Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Pathology
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
174 Terms
Describe the Lobular Model of Liver Anatomy
-hexagonal
-terminal hepatic vein at the center
-portal tracts at the periphery
Describe the Acinus Model of Liver Anatomy
3 defined zones
-zone 1 --> closet to the blood supply
-zone 2--> furtherest from the blood supply
What are the clinical syndromes of the liver?
-hepatic failure
-cholestasis & jaundice
-cirrohis
-portal hypertension
what is the most severe form of liver disease?
liver failure (hepatic failure)
chronic liver disease
widespread necrosis from severe damage of hepatocytes caused by years of progressive liver injury
most common cause of liver failure
associated with fibrosis/cirrhosis
What is the most common cause of liver failure?
chronic liver disease
acute liver disease
less common form of liver disease but more deadly (80% mortality)
*leads to organ failure, respiratory distress syndrome, acute renal failure, & cirrhosis
What can acute liver disease lead to?
-organ failure
-respiratory distress syndrome
-acute renal failure
-cirrhosis
How much of the functional capacity of the liver most be lost for the liver disease to be considered liver failure?
80-90%
Chronic Liver Failure
diffuse remodeling into parenchymal nodules surrounded by fibrous bands & vascular shunting ==> most often associated with advanced fibrosis/cirrhosis
*Leading causes:
-chronic Hep B
-chronic Hep C
-nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFD)
-alcoholic liver disease
Which clinical syndrome of the liver is most often associated with advanced fibrosis/cirrhosis?
chronic liver failure
What are the leading causes of chronic liver failure?
-chronic Hep B
-chronic Hep C
-Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
-alcoholic liver disease
acute liver failure
liver disease that is usually associated with massive heaptic necrosis
-50% of adult cases in the US are from ingestion of acetaminophen
-autoimmune hepatitis, other drugs/toxins, & acute hep A and B infections account for most of the remaining cases
How does acute hepatic failure appear clinically?
1st manifests with nausea, vomiting, & jaundice --> then encephalopathy & coagulation defects + initial swelling as parenchyma is destroyed the liver shrinks -->>> multisystem organ failure occurs --> patients dies (if no liver transplant)
how does chronic hepatic failure appear clinically?
-asymptomatic until advanced stages
-nonspecific symptoms --> anorexia, wt loss, weakness
-displays signs similar to acute failure --> encephalopathy, coagulopathy, & jaundice
bilirubin
toxic end product of heme degradation that is processed by the liver & excreted in bile
cholestasis
retention of bilirubin in response to injured or dysfunctional hepatocytes
-potentially reversible
-may manifest as jaundice & icterus**
What may cholestasis manifest as?
-jaundice --> yellow discoloration of the skin
-icterus --> yellow discoloration of the sclera of the eye
*due to retention of bilirubin
What are the normal adult serum bilirubin levels?
0.3 - 1.2 mg/dL
At what range of serum bilirubin levels does jaundice become evident?
2 - 2.5 mg/dL
How does jaundice appear?
yellow discoloration of the skin due to excess bilirubin accumulation
icterus
yellow discoloration of the sclera of the eye due to excess bilirubin accumulation
hyperbilirubinemia
unconjugated or conjugated bilirubin in the blood (jaundice)
*causes of unconjugated
-excess production due to hemolytic anemia (RBC destruction) --> most common cause
-excess production due to ineffective erythropoiesis (RBC production)
-defective conjugation (due to immaturity or hereditary cause)
*causes of conjugated
-obstruction of bile flow or bile duct injury--> tumor, stricture, gallstones in bile ducts
-hepatocellular disease--> viral or drug-induced hepatitis , cirrhosis
What is the most common cause of unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia (jaundice)?
excess production due to hemolytic anemia (RBC destruction)
What causes unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia (jaundice)?
-excess production due to hemolytic anemia (RBC destruction) --> most common cause
-excess production due to ineffective erythropoiesis (RBC production)
-defective conjugation (due to immaturity or hereditary cause)
kernicterus
brain damage due to excess bilirubin in tissues
what causes conjugated hyperbilirubinemia?
-obstruction of bile flow or bile duct injury
>tumor
>stricture
>gallstones in bile ducts
-hepatocellular disease
>viral induced hepatitis or cirrhosis
>drug induced hepatitis or cirrhosis
cirrhosis
diffuse fibrosis/scarring of the liver==> remodeling of the liver into nodules surrounded by fibrous bands
*due to hepatocellular injury
-chronic hep B or hep C
-alcoholic or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (fatty liver disease)
-autoimmune disease
- iron overload
*associated w/ liver failure but isn't the same thing--> not all cirrhosis leads to liver failure & not all end stage liver disease is cirrhotic
*cirrhosis is not a specific diagnosis --> has varying prognostic implications
what causes cirrhosis?
due to hepatocellular injury
-chronic hep B or hep C
-alcoholic or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (fatty liver disease)
-autoimmune disease
- iron overload
True or False: Not all cirrhosis leads to liver failure, but all end stage liver disease is cirrhotic.
False ==> not all cirrhosis leads to liver failure & not all end stage liver disease is cirrhotic
True or False: Cirrhosis has varying prognostic implications.
True ==> b/c cirrhosis isn't a specific diagnosis
What is the gross presentation of micronodular cirrhosis?
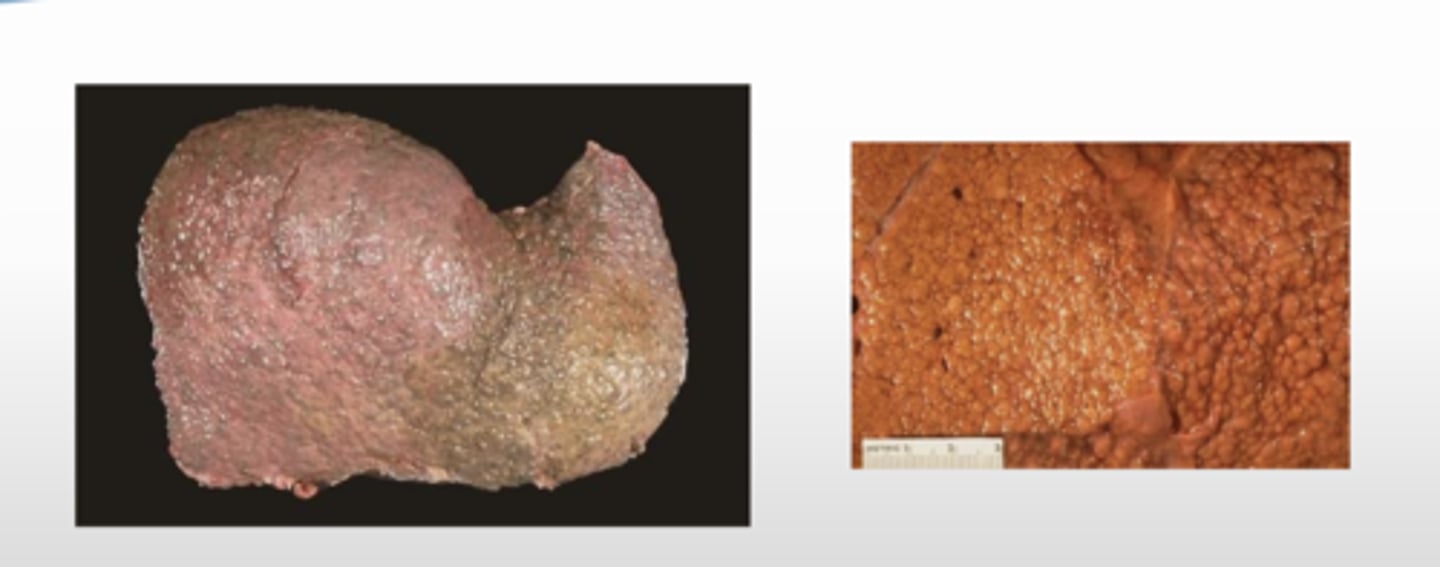
What is the histopathological presentation of micronodular cirrhosis?
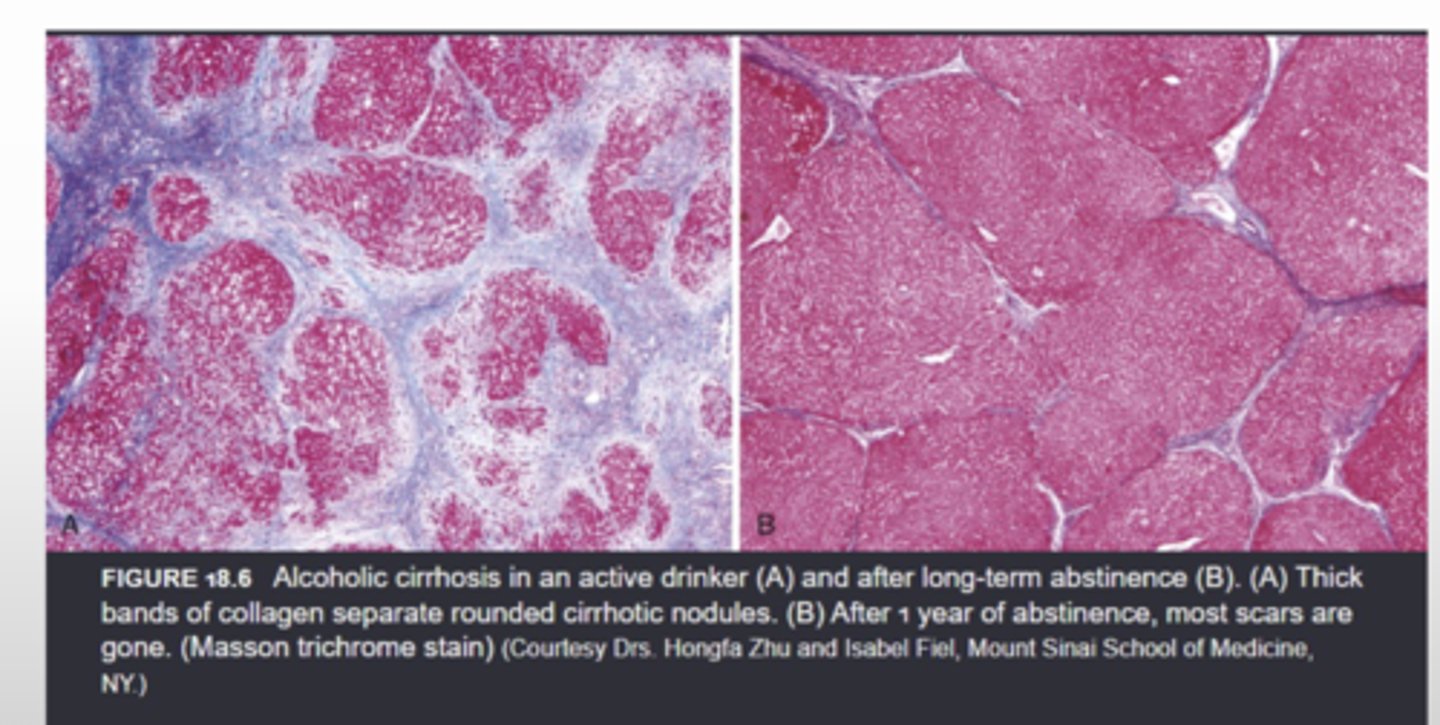
What is the histopatholgical presentation of alcoholic cirrhosis?
*thick bands of collagen separate rounded cirrhotic nodules
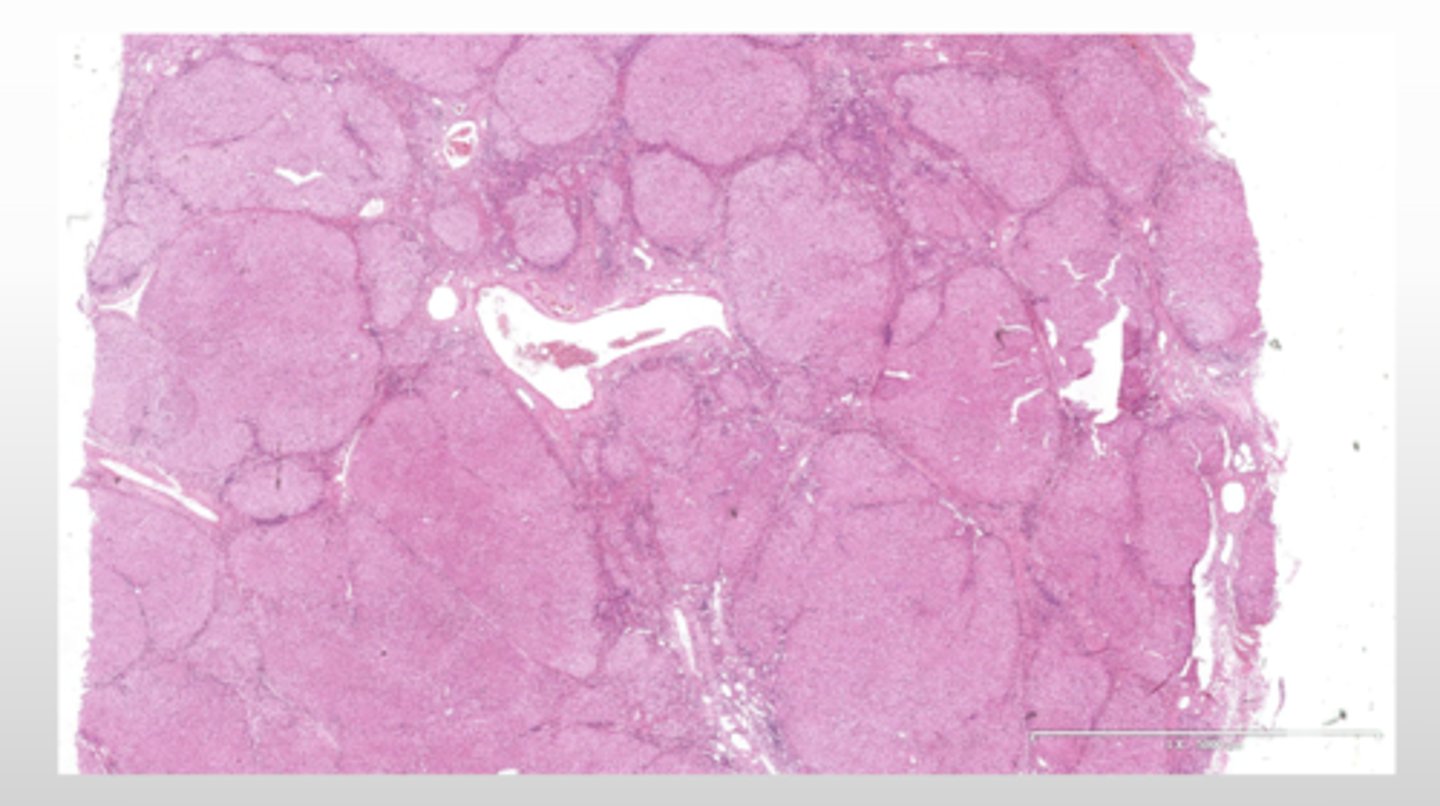
What is the gross presentation of macronodular cirrhosis?
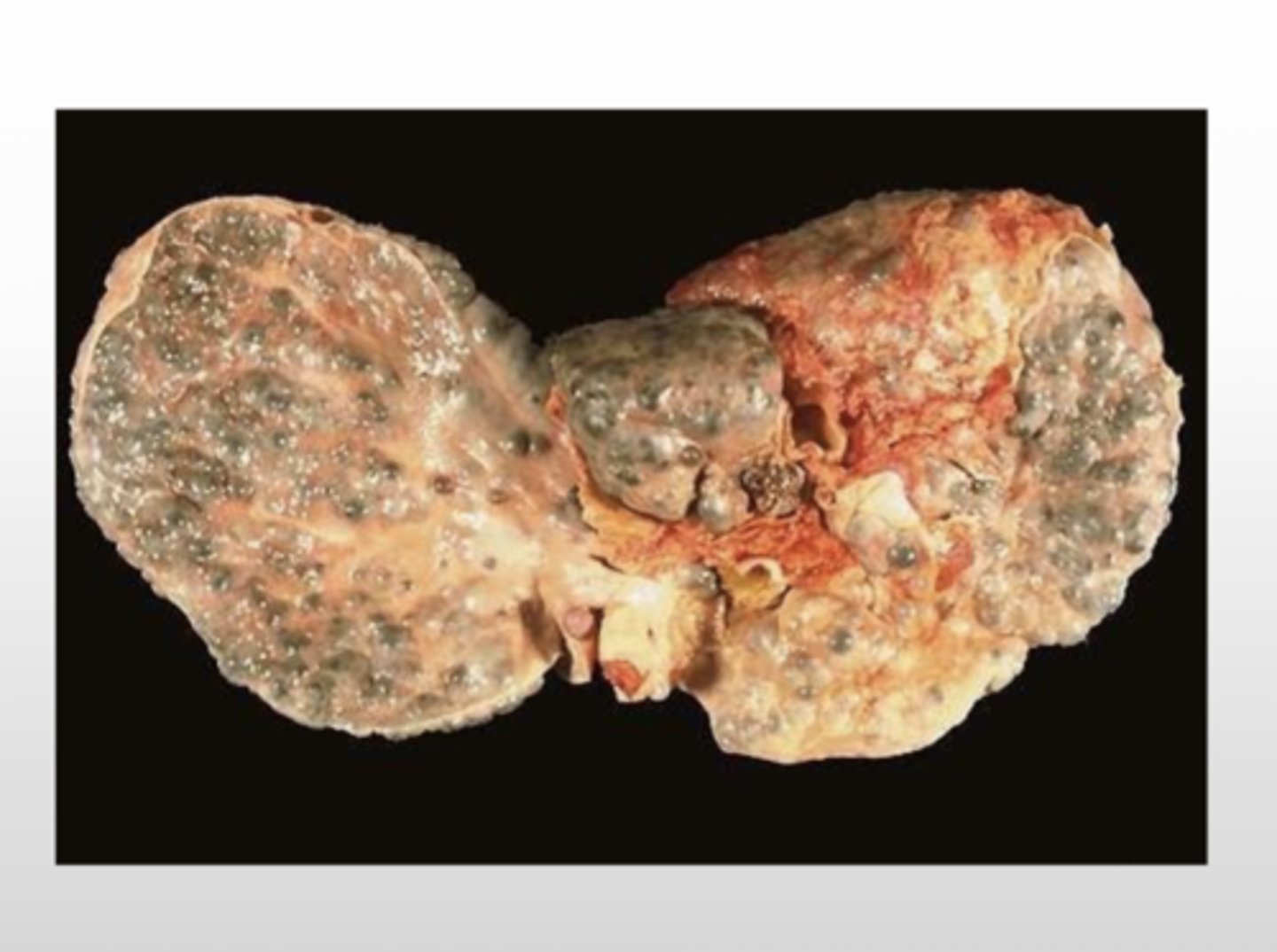
What is the histopathological presentation of macronodular cirrhosis?
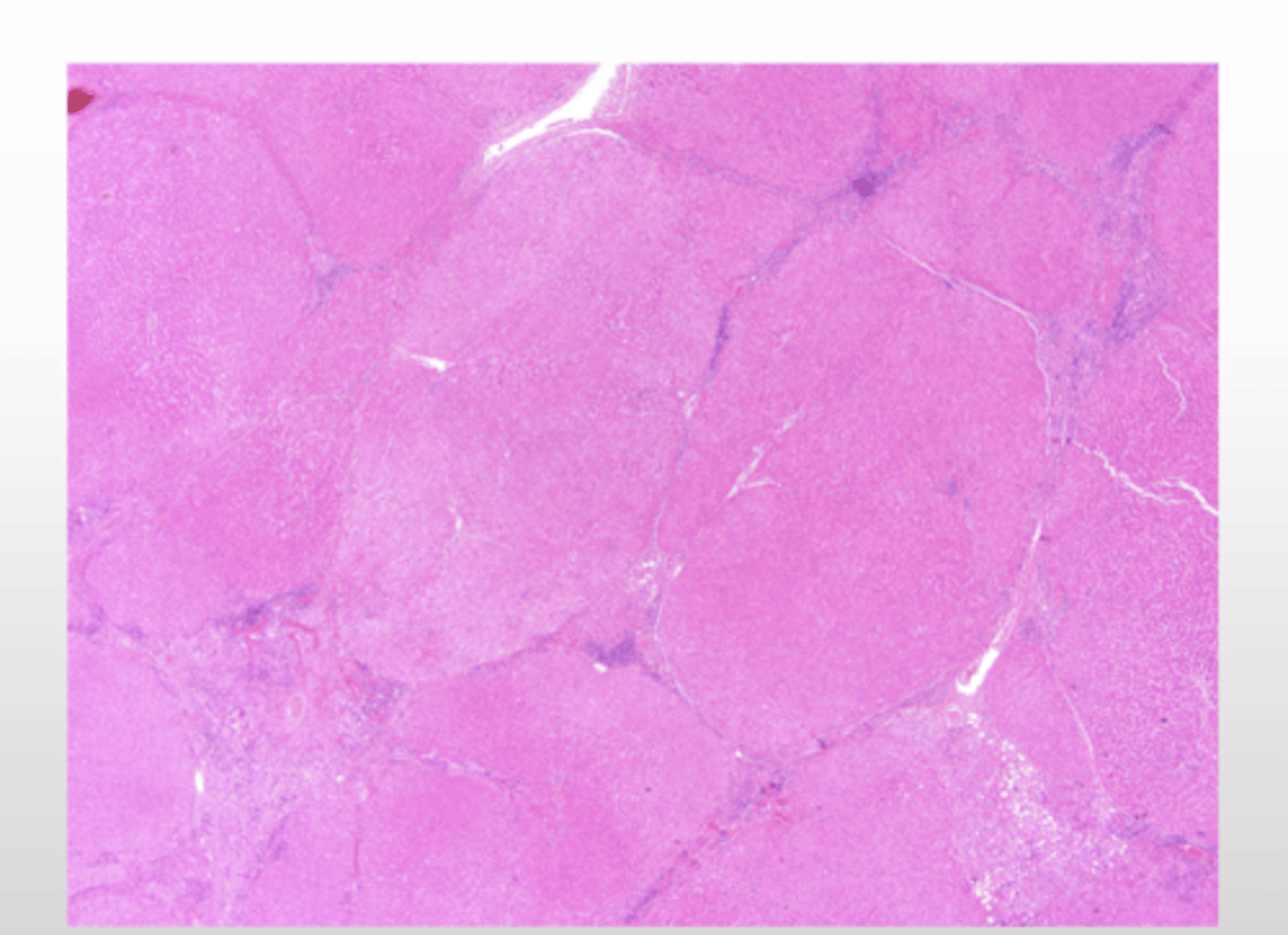
What is the gross presentation of alcoholic cirrhosis?
enlarged liver with nodule formation
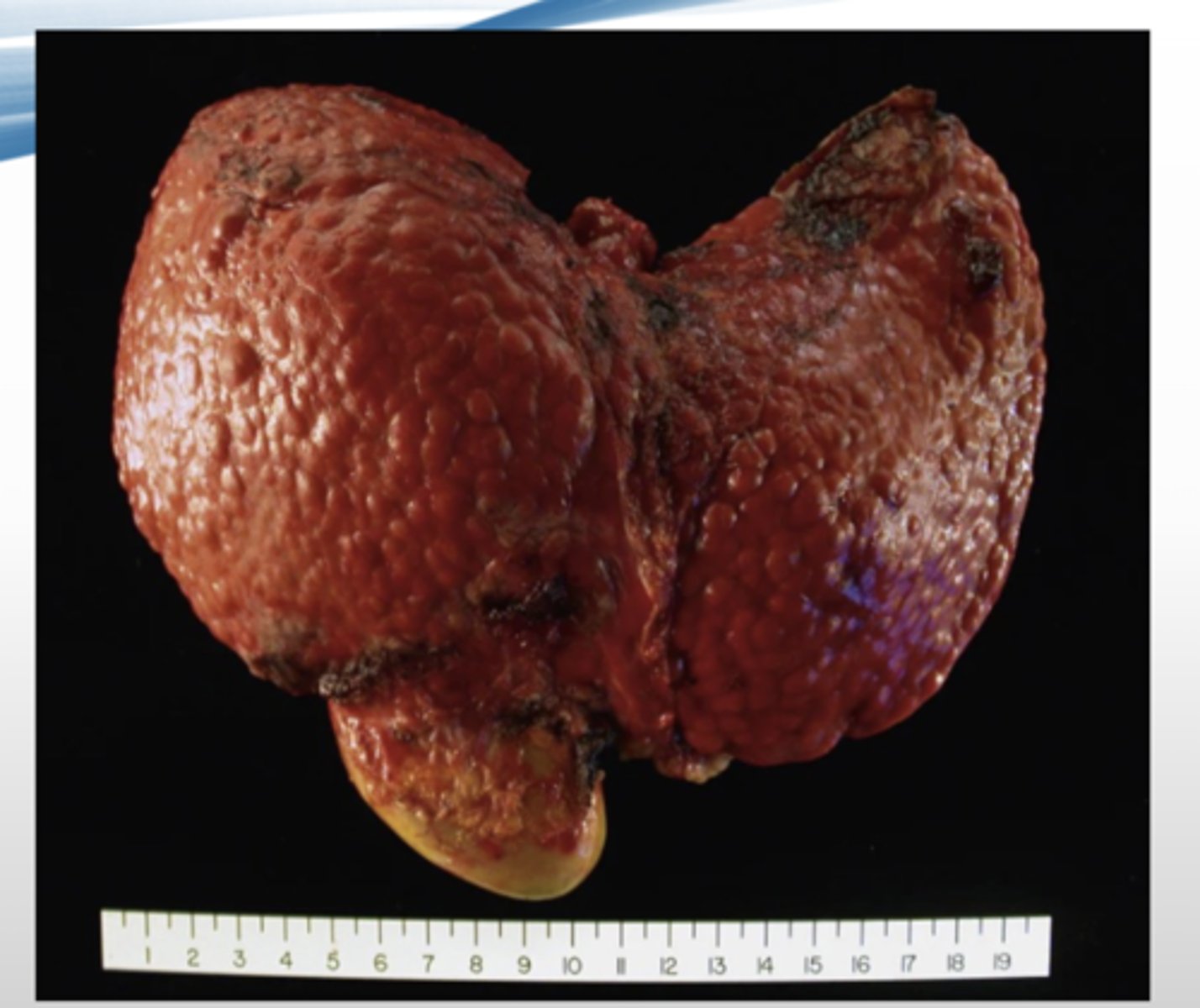
hemochromatosis
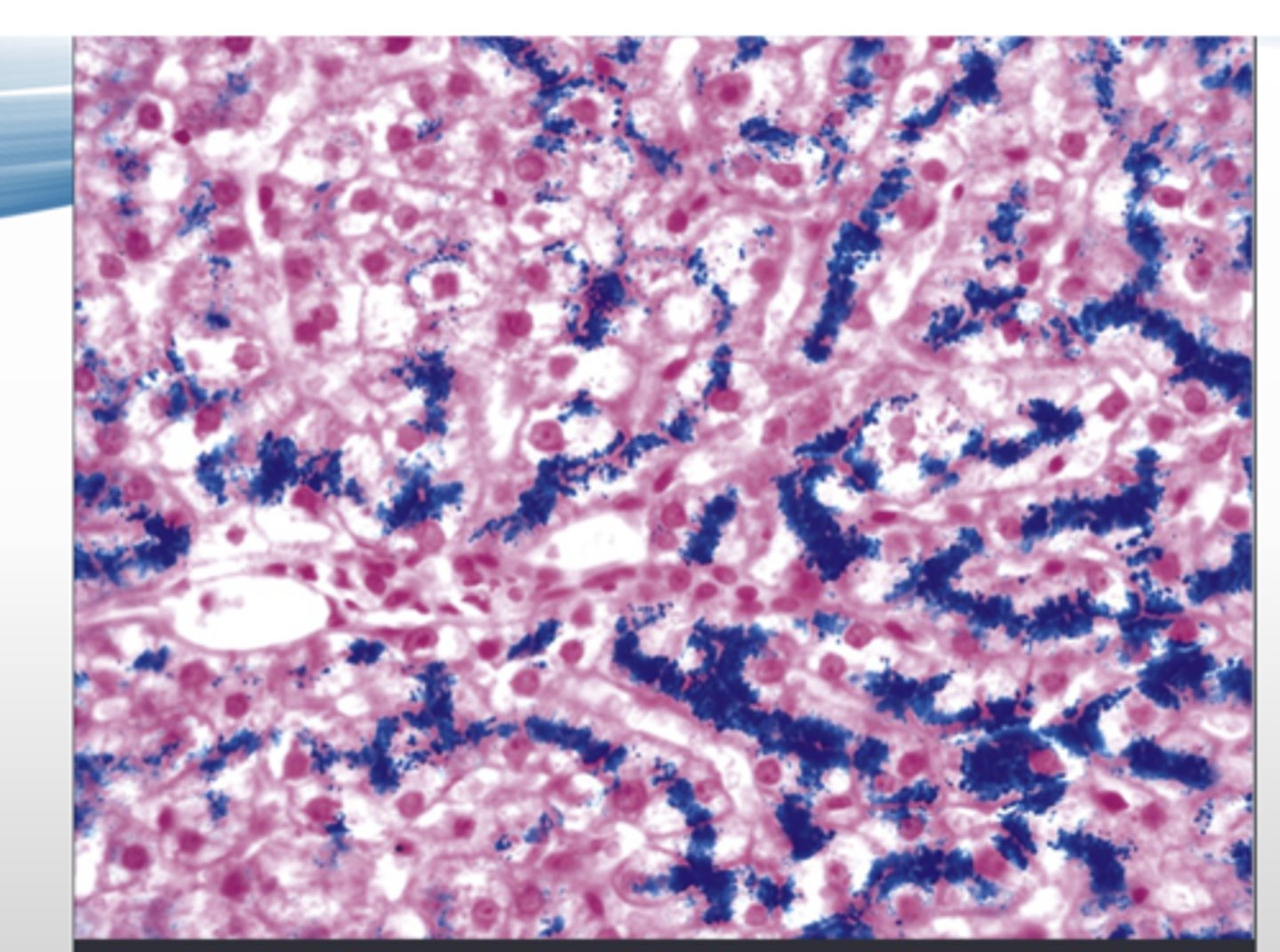
excessive iron absorption that gets deposited in organs (mostly in liver & pancreas)
-most often due to an autosomal recessive hereditary disorder of HFE gene*
-usually manifests after accumulation of 20g of stored iron*
When does hemochromatosis usually manifest?
after accumulation of 20g of stored iron
Which gene is usually mutated in hereditary hemochromatosis?
HFE gene
What is the normal iron storage range?
300mg - 2g
(300 mg in menstruating female)
Which organs are affected the most by hematochromatosis?
-liver
-pancreas
How is the lover effected by hemochromatosis?
-turns rusty brown color
-increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma
hemosiderosis
iron overload due to any cause other than excessive absorption==> secondary hemochromatosis
*ex: can be caused by frequent transfusions or dietary overconsumption
How does hereditary hemochromatosis present histologically?
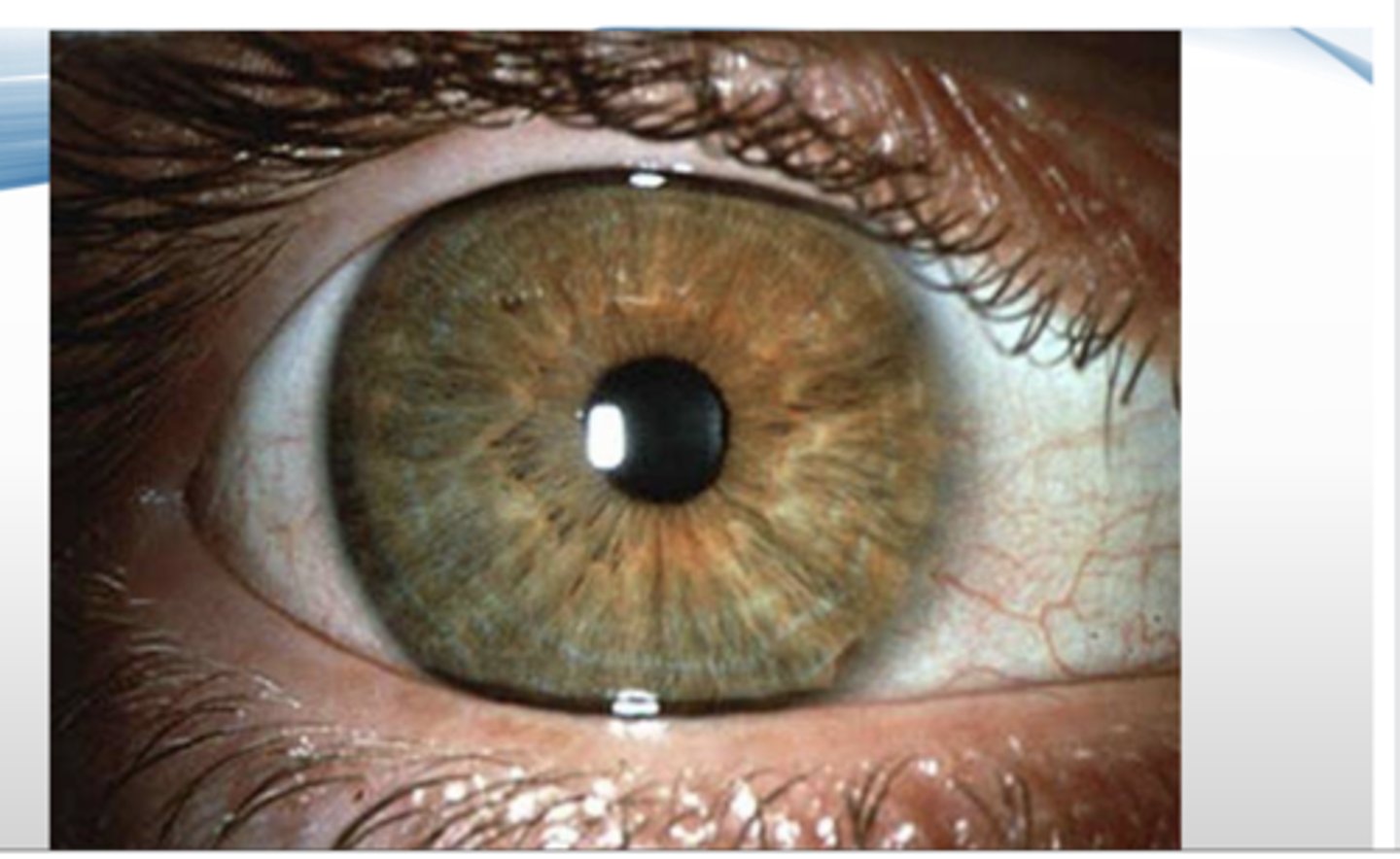
wilson disease
inadequate hepatic excretion of copper that causes copper accumulation in the liver, brain, & eyes due to mutation of ATP7B gene (autosomal recessive)
-kayser-fleischer rings --> deposition of copper in cornea
-causes cirrhosis & degenerative changes in brain--> tremor, poor coordination, gait distrubances, psychiatric symptoms
-diagnosed via decreased serum ceruloplasmin
What gene is mutated in wilson's disease?
ATP7B (autosomal recessive mutation)
Kayser-Fleischer Rings
pathognomonic deposition of copper in cornea seen in wilson's disease
How does wilson's disease affect the liver?
copper accumulation causes cirrhosis
How does wilson's disease affect the brain?
degenerative changes
-tremor
-poor coordination
-gait disturbances
-psychiatric symptoms
how is wilson's disease diagnosed?
decreased serum ceruloplasmin ==> protein that copper is normally bound to for transport to the body
acute hepatitis
necrosis & inflammation of liver cells that's most often due to viral infections or toxins
chronic hepatitis
continued liver inflammation for more than 6 months
*may lead to fibrosis
hepatotrophic viruses
viruses that have an affinity for the liver
-Hep A
-HepB
-Hep C
-Hep D
-Hep E
Non-hepatotrophic infections/viruses that cause hepatitis
-Epstein-barr virus
-cytomegalovirus
-herpes simplex virus
-yellow fever
-autoimmune hepatitis
What kind of hepatitis does Hep A virus cause?
acute hepatitis
What kind of hepatitis does Hep E virus cause?
acute hepatitis
True or False: Hep B causes chronic hepatitis
True
True or False: Hep C causes acute hepatitis
False ==> causes chronic hepatitis
What kind of hepatitis does Hep D virus cause?
chronic hepatitis
What is special about Hep D virus?
it requires hep B co-infection
Which hepatitis viruses put patients at increased risk for hepatocellular carcinoma?
-Hep B
-Hep C
True or False: Autoimmune hepatitis is more common in females
True ==> 2:1 females predilection
True or False: Autoimmune hepatitis is often present with other autoimmune disorders
True ==> other autoimmune diseases in up to 60% of patients
True or False: Autoimmune hepatitis is concurrent with viral hepatitis infections
False ==> autoimmune hepatitis is absent of viral hepatitis
What causes alcoholic fatty liver?
alcoholism
What are some causes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)?
-obesity
-type 2 diabetes
-hypertension
-dyslipidemia
Alcoholic liver disease causes __________% of cirrhosis in the US
50%
hepatic steatosis
fatty liver; increased fat in the liver
True or False: Short-term ingestion of as little as 80g of alcohol over several days produces mild, reversible, hepatic steatosis.
True
The risk of severe liver injury becomes significant with intake greater than __________________ g/day
80 g/day
True or False: Daily ingestion of 160g or more for 10-20 years is frequently associated with liver injury
True
Why do only 10-15% of alcoholics develop cirrhosis?
factors other than alcoholism influence development & severity
-gender
-genetics
-comorbid conditions
Is alcoholic liver disease more common on men or women?
men
Are men or women more susceptible to alcoholic liver disease?
women
-metabolize alcohol differently
-estrogen makes the gut more permeable to toxins
Why are women more susceptible to alcoholic liver disease?
-metabolize alcohol differently
-estrogen makes the gut more permeable to toxins
What ethnic population experiences higher rates of cirrhosis due to alcoholism?
African Americans have higher cirrhosis rates than caucasians despite similar alcohol consumption
*suggests genetic component in alcohol induced liver disease ==> genetic variation in alcohol detoxifying enzymes may play a role in different populations
Despite similar alcohol consumption, different ethnic groups have varying rates of alcohol induced liver disease. Why?
genetic variation in alcohol detoxifying enzymes may play a role in different populations
What are some comorbidities associated with alcoholic liver disease?
-HCV
-HBV
-iron overload
*may synergize with alcohol & increase disease severity
True or False: Hepatic steatosis is irreversible
False ==> reversible --> adequate diet & no alcohol intake is sufficient treatment
True or False: Alcoholic hepatitis appears acutely after a bout of heavy drinking
True
What are common symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis?
-fever & malaise
-anorexia/weight loss
-hepatomegaly
-jaundice
True or False: The outlook of alcoholic hepatitis is unpredictable
True ==> each episode carries a 10-20% risk of death
What percent of patients with alcoholic liver disease induced cirrhosis develops carcinoma?
10-20%
What do patients with alcoholic liver disease induced cirrhosis usually die from?
-hepatocellular carcinoma
-hepatorenal syndrome
-hemorrhage
-hepatic failure
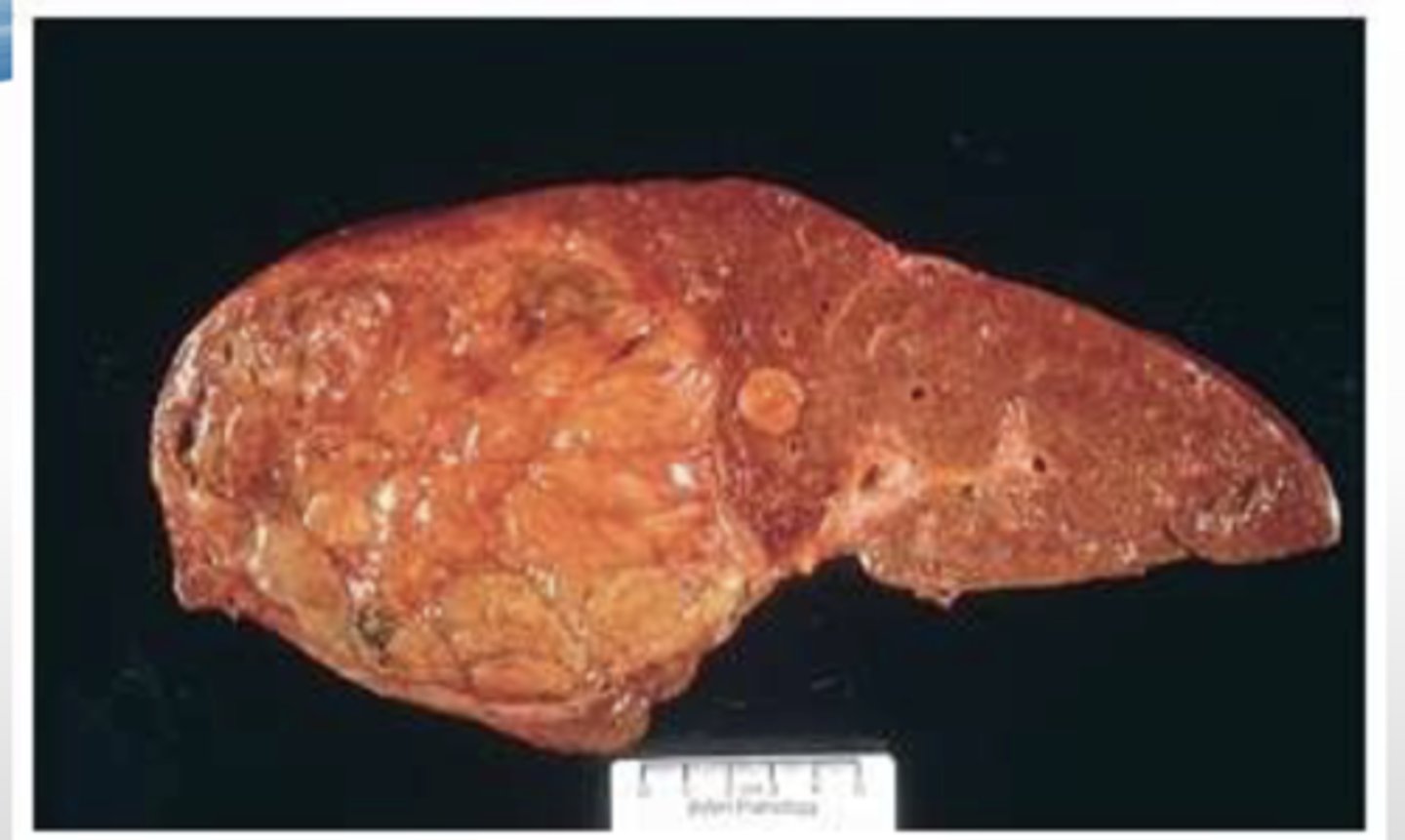
What is the gross presentation of hepatic steatosis?
yellow, greasy, enlarged liver ==> fatty vacuoles displace hepatocellular nuclei peripherally
What are the main characteristics of alcoholic hepatitis?
-swelling and necrosis of hepatocytes
-acute inflammation
-cholestasis
-early fibrosis
What is the histological presentation of hepatic steatosis?
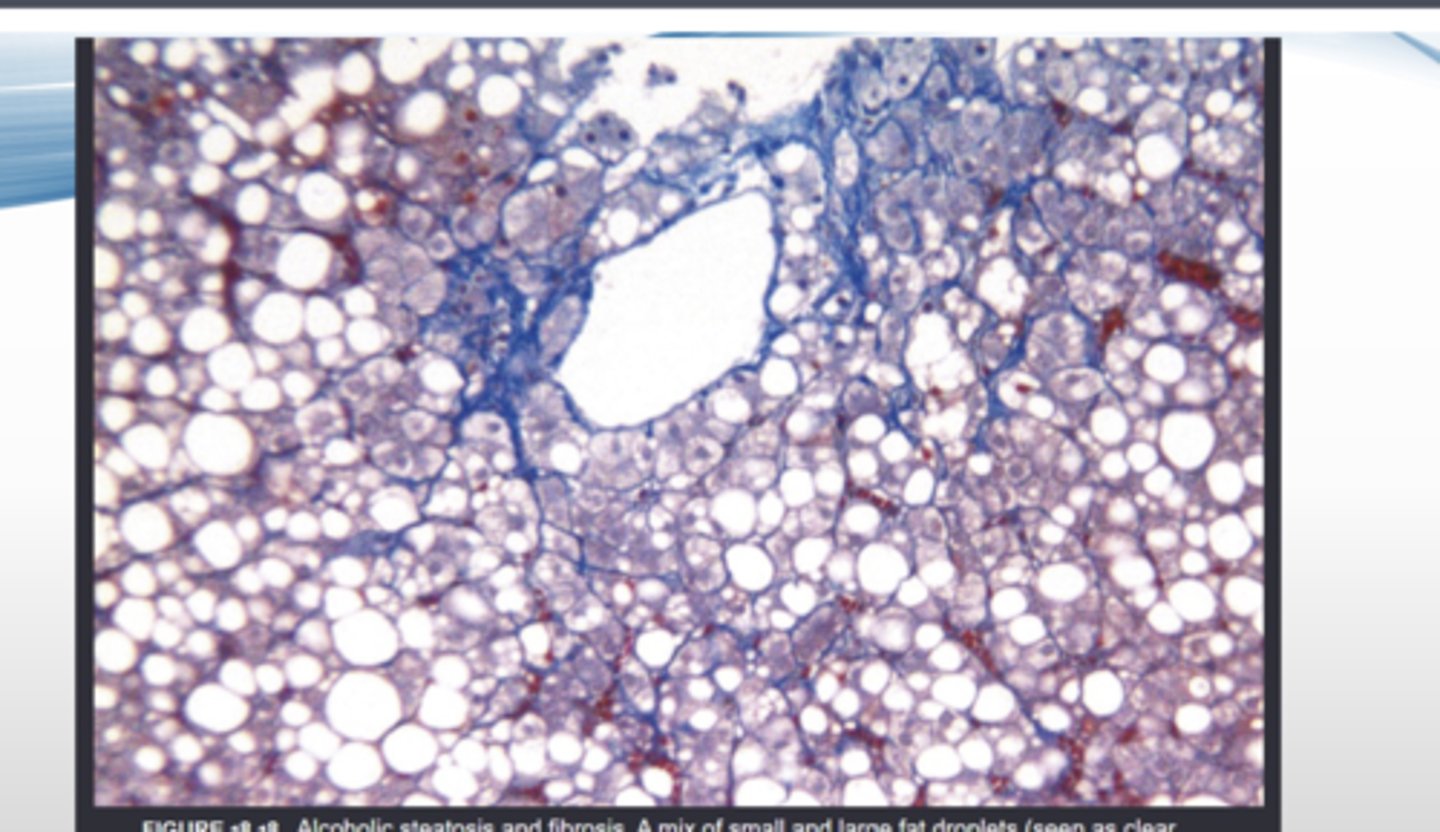
What is the most common primary liver cancer?
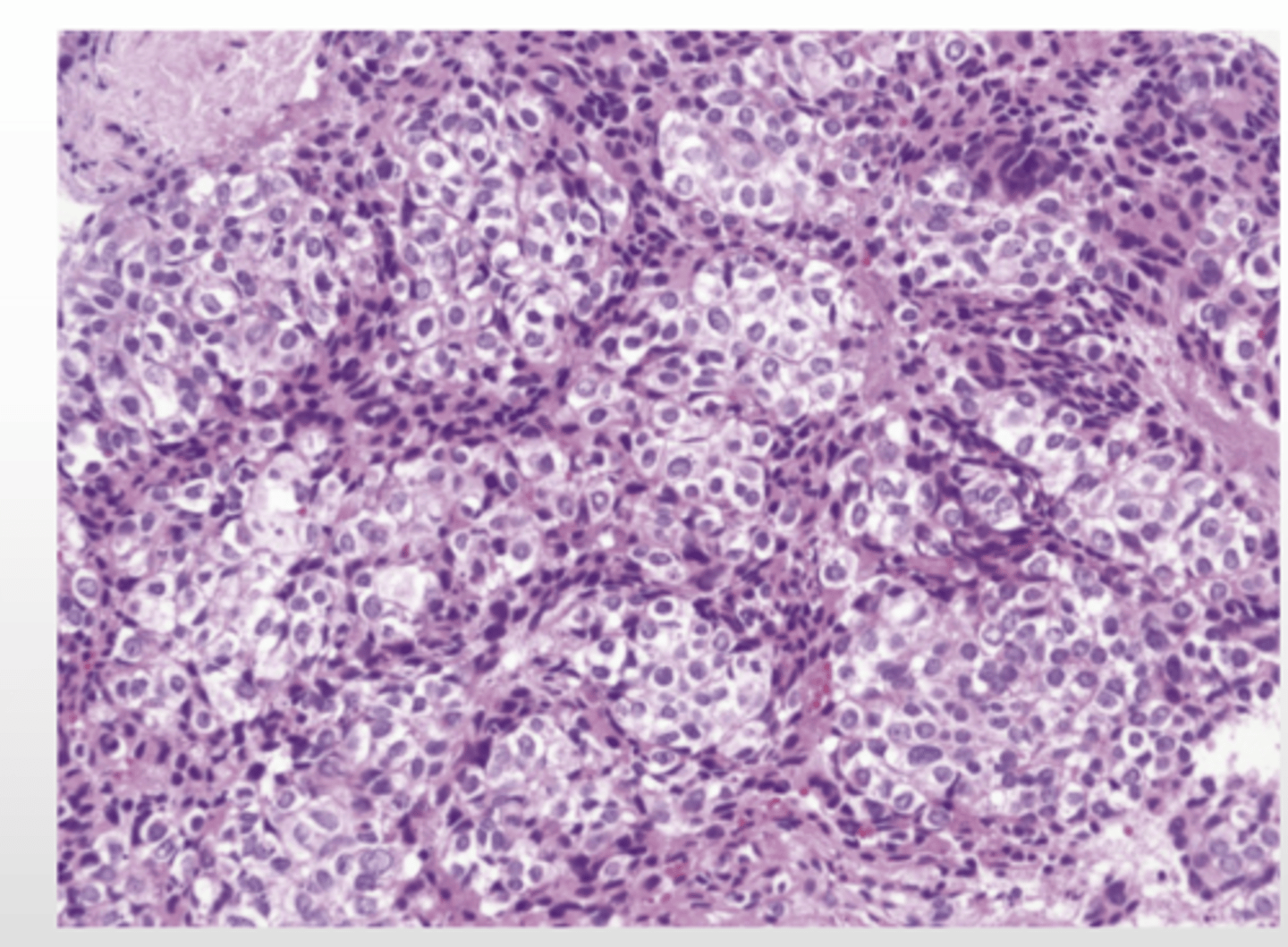
hepatocellular carcinoma (hepatoma)
-associated w/ infection, hepatitis, cirrhosis, hemochromatosis, & AAT deficiency
-symptoms--> ab pain, swelling, weight loss, weakness, jaundice, fever, loss of apeptite
-propensity for vascular invasion (inclination to invade vascular system)
-death due to hemorrhage and liver failure
-may be cured by liver transplant
What is hepatocellular carcinoma (hepatoma) associated with?
-infection
-hepatitis
-cirrhosis
-hemochromatosis
-AAT deficiency
What are the symptoms of hepatocellular carcinoma (hepatoma)?
-abdominal pain
-swelling
-weight loss
-weakness
-jaundice
-fever
-loss of appetite
True or False: Hepatocellular carcinoma has a propensity for vascular invasion.
True
What do patients with hepatocellular carcinoma typically die of?
-hemorrhage
-liver failure
What is the 5 year survival rate of hepatocellular carcinoma?
16%
*only 3% if distant metastasis
what is the the median survival of hepatocellular carcinoma without resection (surgical removal)?
7 months
True or False: Transplants are unable to cure hepatocellular carcinomas.
False ==> transplant may be curative
hepatoblastoma
rare malignancy of the liver that usually occurs in children under 3yrs old
angiosarcoma
malignancy in liver often due to exposure to vinyl chloride or arsenic
What is the most common malignant tumor of the liver?
metastatic carcinoma ==> most commonly from the lung, colon, breast, or pancreas
What is the function of the gallbladder
reservoir for bile made in liver
-stores 30-50ml
-fills passively
-contracts at mealtime