Principles of Chemistry I: Matter and Its Properties
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Chemistry
is the study of matter and the changes in matter.
Matter
is anything that occupies space and has mass.
Pure Substance
is a form of matter that has a definite composition and distinct properties.
Element
is a substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances by chemical means.
Atomic Element
is an element that exists as individual atoms.
Molecular Element
is an element that exists as molecules composed of two or more atoms of the same element.
Compound
is a substance composed of atoms of two or more elements chemically united in fixed proportions.
Covalent Compound
are substances that contain atoms of different types bonded together to form molecules.
Ionic Compound
are substances that contain ratios of ions of different elements.
Mixture
is a combination of two or more components, i.e. pure substances.
Homogeneous Mixture
is uniform throughout, e.g., salt water, milk, air.
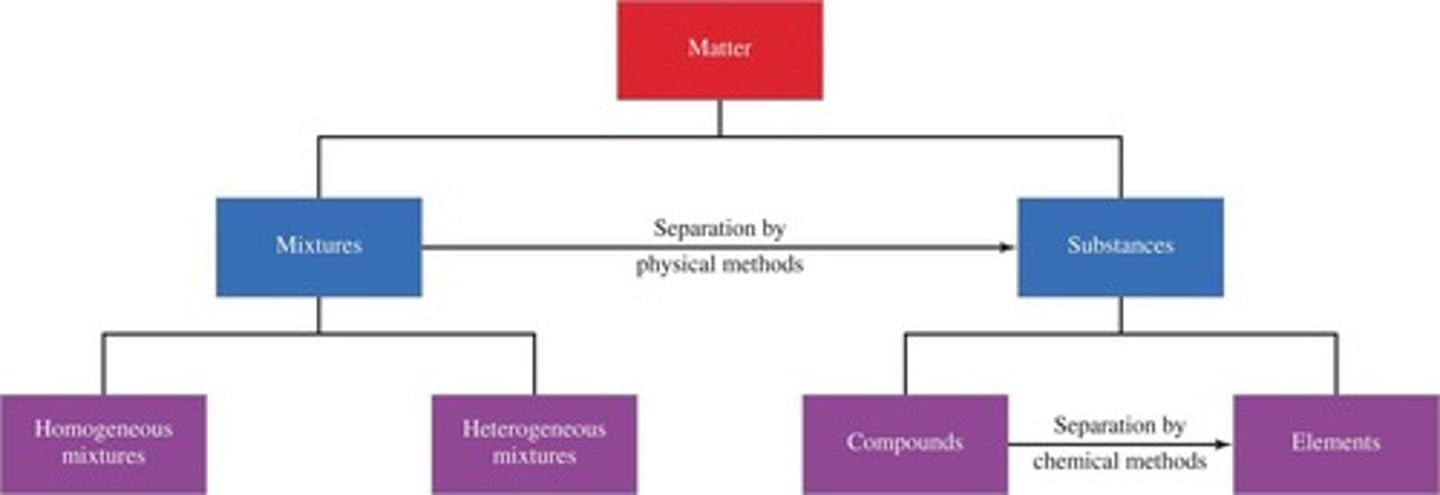
Heterogeneous Mixture
is non-uniform, e.g., sand in water, oil in water.
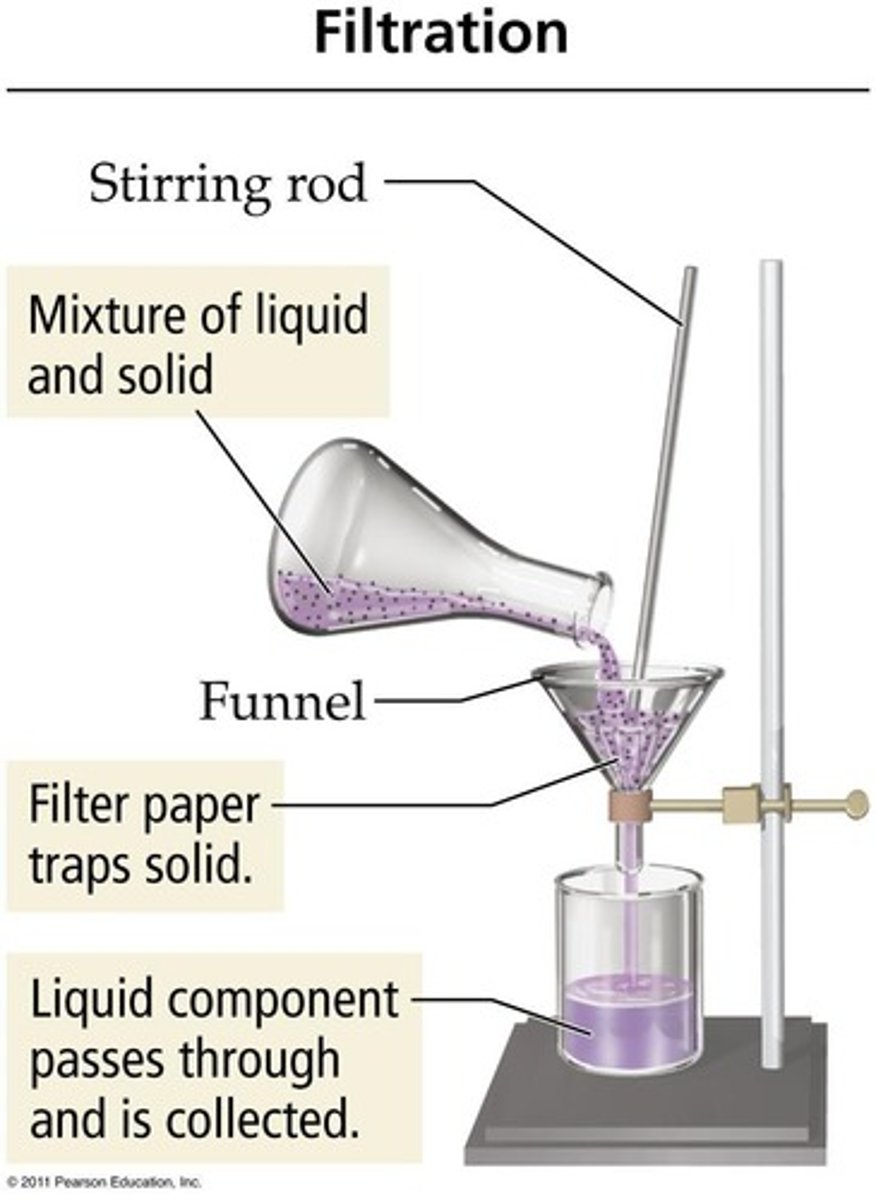
Filtration
is a physical separation technique that uses particle size to separate different components.
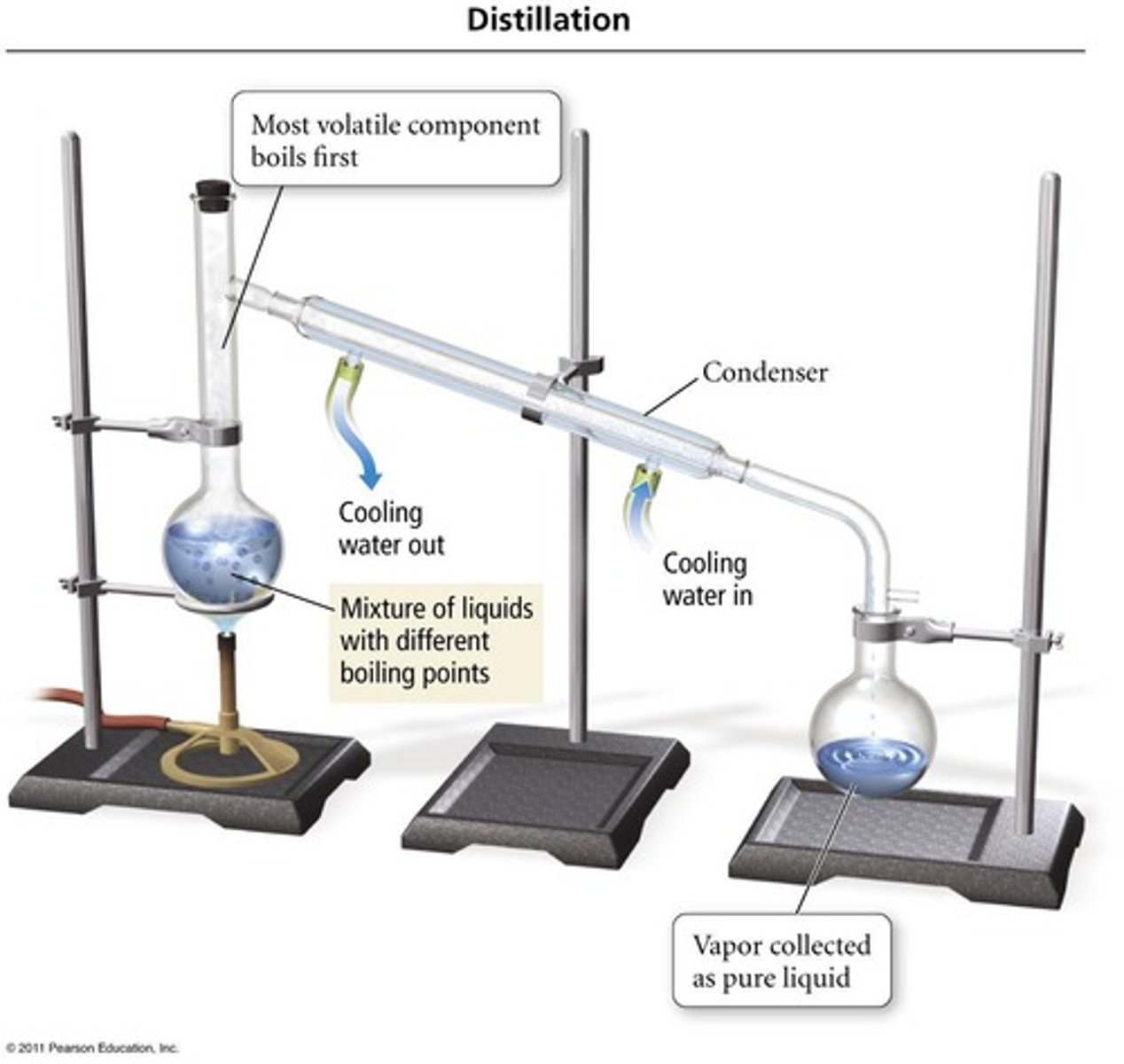
Distillation
is a technique that uses differences in the boiling points of substances to separate a homogeneous mixture.
Evaporation
is used to separate out homogeneous mixtures where there is one or more dissolved solids.
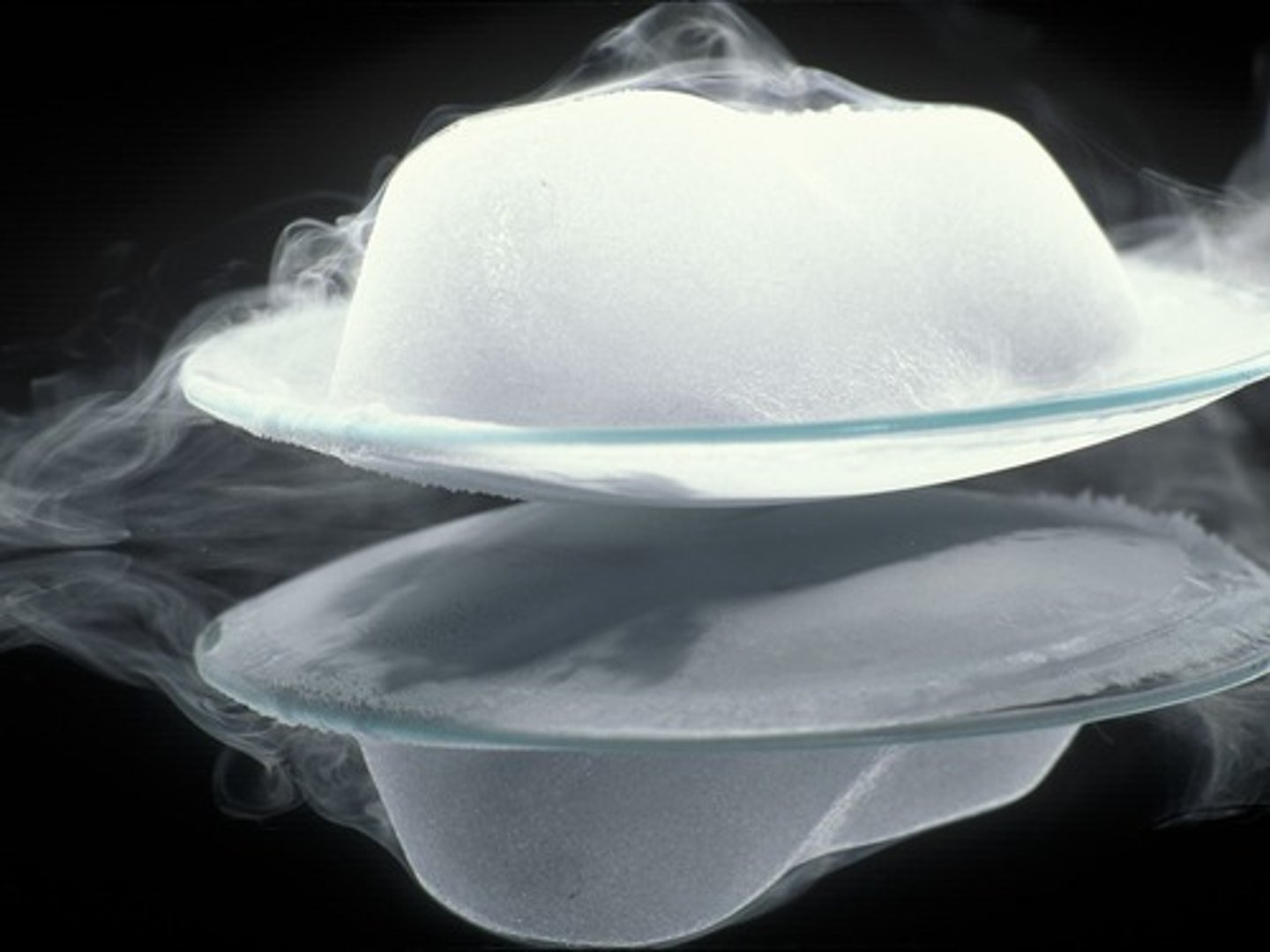
Sublimation
is a physical separation technique where a solid changes directly into a gas.
Chromatography
is a physical separation technique that separates components based on their movement through a stationary phase.
Melting Point of Ammonia
is -77.7°C.
Boiling Point of Ammonia
is -33.3°C.
Number of Identified Elements
114 elements have been identified.
Examples of Covalent Compounds
H2O (water), NH3 (ammonia), SF6 (sulfur hexafluoride), C2H6O (ethyl alcohol), CH4 (methane).
Examples of Ionic Compounds
NaCl (sodium chloride), KOH (potassium hydroxide), MgO (magnesium oxide), CaBr2 (calcium bromide).
Separation by phase change
Occurs when mixed components have different vapor pressures.
Sublimation
Separates a mixture of solids, one of which sublimes from the solid state directly into a gas.
Dry Ice Sublimation
An example is the sublimation of dry ice, which is solid carbon dioxide (CO2).
Chromatography
This technique separates substances on the basis of differences in polarity or solubility in a solvent.
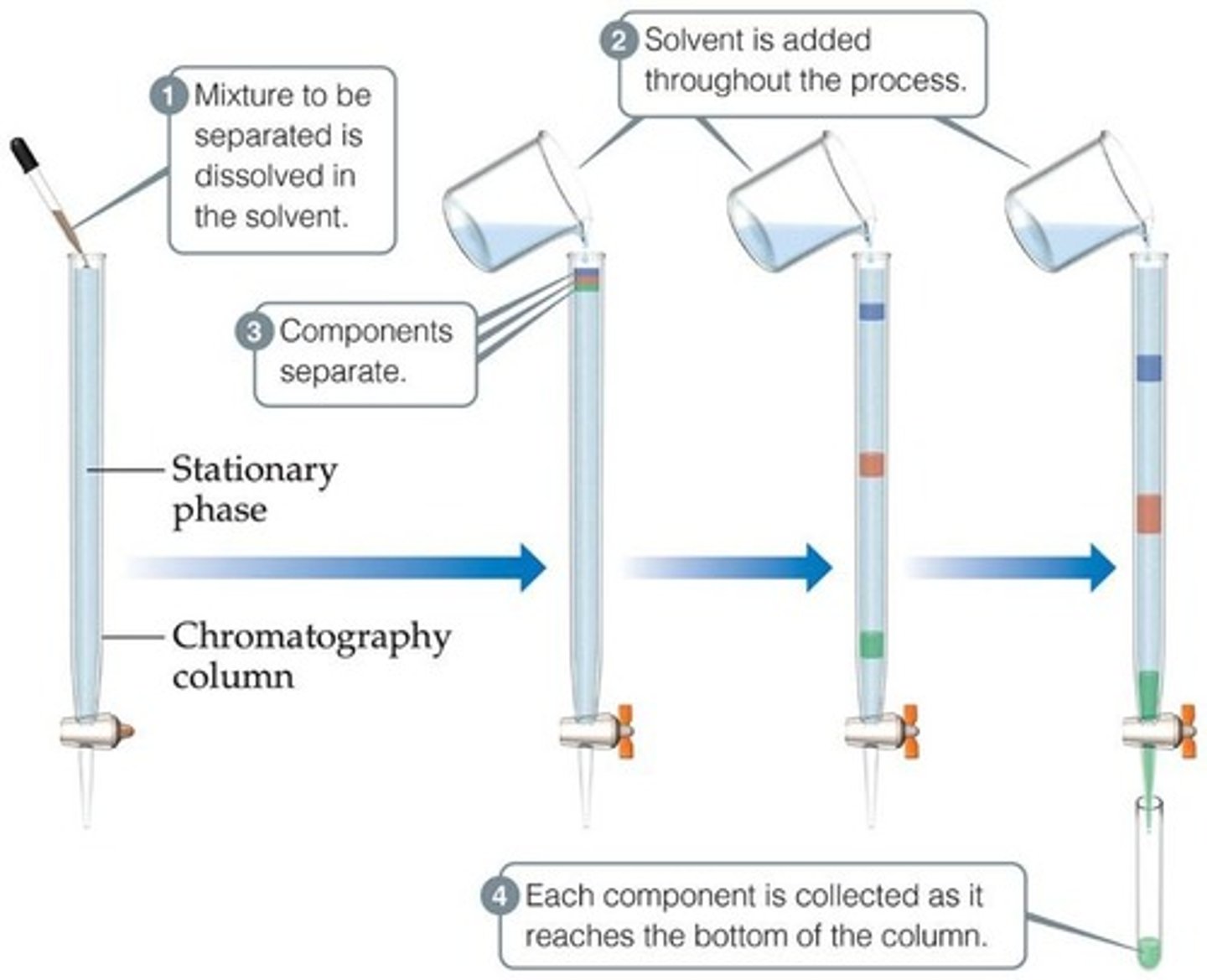
Mobile phase
The mobile phase in chromatography is either a liquid or gas.
Stationary phase
The stationary phase in chromatography is a solid like paper or silica gel.
Physical properties
Can be observed without changing the basic identity of the substance.
Chemical properties
Can only be observed when a substance is changed into another substance.
Intensive properties
Are independent of the amount of the substance that is present.
Extensive properties
Depend upon the amount of the substance present.
Chemical changes
A substance is transformed into a chemically different substance, i.e. the composition is changed.
Physical changes
Changes in matter that do not change the composition or identity of a substance.
Phase changes
A physical change in matter that involves a change in state.
Conditions for phase changes
Temperature and Pressure are important conditions to consider.
Measurements
All measured quantities have three pieces of information: the quantity or number, the unit, and the uncertainty in the measurement.
Système International d'Unités (SI Units)
There are seven base units from which other units of measurement are derived.
Length
Base unit is meter (m), which is slightly longer than a yard (0.9144 m).
Volume (V)
Derived from length cubed (l3).
Mass
Base unit is kg and is a measure of the amount of matter that something contains.
Weight
A measure of the pull of gravity on an object.
Temperature
Measure of 'hotness' or 'coldness' of an object.
Temperature Units
K (Kelvin) - SI unit, oC (degrees Celsius) - a common scientific unit, oF (degrees Fahrenheit) - not used in science.
Volume (m3)
1 m3 is a unit of measurement for volume.
Volume
A unit of measurement obtained by multiplication of appropriate base unit, i.e. l3.
SI unit for volume
Meter cubed (m3), but commonly used units are Liter (L) or milliLiter (mL).
Volume formula
Volume = l x l x l (l3), which is length cubed.
1 Liter (L)
1 L = 1 dm3.
1 milliLiter (mL)
1 mL = 1 cm3.
Scale of milli-
The prefix milli- means that there are 1000 mL in 1 L, thus, the equality 1000 mL = 1 L.
Common Measuring Devices for Volume
Pipettes can also be used to deliver variable volumes.
Mass (m)
Measure of the quantity of matter.
SI unit of mass
Kilogram (kg).
Kilogram to gram conversion
1 kg = 1000 g.
Weight
Force that gravity exerts on an object.
Mass vs. weight
Mass does not equal weight.
Weight of a 1 kg bar on Earth
2.2 lb.
Weight of a 1 kg bar on Moon
0.4 lb.
Temperature relationship (Kelvin and °C)
K = °C + 273.15.
Absolute zero
0 K (-273.15°C), the lowest possible attainable temperature.
Density (D) of Matter
Defined as the amount of mass contained in a unit volume of a substance.
Common units for density
g/mL or g/cm3.
Density of water at 25°C
D = 1.0 g/mL (or D = 1.0 g/cm3).
Density of 1 mL of water
D = 1.0 g/mL.
Density of 20 L of water
D = 1.0 g/mL.
Scientific Notation
How to convert numbers (n) into Scientific Notation (N x 10n).
Scientific Notation Rule #2
If n < 0; then move decimal to right.
Scientific Notation Rule #1
If n > 0; then move decimal to left.
Example of Scientific Notation
0.00000772 = 7.72 x 10-6.
Example of Scientific Notation
568.762 = 5.68762 x 102.
Adding and Subtracting Numbers in Scientific Notation
Write each quantity with the same exponent n and combine N1 and N2.
Multiplying Numbers in Scientific Notation
Multiply N1 and N2 and add exponents, n.
Dividing Numbers in Scientific Notation
Divide N1 and N2 and subtract exponents, n.
Inexact numbers
Obtained from measurements; values have some uncertainty and are subject to error.
Exact numbers
Not obtained from a measurement; values known exactly; infinitely precise.
Significant Figures (Sig. Figs.)
Digits that were measured (certain + uncertain).
Sig. Fig. Rule
All nonzero digits are significant.
Sig. Fig. Rule
Zeroes at the beginning of a number are never significant.
Significant Figures
Digits in a number that contribute to its precision.
Estimated Digit
The last digit in any measurement that is estimated and has error (+/- 1).
Precision
A measure of how closely individual measurements agree with each other.
Accuracy
A measure of how closely individual measurements agree with the correct value.
Dimensional Analysis
A method used to convert one quantity to another using conversion factors.
Conversion Factor
A ratio that expresses how many of one unit are equal to another unit.
Scientific Method
A systematic approach to studying matter involving observation, hypothesis, experimentation, and conclusion.
Hypothesis
A possible explanation of an observation that can be tested with an experiment.
Experiment
A procedure to test a hypothesis, law, or theory.
Conclusion
An interpretation of experimental results to determine the validity of a hypothesis.
Scientific Law
A summary of the connections between observations seen during experiments, often written as an equation.
Theory
A unifying principle that explains a body of facts and/or laws based on observations.
Significant Figures in Addition/Subtraction
Answers are rounded to keep the least number of significant figures to the right of the decimal.
Significant Figures in Multiplication/Division
Answers are rounded to keep the least number of total significant figures from the numbers used in the calculation.
Density
Mass per unit volume, commonly expressed as g/mL.
Molar Mass
The mass of one mole of a substance, expressed in grams.
Molar Concentration
The number of moles of solute per liter of solution.
Percent Error
A calculation used to determine the accuracy of a measurement.
Mean Deviation
A calculation used to determine the precision of a set of measurements.
Ruler A Measurement
Measures a length of 4.8 cm with two significant figures.
Ruler B Measurement
Measures a length of 4.85 cm with three significant figures.