geography: rivers
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What is a tributary?
a river or stream flowing into a larger river or lake.
what is a drainage basin?
an area of land drained by a single river
what is a watershed?
an area or ridge of land that separates waters flowing to different rivers, basins, or seas.
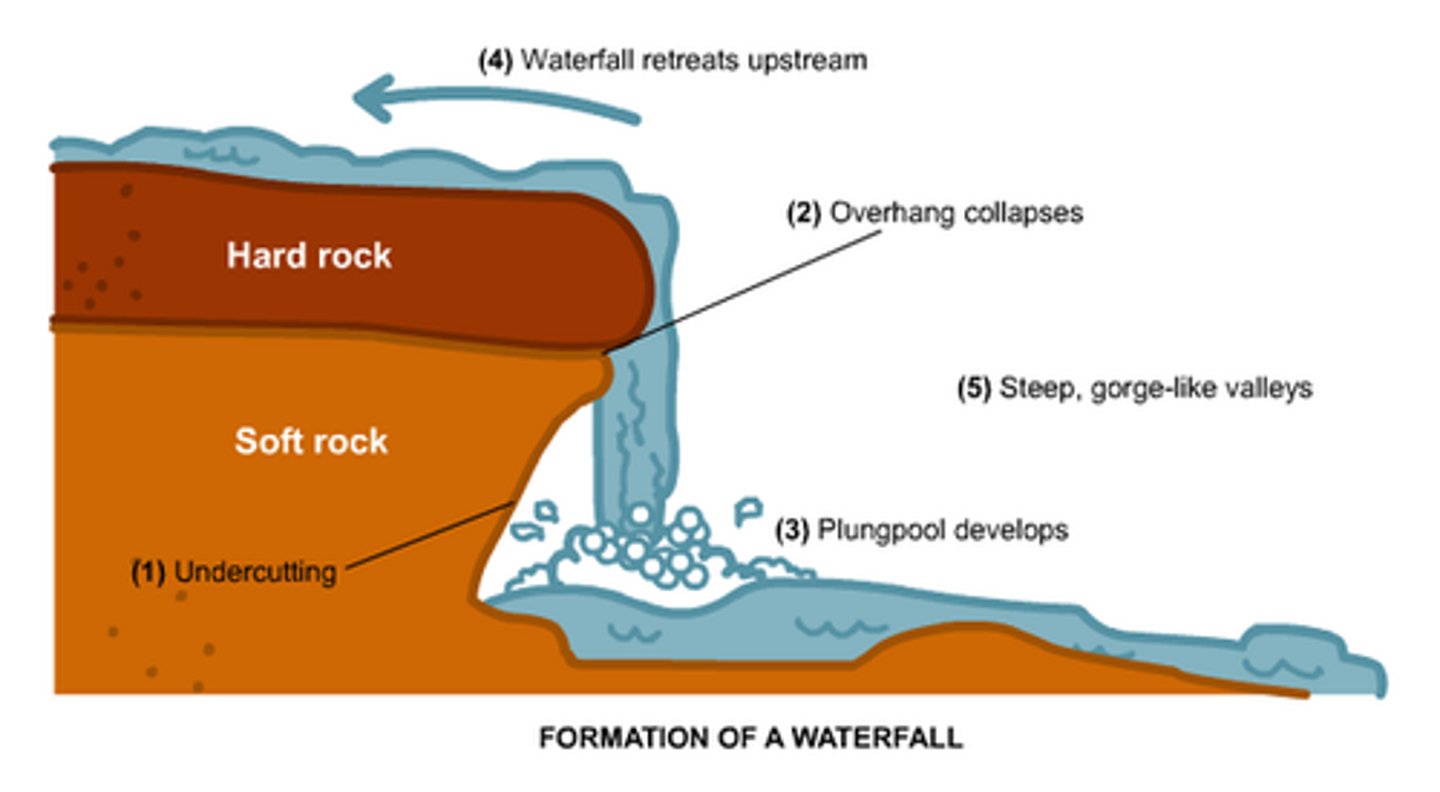
How are waterfalls formed?
waterfalls form over bands of hard and soft rock. The soft rock erodes more quickly that hard rock by hydraulic action and abrasion. This creates a plunge pool where water is swirled around. Any rocks/debris are swept into the plunge pool by abrasion deepening it further.
overtime the soft rock is eroded further crating an overhang of hard rock and because it isn't supported, it eventually collapses. The water then retreats back upstream. This leaves behind a steep-sided river valley- gorge
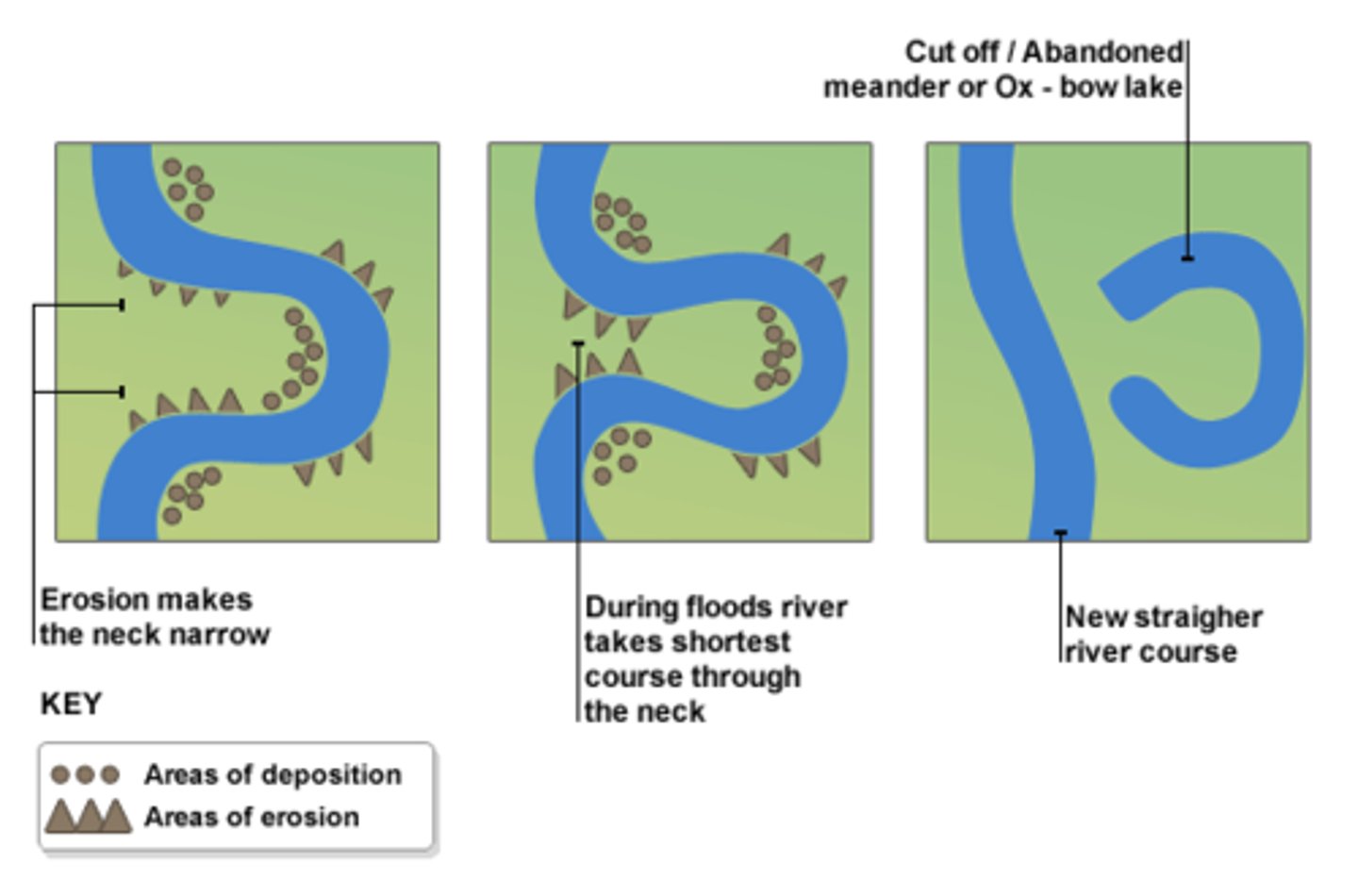
How is an oxbow lake formed?
1)meander forms
2) erosion i.e. hydraulic causes the neck/ outside bend to get get closer together
3)The neck eventually breaks usually due to a flood and so the river flows along the shortest course.
4)Deposition eventually cuts of the meander forming an oxbow lake
What are flood plains?
low-lying flat areas of land that flood, when a river floods onto a floodplain the water slows down and deposits the eroded material that it's transporting. This builds the flood plain.
Meanders may migrate across the flood plain making it wider
deposition that happens on slip of slopes of meanders also builds up the flood plain
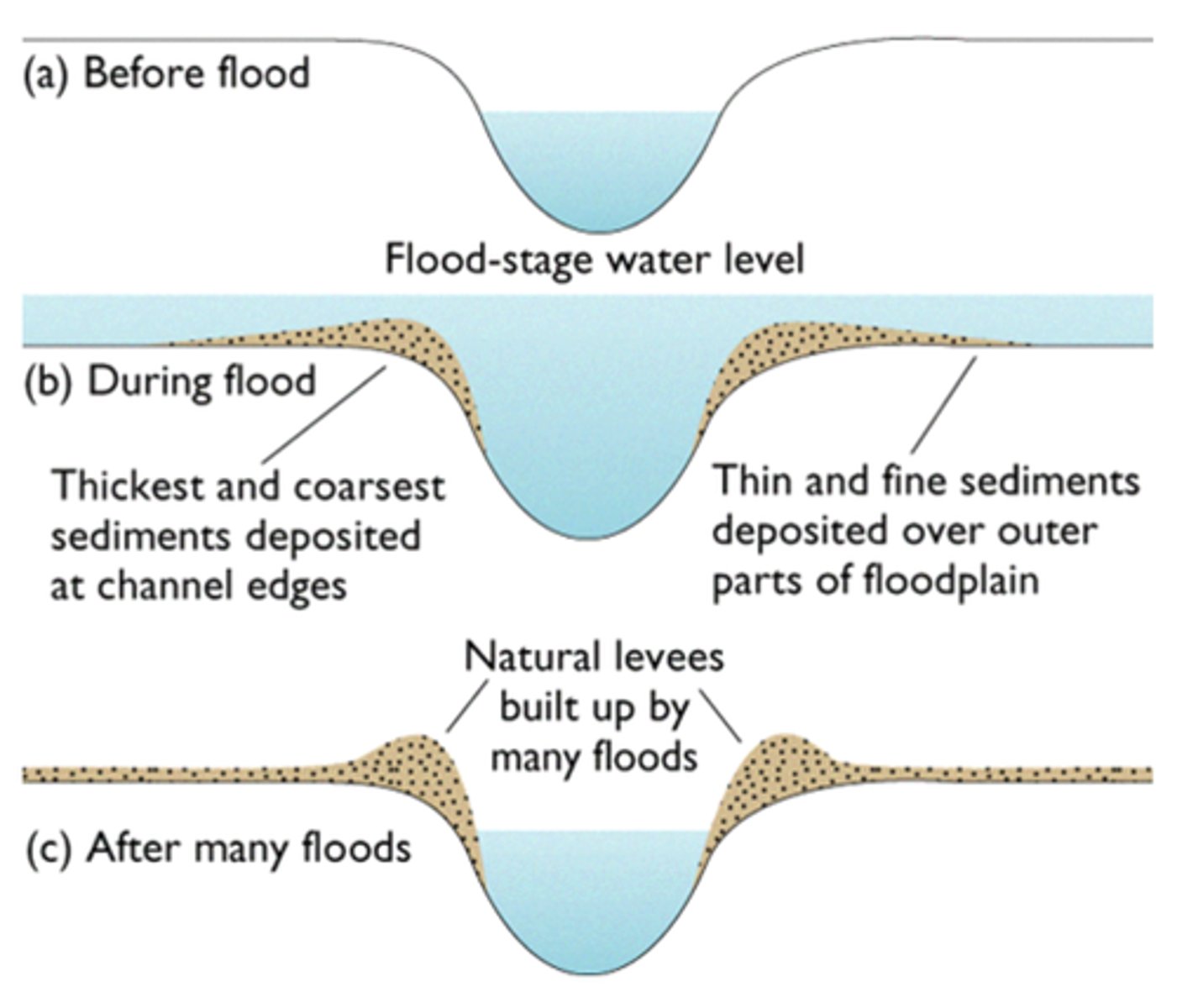
What is a Levees?
a natural embankment along the edges of a river channel
during a flood eroded material is deposited over the whole flood plain, the heaviest material is deposited closest tot he river channel bc it gets dropped first when the river slows down, overtime deposited material builds up creating levees along edges of the channel
what are the physical causes of flooding?
-the rate and volume of precipitation falling,
If there is a storm and large amount of rainfall in a short amount of time the amount of water running into the river increases so increased risk of flash flooding.
-the topography
the shape of land determines how quickly rainwater flows into the river, steep hills with high gradients are more likely to have flash floods than gradual gradients
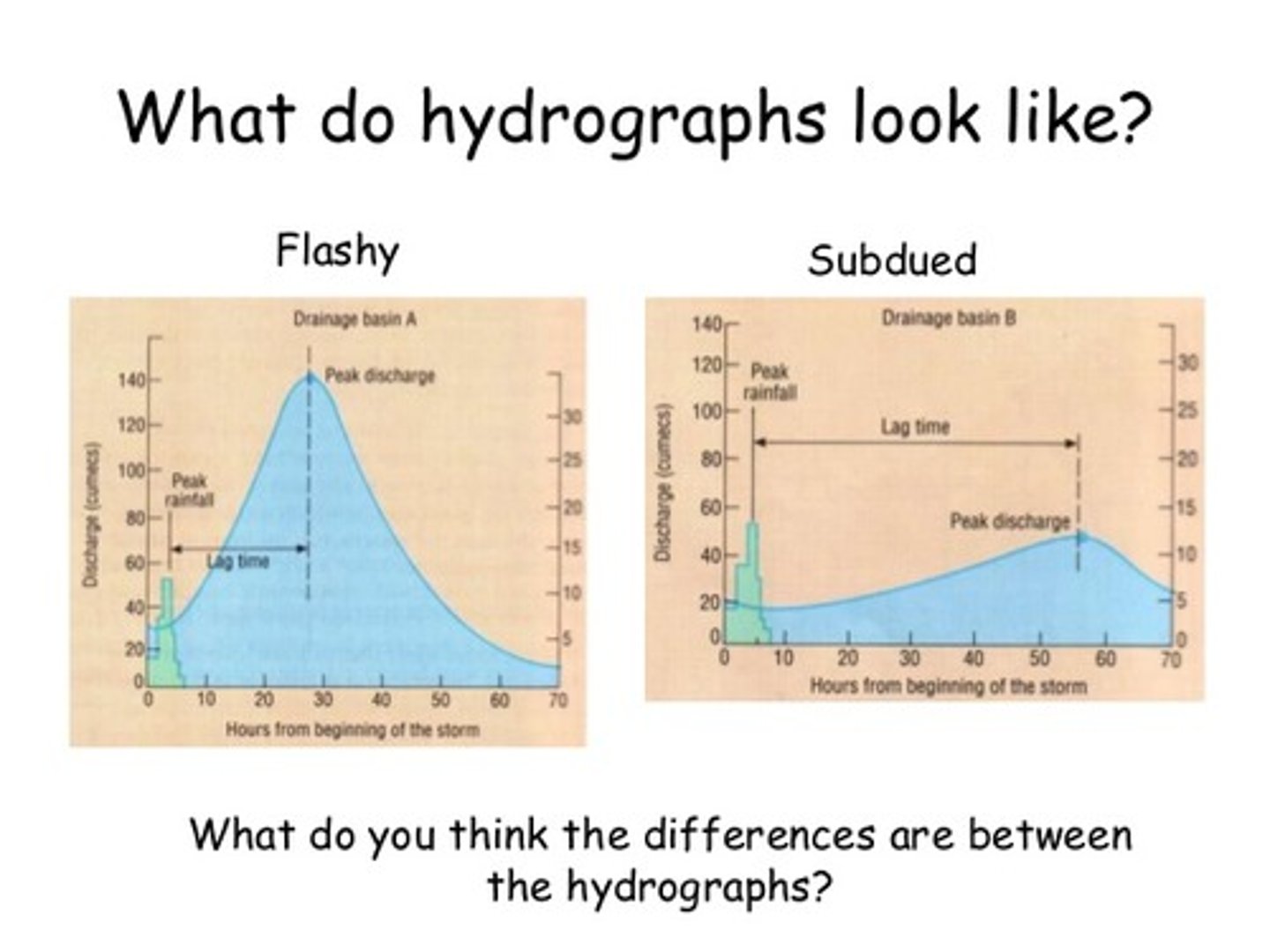
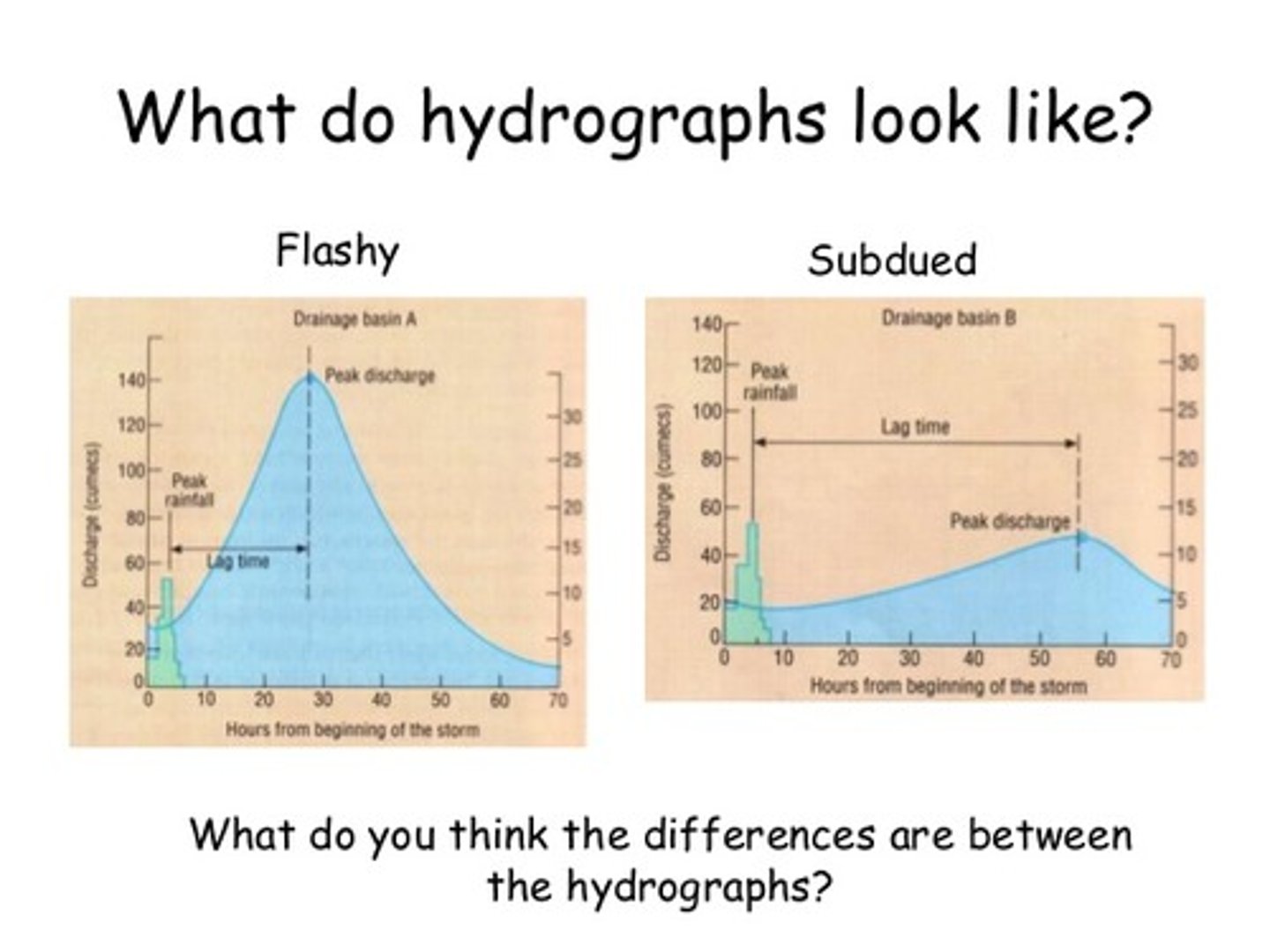
what does a flashy hydrograph look like?
short lag time, high peak discharge
what are hard engineering strategies for river management?
dams and reservoirs, channel straightening, embankments flood relief channels
what is a cross profile?
The side to side cross-section of a river channel and/or valley
what is a long profile?
the gradient of a river, from its source to its mouth
what is lateral erosion?
Sideways erosion by a river on the outside of a meander channel. It eventually leads to the widening of the valley and contributes to the formation of the flood plain.
what is vertical erosion?
Downward erosion of a river bed.
what is confluence?
The point at which two rivers meet
What is a source?
The start of a river
what is the mouth?
Where the river meets the sea
what are the long and cross profile of a typical river?
upper valley- vertical erosion, hydraulic action, abrasion, traction, saltation, v shaped valley
middle- channel deeper and wider, more lateral erosion and deposition, suspension
lower- channel and its deepest, deposition,
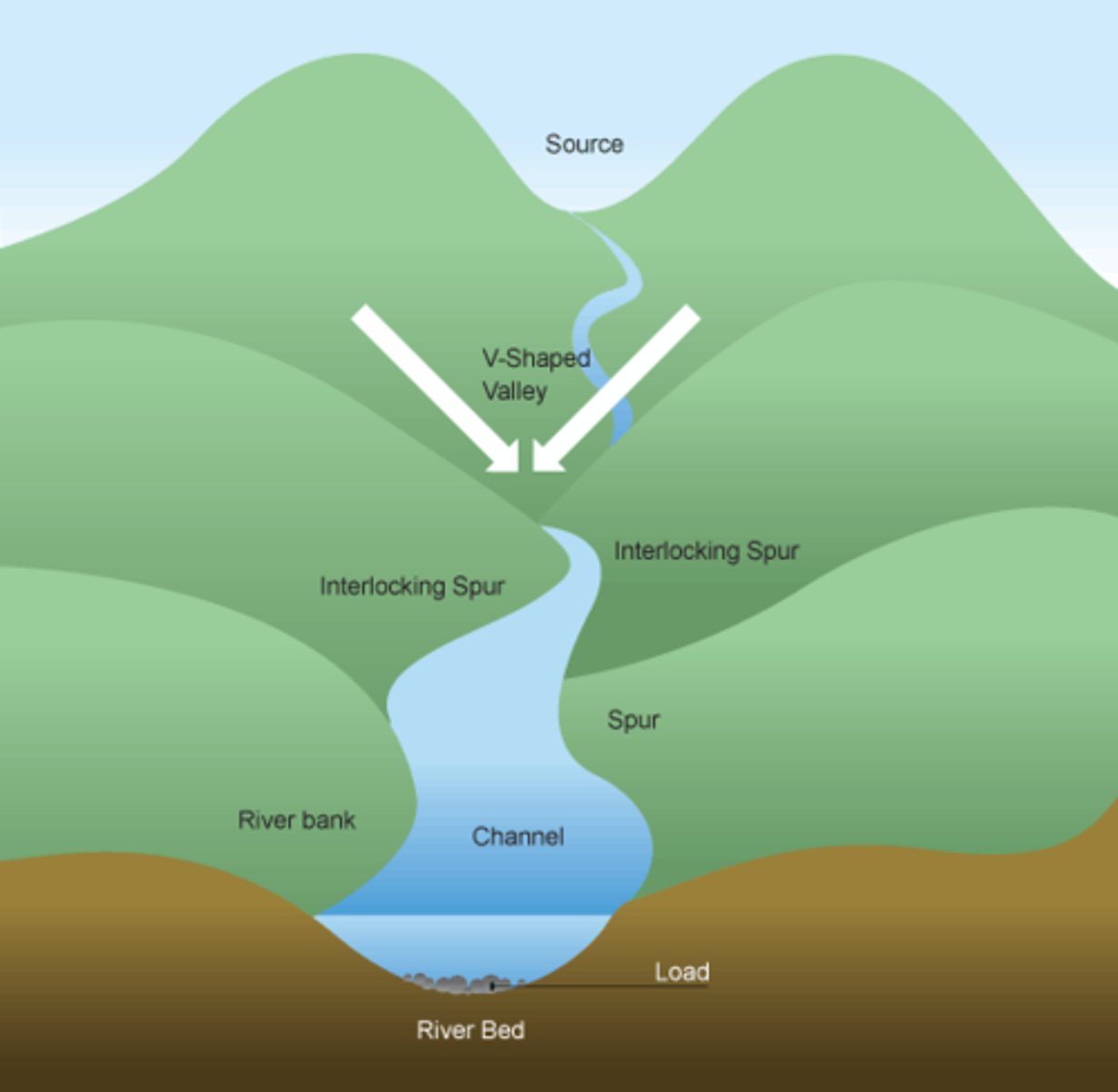
What are interlocking spurs?
In the upper course of river there is more vertical erosion. The river cuts down the valley, the water doesn't have enough energy to erode the resistant rocks, creating interlocking spurs. The river is taking the easiest route downstream.
Why do rivers deposit material?
1) volume of water in the river falls
2) amount of eroded material in water increases
3) water is shallower e.g. inside bend
4)the river reaches is mouth
What is attrition?
When rocks bang against each other and break, creating smooth, round rocks.
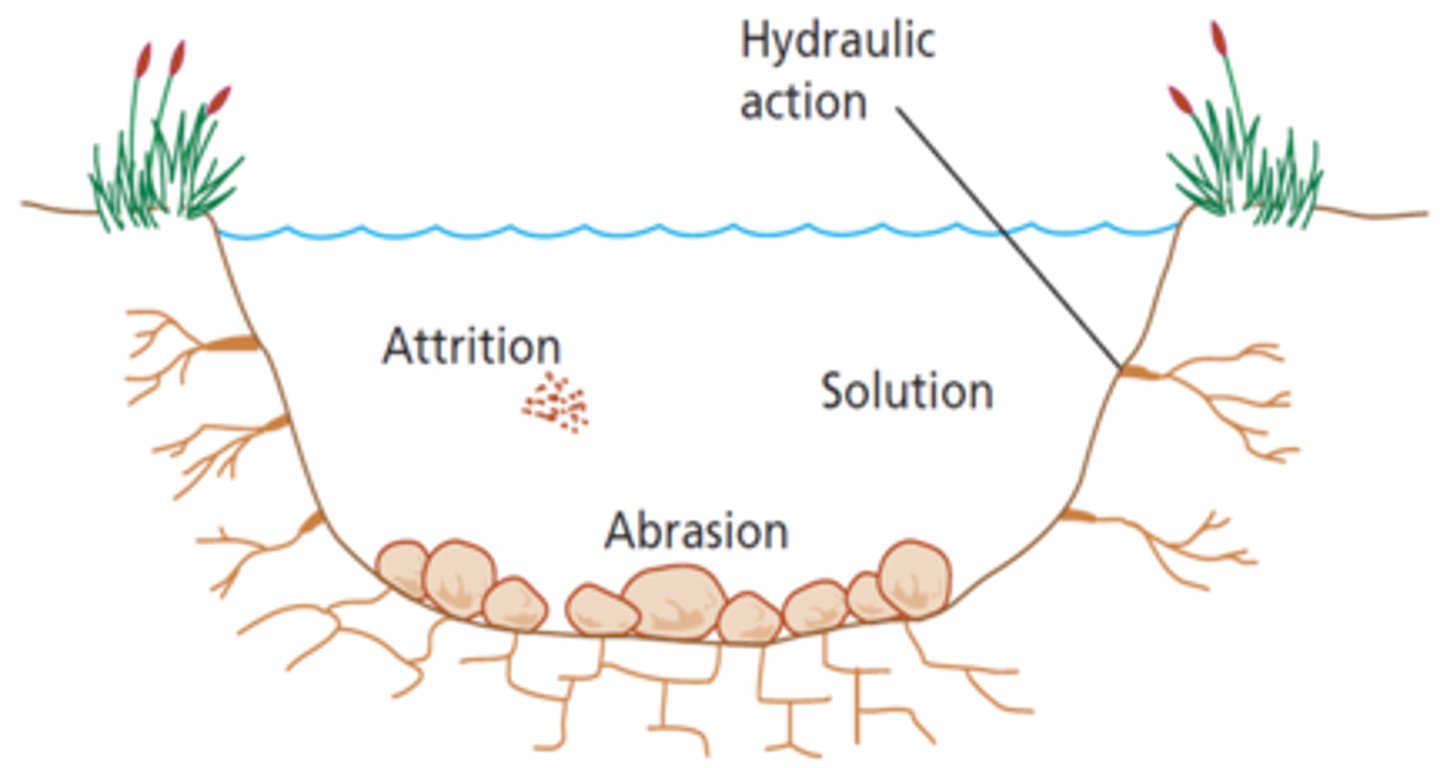
What is abrasion?
Waves smash rocks and pebbles on the shore onto a rock/cliff face, and they break and become smoother.
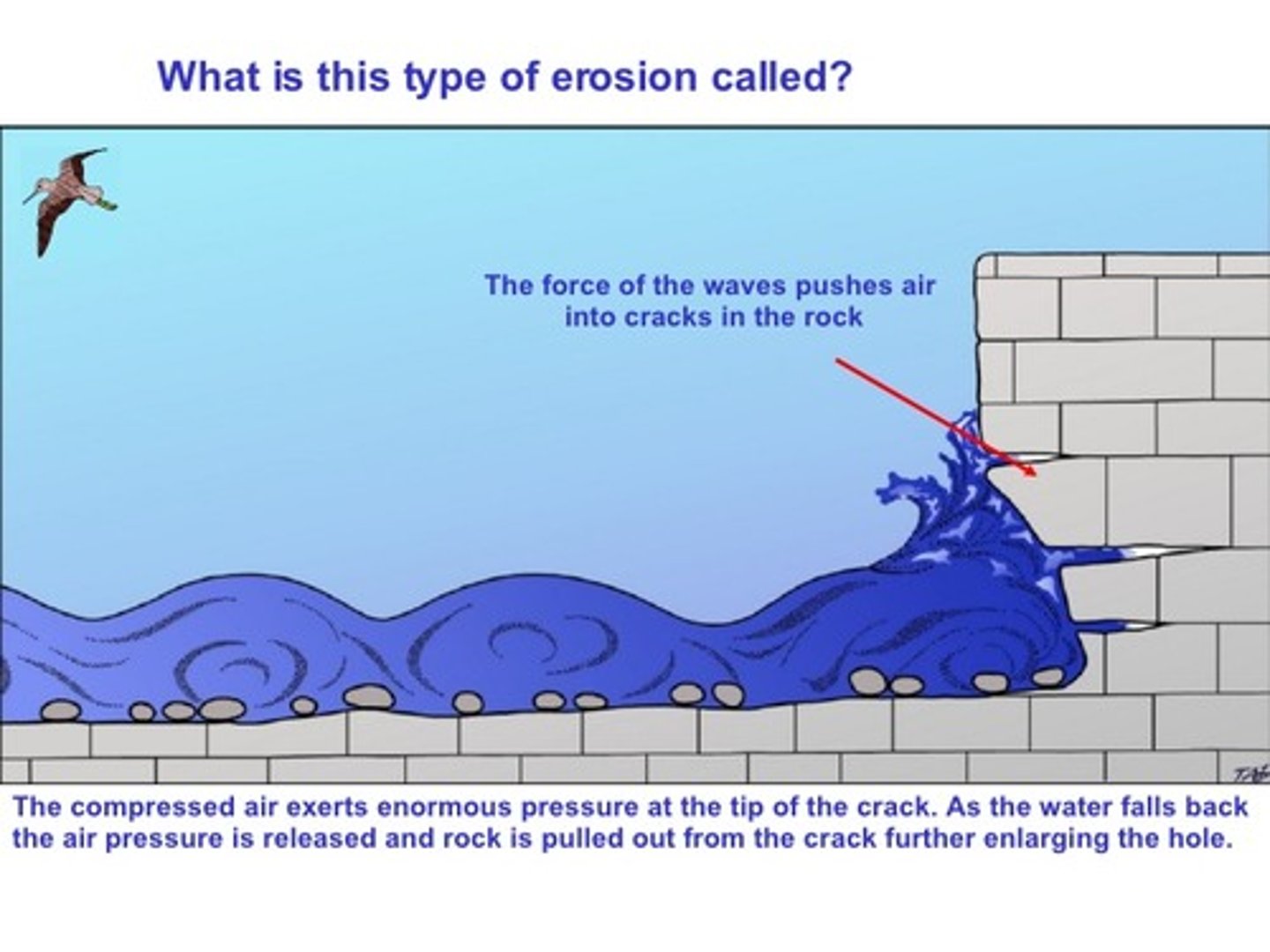
What is hydraulic action?
as a wave crashes onto a rock/cliff face air is forced into cracks within the rock. The high pressure causes the cracks to force apart and widen, when the wave retreats air expands. Over time this causes the rock to fracture
What is traction?
Large material/rocks are rolled along the sea floor by waves
What is saltation?
the bouncing of slightly lighter material across the sea floor
What is suspension?
Small particles of material carried along by the water

What is solution?
material dissolved and carried by water
What do you need to remember to answer a waterfall question?
Gorge
Overhang
Soft
Hard
Hydraulic action
Erosion
Abrasion
Plunge pool
What is a meander?
A large bend in the middle course of a river
How is a meander formed?
1) the current/ flow of water is faster on the outside bend bc the river channel is deeper (there is less friction to slow the water down)
2) Therefore, erosion- hydraulic + abrasion take place on the outside bend
3) the current on inside bend has less energy to carry sediment so deposits it on inside bend - called slip of slope
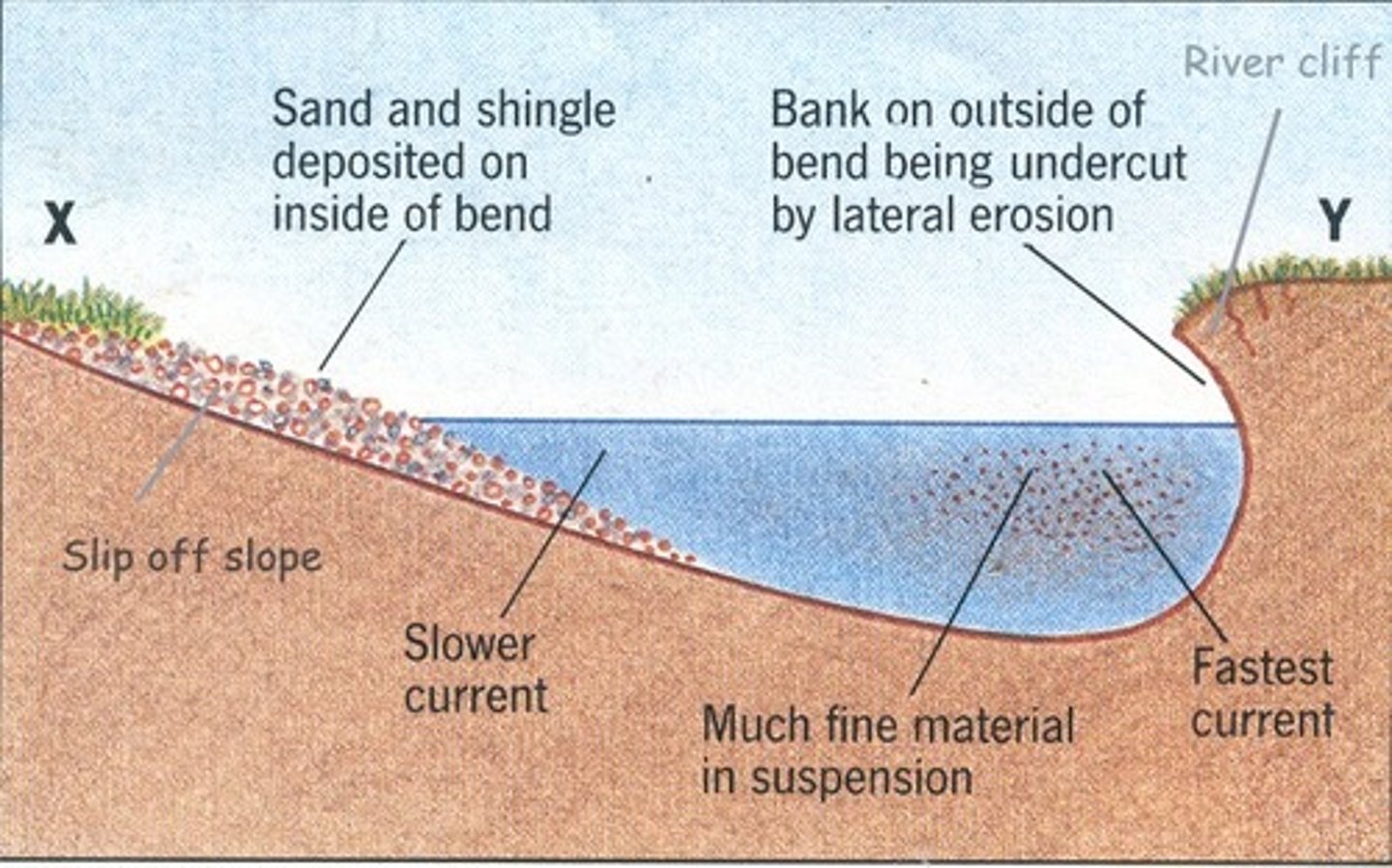
What is an estuary?
found at the mouth of a river where it meets the sea, the water here is tidal (river level rises and falls each day), water floods over the banks of the river carrying the silt and sand onto the valley floor, as the tide reaches its highest point, the water is moving very slowly so the sediment is deposited, this builds up creating mudflat. At low tide these mudflats are exposed
Where is the River Tees located?
North East England
what are the features of the UK River Tees?
waterfall, meanders
What has been done at the river tees for flood management?
concrete walls w metal flood gates, embankment, improved flood warning system
What to close contour lines suggest?
the land is steep and could be the higher course of a river
what are the human causes of flooding?
-Urbanisation
increasing the the amount of impermeable surfaces decreases the time take for water to flow in the river
-Deforestation
trees intercept rain and so it takes longer for the rain to travel through the leaves into the river. Therefore, cutting down trees will speed up the time taken for rainwater to flow into the river, increasing, the risk of flash flooding
what are the factors that affect the shape of a hydrograph?
1)rainfall intensity, relief
2)drainage density, basin size
3)land use, rock type
4)rock type
what are the factors that determine a flashy hydrograph that lead to rapid water flow?
impermeable rock
saturated soil
steep slopes
urbanisation
small basins
heavy rain exceeding infiltration, high density speeds
what are the factors that determine a long/flat hydrograph that lead to rapid water flow?
permeable rock
gentle slopes
rural area
light rain
large basin
dry soil
low density
what does a long/flat hydrograph look like?
longer lag time, low peak discharge
what are soft engineering strategies for river management?
flood warning and preparation, flood plain zoning, planting trees, planting trees, river restoration
What is a dam and reservoir?
walls built across river and a reservoir is formed behind the damn
:) store water reducing flood risk, can be used to power HEP
:( expensive, when built can flood large area of land
What is river straightening?
river course is straightened- meanders cut-off by building artificial straight channels
:) water moves out of area more quickly as water doesnt travel as far-reducing risk of flooding
:( flooding may happen downstream instead and erosion as water is carried faster
What is an embankment?
raised walls built along the river banks
:) river can hold more water so floods less frequently, protecting buildings from flood plain
:( expensive, risk of flooding of they break
How does flood warning and preparation work?
warning people through TV, internet, news and modifying building to reduce damage and making plans
:) impacts reduced- people have to prepare
:( doesnt guarantee safety, flood is not stopped
What is flood plain zoning?
Restricts different land uses to certain locations on the floodplain.
:) risk reduced- as no impermeable surface, no building will be damaged
:( no use if area been built on
How does planting trees work?
increases lag time and interception of rainfall
:) flood risk reduced and soil erosion reduced
:( less land available for farming
What is river discharge?
how much water (volume) that is travelling past a certain point at a specific time