HHB physiology and health - gamete production and hormonal control of reproduction in females
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
name the structure where ova mature
the structure where ova mature is the follicle
describe the role of the follicle
a follicle surrounds the ovum, protecting the developing ovum and secretes hormones (oestrogen)
state the length of the average menstrual cycle
the menstrual cycle takes approximately 28 days
name the first phase of the menstrual cycle
the first phase is the follicular phase
describe the effect of FSH on the ovary
FSH stimulates the development of a follicle and the production of oestrogen by the follicle in the ovary
name the hormone produced by the follicle
the hormone produced is oestrogen
describe the effects of oestrogen
- causes proliferation of the endometrium to prepare for implantation
- thins the consistency of cervical mucus making it easier for the sperm to penetrate
- causes the release of LH from the pituitary gland
explain why the consistency of cervical mucus changes during the follicular phase
the change in consistency makes it easier for the sperm to penetrate through
describe what happens to the LH levels following peak levels of oestrogen
peak levels of oestrogen cause a surge in the release of LH, causing LH levels to increase
name the event which occurs following of a surge in LH
this surge in LH levels triggers ovulation
describe the process of ovulation
ovulation is the release of an ovum from a follicle in the ovary, this usually occurs around the mid-point of the menstrual cycle or at peak levels of LH
during ovulation, the body temperature rises
name the second phase of the menstrual cycle
the second phase is the luteal phase
name the structure the follicle develops into following ovulation
the follicle develops into a corpus luteum which releases progesterone
name the hormone produced by the corpus luteum
the corpus luteum produces progesterone
describe the effects of progesterone
progesterone promotes further thickening and production of blood vessels in the endometrium, this prepares the uterine lining for implantation if fertilisation occurs
identify the pituitary and ovarian hormones from a graph
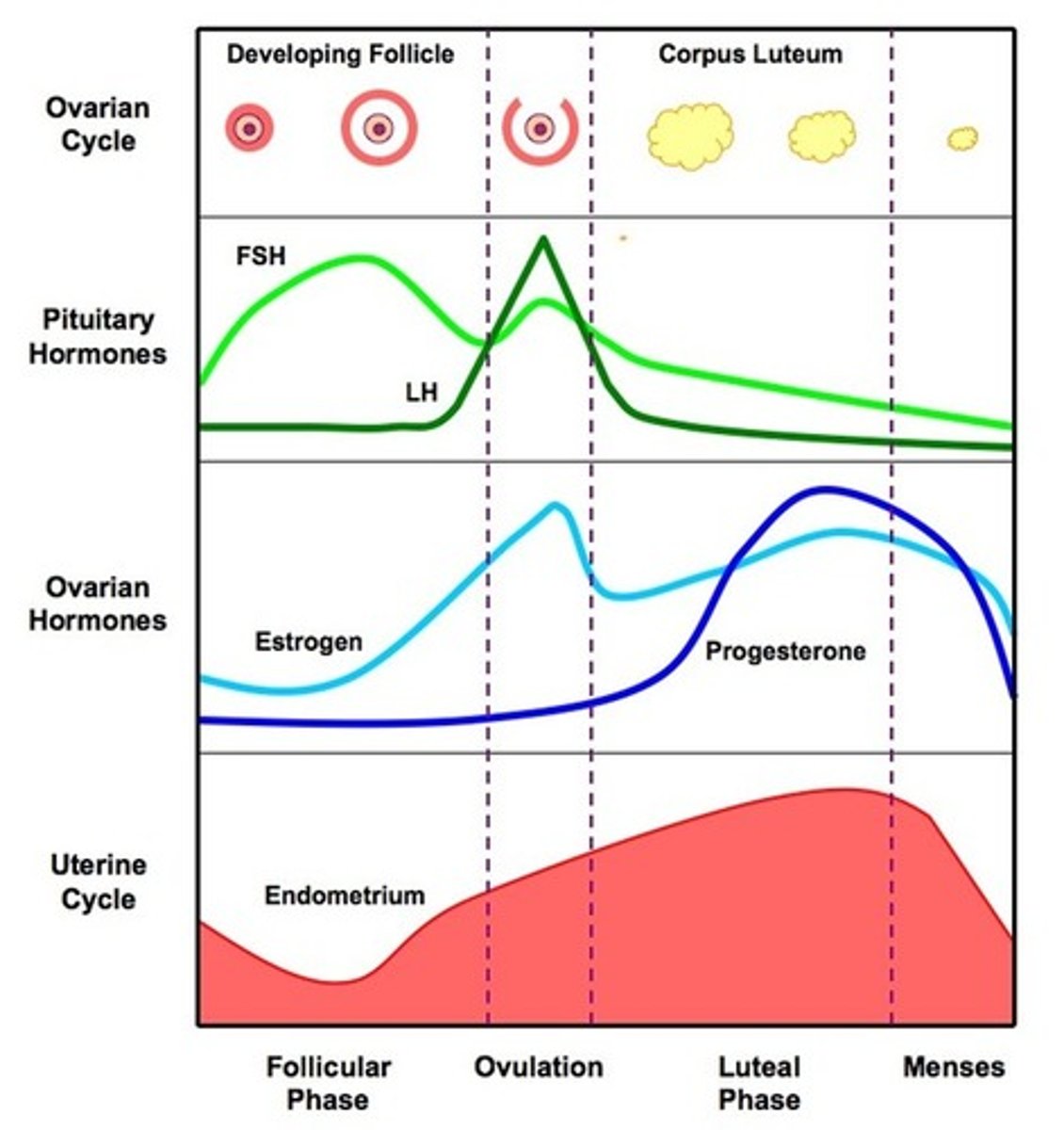
describe the negative feedback effect of the ovarian hormones on the pituitary gland
high levels of oestrogen inhibits the release of FSH by the pituitary gland this prevents further follicles from developing
high levels of progesterone inhibits the release of LH and FSH from the pituitary gland, the decrease in LH causes the breakdown of the corpus luteum causing a decrease in progesterone levels which starts menstruation
describe the effect of a lack of LH
the decrease in LH causes the breakdown of the corpus luteum
describe how menstruation is triggered
due to the decrease in LH this causes a decrease in progesterone levels which starts menstruation
state the site of fertilisation in females
the site of fertilisation is the oviduct
describe the process of fertilisation
fertilisation is the fusion of the nuclei of the two haploid gametes to produce a diploid zygote which divides to form an embryo, the embryo then implants into the endometrium
state what happens to the corpus luteum and progesterone levels if fertilisation occurs
if fertilisation does occur, the corpus luteum does not break down and progesterone levels remain high