quadratic equations and functions pt I
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Quadratic equations
ax² + bx + c = 0, where a is not equal to 0
How to solve equations with square terms
Inverse operations, take the square root out of booth sides,
x² = 49
x = 7, -7
How to solve these equations without a perfect square?
Take square root out of both sides, the number that is not a perfect square can be simplified. Find a multiple that is a perfect square and simplify
The square root of 8 = the square root of 4 • the square root of 2 = 2 • the square root of 2
the square root of a•b can be simplified as what
The square root of a times the square root of b
The quadratic equation of ax² + bx = 0 always has
Two solutions, one of them being zero
5x² +15x = 0
5x(x+3) =0
Using the zero product rule,
5x = 0, x = 0 x+3=0, x = -3
Zero product rule
If A and B are any two quantities such that AB = 0, then A = 0, B = 0, or that both A and B are equal to 0
Grouping method
Find factors of ac whose sum is b
Rewrite equation to put factors on separate sides
Group terms and find GCF of each group
Factor out the common factor
Set each factor equal to 0
Perfect square trinomials have how many solutions
1
Difference of squares have how many solutions
2, one being the opposite of the other but same absolute value
To complete the square,
Factor the perfect square trinomial, take square root of both sides and then solve for x
(x+7)² =121
x +7=11,-11
x =4,-18
To turn a quadratic equation in the form ax² + bx + c where a =1,
Add (b/2)² to BOTH sides AFTER MOVING THE CONSTANT TO THE RIGHT SIDE OF THE EQUATION. If a is not equal to 1, divide the equation by a AFTER ISOLATING THE CONSTANT but BEFORE ADDING (b/2)²
Parabola
The graph of a Quadratic function
The vertex of a parabola
The point in a parabola where it changes direction, lies on the line of symmetry, and EXACTLY halfway between the two x intercepts
Minimum
When a>0
Maximum
When a<0
Vertex form
y = a(x-h)²+k, where (h,k) is the vertex
h is subtracted from, and k is added.
When a is more than 0, vertex is a minimum
To find zeros
Complete the square and solve for x
To put standard ax²+bx+c = y into vertex form
Move the constant on the side of y, add (b/2)² to both sides, simplify y side and put the other side as a perfect square, then move the constant to the other side.
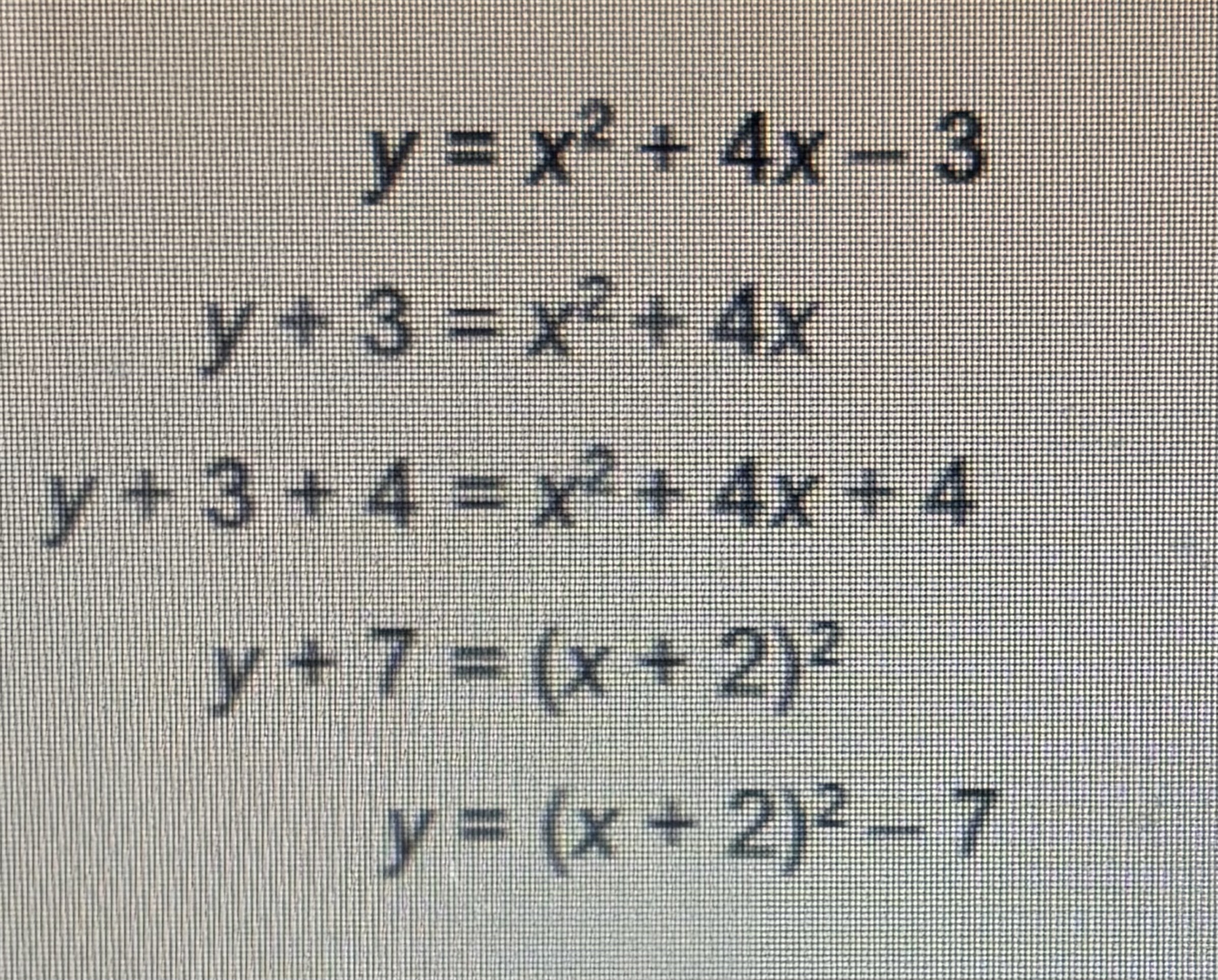
How to find line of symmetry
The line of symmetry is h in y=a(x-h)² + k
The quadratic formula
y = -b±the square root of b² - 4ac/ 2a
When solving the quadratic equations, solutions contain square roots/radicals that can sometimes be simplified
It’s either a perfect square, or can be simplified with the multiplication property of square roots, Some solutions are imaginary numbers
Radicals
Terms in the form of a “square root sign”
Discriminant
The number under the radical in the quadratic formula
b² - 4ac
Positive discriminant
2 solutions
Discriminant = 0
One solution
Negative discriminant
No real solutions