Introduction to Anatomy
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
study of the normal structure of human body and their relationship with one another
Human anatomy
study of the different function of the structure and the involved processes of how they works
Human physiology
study of normal structure big enough to be studied by unaided eye
Gross/ Macroscopic Anatomy
study of specific body system
Systemic anatomy
study of structure by body region
Regional anatomy
study of landmarks in the body surface of different organs
Surface anatomy
study of structure through the use of microscope
Microscopic anatomy
microscopic study of cells
Cytology
study of normal tissues of the body
Histology
study of human body development from fertilization of ovum to the extrauterine period
Embryology
study of normal structure, gross features and development of nervous anatomy
Neuroanatomy
4 division of human anatomy
Gross
Microscopic
Embryology
Neuroanatomy
4 different division of human physiology
Cell physiology
special physiology
Systemic physiology
Pathologic physiology
cornerstone of human physiology
cell physiology
study of the function of living cells
Cell physiology
study of function of specific organs
Special physiology
all aspects of the functions of specific organ systems
Systemic physiology
the effects of disease on organ or system functions
Pathologic physiology
Maintenance of teh body’s internal environment
Homeostasis
two kinds of homeostasis; differentiate
autoregulation - cell lacks oxygen, chemicals would be released to dilate blood vessels (organ fixes itself)
Extrinsic regulation - nervous system commands increase heart rate to circulate blood faster during exercise (regulated by external system such as hormones and nervous system)
give the 6 essential life processes
metabolism
growth
reproduction
responsiveness
differentiation
movement
all the chemicals processes that occur on the body
Metabolism
the body’s ability to react to changes In environment both internally and externally
Responsiveness
motion occurring inside the human body
Movement
an increase in body size thus, an increase in the size/number of cells
Growth
breaking down of molecules to release energy
Catabolism
the building of molecules to release energy
Anabolism
development of unspecialized cell to a specialized state
Differentiation
formation of new cells for growth, repair, replacement, or reproduction of human being
Reproduction
levels of structural organization
chemical level
cell level
tissue level
organ level
organ system level
the smallest unit of life
cells
made up of different type of cells
Tissues
tissues that covers and protects
Epithelial tissue
bond and support other tissue
Connective
tissue for movement
Muscle
tissue that produce blood cells
Hemopoietic
grouped organs performing common funciion
systems
describe anatomical postion
Standing erect/ upright
face directed forward
upper limbs by sides; palm facing forward
lower limbs together; toes facing forward
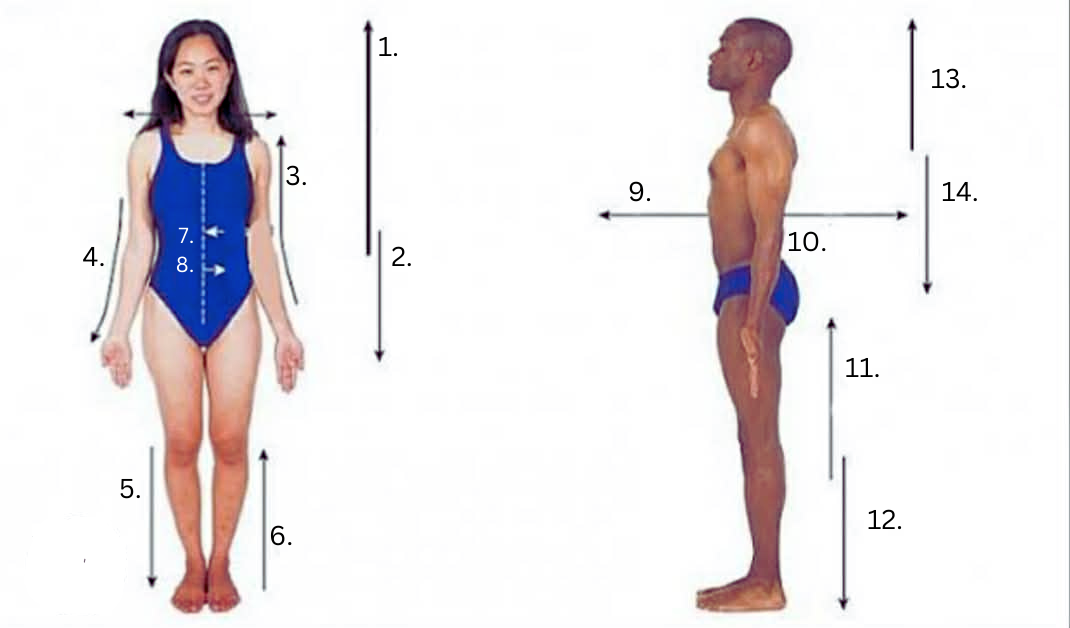
Superior (cephalic)
Inferior (Caudal)
Proximal
Distal
Distal
Proximal
Medial
Lateral
Anterior (ventral)
Posterior (Dorsal)
Proximal
Distl
Superior (cephalic)
inferior (Caudal)
the nose is ____ to the forehead
Inferior
the spine is ___ to the breastbone
Dorsal
the ankle is ____ to the hip
Distal
the nipple is ____ to the breastbone
lateral
the skin is ____ to the muscle
superficial
give the central regions of the body
head
neck
trunk
upper limb
lower limb
the three rsubegions of trunk region
Thoracic
Abdomen
Pelvis
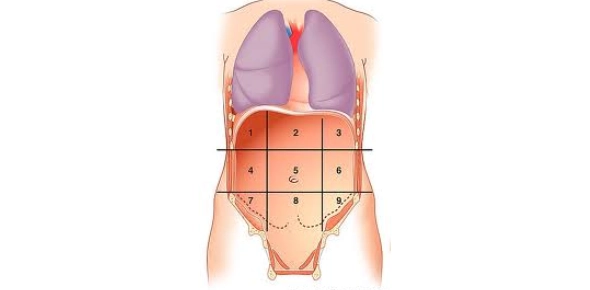
name the following parts
Right hypochondriac region
Epigastric region
Left hypochondriac region
Right lumbar region
Umbilical region
Left lumbar region
Right iliac region
Hypogastric region
Left iliac region
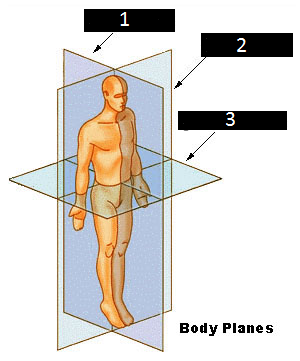
Sagittal plane
Coronal plane
Transvere plane