Chapter 12
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
What is evolution?
Genetic change over time, occurring when there are changes in heritable traits from generation to generation.
In which context does evolution occur?
Evolution occurs in populations, not in individuals, as allele frequencies change over generations.
How is allele frequency calculated?
As the number of copies of an allele divided by the total number of alleles for the same gene in the population.
What does a gene pool represent?
All of the alleles for all of the genes in a population.
What evidence did Charles Darwin provide for evolution?
He documented the variety of organisms in South America and their relationships to fossils and geology, leading to insights on species origin.
What is 'descent with modification'?
Darwin's idea that species evolve from common ancestors, adapting to their environments over time.
What is natural selection?
The process where individuals with traits better suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce.
What is an example of natural selection in action?
Pygmy seahorses that are better camouflaged survive to reproduce, increasing the frequency of camouflage alleles.
How does artificial selection differ from natural selection?
It involves human intervention to breed for desired traits, while natural selection occurs without human influence.
What role does genetic variation play in natural selection?
It is essential for natural selection, as it provides the diversity needed for some individuals to be better adapted to their environment.
What are adaptations?
Heritable features that provide a selective advantage, improving an organism's ability to survive and reproduce.
What is the significance of the sickle cell allele?
It provides heterozygote advantage, protecting against malaria while causing sickle cell disease in homozygotes.
What is sexual selection?
A type of natural selection arising from variation in the ability to obtain mates, influencing reproductive success.
What is intrasexual selection?
Competition among individuals of the same sex for access to mates.
What is intersexual selection?
When individuals of one sex choose mates based on desirable traits.
How do mutations contribute to evolution?
They create genetic diversity, providing the raw material for evolution, with beneficial mutations passed to future generations.
What is genetic drift?
Random sampling error that causes allele frequencies to shift dramatically, often leading to the elimination of alleles.
What is the founder effect?
A phenomenon where a new population is established by a small number of individuals, leading to changes in allele frequency.
What is a population bottleneck?
A drastic reduction in population size due to an event, causing a loss of genetic diversity.
How does gene flow affect populations?
It moves alleles between populations, potentially affecting allele frequencies and reducing genetic differences.
What is nonrandom mating?
Mating patterns influenced by factors such as sexual selection, which can alter allele frequencies in a population.
What does 'survival of the fittest' mean?
Fitness refers to an organism's genetic contribution to the next generation, with the 'fittest' being those most likely to reproduce.
Why do harmful alleles persist in populations?
They may confer advantages in heterozygotes, allowing them to survive better than homozygotes.
What is the role of adaptations in changing environments?
They enhance reproductive success and may change as environmental conditions evolve.
What is a misconception about fitness in evolutionary theory?
Fitness is often misunderstood; it includes surviving, reproducing, and having offspring that survive to reproduce.
What are the three modes of natural selection?
Directional, disruptive, and stabilizing selection, each affecting phenotypes in different ways.
Descent with modification describes the process of
evolution.
What describes an allele frequency?
number of copies of an allele divided by total number of alleles
What is an example of microevolution?
change in allele frequencies in a population from generation to generation
An example of macroevolution would be the appearance of a new
species of finch.
A precise definition of evolution is the
genetic change in a population over multiple generations.
The appearance of a new species of oak tree would be called a(n) ______ event.
macroevolutionary
A(n) ______ is a feature that provides a selective advantage to an organism because it improves its ability to survive and reproduce.
adaptation
Natural selection can act to eliminate
nonadaptive phenotypes.
The genetic contribution of an organism to the next generation is referred to as
fitness.
If 48 individuals have a Dd genotype in a population of 100 individuals, then 0.48 is the ______ of Dd.
genotype frequency
In the state of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, allele frequencies
are not changing.
Random mating, a large population, and no mutation, selection, or migration are all assumptions of
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
What describes genotype frequency in a population?
number of individuals with a particular genotype divided by total number of individuals in the population
In evolutionary terms, fitness of an organism is defined as an organism's
genetic contribution to the next generation.
In the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium, the terms p2, 2pq, and q2 refer to
genotype frequencies in a population.
Directional, disruptive, and stabilizing are all types of ______, in which certain phenotypes are favored over others.
natural selection
The Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium describes the highly unlikely circumstance in which Blank______ are not changing in a population.
allele and genotype frequencies
Selection for one extreme phenotype in a population would be considered a type of natural selection called ______ selection.
directional
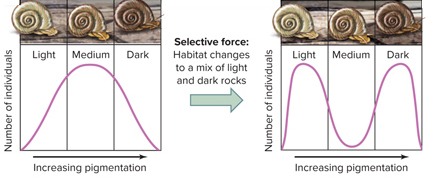
In the image, what mode of natural selection is taking place?
disruptive
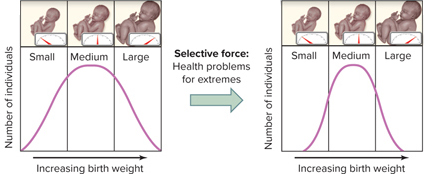
Human birth weight is an example of a type of natural selection called ______ selection.
stabilizing
p2
frequency of homozygous dominant genotype
2pq
frequency of heterozygous genotype
q2
frequency of homozygous recessive genotype
p
frequency of dominant allele
q
frequency of recessive allele
What mechanism of evolution changes the genetic makeup of a population by favoring alleles that increase reproductive success?
natural selection
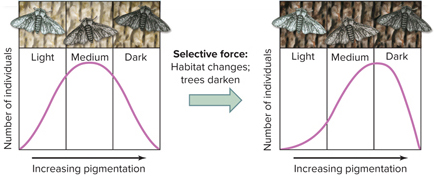
The image shows an example of what type of natural selection?
directional selection
What genotype for the "sickle cell gene" causes mild symptoms of sickle cell disease but confers resistance to malaria?
heterozygous
Disruptive selection is a mechanism of natural selection that
favors two or more extreme phenotypes in a population.
When the intermediate phenotype of a trait is being selected for and the extreme phenotypes are being selected against, the population is probably undergoing
stabilizing selection.
What type of natural selection results in traits that increase ability to obtain mates, even if the traits reduce survival?
sexual selection
In the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium, the terms p2, 2pq, and q2 refer to
genotype frequencies in a population.
What is a mechanism by which harmful alleles can be maintained in a population even though homozygous recessive individuals have greatly reduced fitness?
heterozygote advantage
A ______ is a change in an organism's DNA sequence and is the raw material for evolution, because genes affect phenotypes and evolution acts on phenotypes.
mutation
When two phenotypic extremes of a trait are being selectively favored, then a natural population is undergoing ______ selection.
disruptive
A change in allele frequencies that occurs by chance and that tends to eliminate alleles in a population rather than increase diversity is called
genetic drift.
Genetic drift has a greater effect on
small populations.
In the bottleneck effect, the alleles that are lost when a population's size drops is
random.
What is a mechanism by which harmful alleles can be maintained in a population even though homozygous recessive individuals have greatly reduced fitness?
heterozygote advantage
The bottleneck effect is an example of what mechanism of evolution?
genetic drift
Natural selection acts on the genetic makeup of
populations
Farmers and horticulturalists have bred broccoli, cauliflower, kale, and cabbage from the wild mustard plant through
artificial selection.
In _________ selection, individuals with an intermediate phenotype have low fitness, whereas individuals with an extreme phenotype have high fitness.
disruptive
In _________ selection, one extreme phenotype is the fittest while others are selected against.
directional
The North American bison was hunted to near extinction in the 1800s, and has since recovered, but with decreased genetic diversity. This is an example of
bottleneck effect.