Earth Science: The Universe and Solar System, Earth Systems
5.0(2)Studied by 115 people
Card Sorting
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:16 PM on 10/23/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
1
New cards
The Universe
- comprises all space and time, and all matter & energy in it
- made up of 4.6% baryonic matter, 24% cold matter, and 71.4% dark energy
- it is 13.8 billion years old
- made up of 4.6% baryonic matter, 24% cold matter, and 71.4% dark energy
- it is 13.8 billion years old
2
New cards
Hydrogen, helium and Lithium
The three most abundant elements in the universe
3
New cards
Baryonic Matter
? 4.6%
? 4.6%
- “ordinary” matter consisting of protons, electrons and neutrons that comprises atoms, planets, stars, galaxies and other bodies
- How much of it is in the universe?
- How much of it is in the universe?
4
New cards
Dark Matter
? 24%
? 24%
- matter that has gravity but does not emit light
- How much of it is in the universe?
- How much of it is in the universe?
5
New cards
Dark Energy
? 71.4%
? 71.4%
- a source of anti-gravity; a force that counteracts gravity and causes the universe to expand
- How much of it is in the universe?
- How much of it is in the universe?
6
New cards
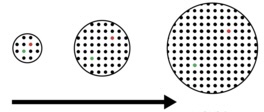
The Steady State Model
- proposed in 1948 by Bondi and Gould and by Hoyle
- pertains that new matter is created as the universe expands thereby maintaining its density
- implies that universe have NO BEGINNING and END
- pertains that new matter is created as the universe expands thereby maintaining its density
- implies that universe have NO BEGINNING and END
7
New cards
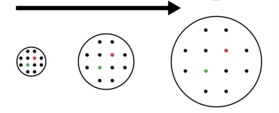
The Big Bang Theory
- states that one time, the entire universe was confined to a dense, hot, supermassive ball. Then, about 13.8 billion years ago, a violent EXPLOSION occurred, hurling this material in all directions
8
New cards
1. General Relativity
2. Cosmological principle
2. Cosmological principle
• what are the 2 ideas the Big Bang Theory rests on?
(1) Gravity is a distortion of space and time
(2) Assumes that the universe is homogeneous and isotropic; means every observer SHOULD see the universe with the same physical properties wherever you like and the same structure whatever direction you see it
(1) Gravity is a distortion of space and time
(2) Assumes that the universe is homogeneous and isotropic; means every observer SHOULD see the universe with the same physical properties wherever you like and the same structure whatever direction you see it
9
New cards
1. Redshift
2. Abundance of hydrogen, helium & lithium
3. uniformly pervasive cosmic microwave background radiation
2. Abundance of hydrogen, helium & lithium
3. uniformly pervasive cosmic microwave background radiation
• The tests for expansion the Big Bang Theory has withstood
10
New cards
Redshift
- the shifting of absorption lines from the light spectrum towards larger wavelength(red light)
- happens when a light source is moving away(receding) towards the observer
- discovered by Edwin Hubble when he noticed that most galaxies have spectral shifts toward the red end of the spectrum
- happens when a light source is moving away(receding) towards the observer
- discovered by Edwin Hubble when he noticed that most galaxies have spectral shifts toward the red end of the spectrum
11
New cards
Hubble’s Law
- states that galaxies recede at speeds proportional to their distances from the observer
12
New cards
Cosmic Microwave Background
- a faint glow of light that fills the universe, falling on Earth from every direction with nearly uniform intensity
- can be observed as a striking uniform glow in the microwave band coming from all directions-blackbody radiation with an average temp of about 2.7 degrees above absolute zero
- can be observed as a striking uniform glow in the microwave band coming from all directions-blackbody radiation with an average temp of about 2.7 degrees above absolute zero
13
New cards
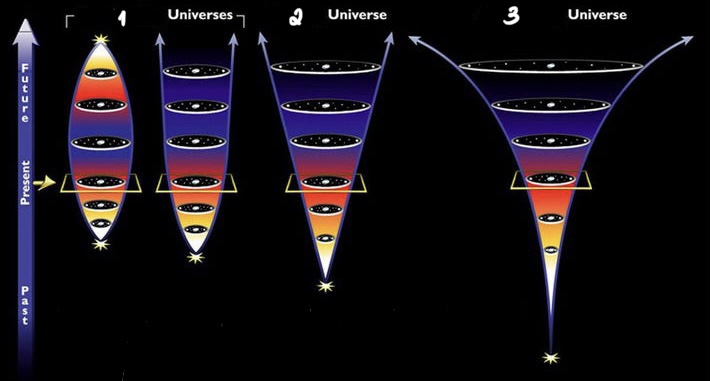
1. Decelerating universes
2. Coasting universe
3. Accelerating universe
2. Coasting universe
3. Accelerating universe
• The three possible fate of Expanding Universe
14
New cards
Stars
- formed when gravity cause matter to accumulate into large “clumps” and “strands” of interstellar matter known as NEBULAE
- first developed approximately after 400,000 millions years after the Big Bang
- first developed approximately after 400,000 millions years after the Big Bang
15
New cards
All stars, regardless of their size, run out of fuel and collapse due to gravity
• How do stars die?
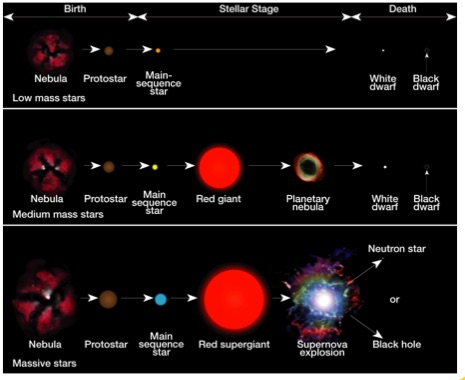
16
New cards
Hertzprung-Rusell Diagram
- a graphical representation of the relationship between the true brightness(absolute magnitude) of stars and their respective temperatures
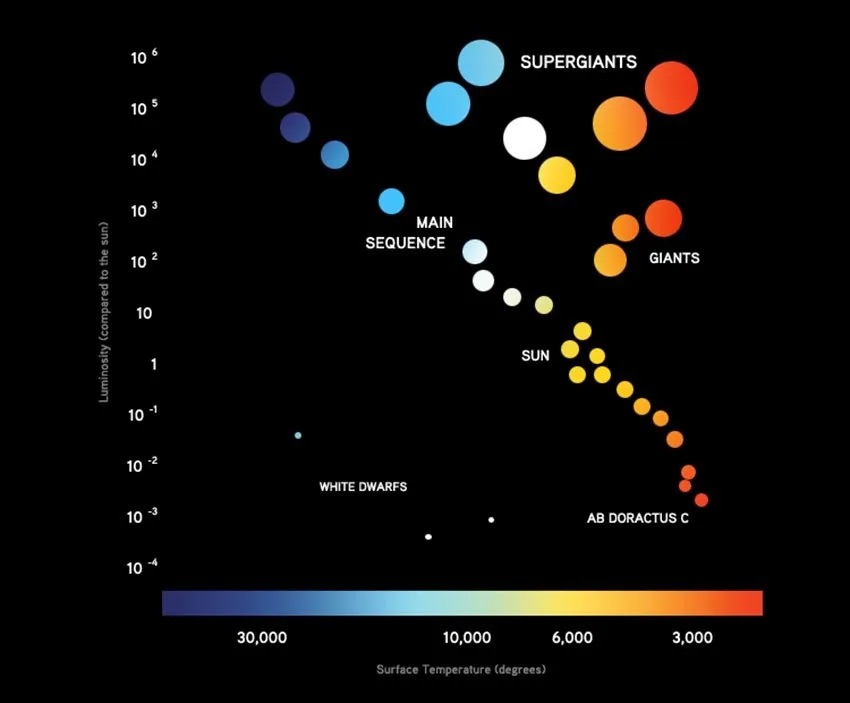
17
New cards
H-R Diagram and Stellar Evolution
- useful for illustrating the changes that take place in an individual star during its life span
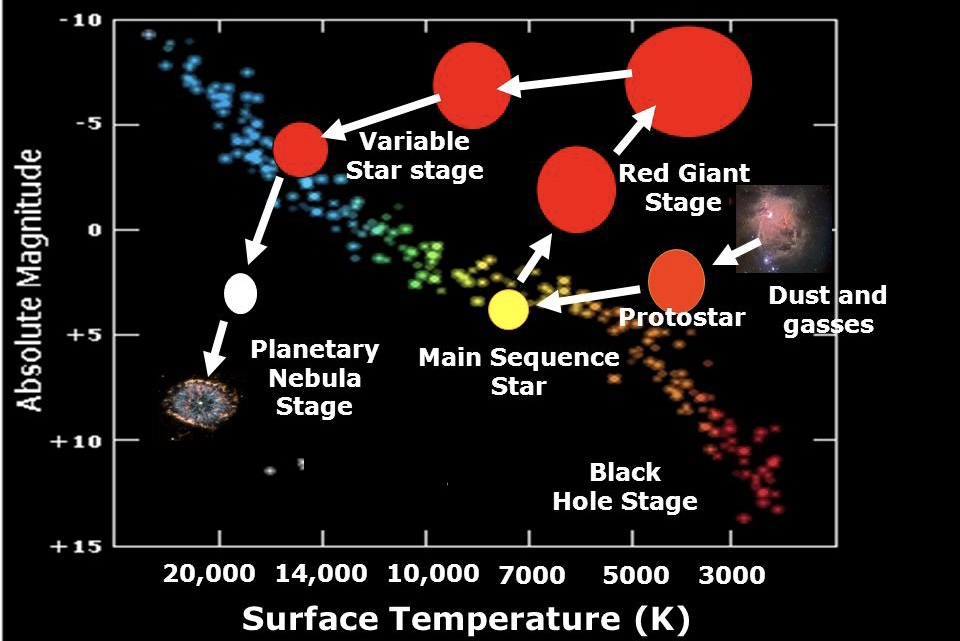
18
New cards
Galaxies
- collections of interstellar matter, stars and stellar remnants that are gravitationally bound
- the first of them were small and composed mainly of massive stars and abundant interstellar matter
- have 3 basic types
- the first of them were small and composed mainly of massive stars and abundant interstellar matter
- have 3 basic types
19
New cards
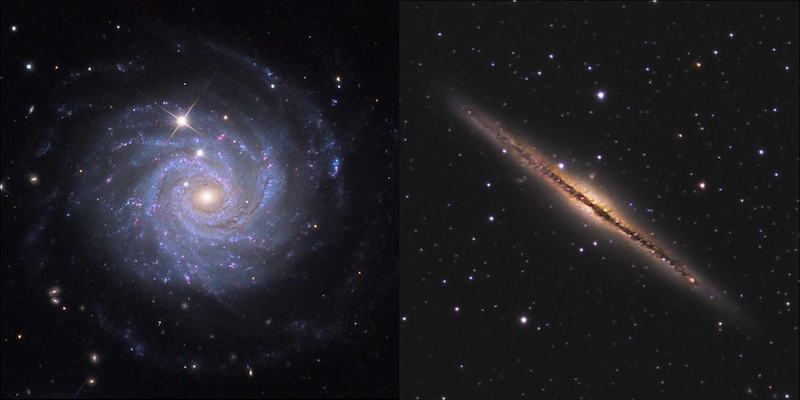
Spiral Galaxies
- flat, disk-shaped objects that range from 20,000 to about 125,000 light-years in diameter
- have a greater concentration of stars near their centers, but there are numerous variations
- makes up 30% of the universe
- have a greater concentration of stars near their centers, but there are numerous variations
- makes up 30% of the universe

20
New cards
Milky Way
- a large SPIRAL GALAXY whose disk is about 100,000 light years wide and about 10,000 light years thick at the nucleus
- has at least 3 distinct spiral arms, with some splintering
- part of the so called Local Group of Galaxies, which in turn is part of the Virgo supercluster of galaxies
- has at least 3 distinct spiral arms, with some splintering
- part of the so called Local Group of Galaxies, which in turn is part of the Virgo supercluster of galaxies

21
New cards
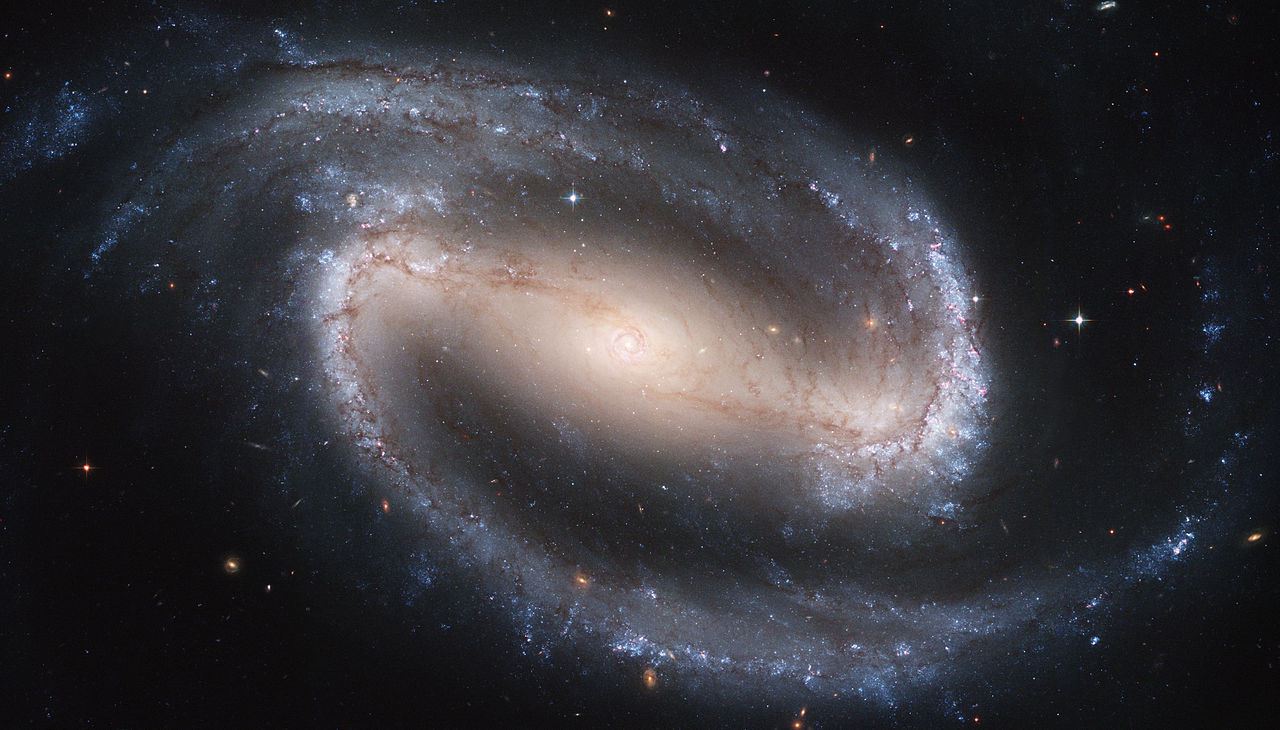
Barred Spiral Galaxy
• Andromeda Galaxy
• Andromeda Galaxy
• what kind of spiral galaxy is this?
• give an example
• give an example

22
New cards
Elliptical Galaxy
• Cygnus A
• Cygnus A
- have an ellipsoidal shape that can be nearly spherical and they LACK SPIRAL ARMS
- some of the largest and smallest galaxies are classified as this
- makes up 60% of the universe
• give an example
- some of the largest and smallest galaxies are classified as this
- makes up 60% of the universe
• give an example

23
New cards
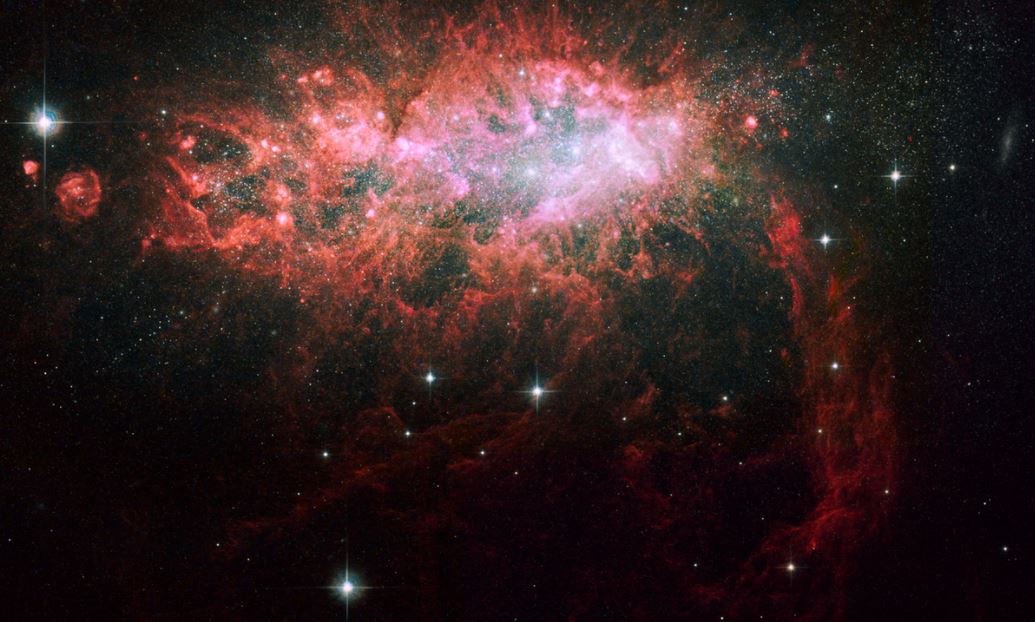
Irregular Galaxy
• Small & Large Magellanic Clouds
• Small & Large Magellanic Clouds
- have no symmetry
- some were once spiral or elliptical galaxies that were subsequently distorted by the gravity of a large neighbor
• give an example
- some were once spiral or elliptical galaxies that were subsequently distorted by the gravity of a large neighbor
• give an example

24
New cards
Galactic Clusters
• Fornax Galaxy Cluster
• Fornax Galaxy Cluster
- galaxies that are grouped intro gravitationally bound clusters
• give an example
• give an example
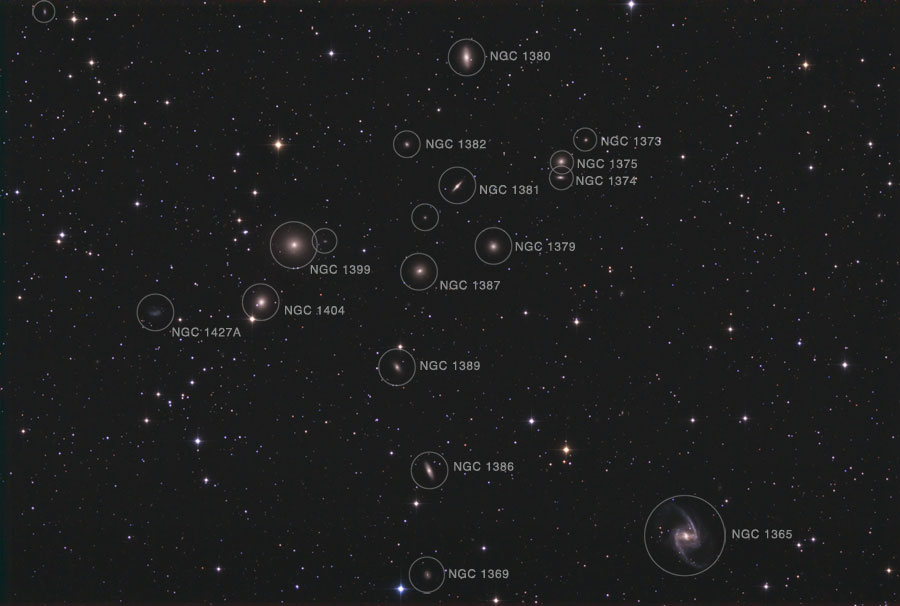
25
New cards
Galactic Collisions
- interactions between galaxies, often driven by one GALAXY’S GRAVITY disturbing another
- common within galactic cluster
- common within galactic cluster
26
New cards
Solar System
- located in the Milky Way galaxy
- comprises the Sun, eight planets, dwarf planets suck as Pluto, satellites, asteroids, comets, other minor bodies suck as those in the Kuiper belt and interplanetary dust
- comprises the Sun, eight planets, dwarf planets suck as Pluto, satellites, asteroids, comets, other minor bodies suck as those in the Kuiper belt and interplanetary dust
27
New cards
• Orbits of the planets are ELLIPTICAL and are on the same plane
• the periods of revolution of the planets increase with increasing distance from the Sun
• the periods of revolution of the planets increase with increasing distance from the Sun
• the solar system in Macroscale
28
New cards
• Most planets rotate prograde(west to east)
• Planets fall into 2 groups based on location size and density; terrestrial and Jovian
• Planets fall into 2 groups based on location size and density; terrestrial and Jovian
• the solar system in Microscale
29
New cards
Terrestrial Planets
• Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars
• Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars
- a planet that is composed primarily of silicate rocks or metals,
• give the 4 examples in the Solar System
• give the 4 examples in the Solar System
30
New cards
Jovian Planets
• Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
• Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
- massive gaseous planets(gas giants) that extent far from the sun
- planets that do not have solid surfaces, have many moons and rings
• give the 4 examples in the Solar System
- planets that do not have solid surfaces, have many moons and rings
• give the 4 examples in the Solar System
31
New cards
Nebular Hypothesis
- hypothesis for the origin of the Solar System
- thought of rotating gaseous cloud that cools and contracts in the middles to form the Sun and the rest into a disc
- in this theory, the whole Solar System starts as a large cloud of gas that contracts under self gravity
- thought of rotating gaseous cloud that cools and contracts in the middles to form the Sun and the rest into a disc
- in this theory, the whole Solar System starts as a large cloud of gas that contracts under self gravity
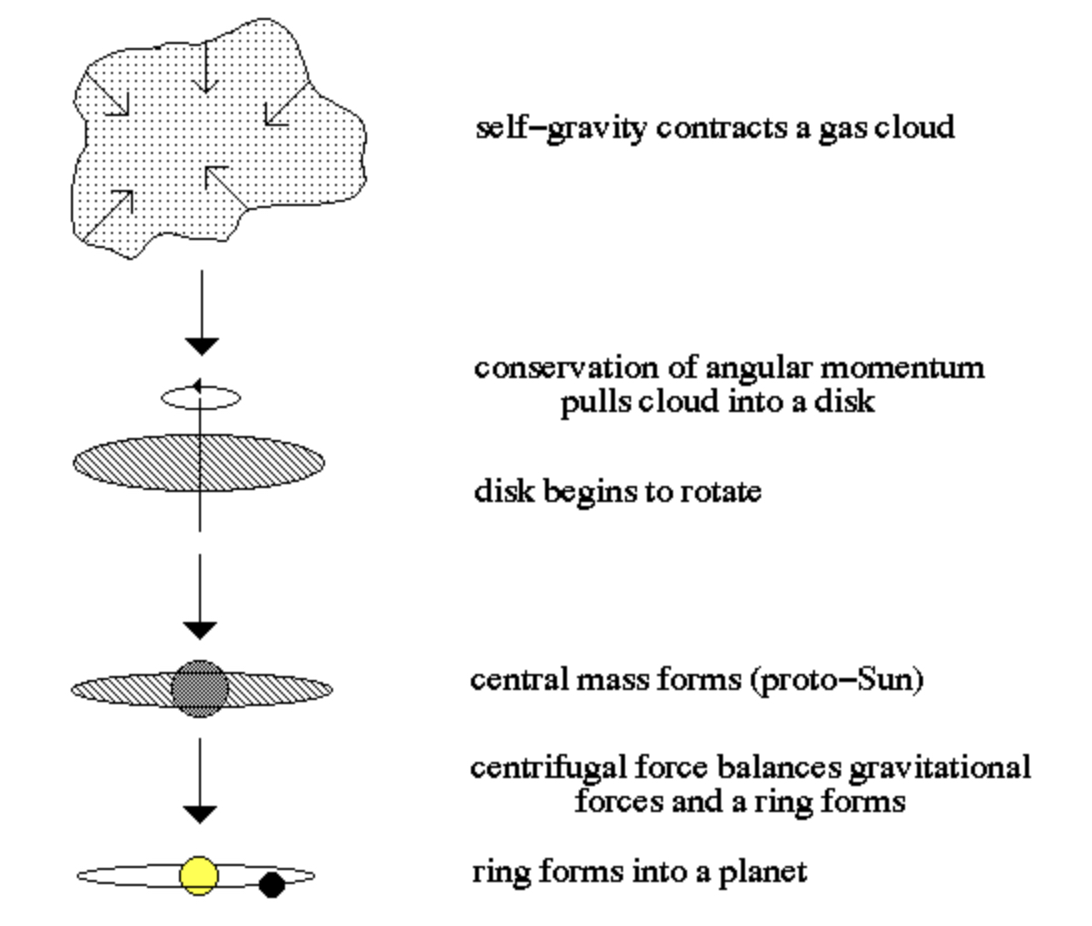
32
New cards
Encounter Hypothesis
- hypothesis for the origin of the Solar System
- a “near miss” encounter occurs between the Sun and a passing star. Material is pulled from the stellar surfaces by tidal forces then cools and condenses to form planetary bodies
• Problems: (1)hot gas expands not contracts and would not form planets. (2) encounter between stars are extremely rare
- a “near miss” encounter occurs between the Sun and a passing star. Material is pulled from the stellar surfaces by tidal forces then cools and condenses to form planetary bodies
• Problems: (1)hot gas expands not contracts and would not form planets. (2) encounter between stars are extremely rare
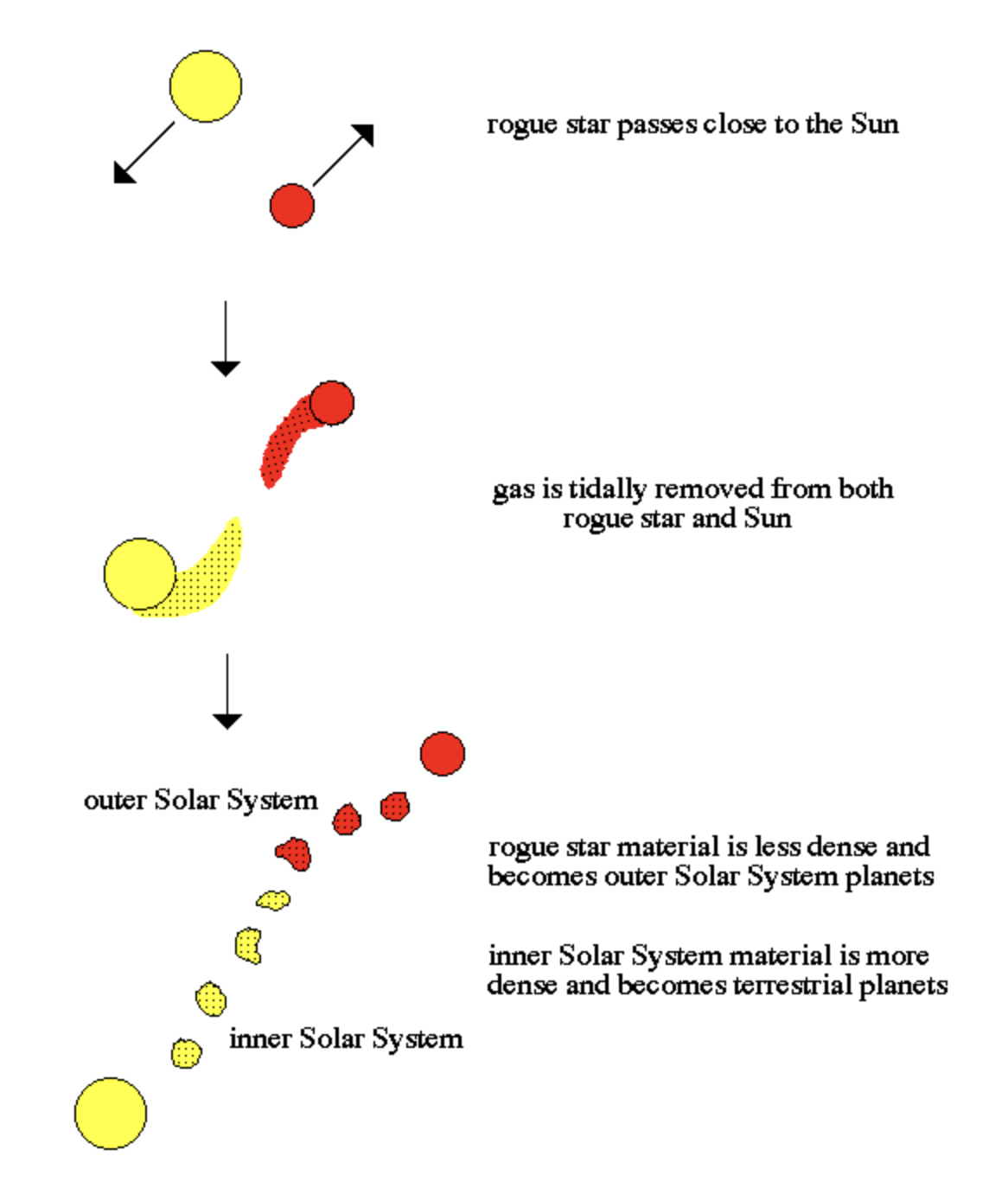
33
New cards
Protoplanet Hypothesis
- hypothesis for the origin of the Solar System
- incorporates many of the components of the nebular hypothesis, but adds some new aspects from modern knowledge of fluids ands states of matter
- In the Orion arm of the Milky Way galaxy, a slowly-rotating gas and dust cloud dominated by hydrogen and helium starts to contract due to gravity
- as most of the mass move to the center to eventually become a proto-Sun, the remaining materials form a disc that will eventually become the planets and momentum is transferred outwards
- incorporates many of the components of the nebular hypothesis, but adds some new aspects from modern knowledge of fluids ands states of matter
- In the Orion arm of the Milky Way galaxy, a slowly-rotating gas and dust cloud dominated by hydrogen and helium starts to contract due to gravity
- as most of the mass move to the center to eventually become a proto-Sun, the remaining materials form a disc that will eventually become the planets and momentum is transferred outwards
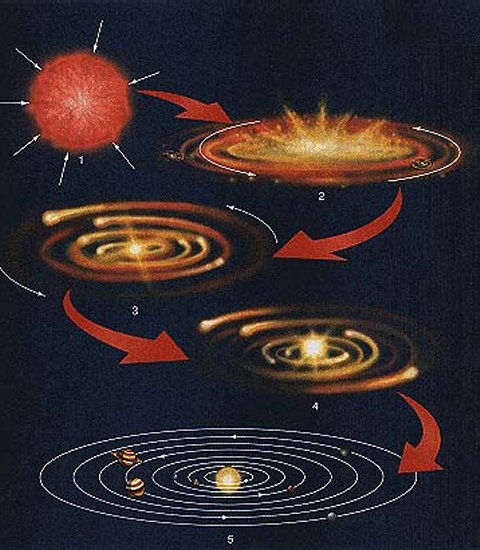
34
New cards
Temperature
• -15ºC to 115ºC
• -15ºC to 115ºC
• factors that make a planet habitable
- influences how quickly atoms and molecules move
• acceptable range in Celsius where liquid water can still exist under certain conditions
- influences how quickly atoms and molecules move
• acceptable range in Celsius where liquid water can still exist under certain conditions
35
New cards
Atmosphere
• 100 miles thick
• 100 miles thick
• factors that make a planet habitable
- keep the surface warm & protects it from radiation and small to medium sized meteorites
• acceptable thickness in miles
- keep the surface warm & protects it from radiation and small to medium sized meteorites
• acceptable thickness in miles
36
New cards
Energy
• factors that make a planet habitable
- can either be light or chemical
- with it, cells can run the chemical reactions necessary for life
- can either be light or chemical
- with it, cells can run the chemical reactions necessary for life
37
New cards
Nutrients
• factors that make a planet habitable
- used to build and maintain an organism’s body
- used to build and maintain an organism’s body
38
New cards
Energy from the sun
• factor on Earth that Sustains Life; Energy
- drives EXTERNAL PROCESSES such as weather, ocean, circulation and erosional processes, PHOTOSYNTHESIS
- drives EXTERNAL PROCESSES such as weather, ocean, circulation and erosional processes, PHOTOSYNTHESIS
39
New cards
Energy from the Earth’s interior
• factor on Earth that Sustains Life; Energy
- drives INTERNAL PROCESSES including volcanoes, earthquakes and mountain building
- drives INTERNAL PROCESSES including volcanoes, earthquakes and mountain building
40
New cards
Water
• factor on Earth that Sustains Life
- one of the most important prerequisites of life4
- important part in regulating temperature, chemical reactions to matter, to aquatic habitat
- one of the most important prerequisites of life4
- important part in regulating temperature, chemical reactions to matter, to aquatic habitat
41
New cards
Gases
• factor on Earth that Sustains Life
- makes up the atmosphere; greenhouse gases helps maintain the heat on Earth
- essential to photosynthesis and other biochemical reactions
- makes up the atmosphere; greenhouse gases helps maintain the heat on Earth
- essential to photosynthesis and other biochemical reactions
42
New cards
Resources
• factor on Earth that Sustains Life
- include water, soil, minerals and energy
- have 2 broad categories: renewable and nonrenewable
- include water, soil, minerals and energy
- have 2 broad categories: renewable and nonrenewable
43
New cards
• In the ‘Habitable Zone” where you have just the right distance away from a star like the Sun
• Made of Rocks
• Big enough to have a molten core
• Have a protective atmosphere
• Made of Rocks
• Big enough to have a molten core
• Have a protective atmosphere
• Characteristics of a Habitable Planet
44
New cards
System
- any size group of interacting parts that form a unified and complex whole
45
New cards
Open System
• type of system
- allows energy and matter to flow in and out of the system
- allows energy and matter to flow in and out of the system
46
New cards
Closed System
• type of system
- allows energy to flow in and out of the system while matter cannot
- allows energy to flow in and out of the system while matter cannot
47
New cards
Atmosphere
• through atmospheric circulation
• through atmospheric circulation
• Earth’s Subsystem
- the thin gaseous layer that envelopes the Earth
- composed of 78% nitrogen(N), 21% oxygen(O), 0.9% argon(Ar), and trace number of other gases
- along with hydrosphere, where the exchange of heat and moisture occur
• How is the heat of Earth’s surface redistributed
- the thin gaseous layer that envelopes the Earth
- composed of 78% nitrogen(N), 21% oxygen(O), 0.9% argon(Ar), and trace number of other gases
- along with hydrosphere, where the exchange of heat and moisture occur
• How is the heat of Earth’s surface redistributed
48
New cards
Geosphere
• Earth’s Subsystem
- associated with solid portion of the Earth
- includes the rocks of the crust and mantle, metallic liquid outer core and the solid metallic inner core
- the physical structure of the surface of the Earth is shaped through process of plate tectonics[a process for this subsystem]
- associated with solid portion of the Earth
- includes the rocks of the crust and mantle, metallic liquid outer core and the solid metallic inner core
- the physical structure of the surface of the Earth is shaped through process of plate tectonics[a process for this subsystem]
49
New cards
Hydrosphere
• through ocean circulation
• through ocean circulation
• Earth’s Subsystem
- the total amount of water on a planet; including water on the Earth’s surface, underground and in the air
• How is heat reabsorbed and redistributed on the surface of the Earth?
- the total amount of water on a planet; including water on the Earth’s surface, underground and in the air
• How is heat reabsorbed and redistributed on the surface of the Earth?
50
New cards
Hypsographic Curve
- a graphical representation of the proportion of land at various elevations(meters above or below sea level)
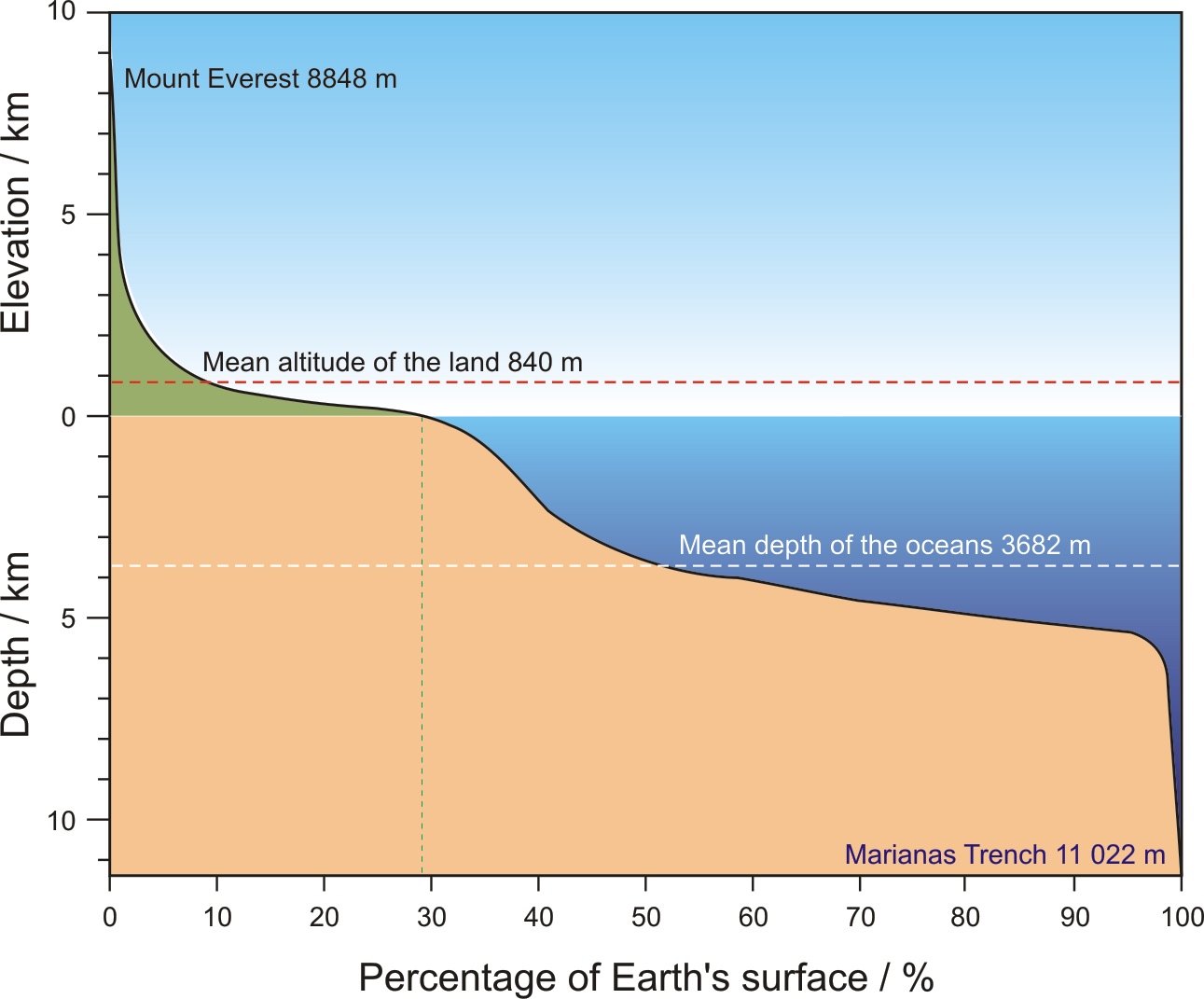
51
New cards
Biosphere
• Earth’s Subsystem
- areas or regions of the Earth that possess life; comprised of living organisms and nonliving factors from which organisms derive energy and nutrients
- the set of all life forms on Earth
- covers all ecosystems
- areas or regions of the Earth that possess life; comprised of living organisms and nonliving factors from which organisms derive energy and nutrients
- the set of all life forms on Earth
- covers all ecosystems