SPSS 1060S: Exam 3
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
social problems & sport
violence
substance abuse
gender inequality
gender in sports
In the past 30 yrs, girls participation in high school athletic programs has increased more than 900%
NCAA gender equity reports
Females comprise 57% of the college student population, but only 43% of NCAA participants are women
Average NCAA member institution sponsors 17 teams: 8 for men, 9 for women
Male college athletes receive 55% of college athletic scholarships, female athletes receive 45%
CT is one of the 17 states that allowed transgender athletes to compete w/ out restrictions in 2019
social capital
ecosystem services: benefits derived by humankind as a result of their interaction in an ecosystem
Broken windows theory (Wilson & Keling 1982): broken windows that remain broken will lead to an increase in negative behavior, litter on the streets
Zimbardo 1969: experiment w/ 2 cars w/ hood up, doors open (in Bronx & Palo Alto)
broken window theory experiments
How NY became safe: Giulliani used the broken window theory: improved design & maintenance, hired homeless to clean streets, eradicated graffiti on subway
Flint, Michigan: popul has fallen below 100k from a peak of 197k, leaving many crumbling neighborhoods, over 6k abandoned homes, in 2011 was #1 on list of top 10 most dangerous cities
Experiment: picked out 3 neighborhoods in Flint & mow them weekly, & apply fertilizer & pest control for 3 years; measure the social, economic, & environmental impacts of maintenance in these lawn areas
Well-kept vacant lots decrease crime
turfgrass benefits
functional
recreational
aesthetic
turfgrass functional benefits
Oxygen production
Reduced erosion
Reduced runoff/leaching
Cooling
Carbon sequestration
Decreased allergy from pollen
Noise abatement & noise control
Decreased nuisance pests (snakes, rodents, mosquitos, etc)
Safety in vehicle operation
Security: provide low cost, high visibility, ground cover,
Wildlife habitat: turfgrass, tree, shrub, & water combinations
recreational
Low cost playing surfaces
Physical health
Mental health
Safety
Spectator entertainment
aesthetic
Compliments trees & shrubs in landscape
Quality of life
Mental health
Social harmony
Community pride
Increased property value
turfgrass’s importance to the nation
Loss of productive soils
Dust in atmosphere
Pollution sediments, nutrients, & chemicals released into water resources
soil erosion (3 step process)
detachment (involves energy)
transport (wind, water, gravity)
deposition (it all goes somewhere)
universal soil los equation
A=R*K*LS*C*P
A= soil loss in tons per acre per yr
R= rainfall energy
K= soil erodibility
L= slope length
S= slope gradient
soil erosion control
mulching (hydro-mulching)
gravel until vegetation has chance to grow
experiment about runoff & soil erosion result: fertilized plots had 94% less sediment
Total P runoff from the No fertilizer treatment > Treatments receiving fertilizer
Clipping management did not impact P runoff
In the presence of N and K, P did not increase turfgrass quality
Do not apply P to high testing soils
P losses greater in runoff from frozen soils
Avoid fall P applications
reducing pathogens in agricultural runoff: why pathogens?
surface waters not supporting uses due to pathogens
73% of CT shellfish harvesting beds
255 CT river segments (70% of river miles)
Bacteria TMDLs in individual streams
Many mention agriculture as potential source
heat dissipation-temperature moderation
Urban areas can be 5º-7ºC warmer than rural areas
Max canopy temp of growing bermuda grass 21º cooler than brown dormant turf
Synthetic turf is worse
carbon sequestration
Recent studies have suggested that turfgrasses have relatively high potential for soil carbon sequestration
- turfgrasses in our climate/region have potential to store significant amounts of carbon in our soil
- tall fescue, 4” HOC, returned clippings, & some N resulted in the highest means of carbon sequestration
- overall carbon sequestration rates similar to what observed in other regions
- results validate important environmental benefit of turfgrass ecosystems
- in future, possible income generation from turfgrass if cap-and-trade systems implemented
How long can we expect soil carbon storage increases?
- models suggest that rates do decline w/ time (across 30-100 yrs)
pest management (integrated pest management options)
Cultural: planting site, crop rotation
Mechanical: cultivation to remove weeds
Biological: use of beneficials, insects, etc
Genetic: plant resistance
Chemical: pesticides
types of pesticides
Herbicides: plants
- selective: only target plants
- non-selective: targets anything green
- pre-emergent: prevents germination
- pos-emergent: controls once germination occurs
Fungicides: fungi
- contact
- systemic: absorbed by the plant
Insecticides: insect
Pesticide toxicity: highest: 1, danger, corrosive; lowest: 4, optional, mild
environmental impact quotient
a formula created to provide growers with data regarding the environmental and health impacts of pesticide (EIQ)
Pre-emergent herbicides: Siduron, dithiopyr, mesotrione, pendimethalin
Post-emergent herbicides: triclopyr, glyphosate, MCPP, 2,4D, Clopyralid, dicamba, quinclorac (all between 6 & 12)
Insecticides: chlorantraniliprole, trichlorfon, imidacloprid, bifenthrin
pesticide bans
Pesticide ban in CT in effect since July, 1, 2010 (proposed in 2007)
41 states have pesticide restrictions related to athletic fields
Pesticide-free areas in 7 states
challenges w/ managing athletic fields w/ out pesticides
Lack of knowledge base
Many current recommendations are NOT based on research
Controlling weeds & damaging insects
Liability issues
cost
Thompson 1984:
irrigation & mowing reduced dislodgeable foliar 2,4D residue
Sears 1987:
granular insecticides 21 times less likely to dislodge from turfgrass than liquid
Putnam 2008:
estimated exposure to golfers following applications of 3 insecticides were 19-68 times below EPA Rfd
2,4D on turfgrass
Dislodgeable 2,4D from athletic field turfgrass: morning dew each day after application makes concentration higher
Conclusion: dislodgeability decreases as time within day increases, & DAT increases
Dislodgeablilty increases as RH increases & leaf wetness increases
Much more 2,4D dislodged in subsequent morning than previous afternoon
granular formulation: less residue that liquid formulations
dithiopyr: in both formulations had less residue initially & both were ND one DAT
2,4D & Diacamba in liquid form:
steps to minimize exposure risk
Coordinate field use around pesticide applications (close fields)
- 5-7 DAT if using granular formulations
- 14 (or more) DAT if using liquid formulations
Irrigate soon after pesticide application
Afternoon field use is safer than morning or evening
IPM considerations
Use sound agronomics to develop a competitive turfgrass stand
Scout and use pest pressure history
Treat broadleaf weeds late in the fall (November)
Consider greater intervals between applications
significance of turfgrass
turfgrass is the largest irrigated crop in America (31,630,000 acres)
What makes turfgrass unique? (recall)
Durability: turfgrasses tolerate traffic better than other grasses/plants
Forms a dense contiguous surface: good for walking on & holding the soil
tolerates frequent mowing (once a week, sports field: 2-3 times a week)
what soil provides plants (SOILF)
support (keeping them upright)
oxygen
ions (essential elements)
liquid (supplies water)
freedom from inhibitory factors
soil physical properties
Texture
Structure
Bulk density
Porosity
Permeability
Organic matter
Components of soil: 45% minerals, 5% organic matter, 25% air, 25% water
benefits of organic matter
Increased water holding
Increased nutrient holding
Decreased bulk density
Soil structure development
Soils construction
Sand construction
evolution of sand textured root zones
1950s researchers investigated sands for golf green construction
1960 1st USGA specifications published
Mid 1960s transition to artificial surfaces for athletic fields
1970: Dr. Daniel at Purdue U develops PAT system
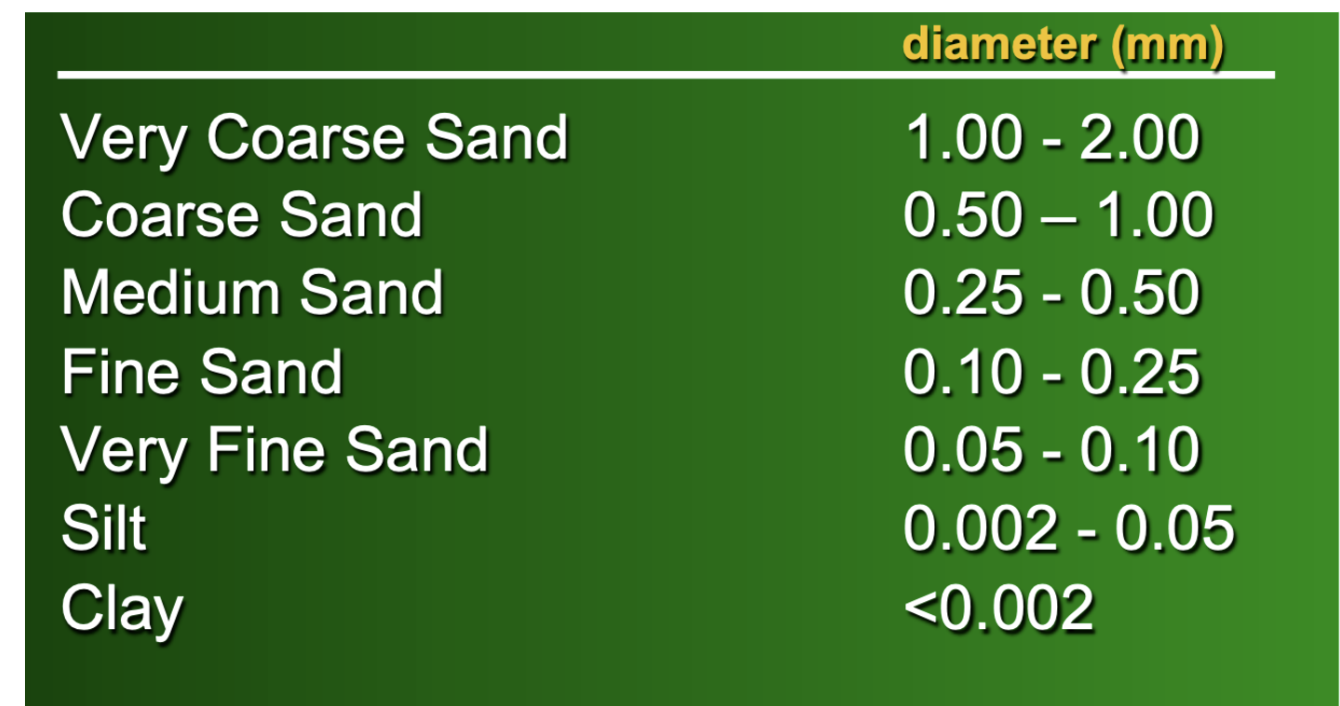
soil particle types
Sand (.05-2mm)
Silt (.002-.05mm)
Clay (<.002mm)
soil textural triangle (12 major textural classes)
preferable soil textures: loamy sand, sandy loam, loam
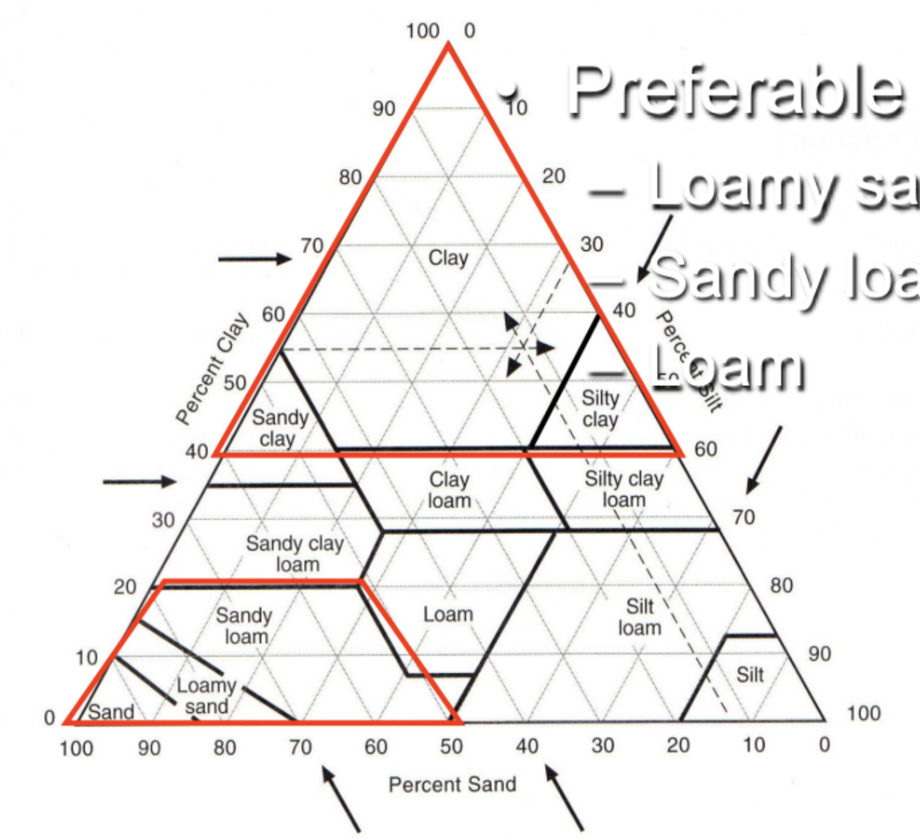
textural classification of soil particles
soil structure
arrangement of primary soil particles into secondary particles
-The large size of aggregates results in large interped spaces
-Interped spaces are much larger than the spaces between adjacent sand, silt and clay particles
-These large spaces allow fine textured soils to drain rapidly and allow root penetration
- 2 structureless conditions: sands (single-grained) & Massive (high clay content)
USGA Green Profile
12 inch” root-zone mix
2” intermediate layer (optional)
4” gravel blanket
Drain tile
Sub-grade
bulk density
weight of a unit volume of dry soil, including voids & solids
BD=Ws/Vt
soil compaction
a decrease in soil pore space, resulting in high soil strength & bulk density
general rule: turfgrasses will always perform better in soils w/ low bulk density than soils w/ high bulk density
3 phases in soil
air (macropores)
water (micropores)
solids
pore size distribution
Macropores (aeration pores)
>.1mm
infiltration, percolation
gas exchange
Micropores (capillary pores)
<.1mm
water retention