ANTH 100L: The Vertebral Column and Forelimbs (set to "Answer with Term")
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
"Skeletal Biology of The Vertebral Column and Forelimbs" Identifying disarticulated vertebral column, forearm, thorax, and shoulder girdle bones. Learning objectives: Be able to identify the following from the vertebral column: Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Atlas Axis Sacrum Cocyyx Know the diagnostic features of each as you will need to justify your identification. Identify the sternum and the three parts of the sternum Be able to identify the bones of the forearm, shoulder girdle and thorax: Scapula Clavicle Humerus Ulna Radius Rib Sternum
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
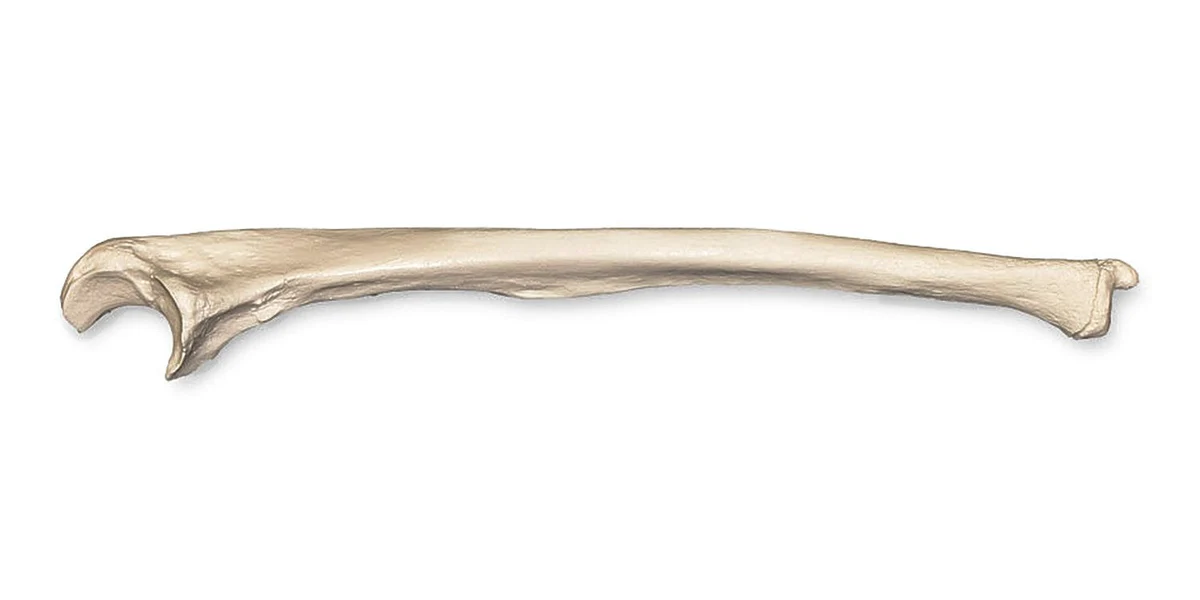
Ulna
Identify the bone in the image
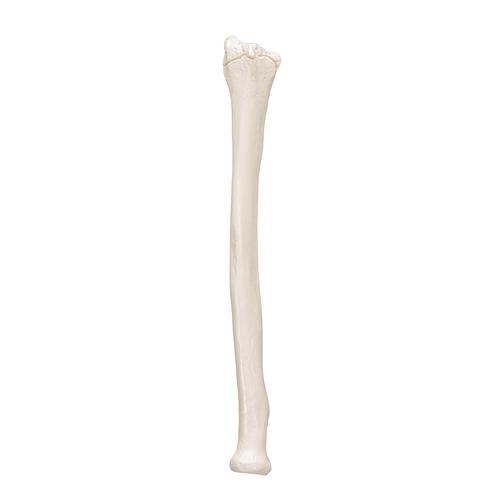
Radius
Identify the bone in the image
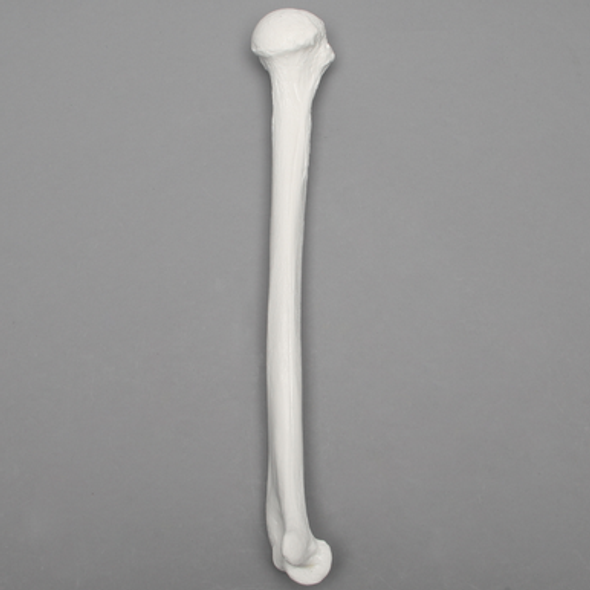
Humerus
Identify the bone in the image
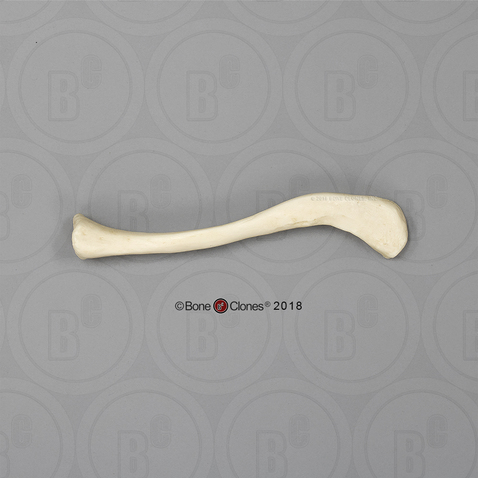
Clavicle
Identify the bone in the image
Rib
Identify the bone in the image
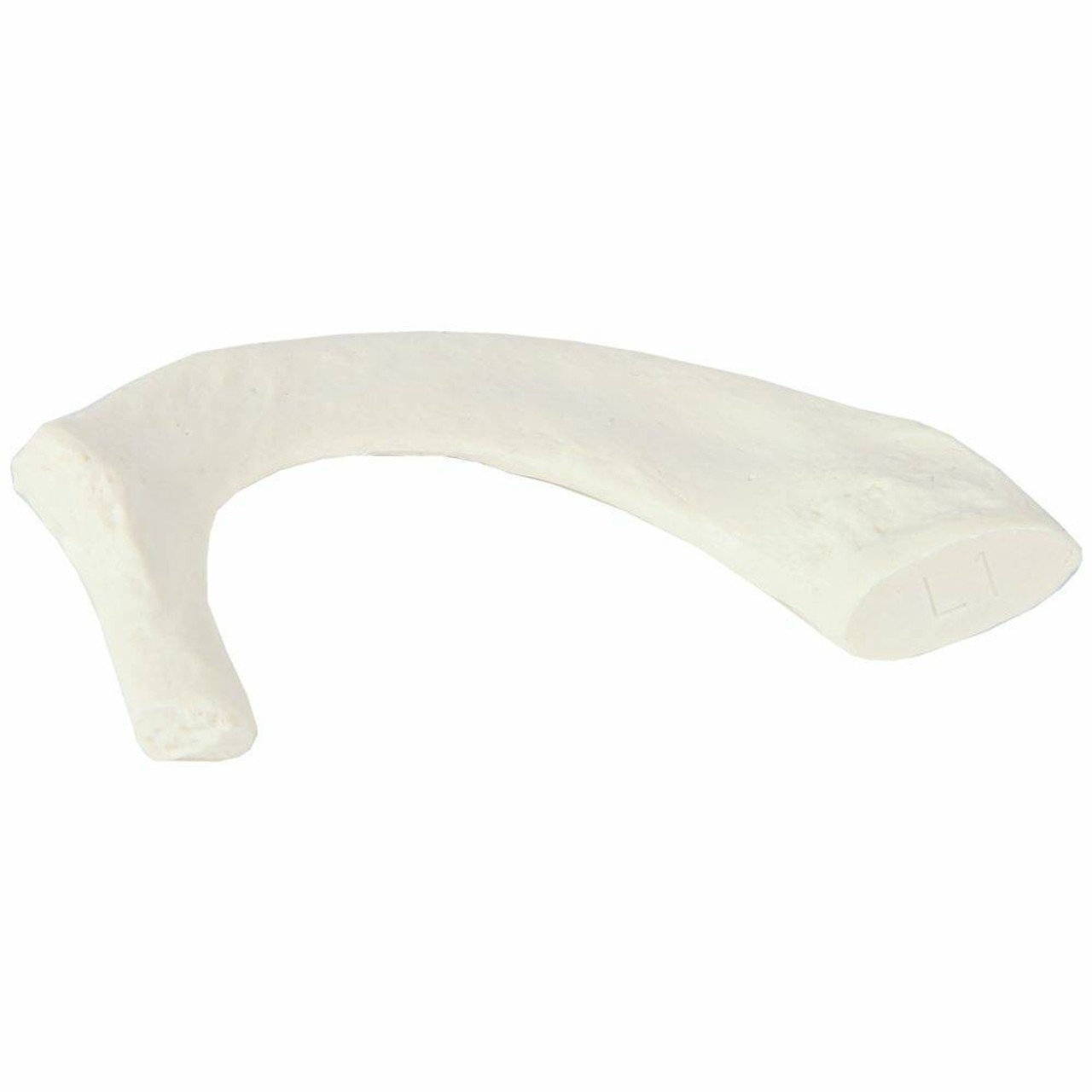

Sternum
Identify the bone in the image
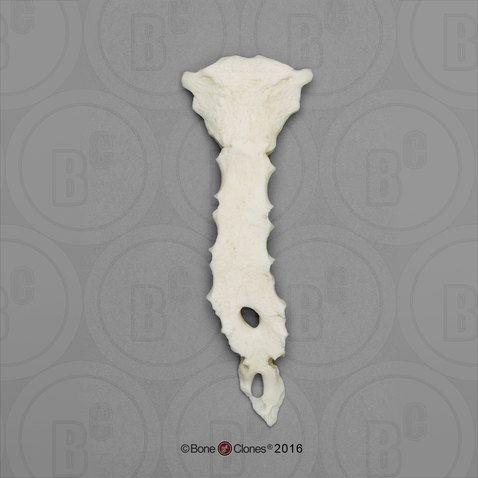

Scapula
Identify the bone in the image
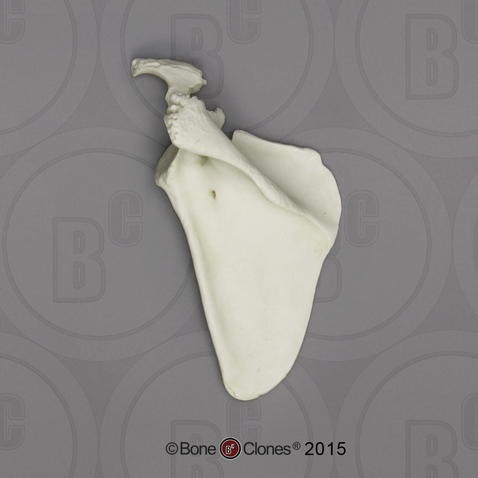

Manubrium (meh-new-bree-um)
Body
Xiphoid process (zi-foid)
Identify the parts of the sternum (top to bottom)
Clavicle
Scapula
What bones are part of the shoulder girdle?
Ribs
Sternum
What bones are part of the thorax?
Humerus
Radius
Ulna
What bones are part of the forearm and upper arm?
The ulna is medial to the radius.
The radius is lateral to the ulna.
The humerus is proximal to both the ulna and radius.
How are the bones of the forearm positioned relative to one another (in SAP)?
Cervical
Smallest body
Transverse foramen
Bifurcated(forked) spinous process
Identify the part of the vertebra and explain what diagnostic features helped you reach your conclusion.
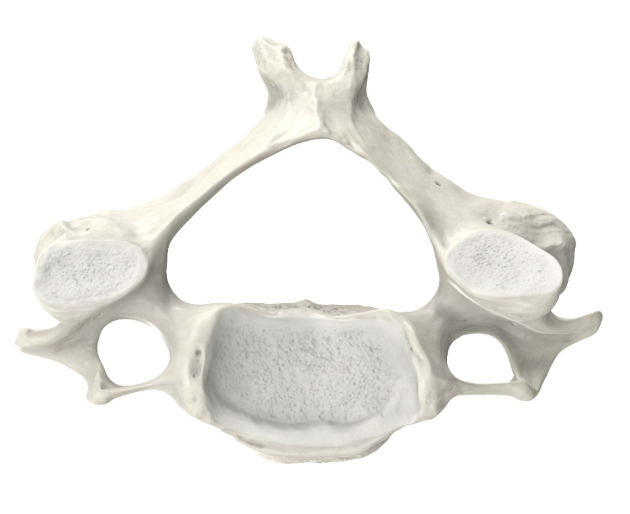
Thoracic
No transverse foramen
Transverse process
Medium-sized body
Long spinus process, pointing toward the feet
Identify the part of the vertebra and explain what diagnostic features helped you reach your conclusion.
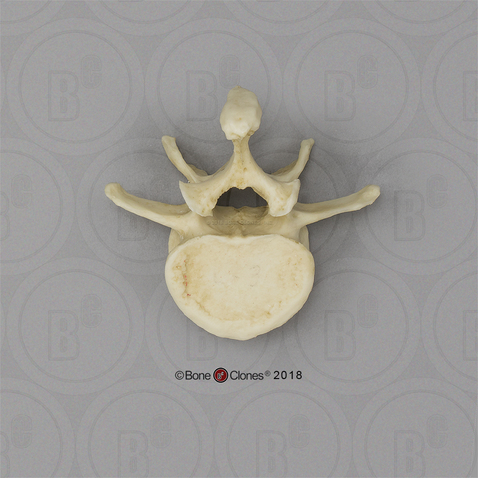
Lumbar
Largest body
Short and blocky (square in shape from the side) spinous process
Short transverse process, sticks out directly laterally
Identify the part of the vertebra and explain what diagnostic features helped you reach your conclusion.
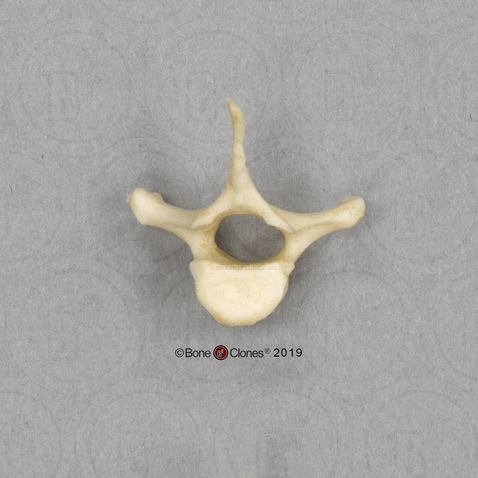
Atlas (C1)
No body (centrum)
No spinous process
Transverse foramen
Identify the part of the vertebra and explain what diagnostic features helped you reach your conclusion.
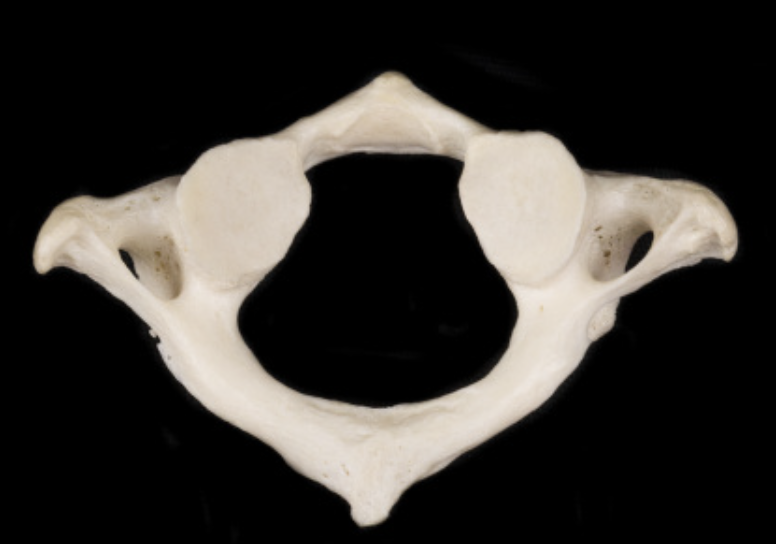
Axis (C2)
Has dens (a peninsula of bone that sticks up)
No transverse foreman
Identify the part of the vertebra and explain what diagnostic features helped you reach your conclusion.
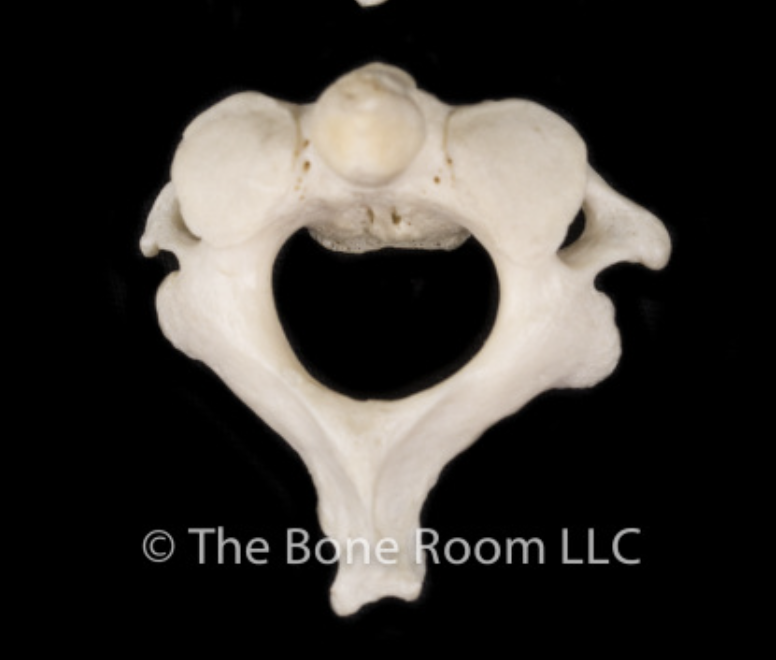
Sacrum
Modified fused vertebra
Identify the part of the vertebra and explain what diagnostic features helped you reach your conclusion.

Cocyyx (cox-six)
Small triangular bone remanent
Identify the part of the vertebra and explain what diagnostic features helped you reach your conclusion.
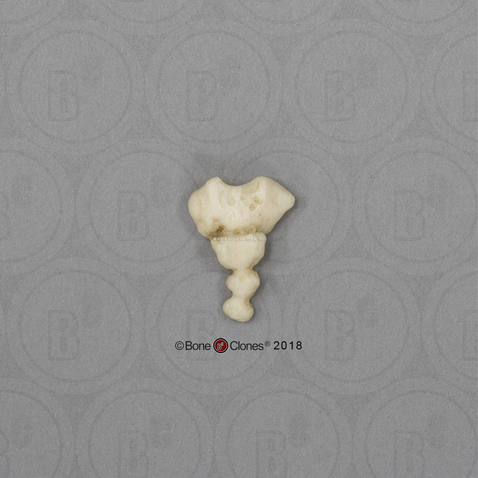
Atlas
Axis
Cervical
Thoracic
Lumbar
Sacrum
Cocyyx
What are the parts of the vertebral column in order top to bottom?
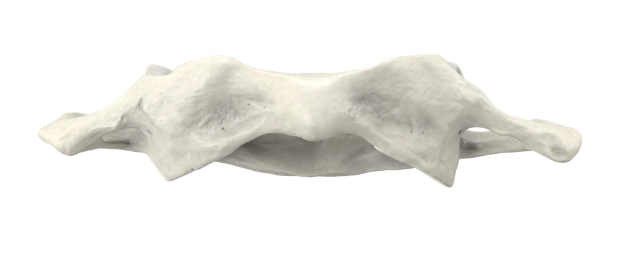
Atlas (C1)
Flat af
Identify the part of the vertebra (side profile) and explain what diagnostic features helped you reach your conclusion.
Axis (C2)
Has dens (a peninsula of bone that sticks up)
Identify the part of the vertebra (side profile) and explain what diagnostic features helped you reach your conclusion.
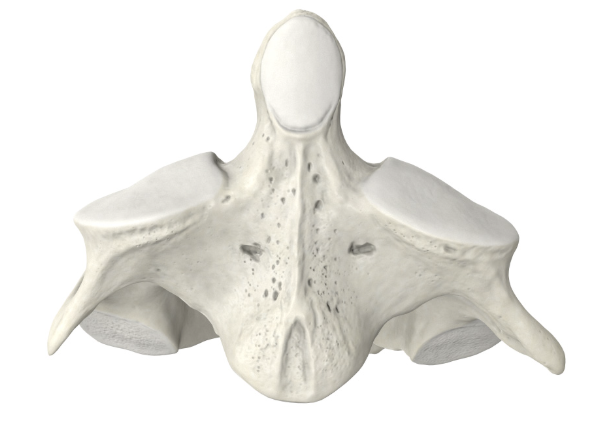
Lumbar
Thick body
Short blocky spinus process
Identify the part of the vertebra (side profile) and explain what diagnostic features helped you reach your conclusion.

Thoracic
Long spinus process, pointing toward the feet
Identify the part of the vertebra (side profile) and explain what diagnostic features helped you reach your conclusion.
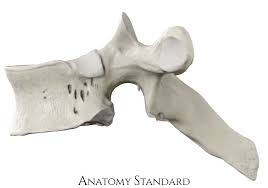
Cervical
flat
forked spinus process
Identify the part of the vertebra (side profile) and explain what diagnostic features helped you reach your conclusion.
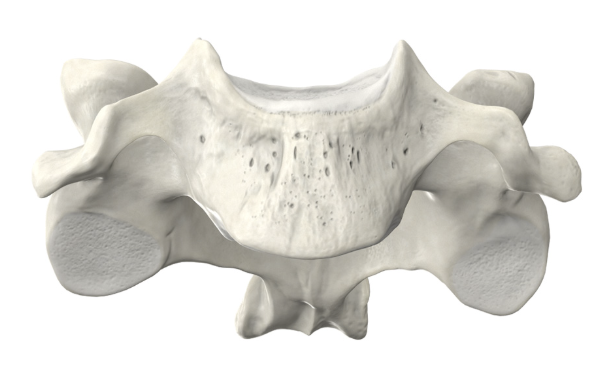
Transverse foramen
only found in cervical vertebra
atlas and cervical bones have obvious foramen, while the axis has foraman further out, which can sometimes be blocked by the facet
Bonus: Dens is unique to the axis
What diagnostic feature belongs only to cervical bone?