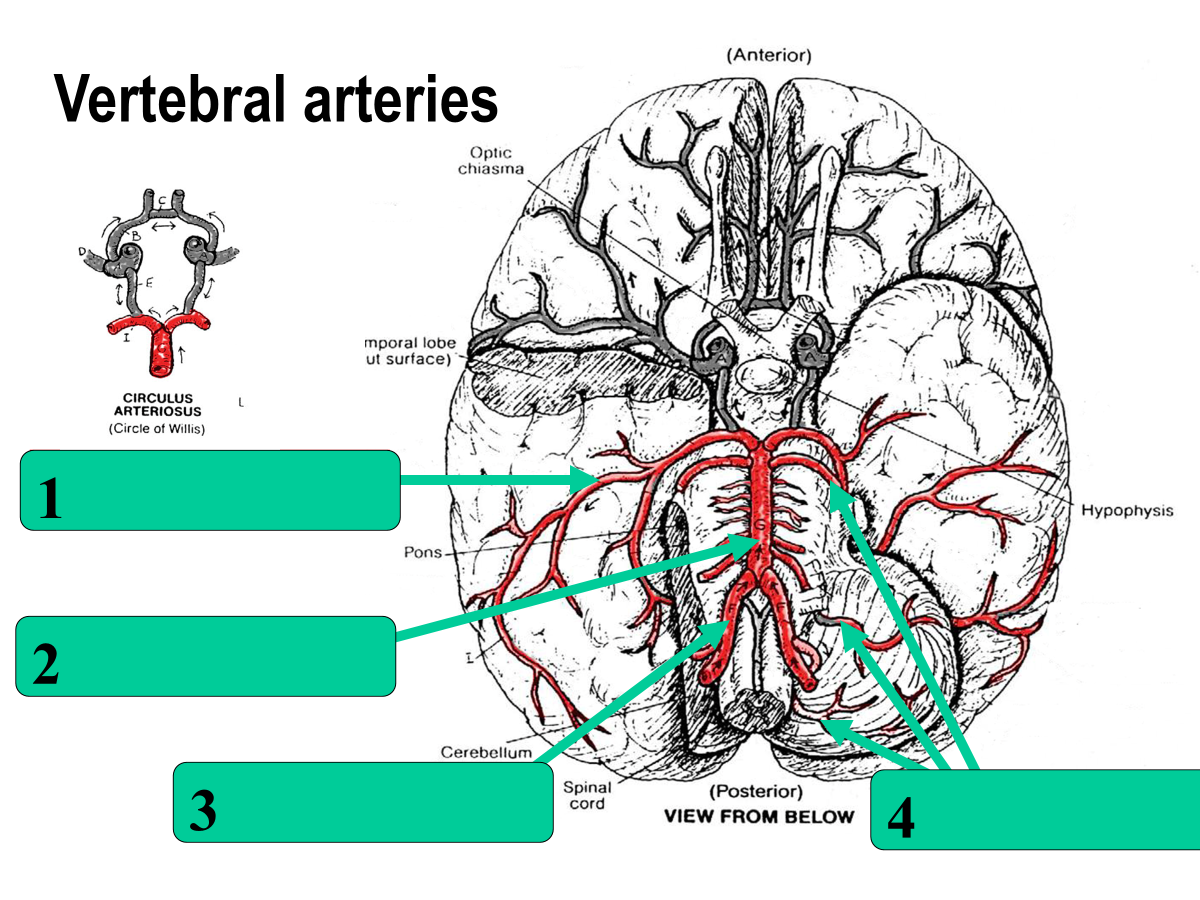
posterior cerebral
basilar
vertebral
cerebellar aa.
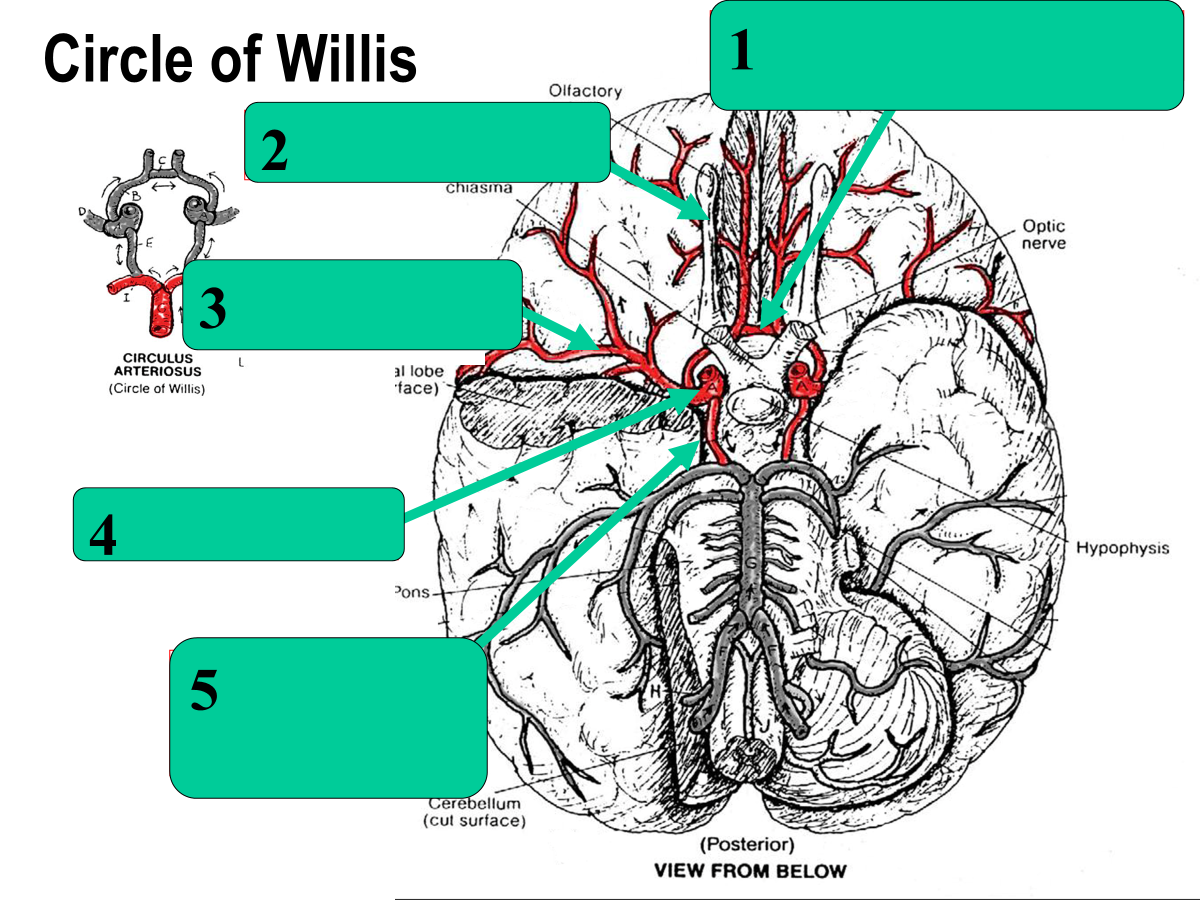
anterior communicating
anterior cerebral
middle cerebral
internal carotid
posterior communicating
What type of stroke is due to a blocked blood vessel?
Ischemic stroke
What type of stroke is due to a blood vessel bleed?
Hemorrhagic stroke
What is a bulging or ballooning of a blood vessel wall due to weakness in the vessel called?
Aneurysm (occur commonly in circle of willis)
Where does the most common stroke occur?
middle cerebral artery
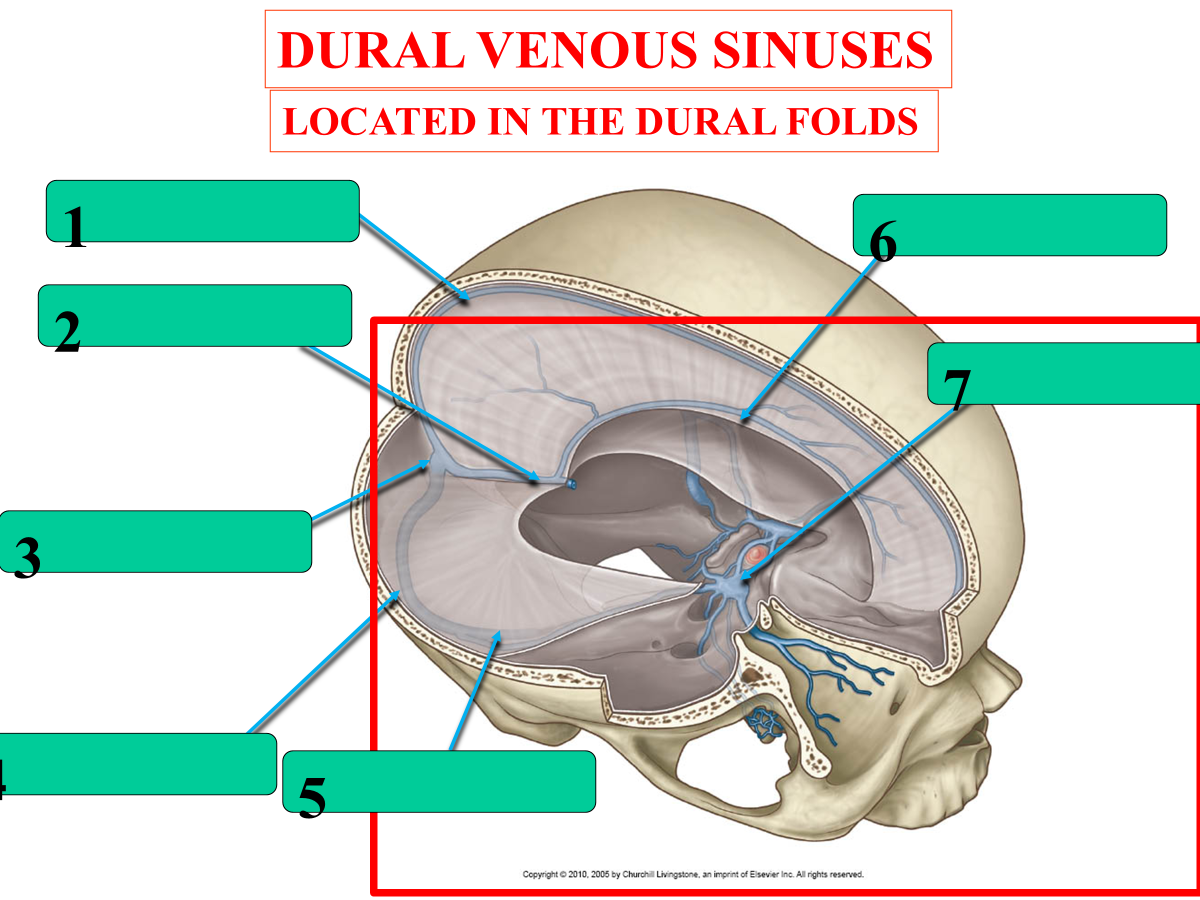
superior sagittal sinus
straight sinus
confluence of sinuses
transverse sinus
sigmoid sinus
inferior sagittal sinus
cavernous sinus
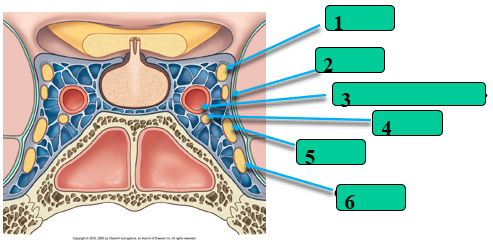
What passes through the Cavernous Sinus?
CN III
CN IV
internal carotid a.
CN VI
CN V1
CN V2