Optics and Vision
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What is the function of photoreceptors
Transducer that changes light energy into electrical energy
Function of the pupl
Control the amount of light entering the eye by dilating (Sympathetic) and constricting (parasympathetic)
What makes up the anterior chamber of the eye
Sclera, cornea, pupil + the muscles and ciliary bodies at move the eye
What makes up the posterior chamber
Vitreous humor
What does the vitreous humor do
Pushes the retina into a globe like shape; contains nutrients that support the eye
A defect of the vitreous humor will cause what defect
Retinal detachment; common in people that are extremely short sighted
What forms the optic nerve
The retina
Which part of the eye DOES NOT have photoreceptor
Optic disc
Where do vessels come out from in the eye
Optic disc
A large blind spot can be caused by a problem in what structure
Optic disc englargement caused by increased intercranial pressure
Which areas of the eye has the highest visual acuity
Fovea and macula which surround it
What are the differences between rod and cone cells
Rod cells > cone cells; rod cells work better without light, cone cells work with light; rod cells do not produce color, cone cells do
What is the process in which photoreceptors receive energy to cause response
Interneuron synapse to excite bipolar cell and inhibit negative surroundings
What is the function of ON center ganglion cells
Creates action potential when light is focused on the CENTER of the receptive field
Function of OFF center ganglion cell
Create action potential when light is focused on the PERIPHERY of receptive field
Parasol cells
Large cells → Detect movement → Go to magnocellular layer of LGN
Midget cells
Small cells → Detect find stimuli and color → Go to parvocellular cells in LGN
How is the image that is seen in the retina altered
The image is inverted and reversed
Parts of the prechiasmatic region
Optic nerve, eye itself, pituitary gland beneath it
Parts of the post chiasmatic region
Cortexes of the brain, LGN, optic tract (optic radiation and Mayer’s loop)
What is the characteristic of pre-chiasmatic region defects
Respect the HORIZONTAL meridian
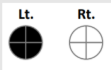
A patient presenting with this visual defect likely has a lesion where
Pre-chiasmatic region; lesion of the optic nerve or ocular media on the LEFT side
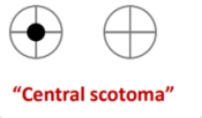
A patient presenting with this visual defect likely has a lesion where
Patient has a central scotoma → Problem with the optic nerve optic nerve on the LEFT side
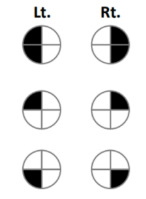
A patient presenting with this visual defect likely has a lesion where
Chiasmatic region; lesion located in the optic chiasm

A patient with partial bitemporal hemianopia on the superior side has a lesion where
Sella region (pituitary) under the optic chiasm

A patient with partial bitemporal hemianopia on the inferior side has a lesion where
Suprasellar region (frontal lobe) above the optic chiasm
What is the characteristic of post chiasmatic and chiasmatic defects
Respects the VERTICAL meridian

A patient presenting with this visual defect has a lesion where
Junctional scotoma; caused by a lesion of the LEFT junction between the optic nerve and optic chiasm
Which nuclei does light information get sent to
Majority to LGN, some to brachium of superior tectum/colliculus
What is the pathway of the optic radiation
Goes to parietal lobe and terminates in the upper bank of the calcarine fissure; controls the lower visual quadrant of the CONTRALATERAL eye
What is the pathway of the Mayer’s loop
Goes to temporal lobe and terminates in the lower bank of the calcarine fissure; controls the upper visual quadrant of the CONTRALATERAL eye
Why do patients with MCA infarction have eye defects
The MCA does not supply the occipital lobe BUT does supply the optic radiation
Which area of the occipital lobe produces images that are the most clear
Area 1; inputs mainly from the fovea with the highest visual acuity
Parasol cell visual processing pathway
Movement → Magnocellular layer of LGN → 4ca → Dorsolateral parieto-occipital cortex
Midget cell visual processing pathway
Fine spatial information → Parvocellular layer of LGN → 4cb → Inferior occipitotemporal cortex
Color → Parvocellular layer of LGN → 2,3 → Inferior occipitotemporal cortex
Which lobe is the where and what pathway located
Where pathway = parietal lobe, what pathway = temporal lobe
Function of Layer 1
Made of mainly dendrite of neuron from deeper layer
Function of layer 2 and 3
Contain neurons that project to other areas
Function of layer 4
Main input area; LGN terminate here
Function of Layer 5
Project to subcortical structure that is not thalamus
Function of Layer 6
Project to thalamus

Right homonymous superior quadrantanopia caused by a lesion where
Inferior part of the head → Left temporal lobe → Mayer’s loop

Left homonymous inferior quadrantanopia
Superior part of the head → Right parietal lobe → Optic radiation

Right homonymous hemianopia with macular sparing caused by lesion where
PCA infarction which supplies the occipital lobe but not the part supplied by MCA
LGN lesion can be caused by stroke of which arteries
Posterior or anterior choroidal arteries
What is the pupillary response
Light → Superior colliculus/pretectal area → EWN (bilateral) → Ciliary ganglion → Pupillary constrictor muscle; enter CN II exit CN III
What is accomodation reflex
Eyes will convert and pupils constrict when an item is held close to the nose
What is the Marcus Gunn pupil/relative afferent pupillary defect
Lesion in optic nerve, retina or eye that causes decreased light sensitivity → pupil of affected eye will not constrict when exposed to light
Left CN III lesion responses
The affected eye will NOT constrict when exposed to light; consensual reflex will make the affected eye more dilated
Left Horner syndrome responses
The affected eye will have a dilation lag from light to dark; affected eye is more constricted than unaffected eye