Anatomy- Axial skeleton The axial
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
the axial skeleton is divided into three parts
skull
vertebral column
bony thorax
two sets of bones form the skull
cranium bones-enclose the brain
facial bones (hold eyes in position and allow facial muscles to express feelings)
bones joined by sutures
only the mandible is attached by a freely movable joint
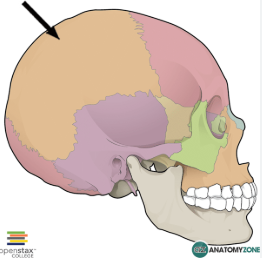
8 cranial bones protect the brain
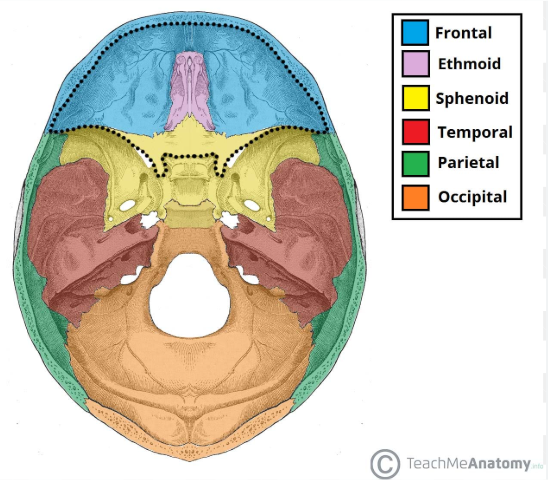
frontal bone
occipital bone
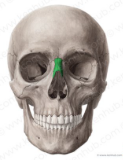
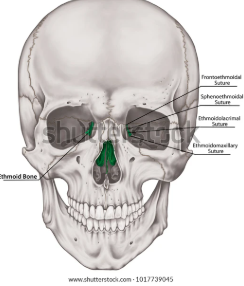
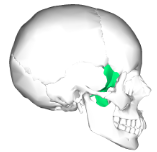
ethmoid bone
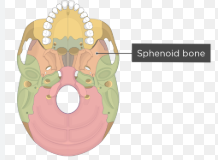
sphenoid bone
parietal bones
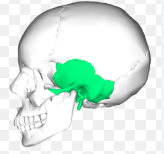
temporal bones
14 facial bones
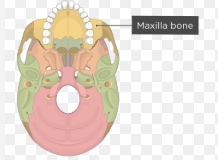
maxillae
palatine bones
lacrimal bones
zygomatic bones
nasal bones
vomer bone
inferior nasal conchae
mandible
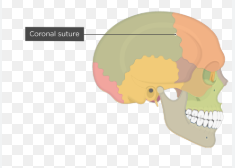
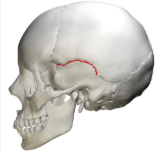
coronal suture
parietal bone
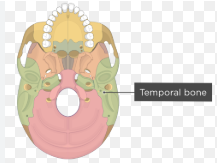
temporal bone
Lambdoid suture
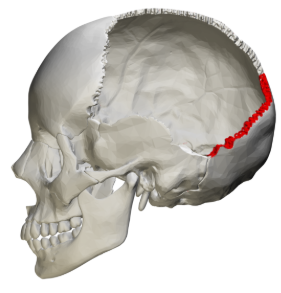
squamous suture
occipital bone
zygomatic process
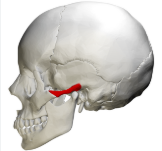
external acoustic meatus
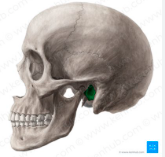
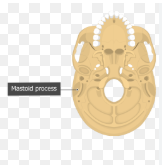
mastoid process
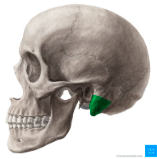
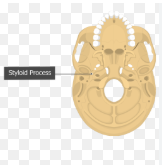
styloid process
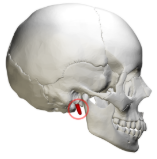
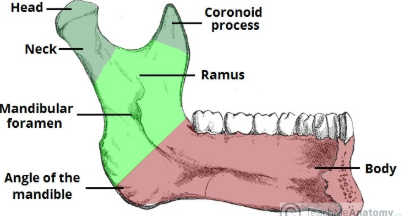
mandibular ramus
mental foramen
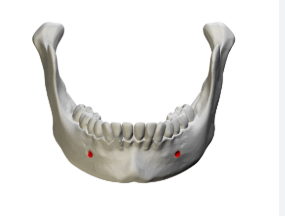
mandible
alveolar process
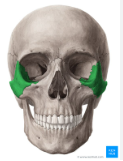
zygomatic bone
nasal bone
lacrimal bone
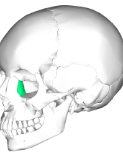
ethmoid bone
sphenoid bone
frontal bone

frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, temporal, parital, occipital (coronal base)
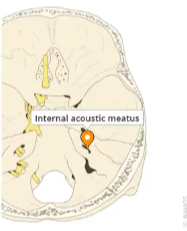
internal acoustic meatus
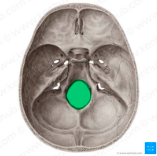
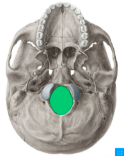
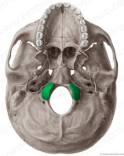
foramen magnum
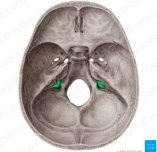
jugular foramen
foramen ovale
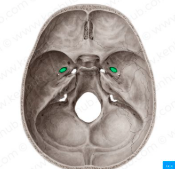
sella turcica
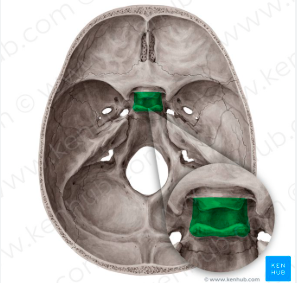
optic canal
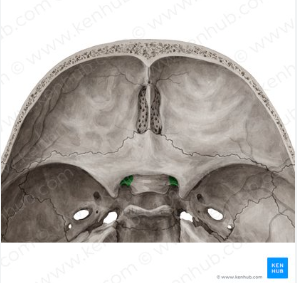
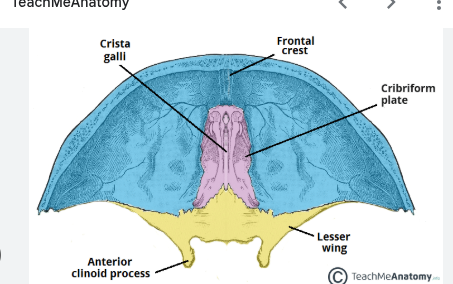
cribriform plate and crista galli
maxilla (palatine process)
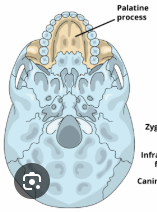
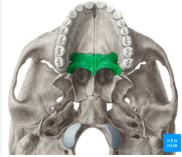
palatine bone (inferior)
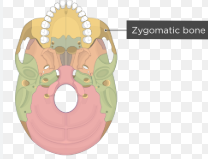
zygomatic bone (inferior)
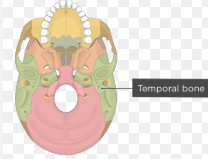
temporal bone ( zygomatic process) inferior
vomer (inferior)

mandibular process (inferior)
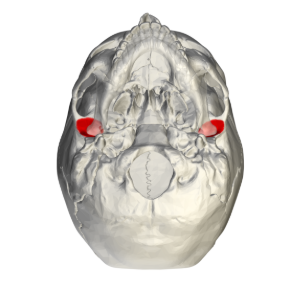
styloid process inferior
mastoid process inferior
temporal bone inferior
parietal bone inferior
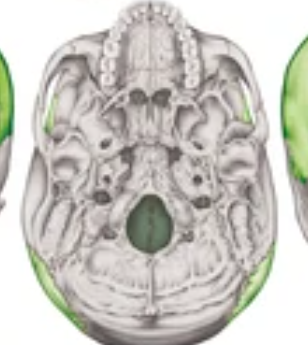
occipital bone inferior
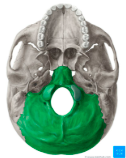
foramen magnum inferior
occipital condyle inferior
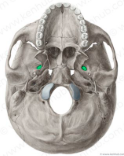
jugular foramen inferior

carotid canal
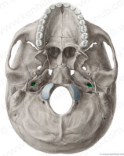
foramen ovale inferior
sphenoid bone (greater wing)
maxilla inferior
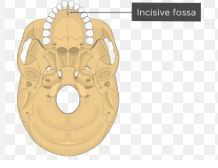
incisive fossa
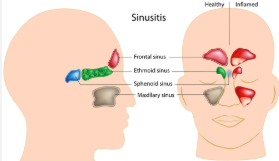
paranasal sinuses
hollow portions of bone surrounding the nasal cavity
functions of paranasal sinuses
lighten the skull
amplify sounds made as we speak
sinus locations (FESM)
hyoid bone
closely related to mandible and temporal bone
the only bone that does not articulate with other bone
serves as a movable base for tongue
aids in swallowing and speech
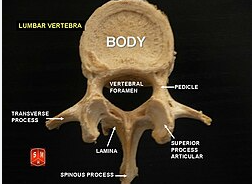
vertebral column provides
axial support (extends for skull to pelvis)
how many vertebral discs
26 and they are separated by intervertebral discs
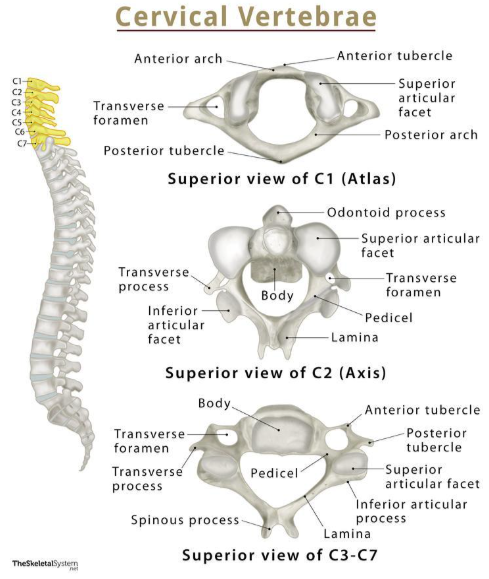
how many cervical vertebrae
7
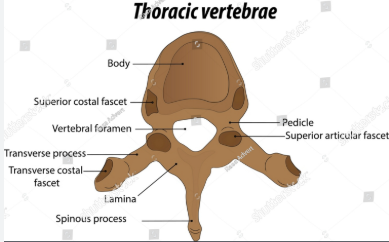
how many thoracic vertebrae
12
how many lumbar vertebrae
5
primary curvatures of the spine
spinal curvatures of the thoracic and sacral regions
present from birth
form a c-shape in newborns
secondary curvatures of spine
spinal curvatures of the cervical and lumbar regions
developed after birth
form an s-shaped curvature in adults
atlas and axis vertebrae
thoracic vertebrae
lumbar vertebrae
thoracic cavity

bones of the shoulder girdle
also called pectoral girdle
two bones attach the upper limb to the axial skeletal (Clavicle and scapula)
light, poorly reinforced girdle
allows the upper limb exceptional flexibility
acromion of scapula
coracoid process
acromioclavicular joint
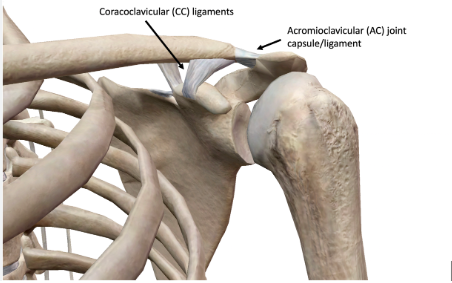
sternoclavicular joint
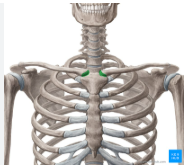
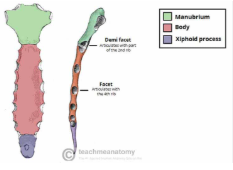
manubrium of sternum and xiphoid process
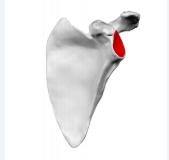
glenoid cavity
superior angle of scapula
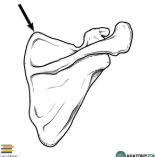
spine of scapula
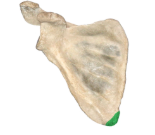
inferior angle of scapula
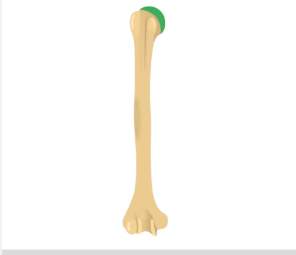
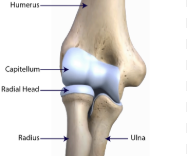
head of humerus
capitulum
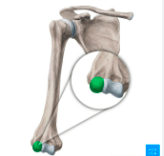
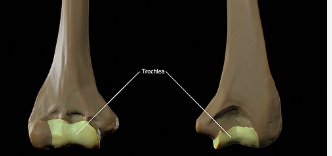
trochlea
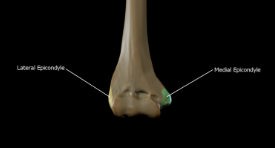
medial epicondyle and lateral epicondyle
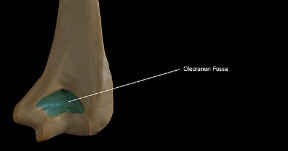
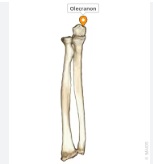
olecranon fossa
head of radius
radial styloid process
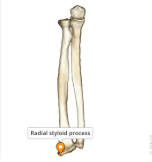
ulnar styloid process
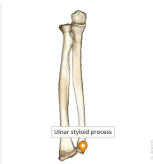
olecranon of ulna
carpals of hand

ilium, pubis, ischium
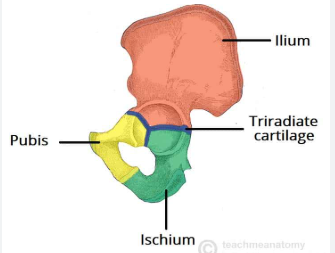
sacrum and coccyx
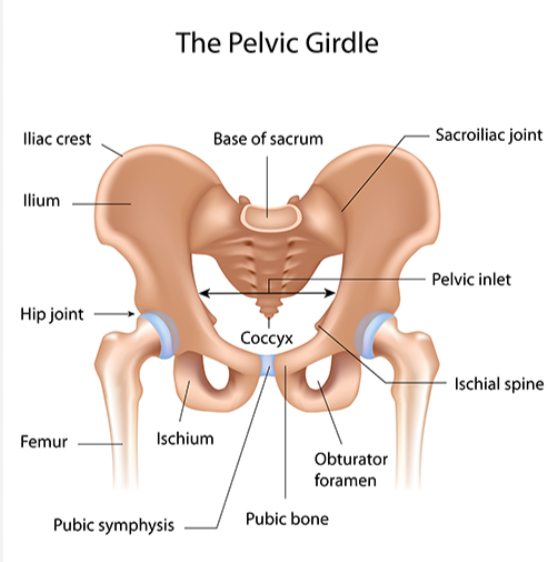
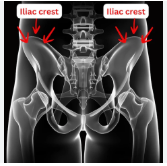
iliac crest
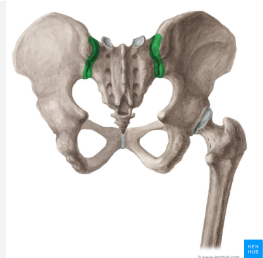
sacroiliac joint
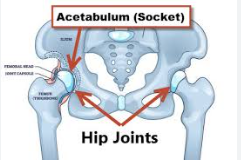
acetabulum
pubic symphysis
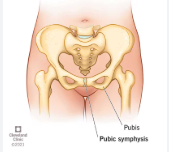
obturator foramen
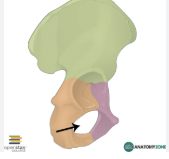
pubic arch
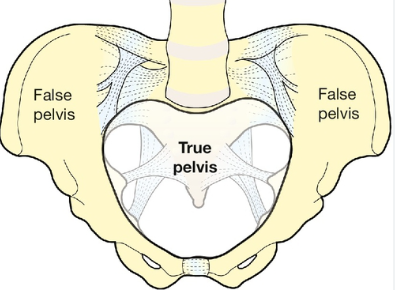
false pelvis and true pelvis
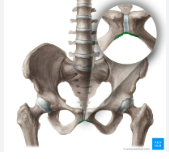
head of femur

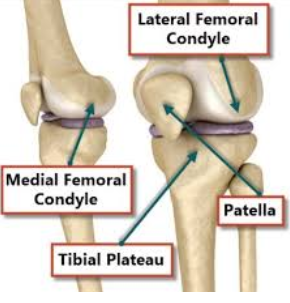
lateral and medial condyle
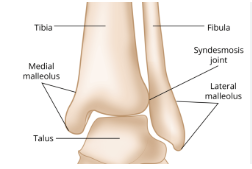
lateral and medial malleolus
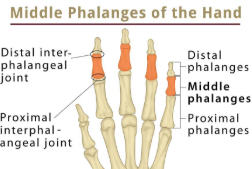
distal, middle, proximal phalanges
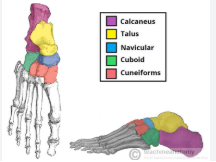
tarsals labeled