Lecture 21: Intro to Nuclear Medicine and Radioactivity Review
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What imaging modalities are included in nuclear medicine?
PET and SPECT
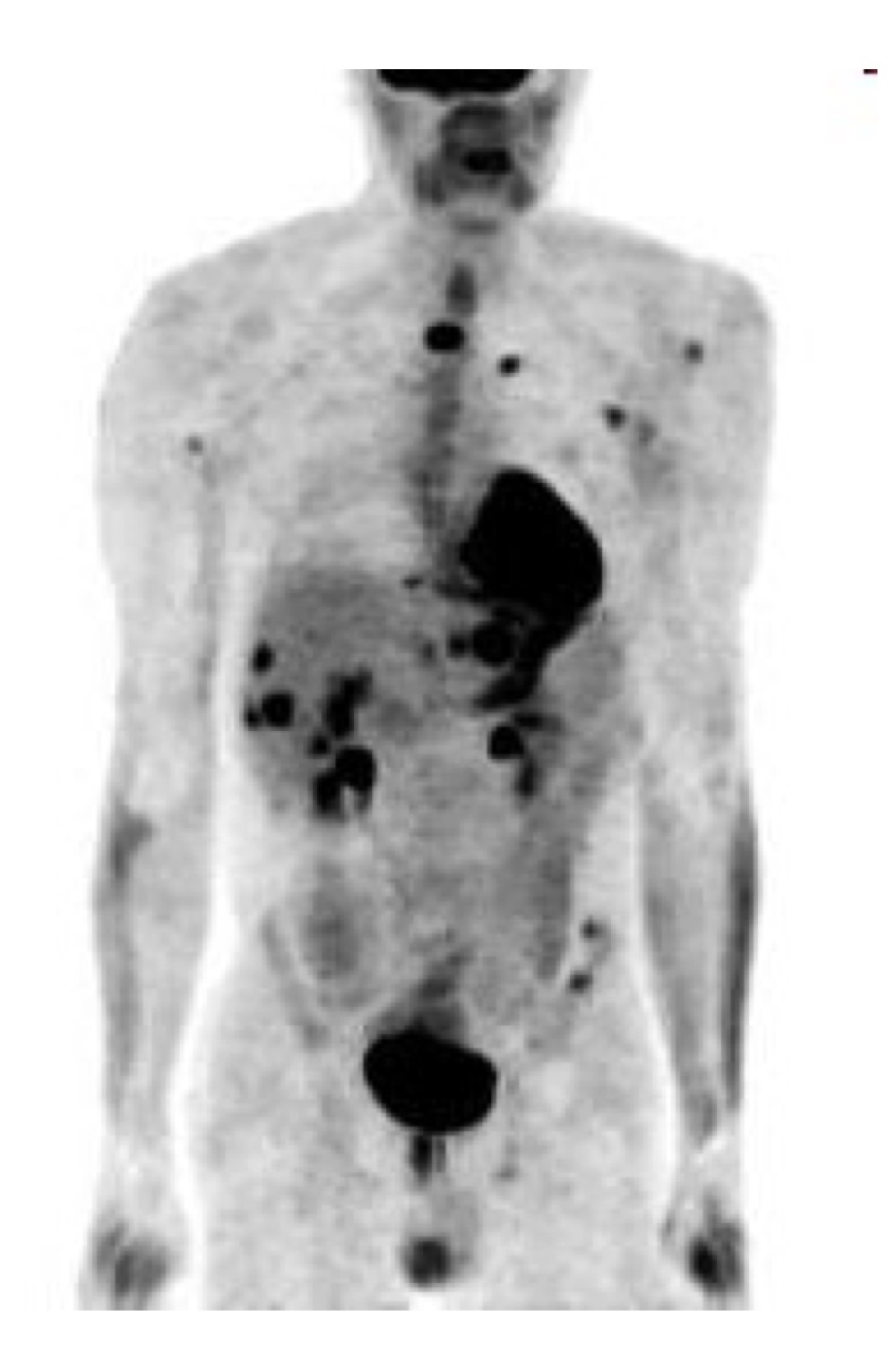
What modality was used to take this image?
PET or SPECT; there is little anatomical detail and there shows uptake of radiotracer
Where does the signal comes from for PET and SPECT?
source of signal comes from the radiotracer
Why is PET and SPECT used?
highlights functionality and uptake of specific chemicals
What PET tracer is mostly commonly used?
[18F]FDG
Why is glucose significant?
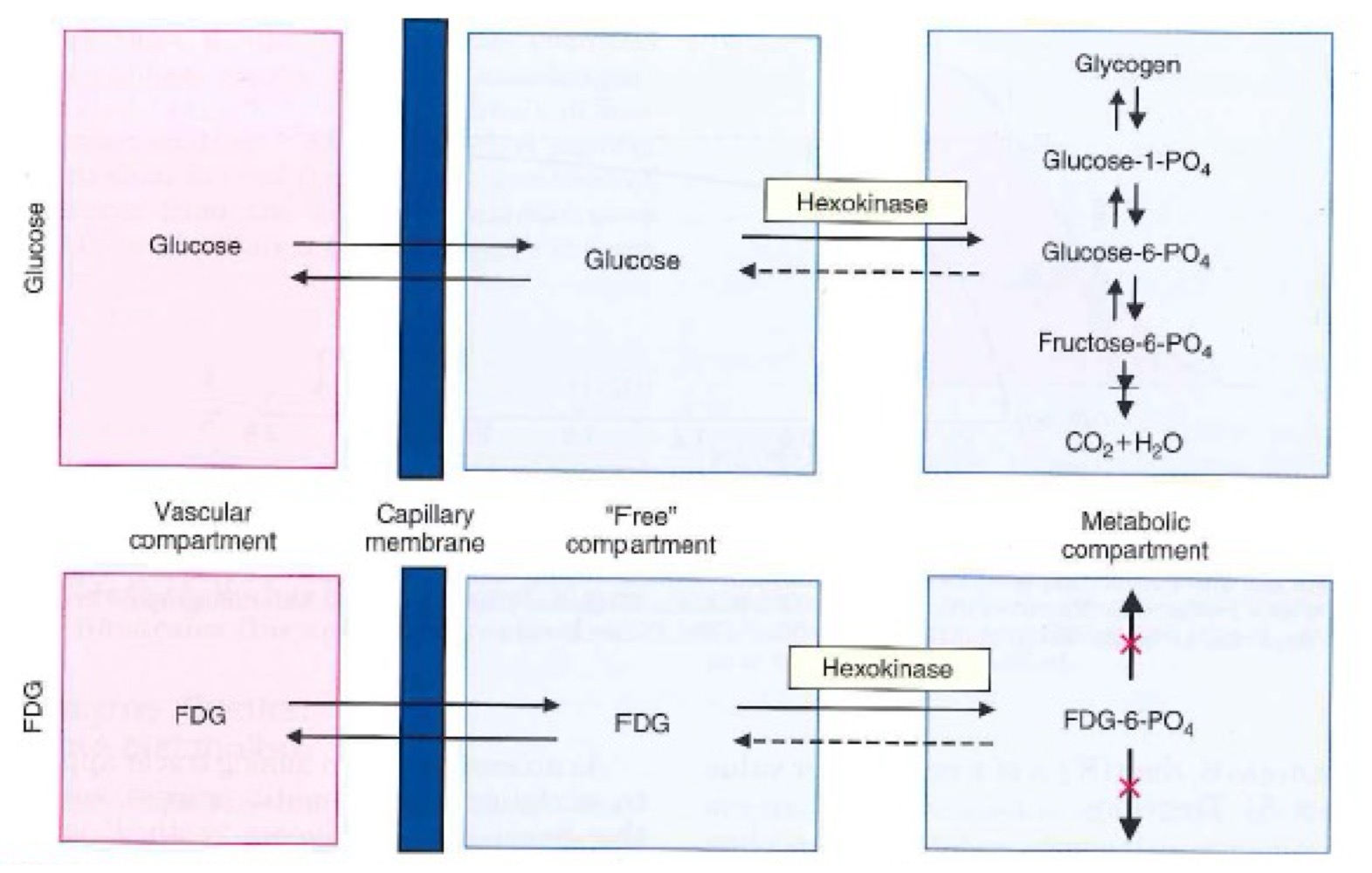
Why does [18F]FDG get trapped in cells unlike glucose?
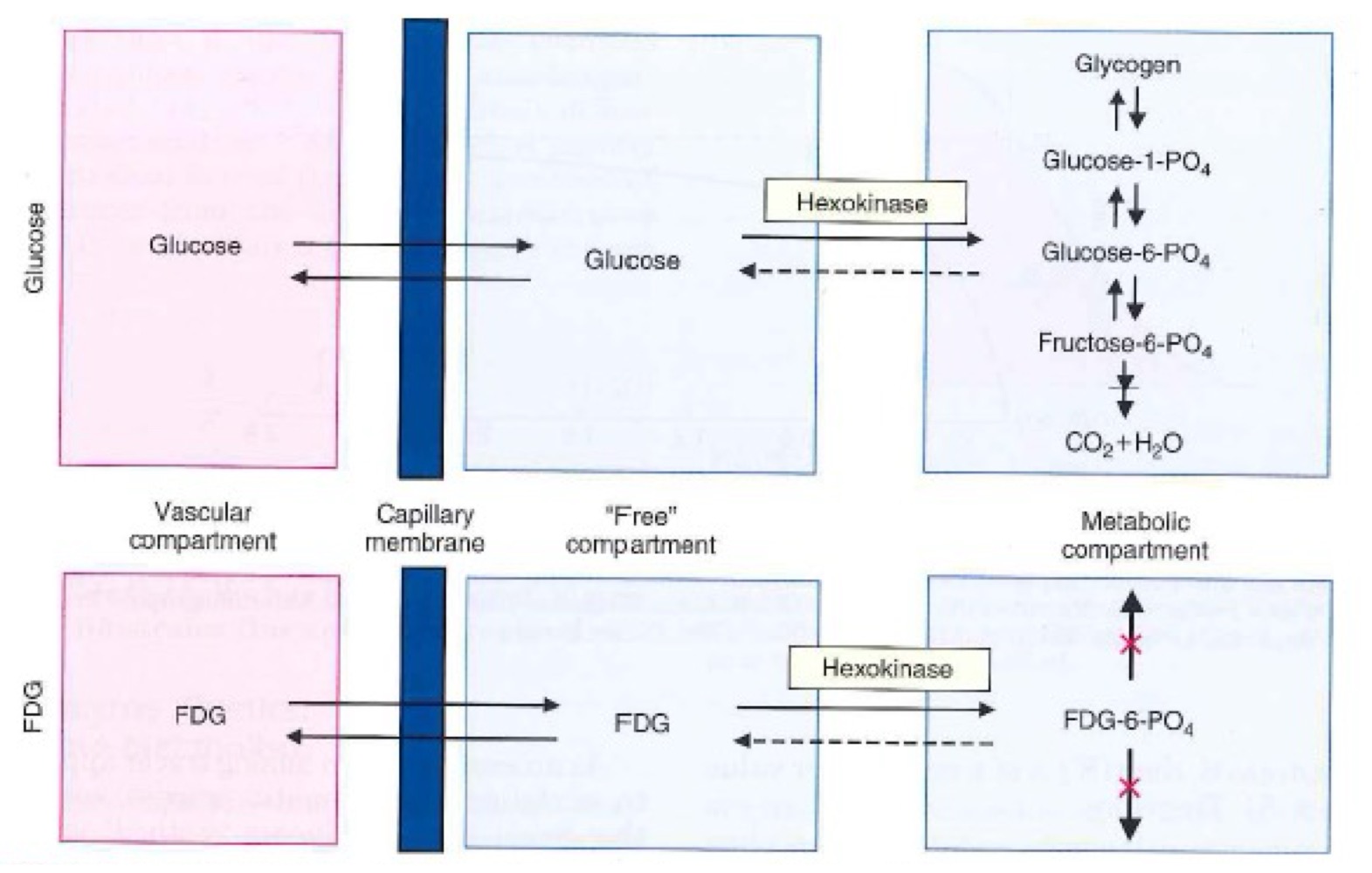
Why does the brain light up with [18F]FDG?
the brain is a highly glucose metabolizing organ
How much dose is generally received from PET and SPECT?
When was Tc-99m discovered?
1938
What is considered the golden age of nuclear medicine?
1930s
When did Tc-99m start being used for imaging?
1964
Why was the development of PET imaging a long process?
There needs to FDA approval for the scanner AND the radiophamaceutical
What is the benefit of a whole-body PET scan?
higher sensitivity leads to less radiotracer injected leading to less dose
Why is eV used over the joule?
we are working with really itty bitty energies
What is an AMU?
one twelfth of a C-12 atom (1 AMU = 1 g/mol)
A container contains approximately 18 grams of water. How many moles of water does the container contain?
~ 1 mol
How many atoms are in 1 mole?
6.022 × 10²³
How is molarity defined?
the amount of moles in a compound or element per liter of solution
ppm
1 part of substance per 10^6 parts solution
Molar Activity
amount of activity per amount of radiopharmaceutical (MBq/nmol)
How is mass and energy related?
E=mc²
How many MeV/c² per u?
931.464 MeV/c²
What is the rest mass of an electron?
511 keV/c²
How is the binding energy (or mass deficiency) calculated?
total mass of atom minus the mass of individual constituents
Why does the binding energy per nucleon matter?
The bigger the ratio, the more stable an atom is
isotope
same proton number
isotone
same number of neutrons
isobar
same number of A (protons+neutrons)
isomer
excited nuclear state of a specific nuclide
Is β- emitters above or below the line of stability?
below
Are EC/β+ emitters below or above the line of stability?
Above
Beta decays result in nuclides that are iso (topes, tones, or bars)?
isobars
Mass excess
Δ = (m-A)c²
What is the mass excess for C-12?
0 MeV
Q-value
mass before - mass after
Do exergonic or endergonic reactions have a negative Q-value?
endergonic
What is the Q-value for β- decay?
Q = [m(parent)-m(daughter)]c²
Q-value for positron decay
Q = [m(parent)-m(daughter)-2me]c²
Q-value for electron capture?
Q = [m(parent)-m(daughter)]c² - EB