Cardiac Panels
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
One time lab refused to report a trop for one of my patients because it was "too high" and we had to wait until he flipped into an unstable rhythm to get him to the cath lab. So I have beef with lab.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
skeletal muscle, myocardium, brain
Major sources of CK
Muscle tissue damage (sensitive not specific)
Clinical significance of CK (Note: correlates to patients muscle mass)
3-4 (rises quick-like)
How long does CK stay in the circulation?
CKMB
What CK is specific to heart injuries?
muscular dystrophy, Rhabdo, hypothyroidism, reye’s
High CKMM can be a biomarker for
trauma, kidney injury, toxins/drugs
Besides heart injuries what else causes a rise in circulating CKMB?
normal childbirth, malignant tumors, shock syndrome
CKBB rises in the case of
reflex
If CK is elevated the lab should run __________ test that break the CK down into isoezymes.
CKMM
What CK is a major component of serum and makes up most of the circulatory total in a healthy person?
CK
What is the 1st cardiac enzyme to rise?
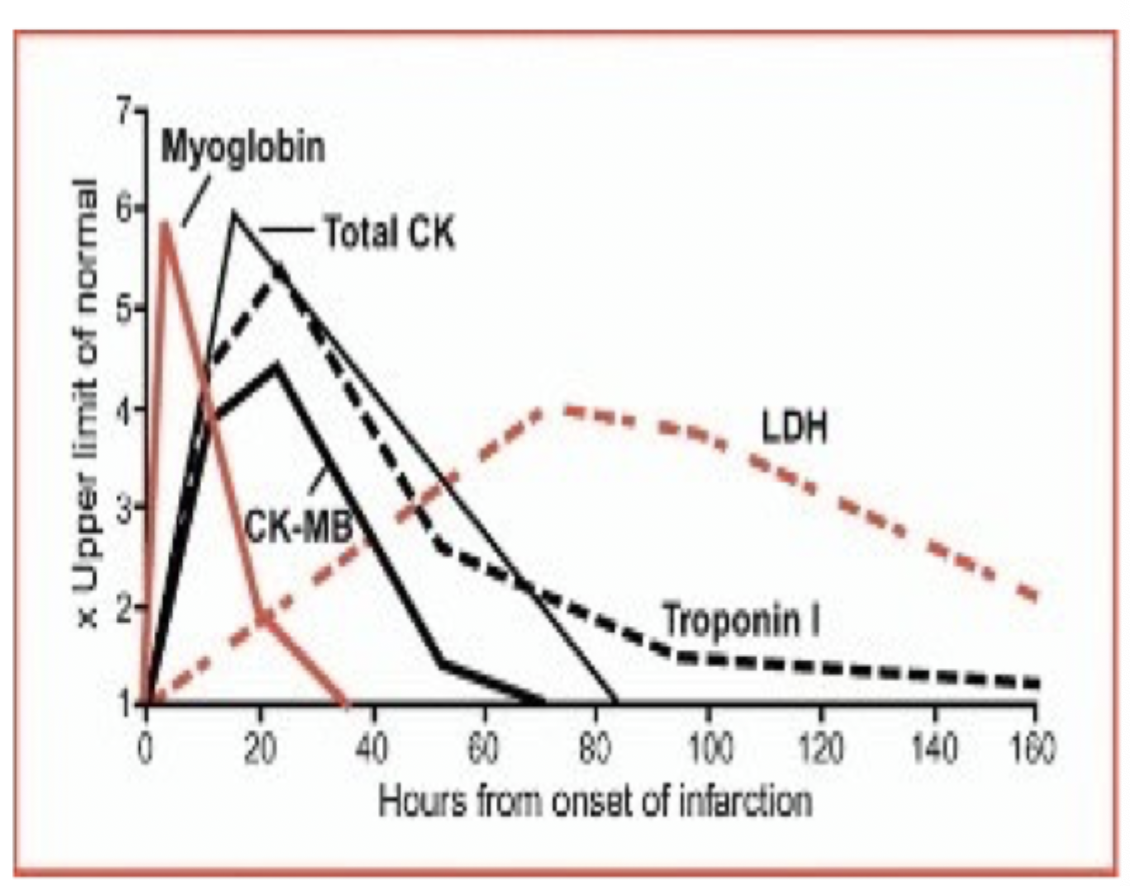
CKMB
Which CK peaks first after an acute MI?
CKMM (3-4 days)
Which CK last longer after an acute MI?
cardiac
If you have a high CK-MB relative index (RI) (above 5%) what are we thinking team?
(CKMB/total CK) X 100
How is CKMB RI calculated
Exercise, trauma, age, gender, early pregnancy, supplements
What factors affect CK interpretation?
Rhabdomyolysis (rhabdo)
A condition that is the result of damaged muscle tissue most often due to traumatic injuries (crush), drugs, toxins, infections, ischemia that can be fatal if left untreated.
CK 5X normal
What is a red flag for rhabdo?
unable to complete task/finish workouts, severe muscle cramps/pain, very dark urine
Signs of rhabdo
Supportive care
Patient presents to the ER for muscle pain and weakness. Patient reports a history of meth use, last used 2 hours ago. Nursing staff reports that the urine sample collected was dark in color. CK level is like 5000. What’s our treatment plan?
Troponin I/T
What is the 1st biomarker to look at in an MI
some type of damage to cardiac muscles
An elevated troponin I is a sign of
Same sensitivity as CKMB, Highly specific for MI (20x normal 3-12 hours post chest pain)
Describe the sensitivity and specificity of troponin I
5-10 days (good for late diagnosis)
How long does troponin I last in the system
12-24 hours
When does troponin I peak?
troponin I
A 56 y/o female presents to the ER 6 days after a episode of chest pain. She states she didn’t want to make a big fuss about it but her daughter implored her for chest pain. What cardiac biomarker could still be elevated, if she had an MI?
consistent with myocardial damage
Any troponin over 1.5 is
high sensitivity trop I
What is internationally accepted as a standard biomarker for MI?
microclots, hemolysis, skeletal muscle disease
What can cause a false increase in cardiac troponin?
autoantibodies, hemolysis, supplements
What can cause a false decrease in cardiac troponin?
myoglobin
What heme protein can be picked up in the urine 2-4 hours after an acute MI?
skeletal/cardiac muscles
Where is myoglobin found?
high, low
Describe the sensitivity and specificity of myoglobin
MI, angina, muscle trauma, renal trauma, open heart surgery, myopathies, IM injections, electric shock, vigorous shock
A high myoglobin could be a sign of what
BNP (B-type natriuretic peptide)
A patient presents to the ER with peripheral edema. What lab test needs to be included in the work up?
AST (aspartate aminotransferase)
What lab test (usually used for the liver) may also be elevated after an MI since it is found in the heart, liver, and skeletal muscles?
lactate dehydrogenase (LD, LDH)
What enzyme catalyzes the interconversion of lactate and pyruvate that can be found in the kidney, liver, and heart?
MI, hemolysis (pre analytical error), liver cirrhosis/necrosis, muscular dystrophy, pernicious anemia, malignancy
What might cause an elevation in LD
LD 1 (heart) and LD 2 (serum)
If LD is high (above 180) the lab will perform isozyme refractive testing, that breaks up _____________________.
Acute MI
If LD 1 > LD2 or if the LD1/LD2 ratio is 0.8 what are we thinking ?
lung disease, congestion, leukemia, lymphoma, and other malignancies, collagen disease, viral infections
Elevation of LD3 and LD4 is consistent with
liver disease, type 1 muscle fiber injury
Elevation of LD5 is consistent with