Cell Cycle Control System - Law of independent assortment
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
1
New cards
what is a cell cycle control system made up of
set of molecules
2
New cards
what does a cell cycle control system do
triggers and coordinates key events in the cell cycle
3
New cards
what is the cell cycle control system analogous to
the time dial of a washing machine
4
New cards
how many check points are in a cell cycle control system
3
5
New cards
what does the first check point in a cell cycle control system do and what is it called
G1, go ahead or stop (checks chromatin)
6
New cards
what does the second check point in a cell cycle control system do and what is it called
G2. into M phase (mitosis begins)
7
New cards
what does the third check point in a cell cycle control system do and what is it called
M, onset of anaphase (kinetochore is in right place)
8
New cards
life cycle of an animal cell
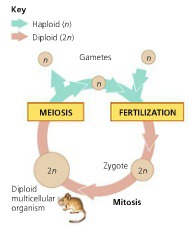
9
New cards
mitosis vs meiosis
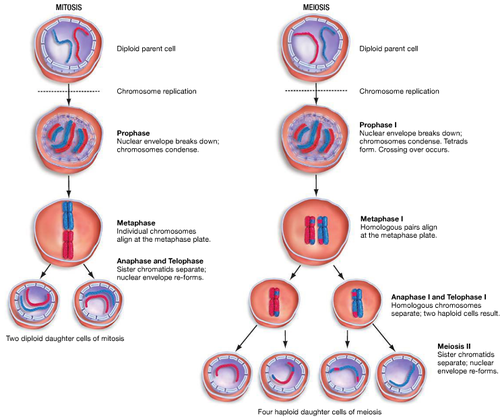
10
New cards
interphase cell in meiosis
11
New cards
what is different in a cell in interphase in meiosis
homologous pairs
one from each parent
genes for some character at corresponding loci
chiasmata
points where strands hold together
one from each parent
genes for some character at corresponding loci
chiasmata
points where strands hold together
12
New cards
define cross over
reciprocal exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids
13
New cards
cell in prophase 1 (meiosis)

14
New cards
cell in metaphase 1 (meiosis)
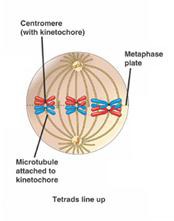
15
New cards
how to homologous pairs arrange themselves in metaphase 1
independent of each other (equal parts on each side of the plate)
16
New cards
cell in anaphase 1
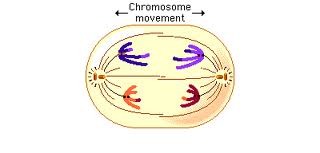
17
New cards
cell in telophase and cytokinesis meiosis
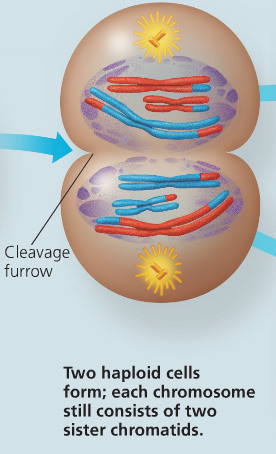
18
New cards
cell in prophase 2

19
New cards
in what phase do spindles form
prophase 2
20
New cards
cell in metaphase 2
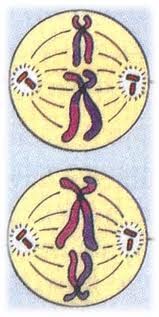
21
New cards
cell in anaphase 2

22
New cards
cell in telophase 2 and cytokinesis
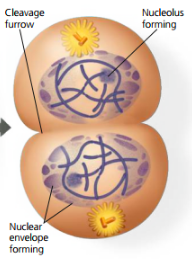
23
New cards
what is the result of telophase 2 and cytokinesis
four daughter cells
24
New cards
what experiment did Gregor Mendel do (1857)
grew peas at a monastery in Europe
25
New cards
what did Gregor Mendel study
inheritance
26
New cards
in dom and recessive traits what is controlled breeding
when plants are one or the other
27
New cards
what were the steps Gregor Mendel did in his experiment
1. removed stamens from purple
2. pollen from white to purple
3. carpel developed into pod
4. planted resulting seed
5. examined off spring
2. pollen from white to purple
3. carpel developed into pod
4. planted resulting seed
5. examined off spring
28
New cards
what is the law of segregation
alleles account for variation
an organism inherits two alleles for each character
allele is dominate when expressed in the heterozygous state
the two alleles for each character seperate during meiosis
an organism inherits two alleles for each character
allele is dominate when expressed in the heterozygous state
the two alleles for each character seperate during meiosis
29
New cards
where do they two inherited alleles come from
each parent
30
New cards
what is the locus
specific location of a gene on a chromosome
31
New cards
what allele is not expressed in the heterozygous state
recessive
32
New cards
how many likely combiantions will there be for any given fusion between gametes
4
33
New cards
what is genotype
resulting alleles
34
New cards
what is phenotype
expression of these alleles
35
New cards
what did mendel originally try to work on
mice
36
New cards
what is the law of independet assortment
each pair of alleles segregates themselves independently during gamete formation
37
New cards
what is each character determined by
one gene, two alleles
38
New cards
is one character always dominant to the other
no