Brit Lit English History
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:29 PM on 1/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
1
New cards
fourth (4th)
In the _______ century the Roman Empire began to collapse
2
New cards
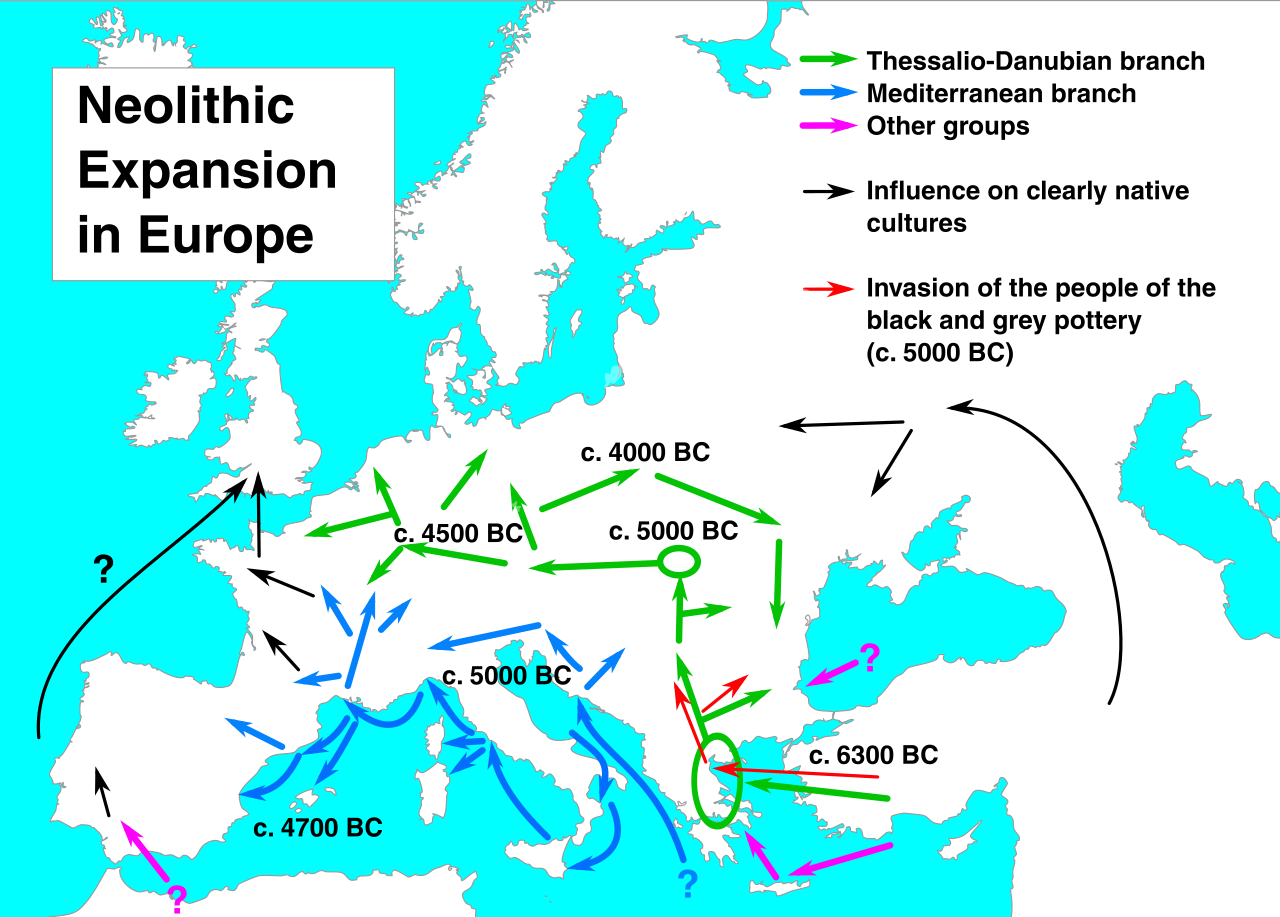
Iberians
The first great civilization came from the Mediterranean through the AtlanƟc coast of Portugal, Spain, and France (2500- 2000 BCE) and spread along the west coast of Britain and Ireland.
3
New cards
megaliths
Iberians, left behind great monuments in stone, or _________(such as Stonehenge) in Salisbury Plain similar to those (nuraghi) which can sƟll be seen in Sardinia.
4
New cards
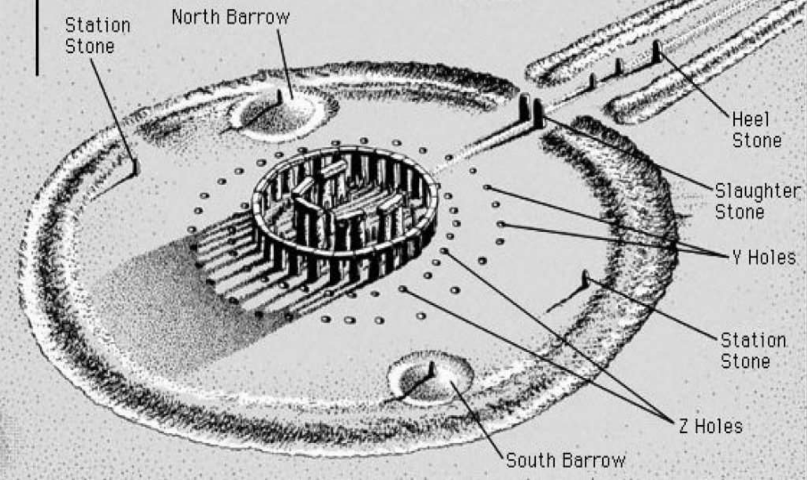
Stonehenge
__________ may have been a place of worship and an astronomical observatory made of giant stones. Archaeologists have recently established that the stones were transported by sea from Wales.
Remarkably accurate solar calendar
Remarkably accurate solar calendar
5
New cards
Britons
Central Europe invaders that were organized in warlike tribes, and were well advanced in craftsmanship (they were quite skilled at working iron) but rather backward in agriculture.
6
New cards
Druids
Among the most influential Celts were the ______, who administered religion, justice, and the education of the young.
7
New cards
Celts
The ____were a group of peoples loosely tied by similar language, religion, and cultural expression.
They worshipped the natural elements such as the Sun, the Moon, the trees, and the rivers. Water was regarded as a holy element that generated life and was the door to the world after death.
They worshipped the natural elements such as the Sun, the Moon, the trees, and the rivers. Water was regarded as a holy element that generated life and was the door to the world after death.
8
New cards
iron working
The Celts were the people who brought ___________ to the British Isles.
9
New cards
oral
The Celts were ____cultures (there was no writing or recorded history)
10
New cards
bards, poets
The role of __and ___was tremendously important in CelƟc society: much of what we know of their tradiƟons comes to us today through the old tales and poems that were handed down orally for generaƟons before eventually being wriƩen down.
11
New cards
runes
The first English written texts are in a strange language used by Anglo-Saxon invaders
12
New cards
coloniae
Colonial Roman Conquest: inhabited by Roman settlers
13
New cards
municipia
Colonial Roman Conquest: whose inhabitants were given Roman ciƟzenship
14
New cards
civitates
Colonial Roman Conquest: which were the old CelƟc tribal capitals.
15
New cards
122
In ___A.D. Emperor Hadrian ordered a wall (Vallum Hadriani) to be built to mark the border between the conquered Britons and the Scots and Picts of Caledonia (now Scotland) in the north.
16
New cards
43-47
the region was really conquered in the years 43-47 AD under emperor Claudius for Rome
17
New cards
449
In the 5th century three Germanic tribes, the Angles, the Saxons, and the Jutes came by sea. According to tradition, their seƩlement started in ___A.D.
18
New cards
Jutes
The ______were probably the first to come to Britain (about 450). • They founded the kingdom of Kent.
19
New cards
Saxons
The ______followed and established the kingdoms of Sussex (South Saxons), Wessex (West Saxons), Essex (East Saxons) and Mercia
20
New cards
Angles
The ______ founded East Anglia and Northumbria and gave their name to the country. (England mans “land of the Angles”).
21
New cards
Britons
The _______ either became serfs of the conquerors or fled to the mountainous west, where they resisted for over 150 years. They were called Welsh (that is, “strangers”) by the Anglo-Saxons.
22
New cards
King
elected by the Witan or council of
wise men an chosen among the
members of the royal family
wise men an chosen among the
members of the royal family
23
New cards
Earls
Hereditary aristocracy, magistrates and military chiefs of the shires (or counties)
24
New cards
Thanes
High-ranking warriors: • hunƟng, war, taxes, and administration of justice
25
New cards
Churls
Peasants –who were freemen
26
New cards
Thralls
Slaves by birth, conquest , or purchase
27
New cards
Tiw
the god of war, swordsmanship, and the sky (Tyr in Norse)
28
New cards
Woden
king of the gods, the god of death and baƩle
(Odin in Norse)
(Odin in Norse)
29
New cards
Thunor
the god of thunder and lightning, the strongest of gods (Thor in Norse)
\
\
30
New cards
Barons
______ were responsible for providing knights and soldiers for the king's army.
31
New cards
King Canute
He was the first king to successfully rule over a truly united realm of England
32
New cards
Bayeux Tapestry
•The main events of the Norman conquest of England are depicted in the ____________\*. •An embroidered cloth – not an actual tapestry
• The tapestry consists of some fifty scenes with Latin captions, embroidered on linen with coloured woollen yarns. • it was probably commissioned by Bishop Odo, William's half brother, and made in England – not Bayeux—in the 1070s.
• The tapestry consists of some fifty scenes with Latin captions, embroidered on linen with coloured woollen yarns. • it was probably commissioned by Bishop Odo, William's half brother, and made in England – not Bayeux—in the 1070s.