1_Biology_Core_Concepts_Lecture_Slides__No_videos_
Chapter 1: Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry
Introduction to Biology
Biology is the scientific study of life.
Recognizes life through the activities of living organisms.
Biology is a subject of enormous scope.
Taxonomy: study of biological names
Unifying Themes in Biology
Five unifying themes:
Organization: Life is structured hierarchically.
Information: Genetic information guides development and functioning.
Energy and Matter: Life relies on energy transformation.
Interactions: Interactions shape ecosystems and biological processes.
Evolution: Explains the unity and diversity of life.
Properties of Life
Key characteristics include:
Order: Organized structures of living organisms.
Regulation: Homeostasis and regulation of internal environments.
Reproduction: Ability to reproduce and pass on genetic information.
Adaptation: Adjustments to environmental changes over generations.
Response to Environment: Organisms react to stimuli from their surroundings.
Energy Processing: Utilization of energy for growth and survival.
Biological Organization
Life can be studied at various levels:
Molecules, Cells, Tissues, Organs, Organisms, Populations, Communities, Ecosystems, Biosphere.
Reductionism: Breaking complex systems into simpler parts for study.
Emergent Properties
Result from the arrangement and interactions of components.
Nonbiological examples, like bicycles, illustrate emergent properties.
Systems biology examines interactions among biological system parts.
Can be used to study life at all levels.
Structure and Function
At each level of the biological hierarchy we find a correlation between structure and function.
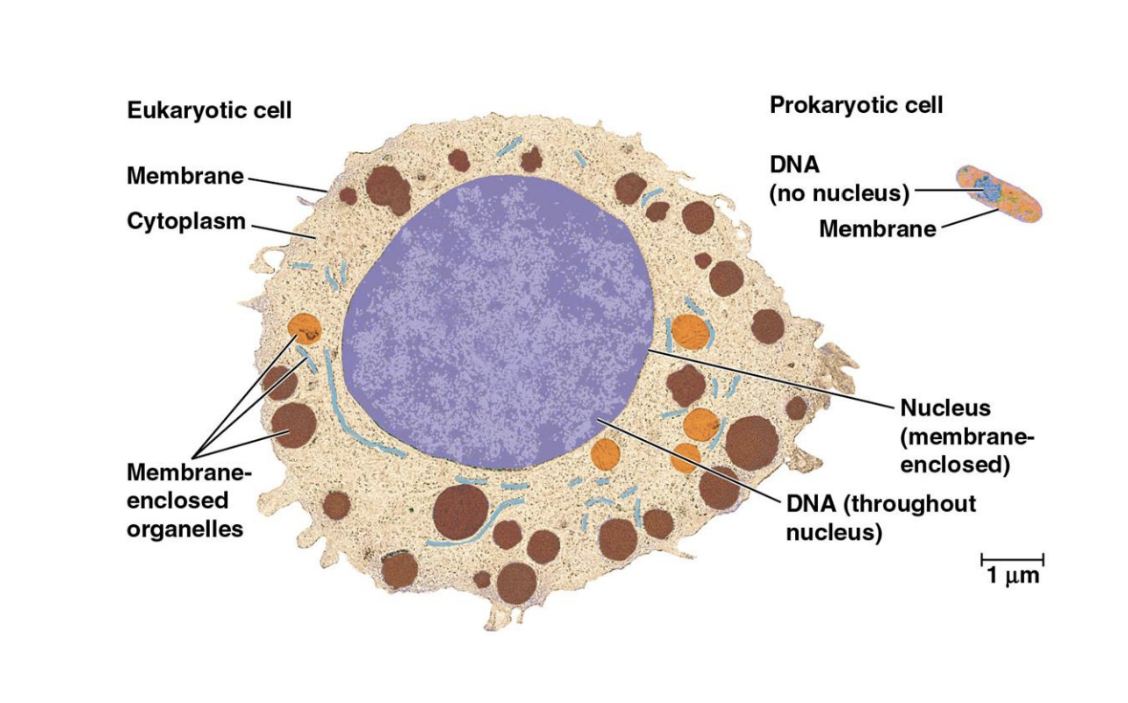
The Cell
Basic unit of structure and function in life.
Smallest unit of organization that perform all activities required for life.
Cell Theory: All living organisms are composed of cells.
Two types:
Prokaryotic: Simple, no nucleus (e.g., bacteria and archaea).
Eukaryotic: Complex, membrane-enclosed organelles, with nucleus (e.g., plants, animals).
Genetic Information
Chromosomes contain DNA, the genetic material.
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
DNA holds genes that encode for proteins and direct development.
Genes: the units of inheritance.
Made up of two long chains arranged in a double helix; each chain made up of four kinds of chemical building blocks called nucleotides and abbreviated A, C, G, T.
A: adenine
C: cytosine
G: guanine
T: thymine
(A+T) (G+C)
Gene expression: the process of converting information from gene to cellular product.
Genomics and Proteomics
Genomics: Study of entire genetic sequences.
Genome: entire “library” of genetic instructions.
Proteomics: Analysis of whole sets of proteins in organisms.
Proteome: the entire set of proteins expressed by a given cell, tissue, or organ.
Bioinformatics: the use of computational tools to process a large volume of data very rapidly.
Energy and Matter Transfer
Energy input from the sun drives life processes.
Photosynthetic organisms convert solar energy into chemical energy.
Energy flows through ecosystems; chemicals cycle among organisms.
Interactions in Biological Systems
Essential for organism function and ecosystem stability.
Feedback mechanisms (negative and positive) regulate biological processes.
Feedback regulation: the output, or product of a process, regulates that very process.
Ecosystem Interactions
Organisms interact with each other and their physical environment.
Human impacts contribute to climate change and habitat loss.
Core Theme: Evolution
Key unifying concept explaining diversity of life.
Understanding of evolution aids in comprehending biological relationships.
Natural Selection: Mechanism through which evolution occurs.
Classification of Life
Approximately 1.8 million species identified.
Each species is given a two-part name: The genus, to which the species belongs, and a species name unique to that species. (e.g., Homo sapiens)
Organisms classified into three domains:
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya.
Eukarya includes the four subgroups:
Plants; which produce their own food by photosynthesis.
Fungi; which absorb nutrients.
Animals; which ingest their food.
Protists; which can either consume or produce their foods.
Darwin and Evolution
On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection (1859).
Introduced natural selection as a driving force behind adaptation.
He made two points:
Species showed evidence of “descent with modification” from common ancestors.
“Natural Selection” is the mechanism behind descent with modification.
Observed variations in traits and implications for species survival.
Scientific Inquiry
Science is a process of inquiry involving observation and hypothesis testing.
The word science is derived from Latin and means “to know”.
Methods include gathering data, forming and testing hypotheses, and utilizing inductive and deductive reasoning.
Controlled experiment: an experimental group is compared with a control group.
Independent variable: the one that is manipulated by the researchers.
Dependent variable: the one predicted to be affected in response.