Lecture 20 - Therapeutic and Accidental Total Body Irradiation
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ONCOL 335 - Radiobiology. University of Alberta
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
what two categories can radiation exposure be divided into
whole body exposure
localized radiation exposure
two categories of tissues radiation can have effects on
somatic tissues
germ tissues
two categories of radiation effects
acute effects
late effects
what is acute radiation syndrome (ARS)
a collection of health effects which present within 24 hours of exposure to high amounts of radiation
what three places did we get initial data on ARS from?
demon core
atomic bombs
chernobyl
what are hibakusha?
survivors of the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945 who were exposed to the bomb's radiation and suffered from physical and psychological effects, including cancer and other long-term health issues.
what commission was founded to study hibakusha, and who started it?
the atomic bomb casualty comission was founded by Dr. Terufumi Sasaki
what did the atomic bomb casuallty commission become?
the Radiation Effects Research Foundation
What is the LD50/60 for young healthy adults without medical attention?
4.5 Gy
nobody has ever survived ___ Gy
10 Gy
Examples of ARS in history (don’t need to memorize all)
Atomic Bombs
Demon core
Chernobyl
Goiania incident
Fukushima
what is a criticality accident?
an uncontrolled nuclear chain reaction that occurs with the unintentional assembly of a critical mass
difference between critical reaction and accident
critical reaction occurs within reactor cores and test environments, accidents occur when same reaction is acheived unintentionally and in an unsafe environment
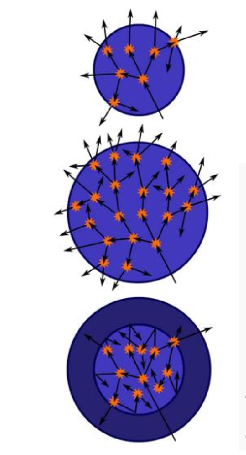
what does the top sphere represent
a sphere of fissile material that is too small to cause self-sustaining chain reaction
neutrons can escape too easily
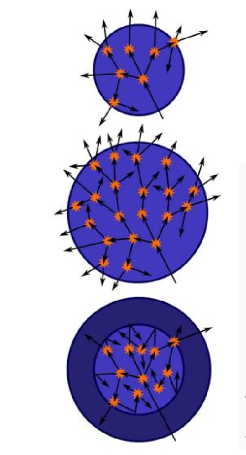
what does the middle sphere represent
by increasing the mass of the sphere, the reaction is made self sustaining, neutrons can hit other atoms
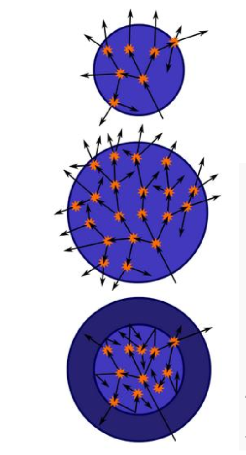
what does the bottom sphere represent
the original sphere is surrounded with a neutron reflector to increase the efficiency of reactions to allow reaction to become self-sustaining
What happened in the Harry Daghlian Demon Core incident?
Harry Daghlian accidentally dropped a neutron reflector (tungsten carbide) brick onto the plutonium pit during a criticality experiment, causing a brief critical reaction and exposure to lethal radiation. He died 25 days later from radiation poisoning.
how much dose did Daghlian receive?
5.1 Sv of neutron radiation
what was the Litvinenko case
The Litvinenko case involved the poisoning of Alexander Litvinenko, a former Russian FSB agent, who was fatally poisoned with polonium-210 in 2006 in London. Litvinenko died after ingesting the radioactive substance
what radioactive isotope was Alexander Litvinenko exposed to?
Po-210
alpha emitter = high LET
what are stochastic effects?
all or nothing random radiation effects
stochastic effects occurance is a probabilty of …
dose
examples of stochastic effects
cancers, inheritable mutations
deterministic effects
effects that severity increase as a function of dose
do deterministic effects have a threshold?
yes
examples of deterministic effects
organ failure, fibrosis, cataracts
is ARS (and other early radiation responses) a deterministic effect?
yes
they have a threshold
what is a syndrome?
a set of medical signs and symptoms that correlate with eachother
what are the three ARS syndromes?
hematopoietic syndrome
gastrointestinal syndrome
cerebrovascular syndrome
at what doses does CV syndrome happen at?
very high doses
will CV syndrome cause you to develop the other two syndromes
theoretically yes, but it will kill you before the onset of the other syndromes
what are the four stages of ARS?
prodromal (initial) stage
latent stage
manifest illness
death or recovery
how does the length of the prodromal stage vary with dose?
the higher the dose, the quicker you will develop the symptoms
if you are exposed to 40 Gy, when will the prodromal stage begin
5-15 minutes after exposure
two categories of prodromal symptoms
neuromuscular
GI
3 neuromuscular prodromal symptoms
fatigability
fever
hypotension
4 GI prodromal symptoms
anorexia
nausea
vomiting
immediate diarrhea
what are the three causes of the prodromal stage of ARS?
immediate cell membrane damage
inflammatory elements of cell destruction
neurologic mediation by parasympathetic nervous symptom
what is the latent stage of ARS
the stage after the prodromal stage where the patient may become symptom free
how is the latent stage related to dose?
the higher the dose, the shorter the latent stage
if a patient does not experience a latent stage, what do we know about the dose of radiation they received?
it was very high
what what dose to lymphocyte counts drop at
0.5 Gy
what does the Law of Bergonie and Tribondeau state?
radiosensitivty of cells is higher in cells that are less differentiated and faster at proliferating
what are the two exceptions to the Law of Bergonie and Tribondeau?
lymphocytes
highly differentirated, but the most sensitive cell
oocytes
non-proliferating, but sensitive
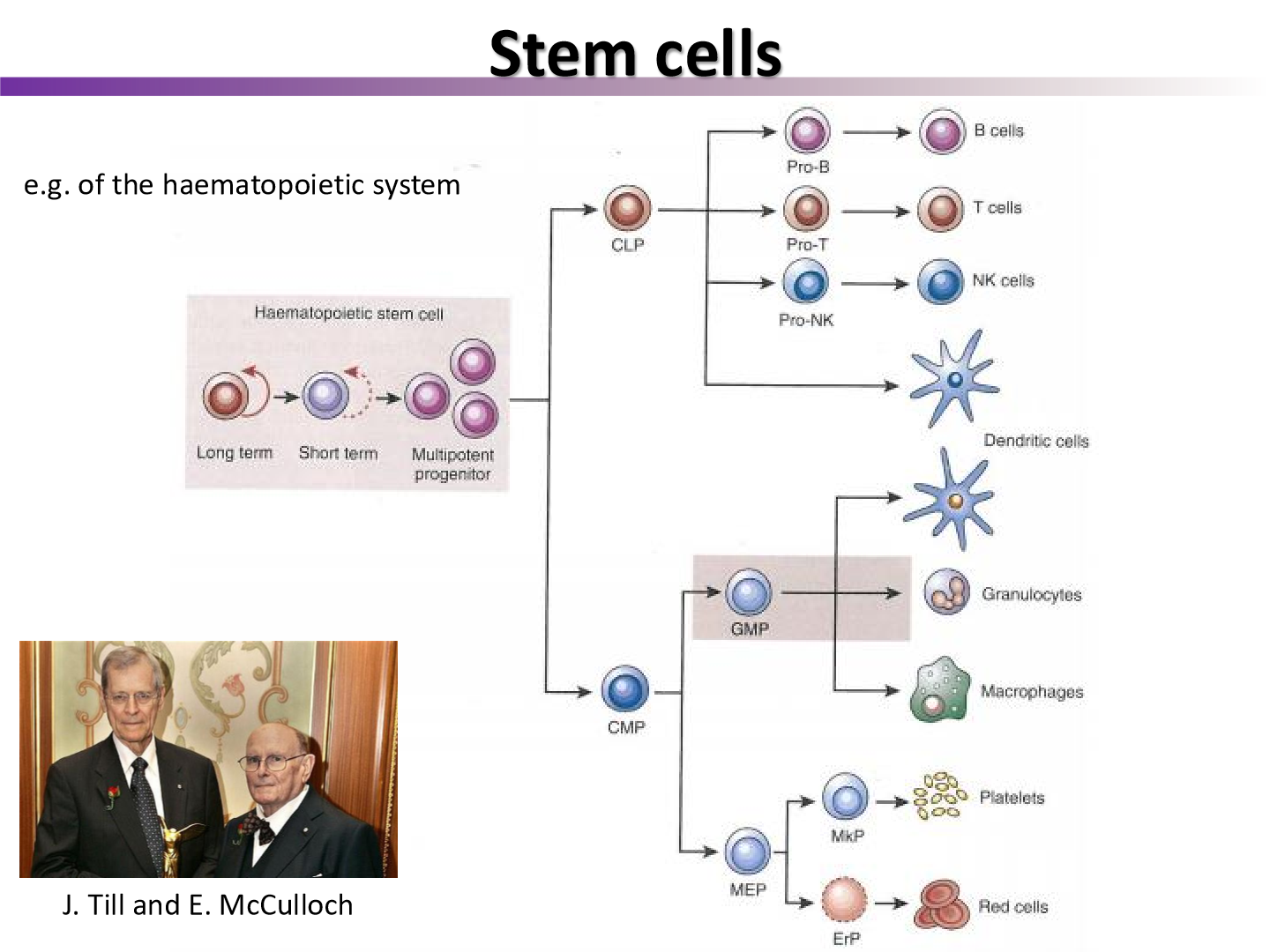
what stem cell line is more radiosensitive, the lymphoid or myeloid lineage?
the lymhpoid lineage
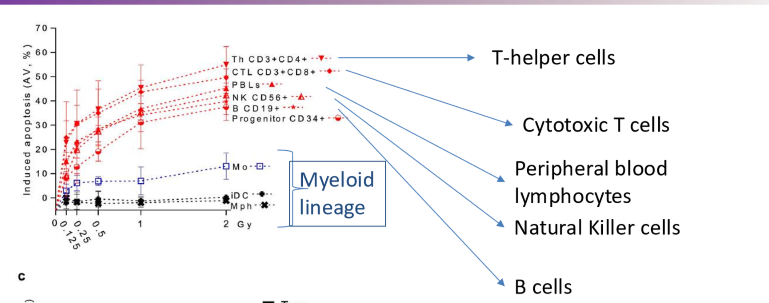
6 radiosensitive cells/tissue
cells of red bone marrow
epithelial cells of GI and lung
epithelial cells of lens
germ cells of testis and ovaries
endothelial cells (vasculature)
salivary glands
If you receive higher doses, which ARS syndrome will you die of?
CV syndrome
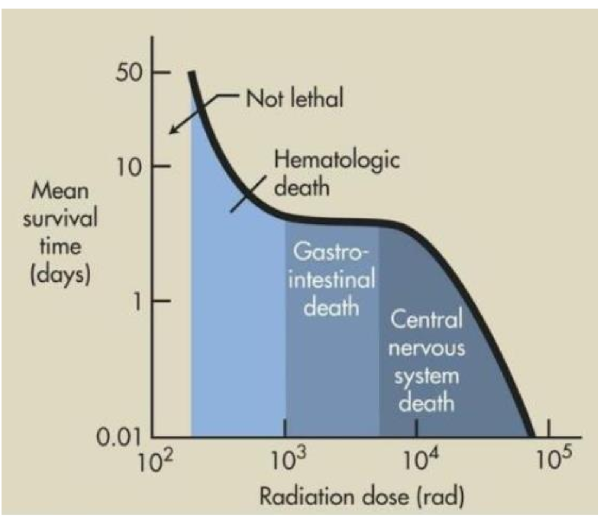
if you received a low dose, which ARS syndrome could you potentially die of?
Hematopoietic syndrome
above what dose will progression to death stage of ARS be the quickest
above 8 Gy
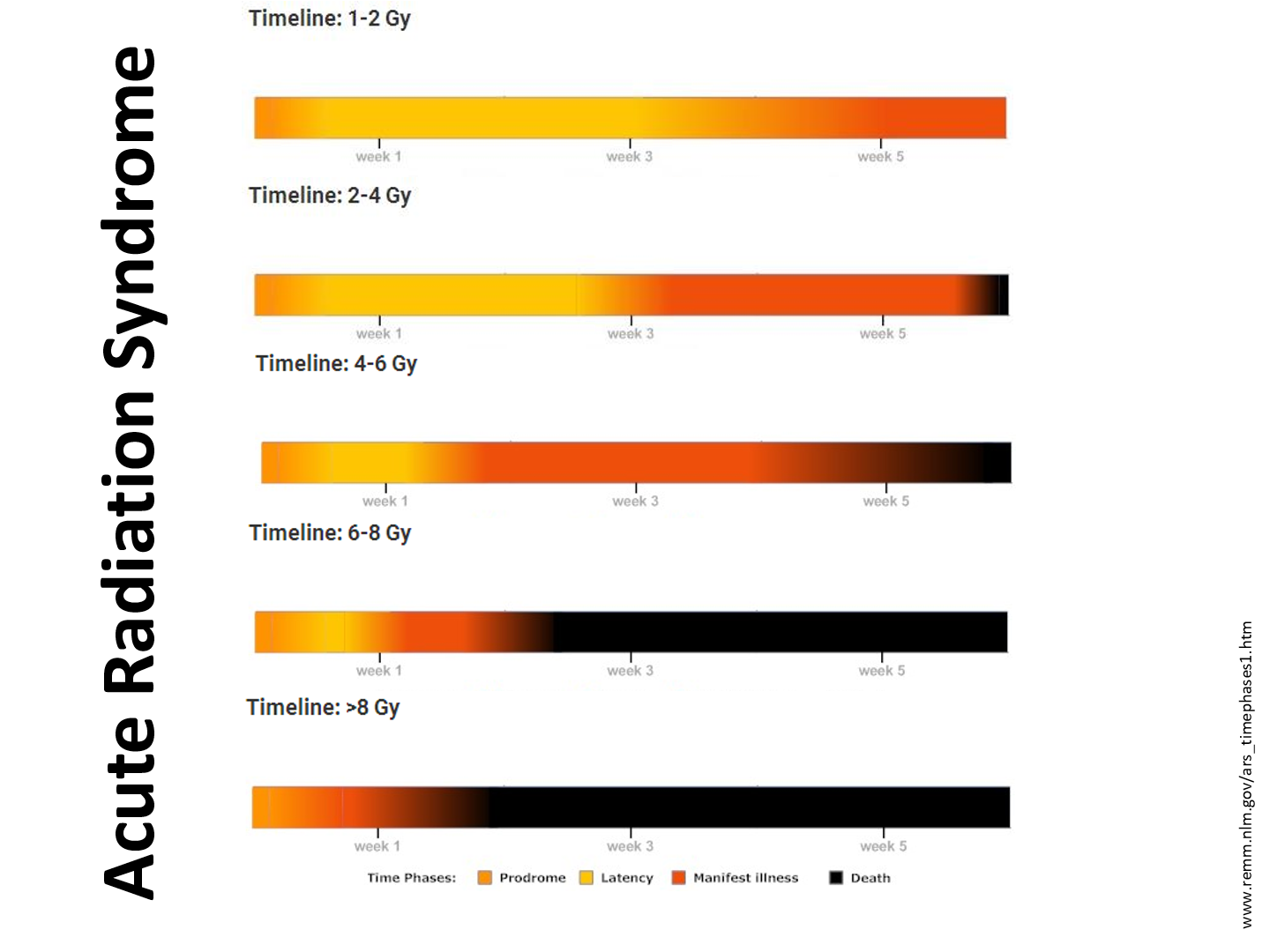
what is the caveat to ARS data?
all of the data that has been collected is for healthy young adult males (like soldiers).
limited data in older people, babies, or even females
clinicians should not expect a specific dose or dose range for ARS syndromes to occur at
which ARS syndrome do we know the least about?
CV syndrome
what dose will cause CV syndrome death within 24-48 hrs
greater than 100 Gy of gamma radiation
symptoms of CV syndrome
nausea and vomiting within minutes —> disorientation, loss of muscle coordination, breathing problems, seizures, coma, death
what incident resulted in a person dying from CV syndrome?
Rhode Island Criticality Accident
what was the rhode island criticality accident
a worker at a uranium 235 recovery plant was exposed to 88 Gy of neutrons (22 of them were neutrons).
died 49 H after
which ARS syndrome did Daghlian die of after his demon core exposure?
GI syndrome
died of sepsis in 24 days
what dose will cause GI syndrome death in 7-10 days?
10 Gy of gamma rays
symptoms of GI syndrome
nausea, vomiting, prolonged diarrhea, lethargy, lack of appetite
if person has prolonged diarrhea after exposure, how much dose did they receive?
more than 10 Gy
describe how GI syndrome causes death
GI syndrome leads to death primarily due to damage to the intestinal lining, resulting in severe dehydration and sepsis from gut bacteria entering the bloodstream. The rapid loss of intestinal function hinders nutrient absorption and fluid balance, contributing to mortality.
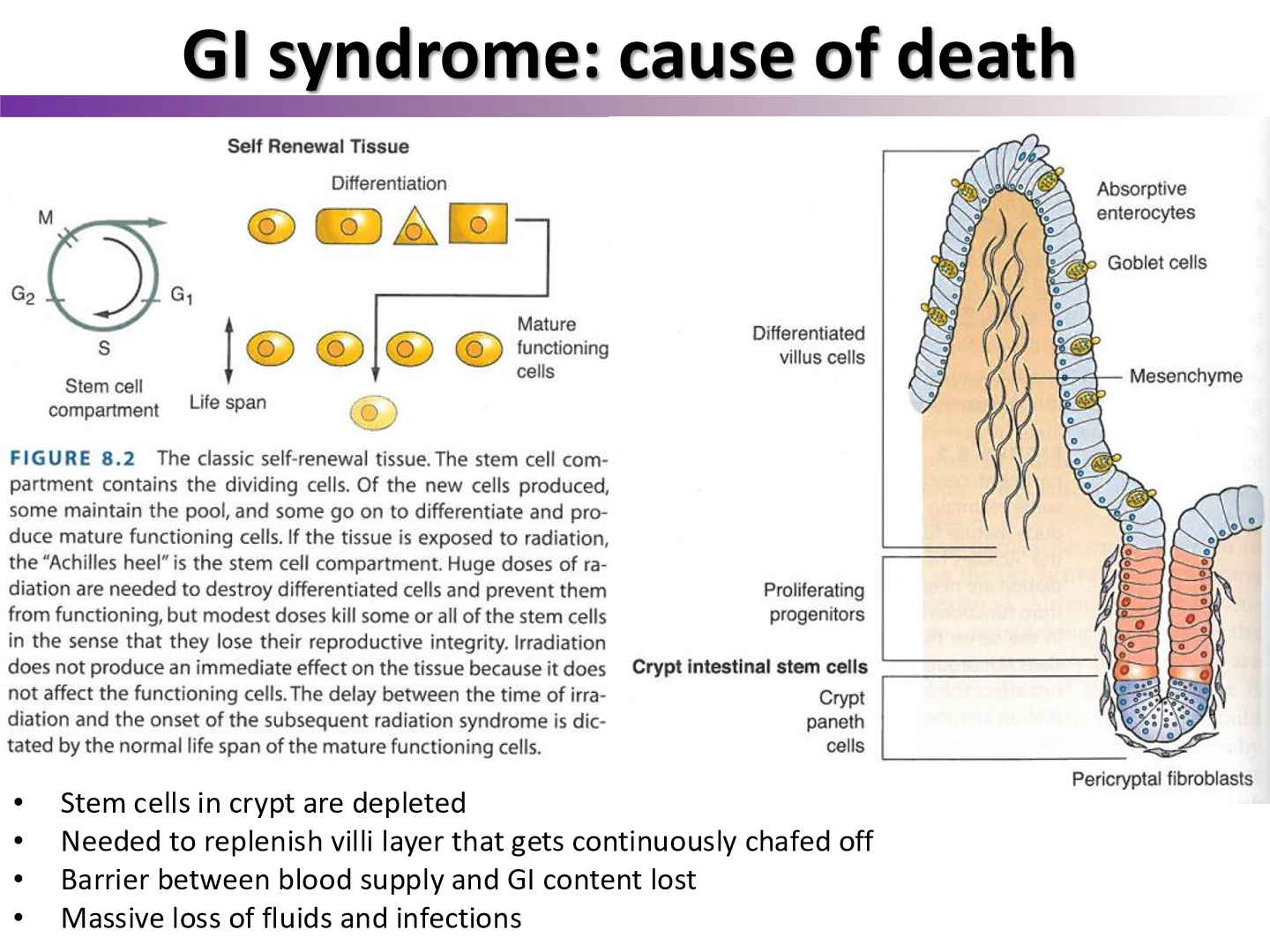
if patients have GI syndrome get bone marrow transplant, will they survive?
no, they will die of GI syndrome
treatment of hematopoeitic syndrome has not effect
if we looked at the GI tract of a patient who died of GI syndrome, what would we see?
complete erosion of jejunum and ileum, and system is full of bacteria
sepsis often occurs
if death occurs after 2.5-5 Gy, what syndrome caused it?
hematopoietic syndrome
what happens in hematopoietic syndrome
mitotic stem-cell precursors of RBC, WBC, and platelets are killed
why is the onset of hematopoietic syndrome delayed by weeks?
syndrome is only displayed when mature cells are depleted below a threshold
when will a patient diet of hematopoietic syndrome
30-60 days
who are more sensitive to hematopoietic syndrome?
older people, children, and men (compared to women)
early symptoms of hematopoeitic syndrome
chills, fatigue, loss of hair, petechial hemorrages of skin
late symptoms of hematopoietic syndrome
anemia, impaired immune function
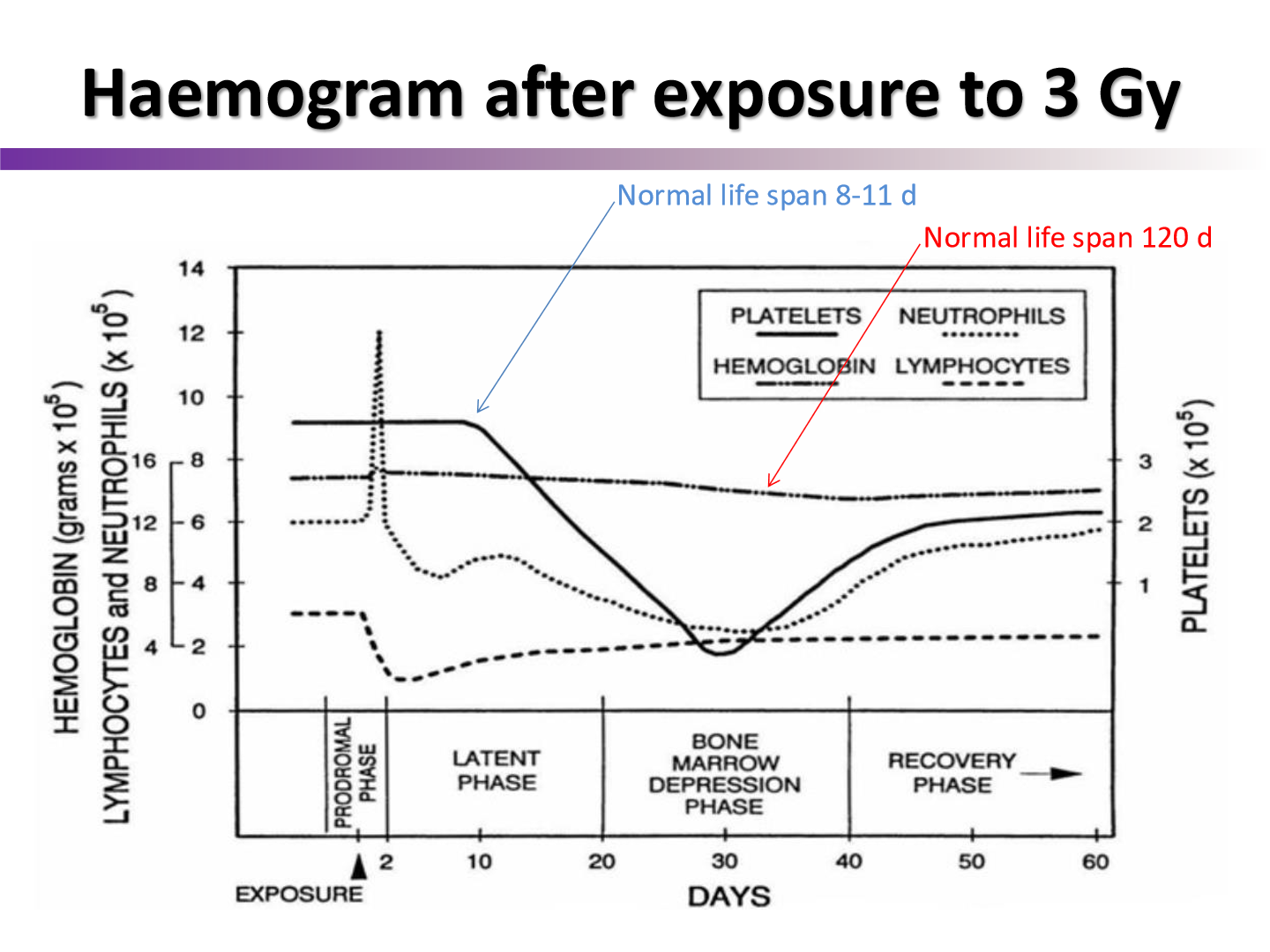
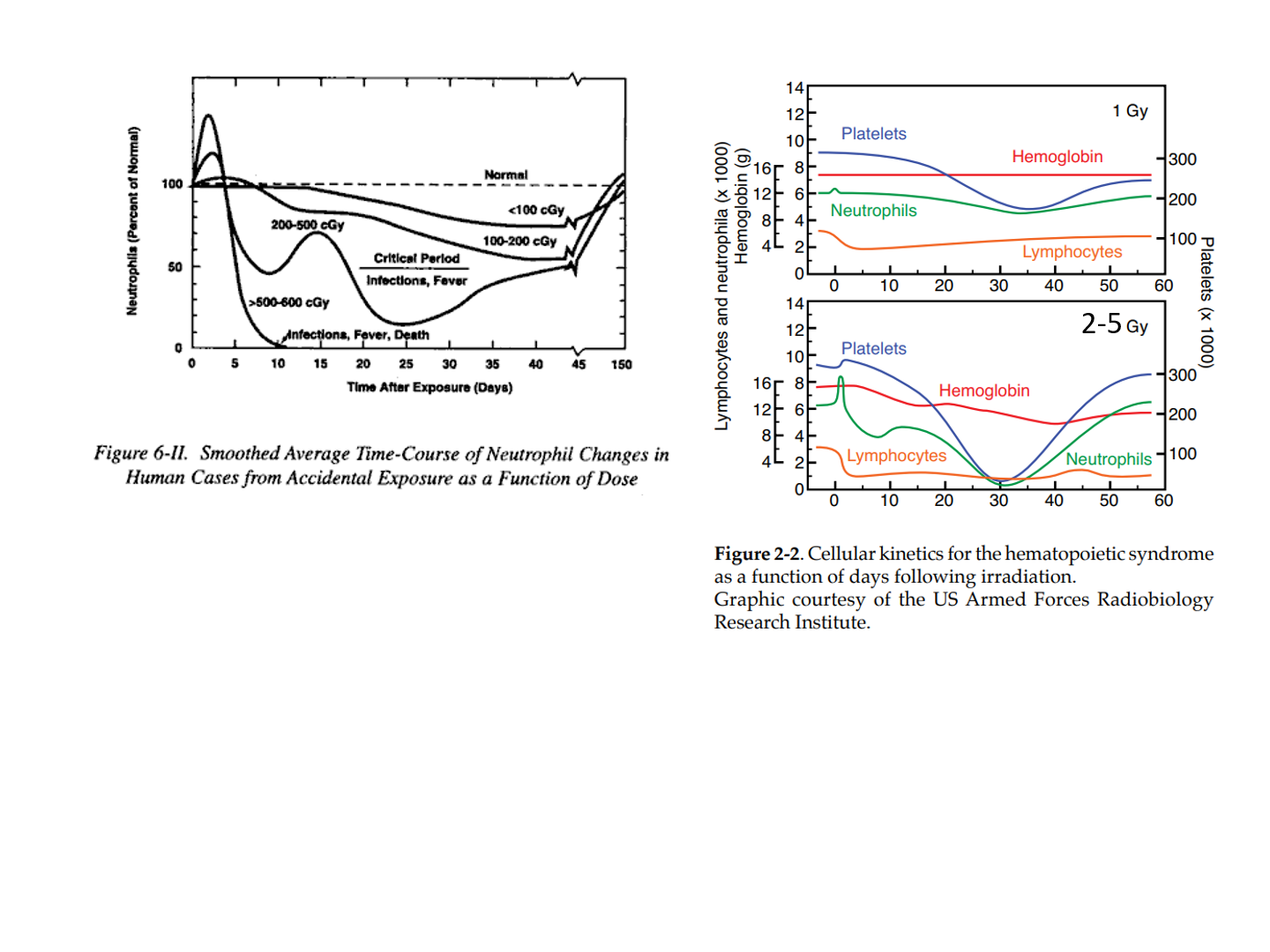
why is there a spike in neutrophil numbers after irradiation?
neturophil spike is often due to infection
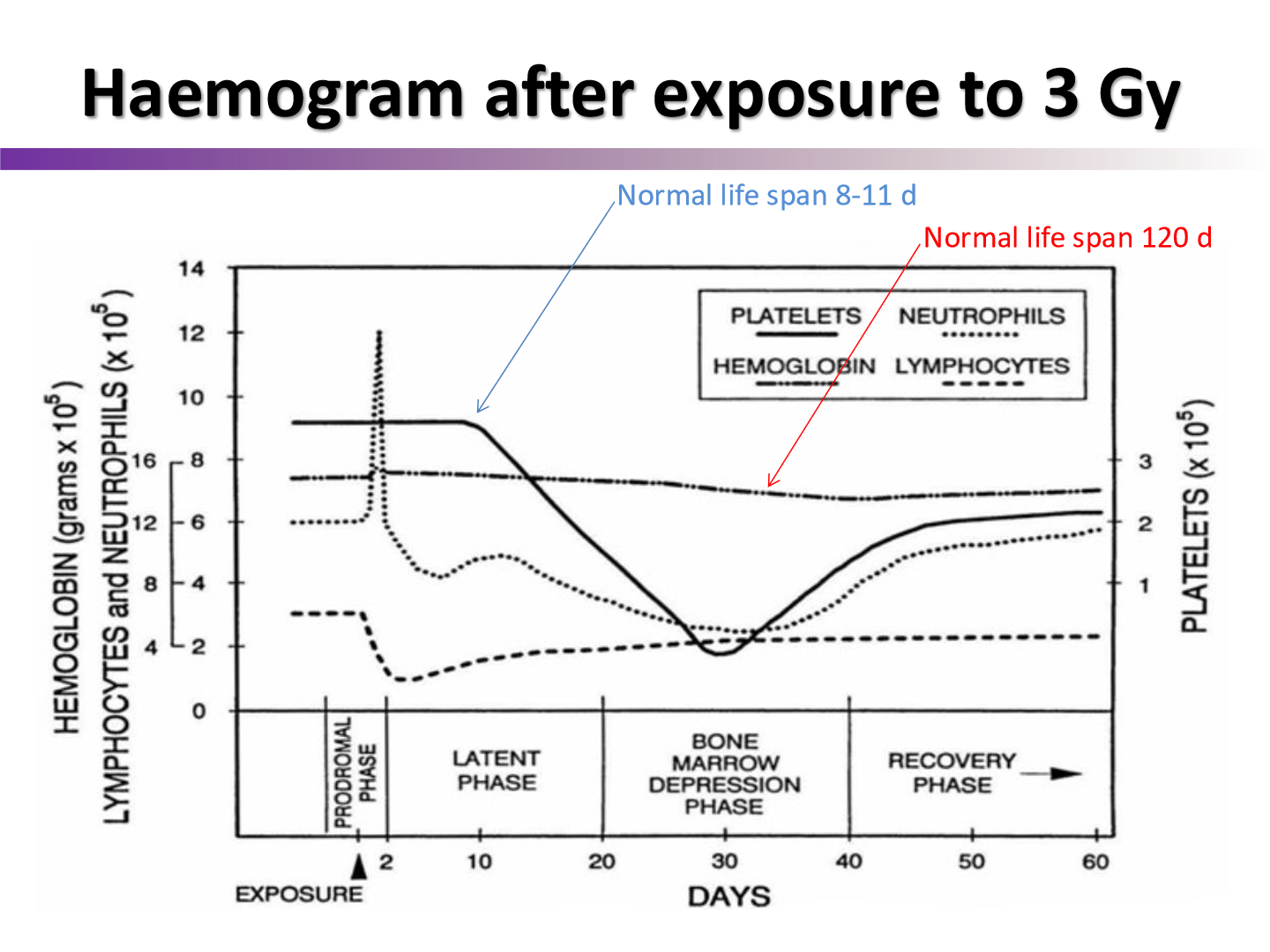
why does the RBC not drop?
RBC have life spand of 120 days, they wont be affected as much
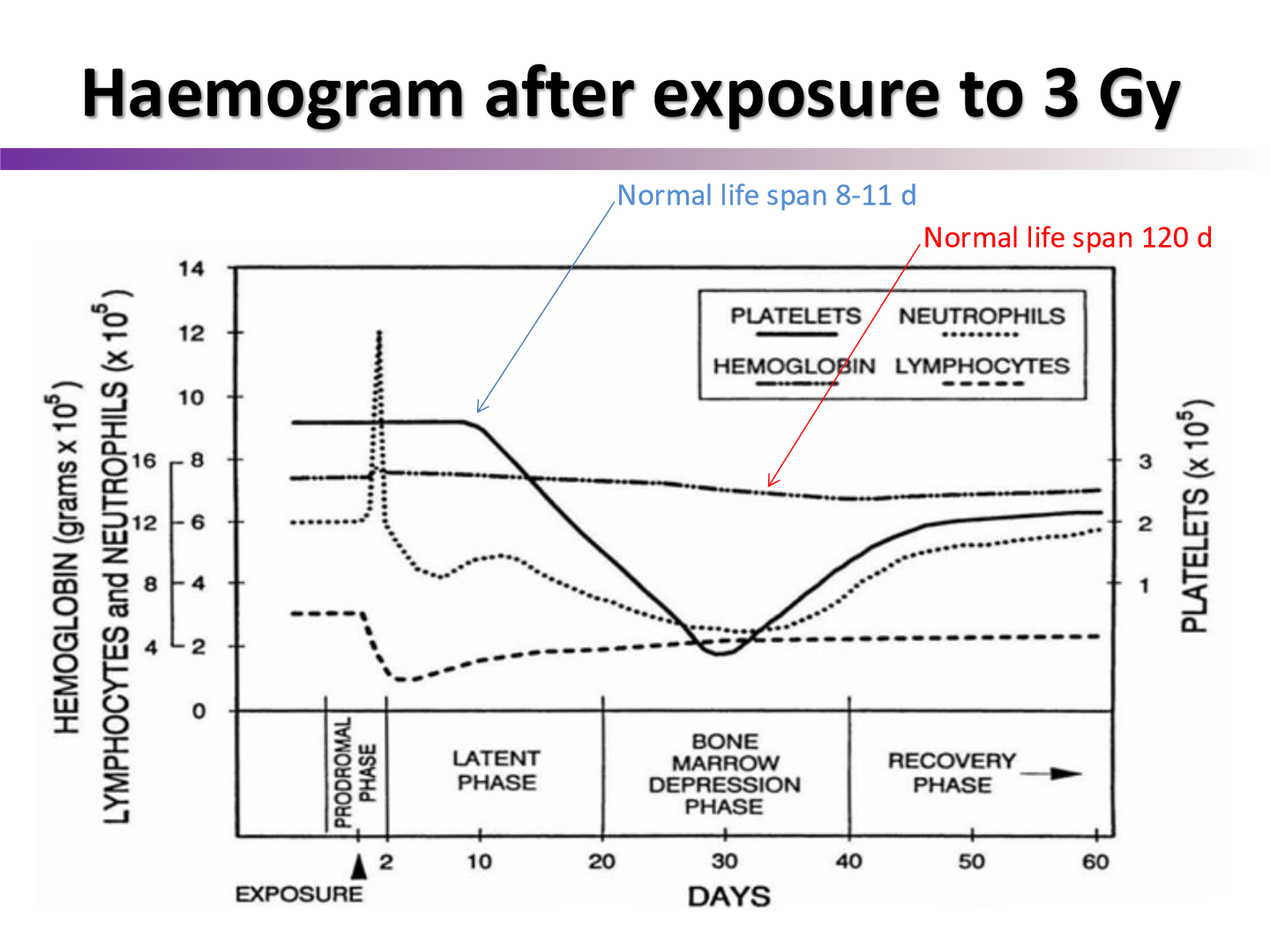
why do we see a drop in platelets at 10 days
Platelets have a shorter lifespan of about 7-10 days, leading to a drop in numbers after irradiation.
what cells do we often use as a measure of how much radiation a person got?
lymphocytes
the larger the dose, what happens to lymphocytes
lymphocyte count drops
why can skin effects occur in the absence of ARS?
lower energy photons only deposit dose to surface of body
examples of cutaneous radiation injury

severity of ARS is a function of ____
dose
time of latent period is ______ to dose
inversely proportional
again, what cells do we look at to classify exposure?
lymphocytes
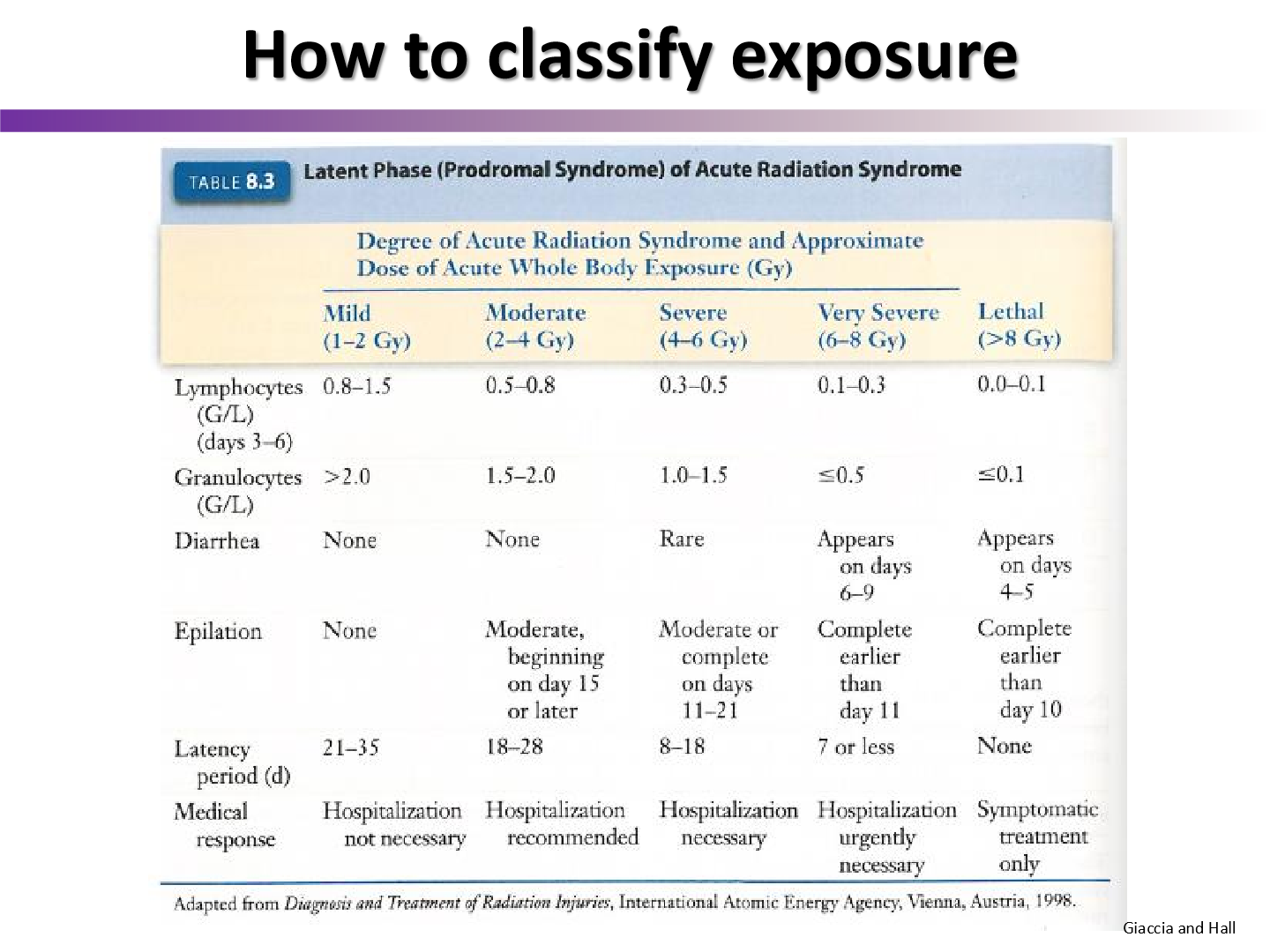
what is another thing we can look at to classify exposure?
the probability of vomiting
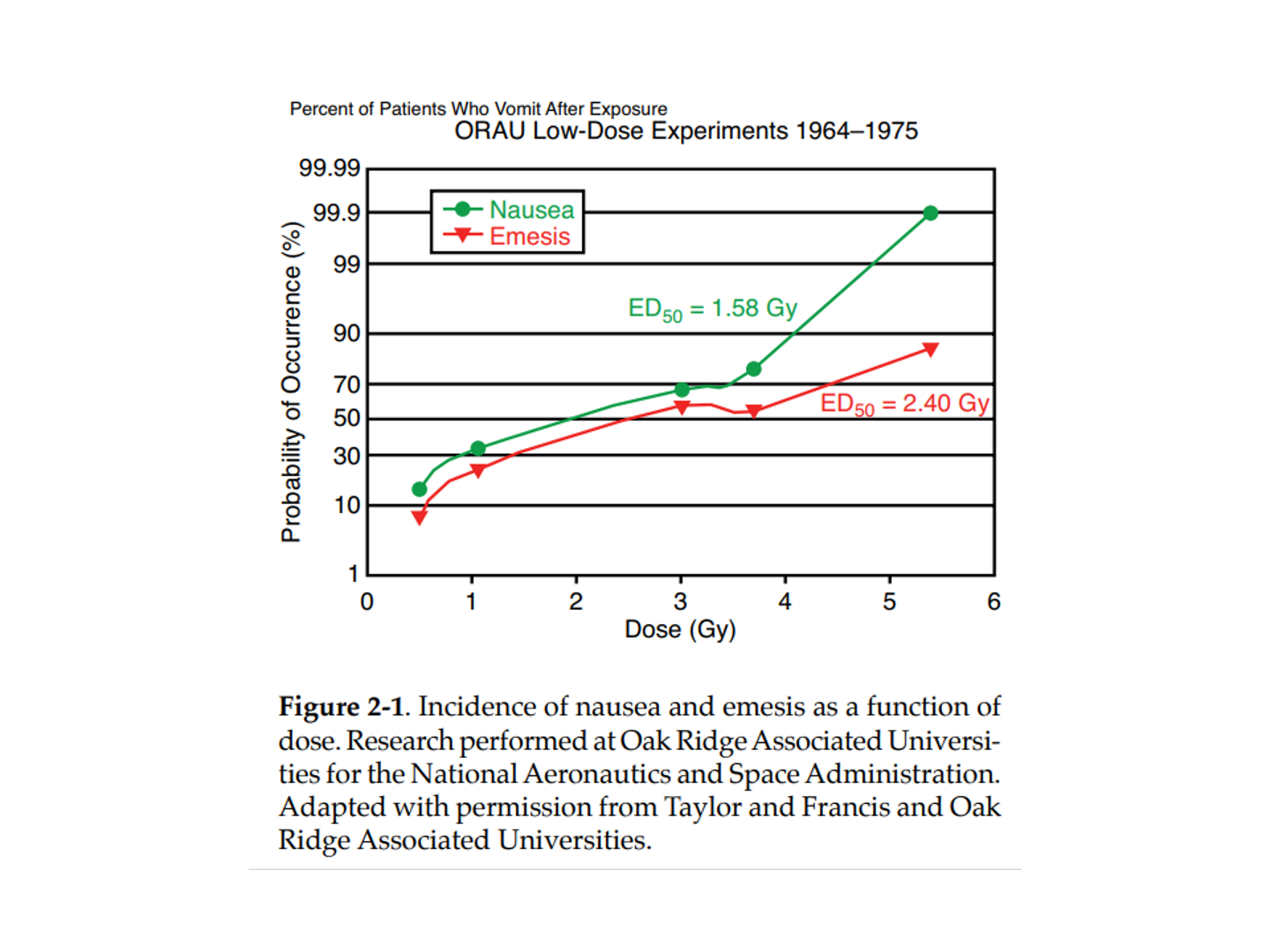
2 methods to confirm radiation exposure
lymphocyte count
vomiting time
treatment plan of radiation exposure
supportive care
gut decontamination
bone marrow transplant
radiation mitigators
examples of supportive care for radiation exposure
electrolyte/fluid replacement, isolation, antibiotics
what is sucralfate used for?
sticks to gut lining, forming a barrier to protect against sepsis
reduces radiation ulcers as well
what are the four uses of Therapeutric total body irradiation?
leukemia
lymphoma
myeloma
stem cell transplants
who was the first person to describe TBI?
Friedrich Dessauer in 1905
what cancers was TBI found most effective on?
hematopoeitic and lymphoid stem cells
how was TBI used for transplant surgeries?
was used for immunosupression before the surgery
now we just use drugs
what is graft vs. host disease
a complication that arises when newly transplanted donor cells attack reciepient’s body
TBI definition
irradiation of entire body
leukemia defintiion
group of cancers that begin in bone marrow and result in abnormal WBCs
lymphoma definition
any group of blood cell tumor that develops from lymphatic cells
multiple myeloma definition
cancer of plasma cells
HSCT definition
hematopoietic stem cell transplant: transplant stem cells derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord
most common type of lymphoma
non-hodgkins
what percent of diagnosed cancers are hematologic malignancies in adults?
10%
what percent of diagnosed cncers are hematologic malignancies in children?
40%
4 main subtypes of leukemia
acute lymphocytic
acute myelogenous
chronic lymphocytic
chronic myelogenous
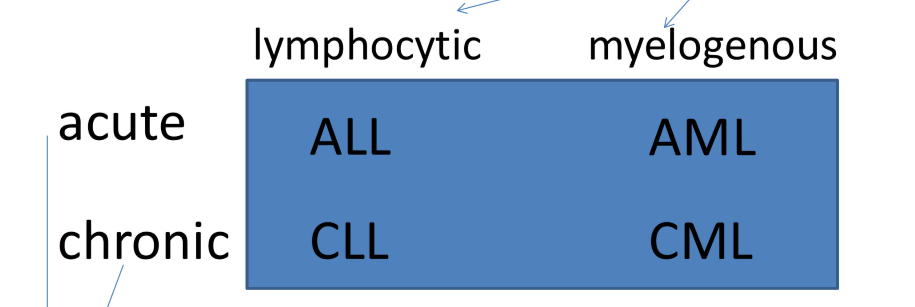
myelogenous meaning
arising from hematopoietic stem cells
lymphocytic meaning
arising from other cells in the bone marrow