Unit 5: land and water use
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Ecological footprint
-Measure of how much a person/group consumes, expressed in area of land (gha: a biologically productive hectare)
-how much "land" is required for all consumption
Carbon footprint
measured in tonnes of CO2 produced per year; all CO2 released from an individual or group's consumption & activities
Clearcutting
-The process of cutting down all the trees in an area at once
-causes soil erosion (lack of stabilizing roots), increased soil and stream temperature, flooding and landslides
Tilling
-mixing and breaking up soil to make planting easier (also loosens soil for roots)
-increases soil erosion (loosens topsoil + breaks root structure), loss of organic matter and top soil nutrients over time, increased particle matter in air (respiratory irritation) and water (pollution)
Slash-and-burn
-cutting down vegetation and burning it to clear land for agriculture and return nutrients to soil
-causes deforestation so loss of habitat, biodiversity, CO2 sequestration, air pollution filtration, releases CO2, CO, NO2 (GHG increasing global warming), increases particle matter in air (asthma), decreases albedo (increases temp.)
Synthetic (inorganic) fertilizers
don't return organic matter to soil; no increased H2O holding cap. & no soil decomposers
Sustainability
consuming a resource or using a space in a way that does not deplete or degrade it for future generations
Maximum sustainable yield
the maximum amount of a renewable resource that can be harvested w/out reducing or depleting the resource for future use
Fire suppression
practice of putting out all natural fires as soon as they start which leads to biomass buildup and worse fires
Prescribed burns
small controlled fires which promotes nutrient cycling and decreases biomass build up
Green Revolution
-shift away from small, family operated farms to large, industrial-scale agribusiness
-increase in mechanization, GMOs, irrigation, fertilizers and pesticides
-positive: increased land efficiency, short-term profits, food supply, and earth's carrying capacity for humans
-negatives: soil erosion, biodiversity loss, ground and surface water contamination, emission of GHGs, compaction of soil
GMOs
-crops with new genes "spliced" into genome
-positive: increased profits with fewer plants lost to disease/drought, larger plant size and yield
-negative: genetic diversity decreased, increased susceptibility to diseases and pests
Acid mine drainage
-sulfur-rich tailings from coal mines (FeS2/pyrite/Fool's Gold) mix with oxygen and water to create sulfuric acid and yellow boy (O2 + H2O + FeS2 → H2SO4 & Fe(OH)3)
-when this leaches into a water source, its pH is lowered and acidity rises, dissolving other minerals nearby
-as it runs down the water source, pH rises and yellow boy precipitates out increasing turbidity and decreasing water quality & stream ecosystem
Annual crop
crops that grow, produce seeds, and die in a single year and must be replanted each season
Aquaculture
The cultivation of seafood in pens/enclosures in the ocean or other water sources
Aquifer
A body of rock or sediment that stores groundwater and allows the flow of groundwater.
Arable land
land that can be used to grow crops
Artificial selection
Breeding organisms with specific traits in order to produce offspring with identical traits.
Biocapacity
a measure of the area and quality of land available to supply a population with resources
Biological pest control
the use of living organisms to control pests
Brownfields
abandoned polluted industrial sites in central cities
Bycatch
The unintentional catch of nontarget species while fishing
Coliform bacteria
a type of bacteria that occurs naturally in the intestines of humans and other animals, and indicates the presence of fecal contamination in water
Concentrated Animal Feeding Operation (CAFO)
a method in which large numbers of meat or dairy animals are reared at high densities in confined spaces and fed a calorie rich diet to maximize growth
Contour plowing
An agricultural technique in which plowing and harvesting are done parallel to the topographic contours of the land
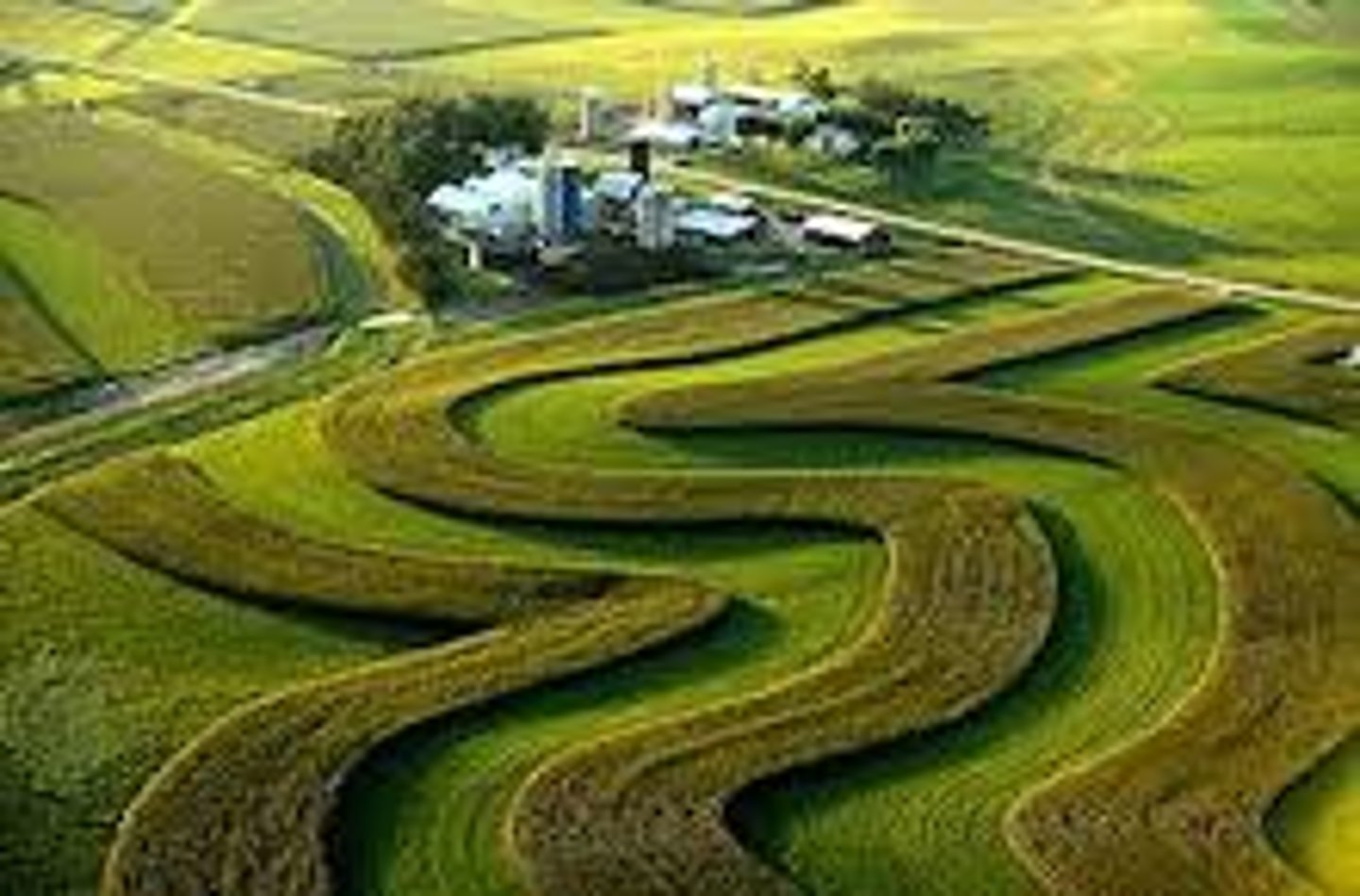

Crop rotation/intercropping
Planting a different crop each season/ plant different crops together as a form of pest control, making it more difficult for pests to get at crop
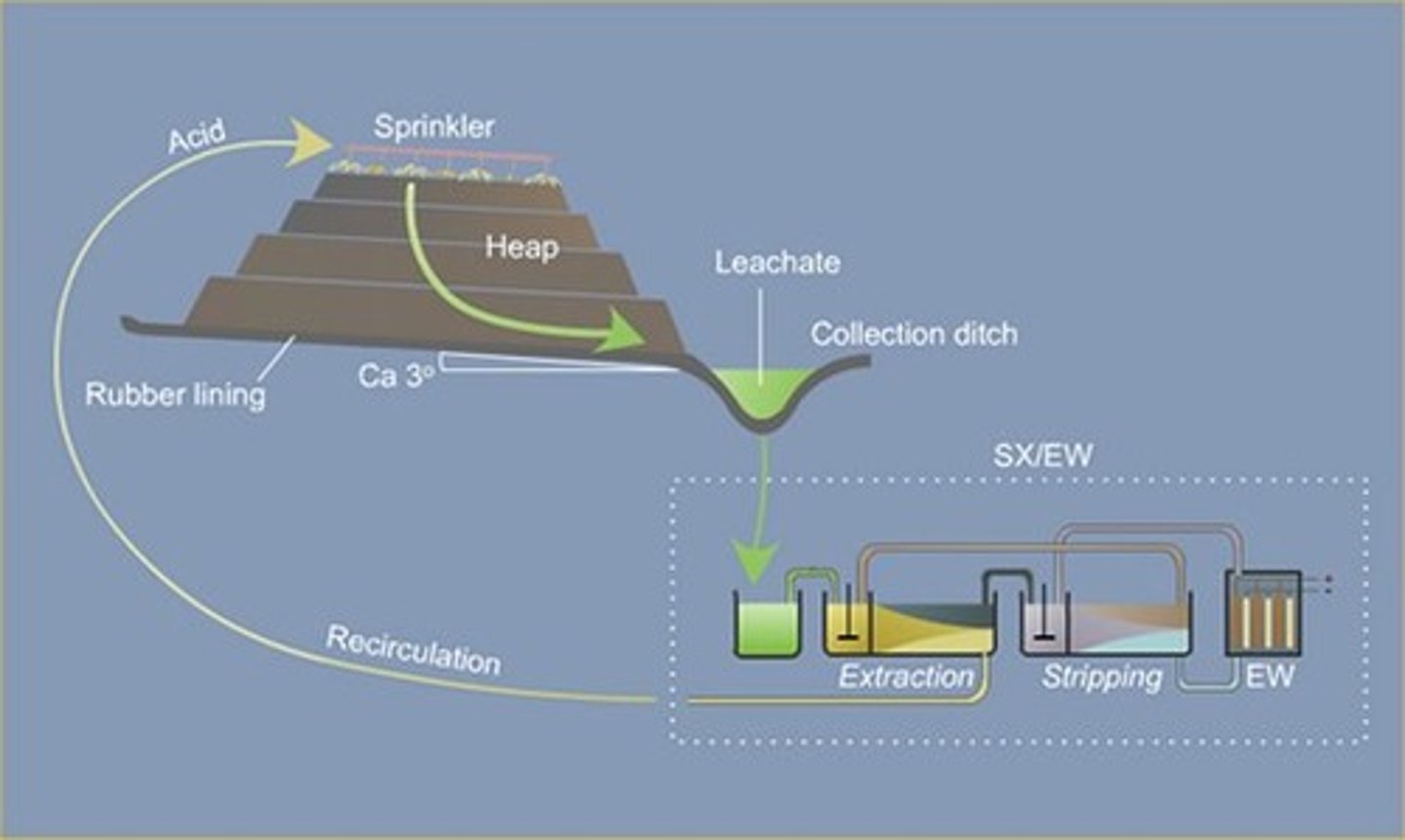
Cyanide heap leaching
Extraction of Au (gold) can employ the application of cyanide-based fluids to extract gold in open-air sediment 'heaps' with slurry retained in holding ponds
Desertification
the process by which fertile land becomes desert, typically as a result of drought, deforestation, or inappropriate agriculture.
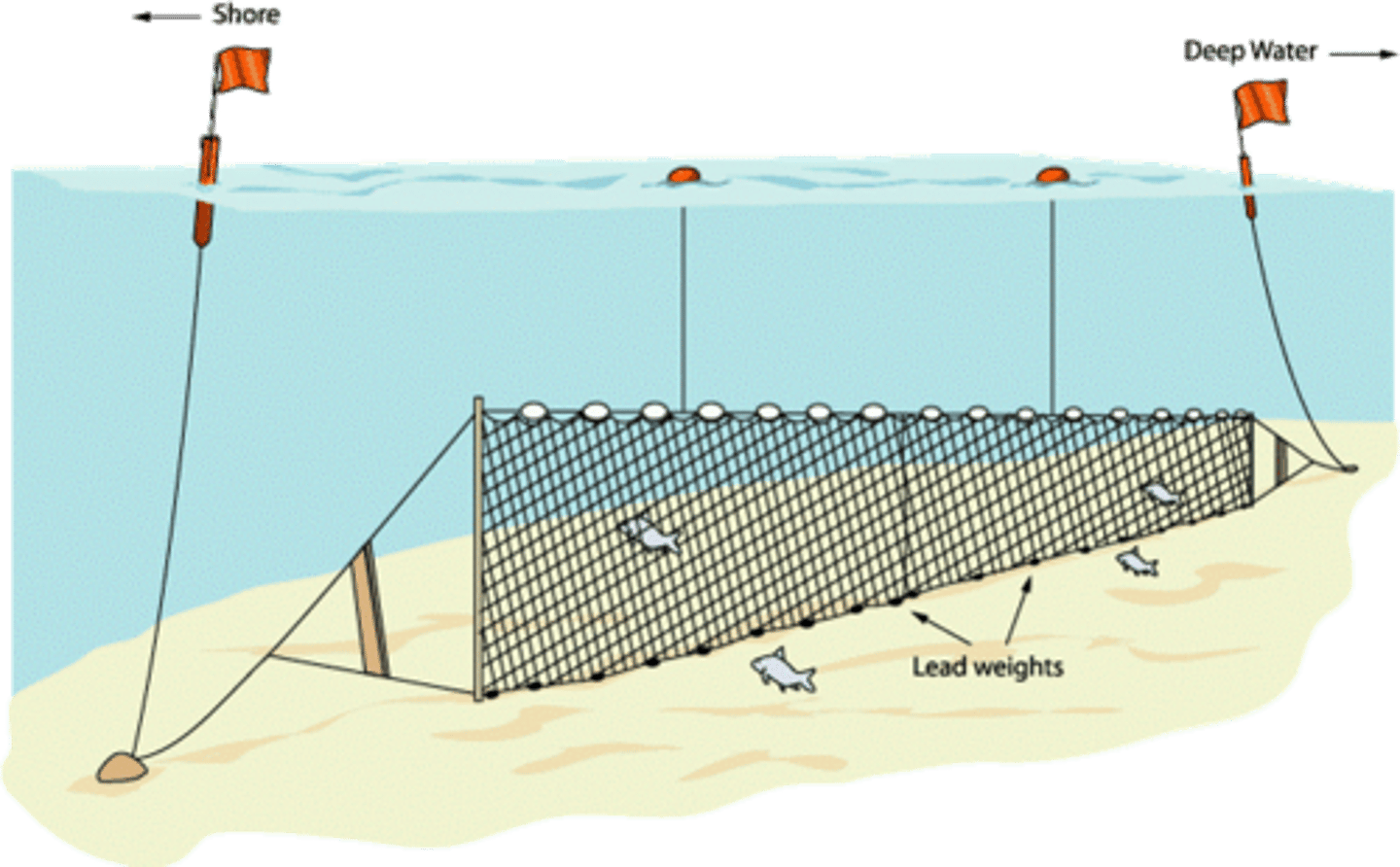
Drift/gillnetting
curtains of netting suspended by a system of floats and weights; they can be anchored to the seafloor or allowed to float at the surface, net is almost invisible to fish, so they swim right into it
Drip irrigation
the practice of using small pipes that slowly drip water just above ground to conserve water to use for crops

Externalities
A side effect of an action that affects a third party other than the buyer or seller
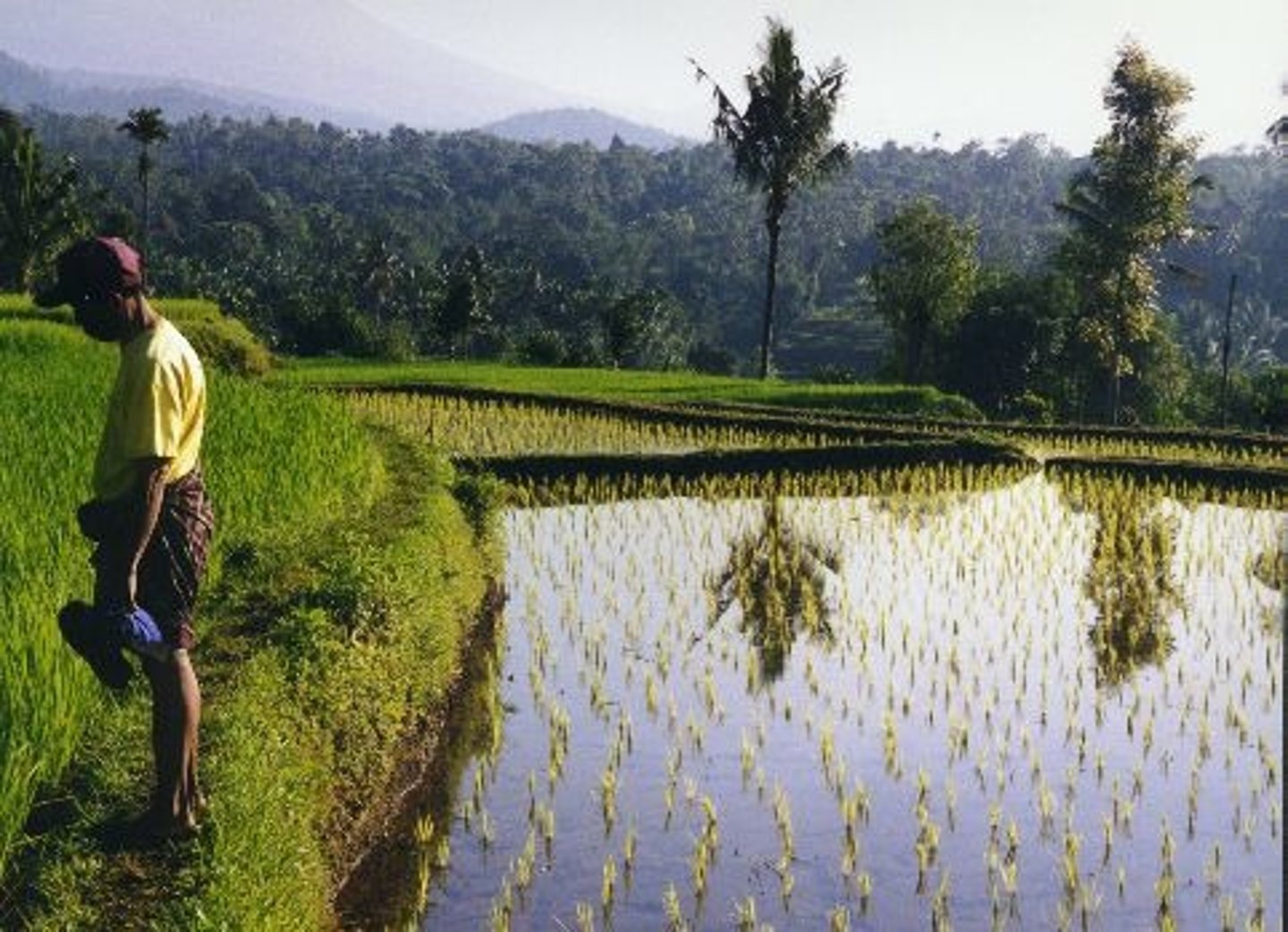
Flood irrigation
the entire field is flooded with water

Free range grazing
Animals (usually cows) graze on grass & grow at a natural rate without growth hormones
Furrow irrigation
easy and inexpensive, farmer digs trenches along the crop rows and fills them with water, which seeps into the ground and provides moisture to plant roots

Green manure
consists of freshly cut or growing green vegetation that is plowed into the topsoil to increase the organic matter and humus available to the next crop

Greenways
strips of land connecting parks or neighborhoods

Heat island effect
Warmer temps are experienced in urban landscapes due to solar energy retention on constructed surfaces. Principal surfaces include streets, sidewalks, parkings lots and bldgs.
Impermeable surfaces
A surface that does not allow water penetration (Tar, buildings, drought soil, etc.)
Integrated pest management
An agricultural practice that uses a variety of techniques designed to minimize pesticide inputs
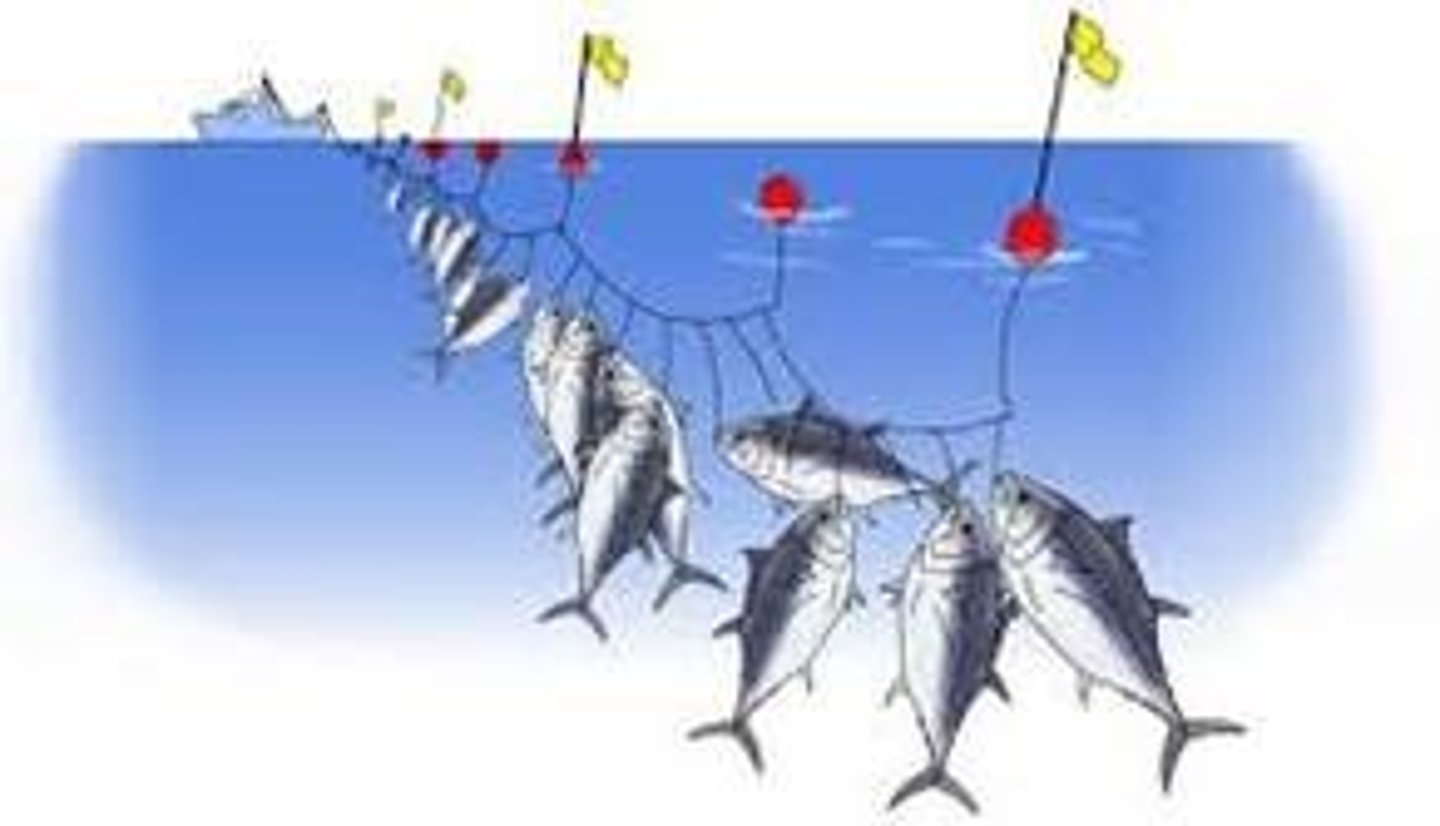
Long-line fishing
Fishing by dragging extremely long lines with baited hooks spaced along their lengths

Mass transit
Transportation system designed to move large numbers of people along fixed routes
Monoculture
the cultivation of a single crop in a given area.
Multi-use landscape
a U.S. classification used to designate lands that may be used for recreation, grazing, timber, harvesting, and mineral extraction
Nonpoint source pollution
pollution that comes from many sources rather than from a single, specific site
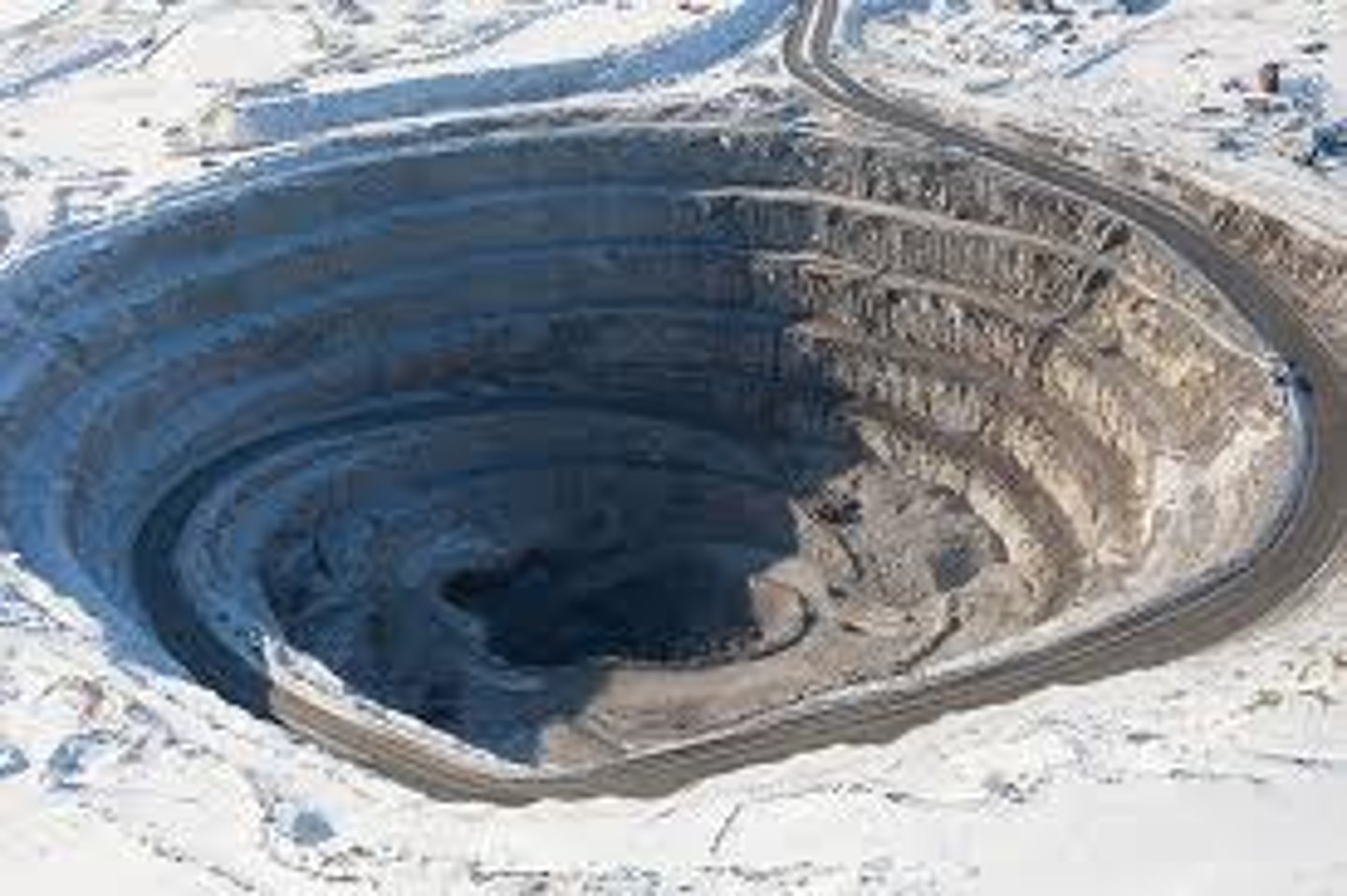
Open-pit mining
a mining technique that uses a large visible pit or hole in the ground

Ores
concentrated accumulations of minerals from which economically valuable materials can be extracted
Overburden
the rocks and Earth that is removed when mining for a commercially valuable mineral resource.
Overgrazing
Destruction of vegetation caused by too many grazing animals consuming the plants in a particular area so they cannot recover
Perennial crop
Crops that live year round and are harvested numerous times- longer, more established roots and prevention of bare soil in offseason
Pesticide treadmill
A cycle of pesticide development, followed by pest resistance, followed by new pesticide development (artificial selection of pesticide resistant pests)
Placer mining
method of extracting mineral ore by hand using simple tools like picks, shovels, and pans
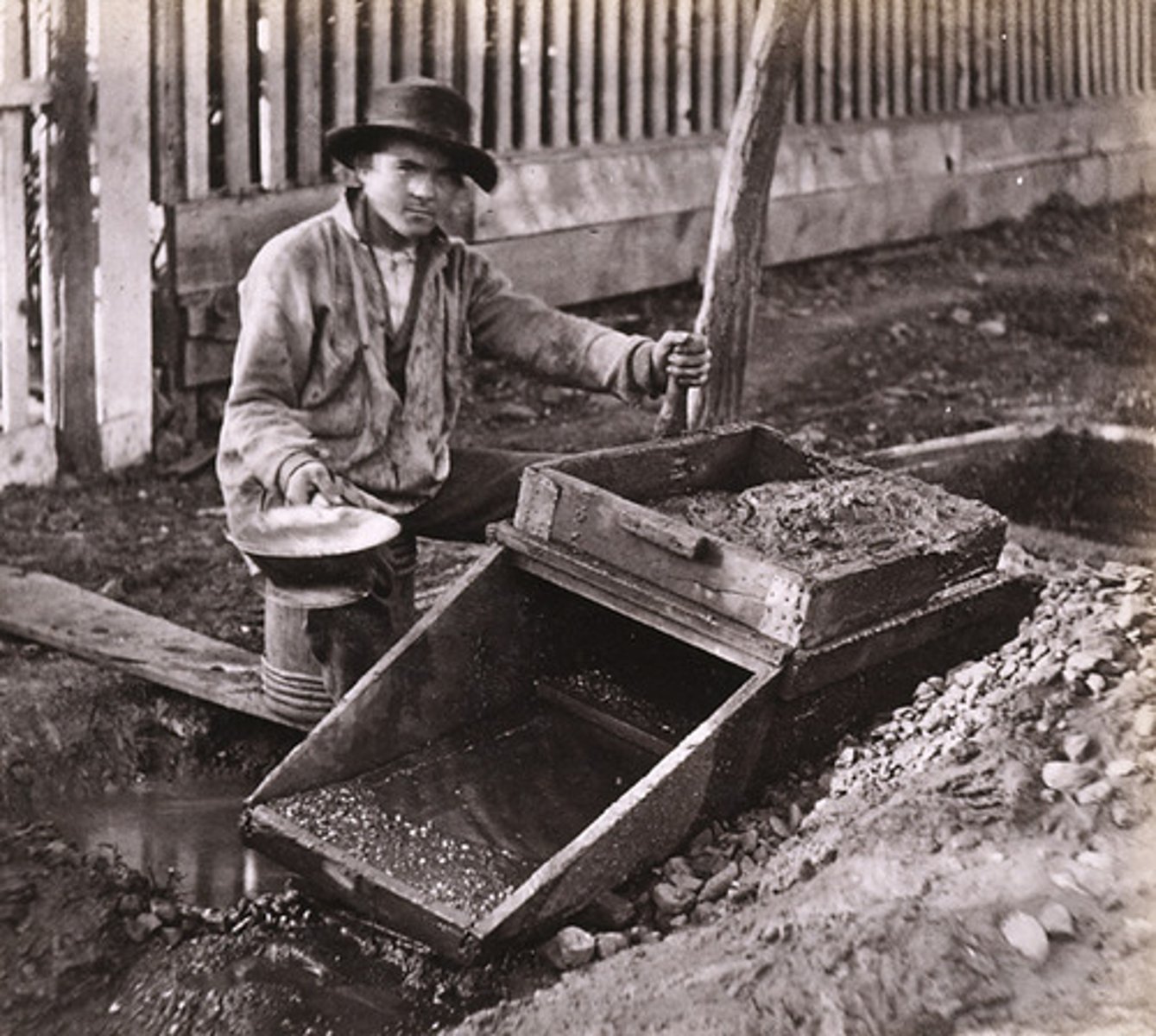

Polyculture
growing several crops on the same plot simultaneously
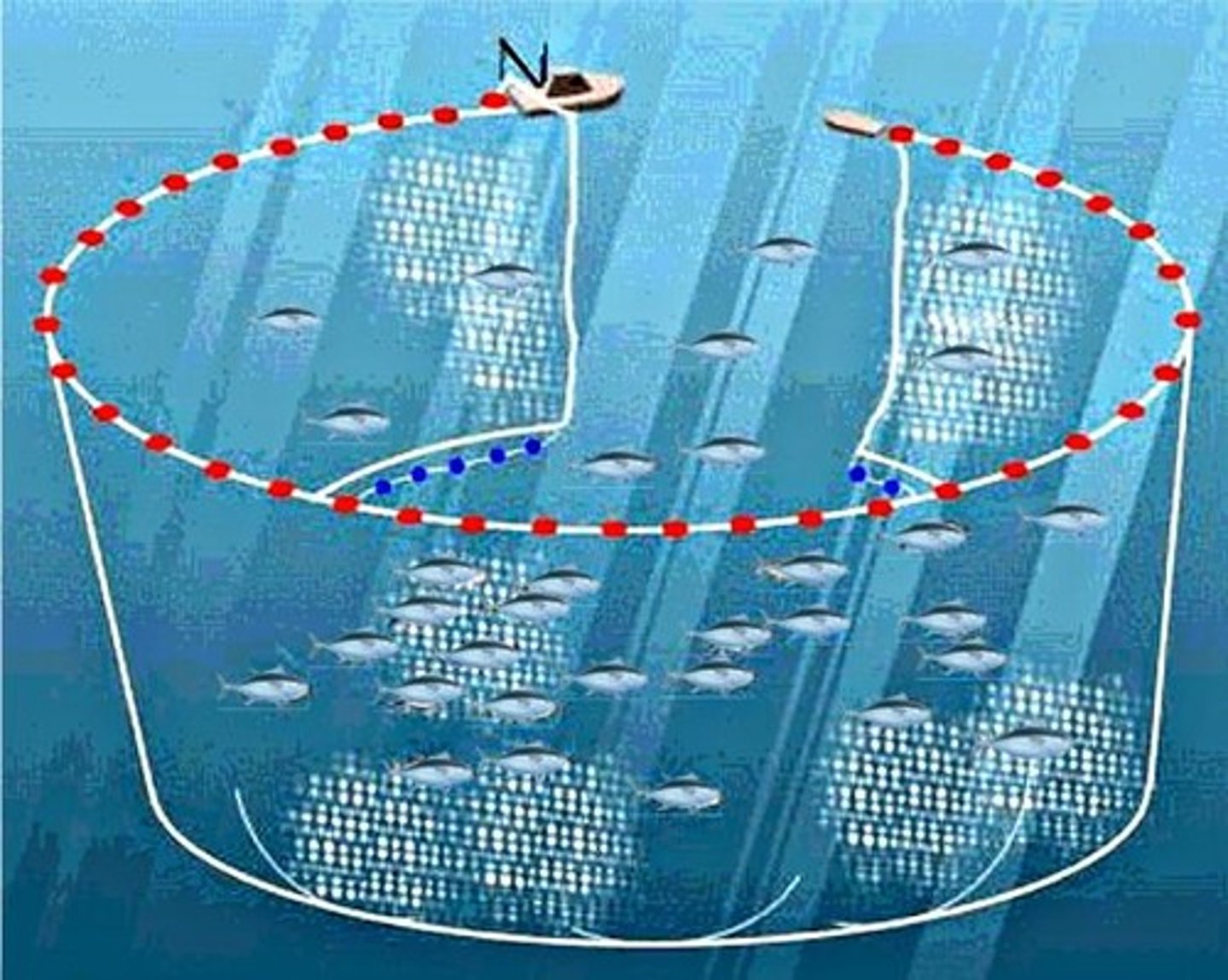
Purse seining
a large net in the shape of a purse that encloses a school of fish and closes at the bottom
Reclamation
the process of returning land to its original condition after mining is completed
Remediation
Containment, treatment or removal of contaminated groundwater. May also include containment, treatment or removal of contaminated soil above the water table.
Reserves
known quantity of a resource that can be economically recovered
Salinization
A form of soil degradation that occurs when the small amount of salts in irrigation water becomes highly concentrated on the soil surface through evaporation.
Saltwater intrusion
Movement of salt water into freshwater aquifers in coastal and inland areas as groundwater is withdrawn faster than it is recharged by precipitation.
Selective/Strip cutting
only cutting some of the trees in an area (biggest and oldest) to preserve habitat (biodiversity) and topsoil
Single-use zoning
Government designation of specific areas for residential, business and commercial use, causing separations between where people live and where they work.
Spoils
Unwanted rock and other waste materials produced when a material is removed from the earth's surface or subsurface by mining, dredging, quarrying, and excavation.
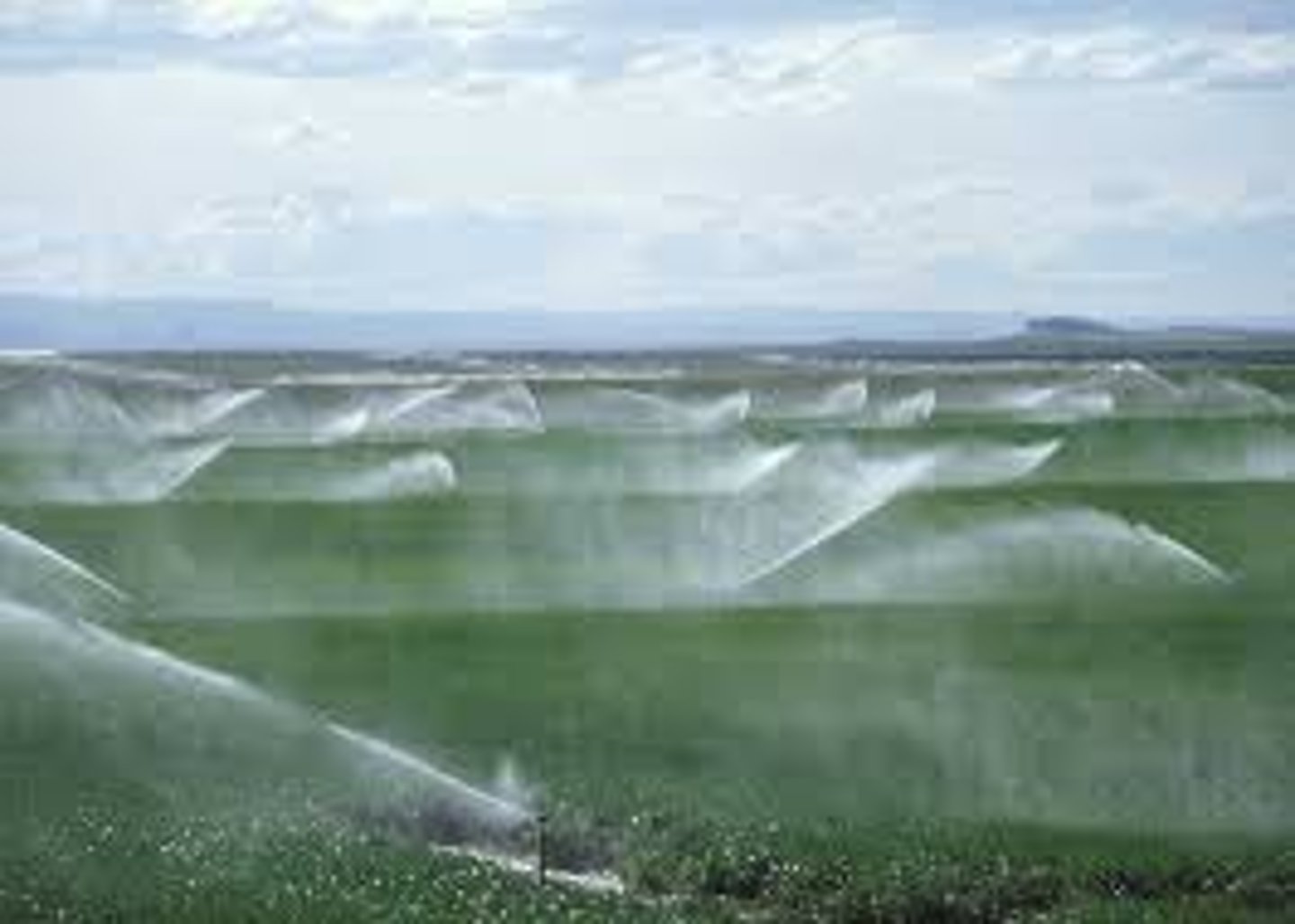
Spray irrigation
expensive and energy-consuming; 75-95% efficient; water is pumped from a well into an apparatus that contains a series of spray nozzles that spray water across the field

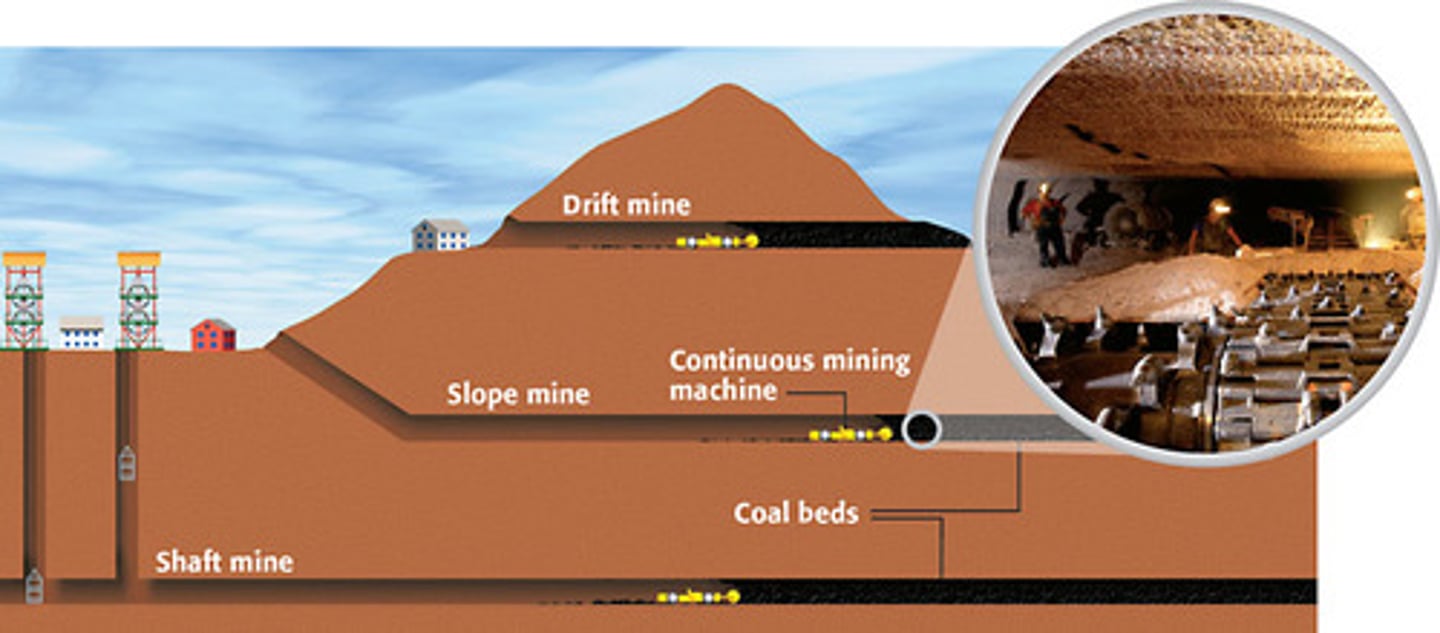
Strip mining
A process whereby miners strip away at the surface of the earth to lay bare the mineral deposits

Subsurface mining
The extraction of mineral and energy resources from deep underground deposits.
Tailings/Slag
leftover waste material separated from the valuable metal or mineral within ore
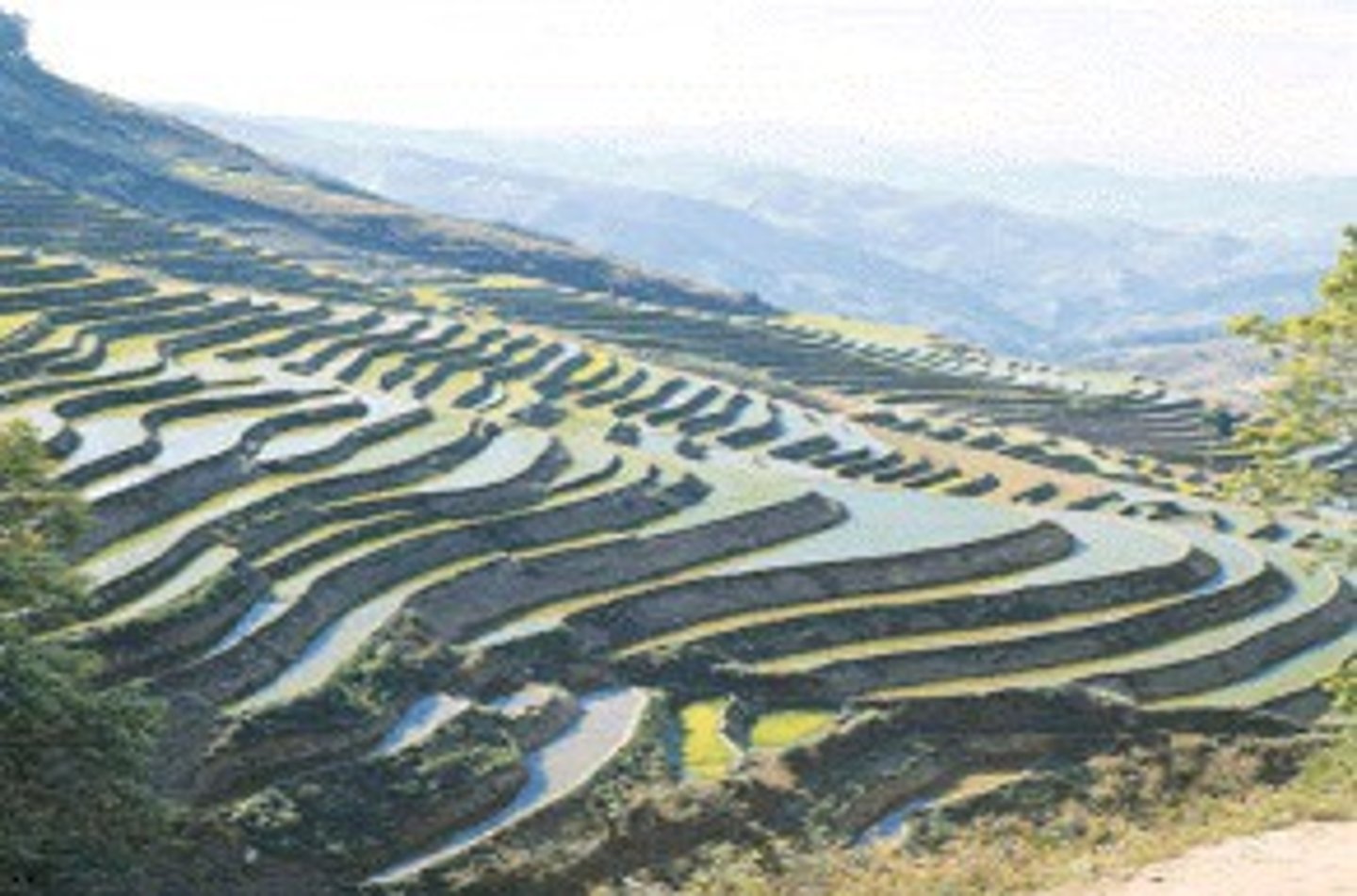
Terracing
Carving small, flat plots of land from hillsides to use for farming

Timber vs. Lumber
timber when it is first cut down; lumber after it is shaped in any way
Tragedy of the Commons
situation in which people acting individually and in their own interest use up commonly available but limited resources, creating disaster for the entire community
Transpiration
Evaporation of water from the leaves of a plant
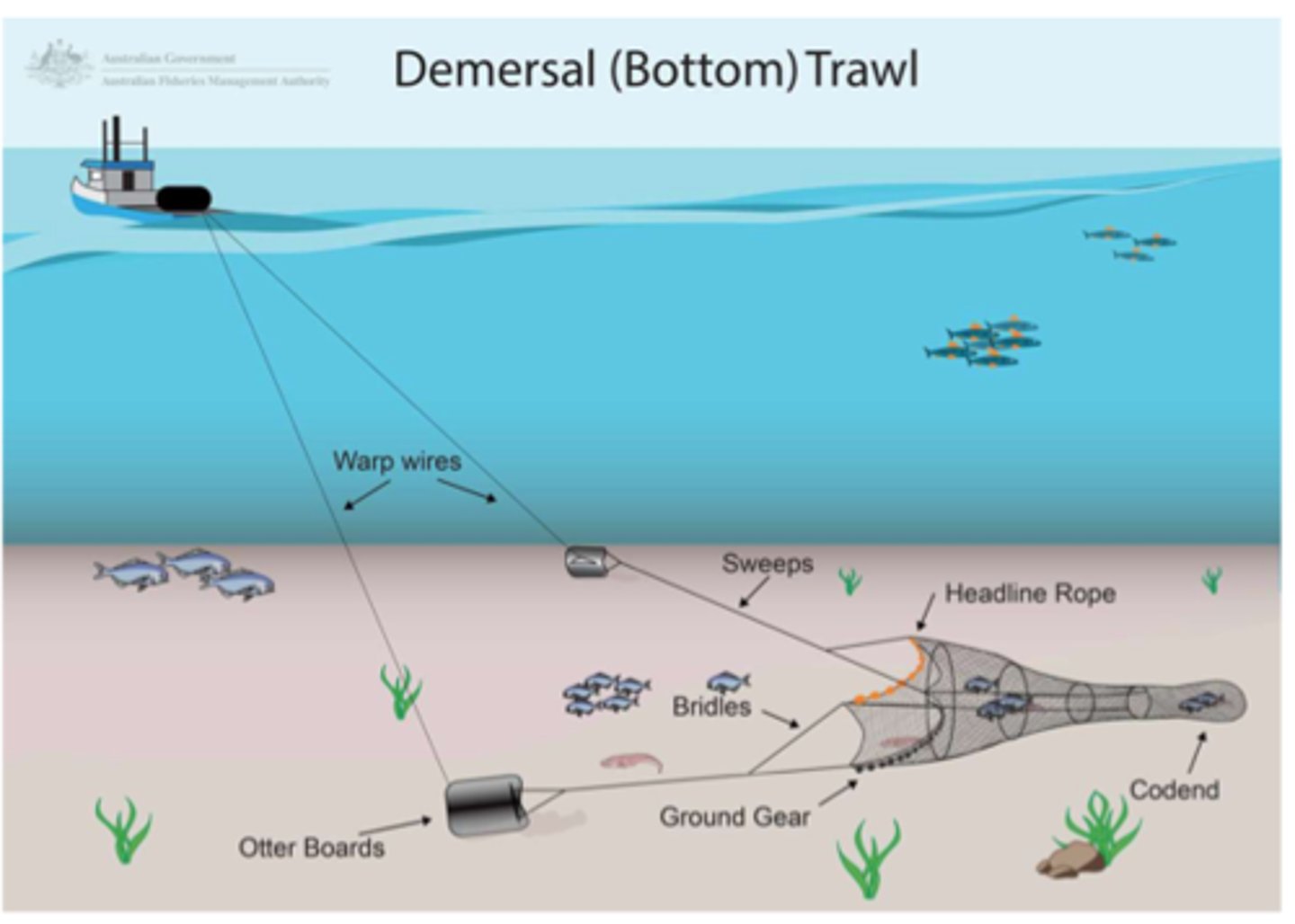
Trawling (bottom)
Especially harmful fishing method that involves dragging a large net along ocean floor- stirs up sediment (turbidity), destroys coral reef structure and large amount of bycatch
Turbidity
A measure of how clear water is.
Urban planning
A plan or thought for the design of a city
Urban sprawl
The process of urban areas expanding outwards, usually in the form of suburbs, and developing over fertile agricultural land.
Urbanization
An increase in the percentage and in the number of people living in urban settlements.
Waterlogging
water saturation of soil that fills all air spaces and causes plant roots to die from lack of oxygen; a result of over irrigation
Wind breaks
Rows of trees or tall shrubs which slow down the movement of wind across a field
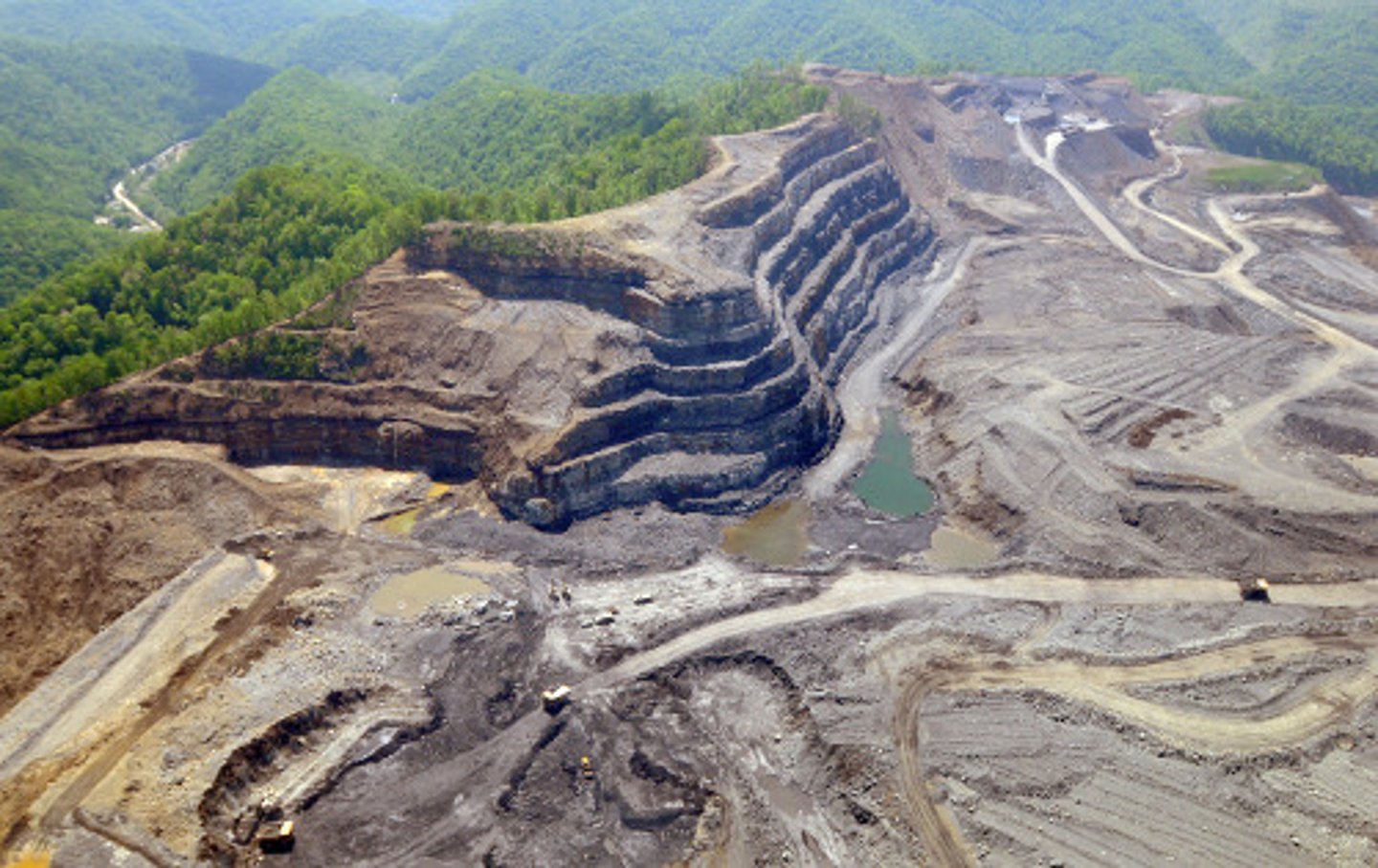
mountain top removal
a mining technique in which the entire top of a mountain is removed with explosives

Confined and unconfined aquifers
Confined - An aquifer that is separated from Earth's surface by materials with low permeability above and below it.
Unconfined - An aquifer where the water-bearing unit is unrestricted to Earth's surface and atmosphere