Plastics (natural sciences)
}}Pros and cons}}
Pros
- light
- clear
- cheap
- airtight
- printable with text and images
Cons
- a lot of (undegradable) waste = harmful impact on the natural environment
our reserves of petroleum in the soil are running out
}}What are plastics?}}
• Definition: Polymers ( poly= a lot; meros=parts)
=> long man-made molecular chains made up of short monomers that repeat over and over
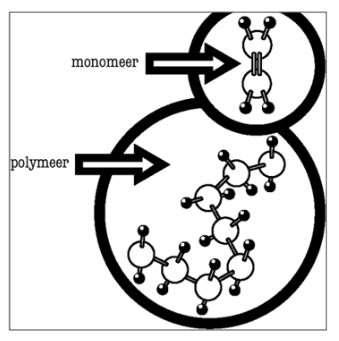
• Natural polymers and synthetic polymers
- Natural: polymers that occur in nature for example starch, protein,…
- Synthetic: man-made
}}Three types of plastic reactions}}
1) polymerization 2) polycondensation 3) polyaddition
Polymerization: → one kind of monomer with double c-c bond
→ c-c double bond is broken
→ the monomers are connected with single c-c bonds 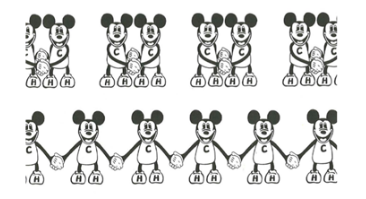
Polycondensation:
Two different types of monomers react to form a long polymer. A small residual product remains after each reaction between two monomers. (water, methanol,…) 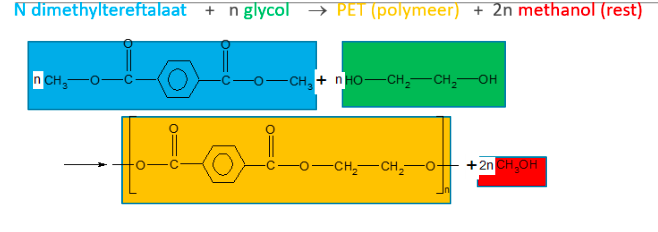
Polyaddition:
Two different types of monomers react to form a long polymer. There is NO residual product after reaction between two monomers
}}Thermoplastics, thermosets and elastomers}}
Thermoplastics:
Thermoplastics soften when heated, they can change shape. After cooling they keep their new shape. The polymer chains are not covalently linked to each other. (They become single held together by the weak intramolecular forces) causing them to heating away from each other to move.

Thermosets:
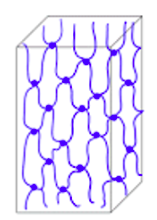
If the macromolecules form a three-dimensional net with form close meshes, have formed from them plastics have an insoluble and rigid structure. Plastics formulated in this way we call thermosets. When heated, the condition of the thermosets virtually none. They are plastics that once molded are not shape more. Here, too, the molecules consist of long chains, but in the cooling process during the production of the plastic, very strong ones are formed between them bindings. These are no longer broken when heated again. Thermosets therefore irreversibly retain their shape and their stiffness they acquired during their manufacture.
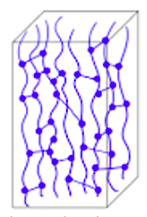
3. Elastomers:
Zijn de macromoleculen driedimensionaal in grote mazen met elkaar verbonden zijn, is de kunststof elastisch. Zulke stoffen noemen we elastomeren. Ze zijn veerkrachtig. Een voorbeeld hiervan is rubber.