Chapter 2: MGTA01 (Textbook Notes)
Chapter 2: MGTA01 (Textbook Notes)
Satisfying Customers And Making A Profit
- A business must both gain profits and satisfy customers. They are both dependent on each other
- Businesses must listen to their customer to get profit (personally this is probably why the phrase “the customer is always right” exists)
The Things That People Need And Want
Product: Whatever a purchaser hopes to get, or believes they are getting whenever they purchase from another individual or organization
Public sector organization: An organization that is owned or funded by the government
- 20% of working population are in public sector
Private Sector: Part of the economy that is run by private individuals, usually to make a profit
Goods: Products which can be seen and touched (tangible)
Services: Products which are experienced, not seen or touched (intangible)
Immediacy: Quality that makes something important/relevant because it’s happening there/then
- Eg. taxi
High-contact services: Services that require personal interaction with the customer
- Eg. Nursing home, haircut
Low-contact services: Service operations that don’t necessarily involve interaction with the customer
- Internet banking, fast food
Customization: The characteristics of a service that means that no two customers want the same thing delivered in the same way
- Eg. fast food delivery
Diversification: Owning a wide variety of investments to reduce risk
- Eg. don’t put all your eggs in one basket in case in breaks
- The intention should be there
- Eg. kids selling lemonade. Intention is either selflessness or money (business)
Value Proposition: Why you should buy from the business
- Eg. Jerusalem dancing
- Eg. Build a bear experience
Examples of different services/experiences: escape room (stressful), wonderland (scary)
Differences Between Goods And Services
Goods | Services |
|---|---|
|
|
- Roughly 70% of Canadian products are services
Products: Filling Needs and Satisfying Wants
People want a product to have 3 elements:
- Function
- Features
- Benefits
- Function
Function: What a product is intended to do
- Eg. car’s function is transport, hotel is night accommodations
Features: Additional attributes/offerings that contribute to usefulness/better experience of product
- Eg. air condition in a car doesn’t affect the function, but it makes the car nicer to ride in
Benefit: An advantage that is derived from purchasing a product
- Difficult to measure
- Eg. sense of achievement/social status from buying a car
Value: worth or importance of product, usually in terms of usefulness, desirability, or financial (mostly financial)
Value package: function + features + benefit
Eg. 3 star hotel, 5 star hotel
Understanding Different Products And Their Consumers
Consumer products: Products purchased by the end user, for personal use
- Eg. cereal
Industrial Products: Parts, ingredients, materials, supplies are brought by one business in order to make a consumer products
- Eg. one cereal business buying industrial products like cardboard and ingredients to make cereal, a consumer product
3 types of consumer products:
- Convenience products: inexpensive products, purchased frequently, little time and effort used for product
- Eg. razors, coffee, chocolate
- Shopping products: Moderately expensive, purchased infrequently
- Consumers spend time comparing features, benefits, and price
- Eg. cars & laptops (goods), life insurance & house contractor (services)
- Specialty products: very important products that may be purchased only once
- Eg. ring, wedding gown, wedding catering
Research and Development (R&D): Looking for innovations and ideas which will lead to the next generation of products
Product Life Cycle
Product life cycle: introduction, growth, maturity, decline, and demise of products & industries as consumer preferences change
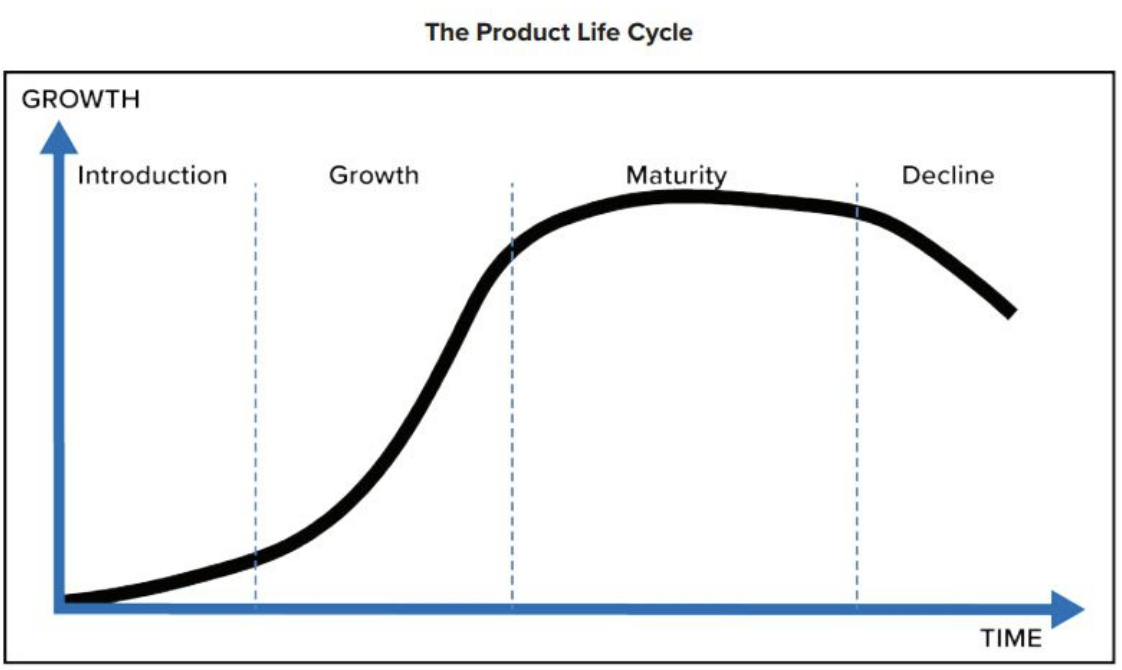
Stages:
- Introduction
- Growth
- Maturity
- Decline
- Introduction
- Product is new, not well-known
- # of units small, selling price high
- Growth
- Demand for product expands rapidly
- Economies of scale: A decrease in the cost to produce a product as the volume of product increases
- Note to self: This probably relates to why it’s cheaper buying in bulk
- Easier to purchase = more it will be purchased
- This stage is when product begins to make profit
- Maturity
- Sales peak
- Product most profitable
- Most purchase that consumers make are replacements of the product (aka everyone’s already got a product)
- This is called saturation
- Decline
- # of purchase falls after saturation/being outdated
- Sometimes forced to cut product price = profits falling
Life Cycle Extension
- One tactic to delay product decline is to launch new variation/update
Life cycle extension: Any effort by a business to re-package, re-launch, or update mature but well-known product
- Eg. new flavours of coke