HAPII Test 3: Digestive System, Nutrition, Urinary System, and Fluid + Electrolyte Balance
1/457
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
458 Terms
6
How many activities are involved in Digestion
Ingestion, Propulsion/Motility, Mechanical Breakdown, Chemical Digestion, Absorption, Defecation
What are the 6 activities of Digestion?
Ingestion
-Taking food into the mouth
-Step 1 of Digestion
Propulsion/Motility
-Moving Food through alimentary canals
-Includes Deglutition and Peristalsis
-Step 2 of Digestion
Deglutition
-Swallowing the food
-Begins as a voluntary activty
*Part of Propulsion/Motility
Peristalsis
-Rhythmic wave-like contractions moving food through GI Tract
-Part of Propulsion/ Motility
Mechanical Breakdown
-Mastication
Churning food in stomach
Segmentation
-Step 3 of Digestion
Mastication
-Chewing the food
Small enough to swallow
Mixing with saliva
Segmentation
-Rhythmic contractions that mix food
Occurs in the small intestine
Chemical Digestion
-Involves enzymes breaking down food molecules into chemical building blocks
Step 4 in Digestion
Absorption
-Passage of digested fragments from lumen of the GI tract into blood or lymph
Step 5 of Digestion
Defecation
-Elimination of indigestible substances
-Waste material passes to the rectum
-Occurs when the rectal pressure rises and external anal sphincter relaxes
Step 6 in Digestion
Gastrointestinal Tract, GI Tract, Gut
What are the three other names for the Alimentary Canal?
Alimentary Canal
What’s another name for the Gastrointestinal Tract, GI Tract, and Gut?
Alimentary Canal
-Continuous muscular tube from the mouth to the anus
-Digests food: Breaks the food into smaller fragments
-Absorbs fragments through lining into blood
Mouth, Pharynx, Esophagus, Stomach, Small intestine, Large intestine, and Anus
What are the structures of the Alimentary Canal?
Teeth, Tongue, Gallbladder, Digestive Glands
What structures are a part if the Accessory Digestive Organs?
Digestive Glands
-Produce secretions to break down food
Includes the salivary glands, Liver, and Pancreas
Salivary Glands, Liver, and Pancreas
What are the Digestive Glands?
Parietal Peritoneum
-Line the cavity wall
Orange
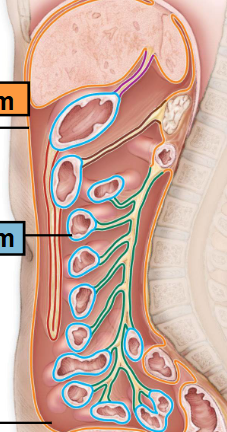
Visceral Peritoneum
-Lines the Organs
BlueP
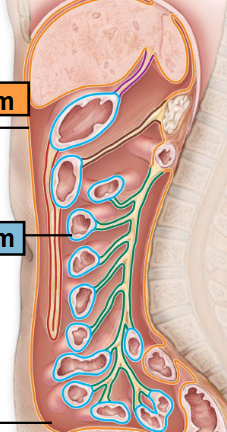
Peritoneal Cavity
-Space between
-Filled with Serious Fluid
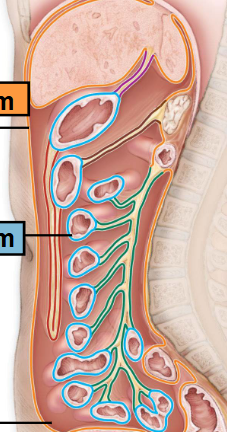
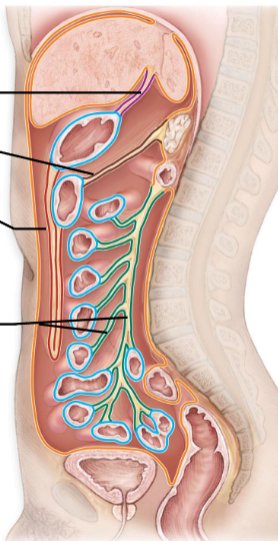
Mesenteries
-Double layered folds of membrane
-Stabilize Organs
-Types
Greater Omentum
Lesser Omentum
Mesentery Proper
Mesocolon
Greater Omentum
-Red
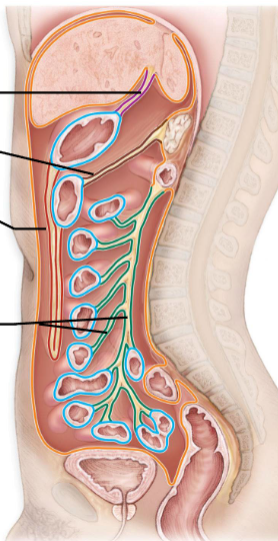
Lesser Omentum
-Purple
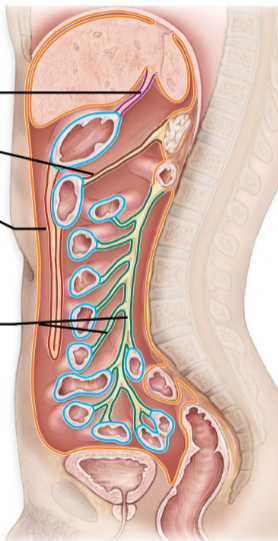
Mesentery Proper
-Green
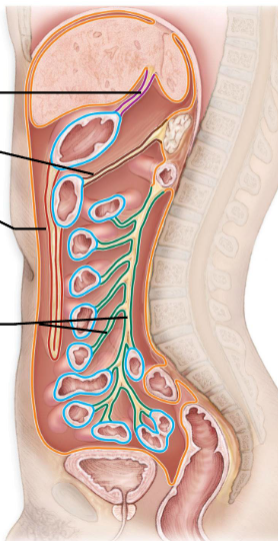
Mesocolon
-Brown
Intraperitoneal Organs
-Organs located within the peritoneum
-Stomach, spleen, liver, small intestine, and transverse colon
Stomach, Spleen, Liver, Small Intestine, and Transverse Colon
What are the Intraperitoneal Organs?
Retroperitoneal Organs
-Outside, or posterior to, peritoneum
-Include most of pancreas, duodenum, and parts of large intestine
Pancreas, Duodenum, and Parts of Large Organ
What are the Retroperitoneal Organs?
Mouth, Esophagus, Stomach, Pancreas, Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum, Cecum, Large intestine, Anus
What is the order of the Alimentary Canal
Oral Cavity
-Mouth
Cheeks
Teeeth
Salivary Glands
Tongue
Palate (Hard and Soft)
Uvula
-Digestion Begins here
Mechanical and Chemical
Mouth
Where are the salivary Glands Located?
Mouth
Where does digestion begin?
Mechanical and Chemical
What are the two types of Digestion?
Teeth
-Parts
Crown
Neck
Root
-Composition
Dentin
Cementum
Enamel
Salivary Glands
-3 Major Parts
Parotid
Sublingual
Submandibular
-1-2 L Saliva/day
-Saliva
1-2 Liters a day
How many Liters of Saliva do we make a day?
Saliva
-Moistens food
-Cleans Teeth (lysozome)
-Protects/ Lubricates Mouth (mucus)
-Digests starch (amylase)
**Form of Chemical Digestion
Lysozome
What enzyme cleans teeth?
Mucous
What enzyme protects the mouth?
Amylase
What enzyme digests starch?
Nasopharynx, Oropharynx, Laryngopharynx
What is the order of the Pharynx?
Lumen
Open tube of the Gastrointestional Tract
4
How many Layers (tunics) are there?
Tunica Serosa and Adventitia, Tunica Muscularis, Tunica Submucosa, Tunica Mucosa
What are the 4 tunics?
Tunica Serosa and Adventitia
-Outermost layer
-Serosa
Made of Areolar Tissue
-Adventitia
Made of Areolar Connective
Retroperitoneal
Tunica Muscularis
-2 Layers of Smooth Muscle
Outer Layer = longitudinal
Inner Layer = Circular
Peristalisis
Peristaltic Waves
Segmental Contractions
Longitudinal
What is the outer layer of the Tunica Muscularis?
Circular
What is the inner layer of the Tunica Muscularis?
Tunica Submucosa
-Dense irregular Connective Tissue
-Lots of Elastic Fibers
-Large # of Vessels, glands, nerves
Tunica Mucosa
-Internal
-3 Sublayers
Muscularis Muscosae
Thin layer of smooth muscle
Laminal Propria
Areolar tissue, Capillaries, Lymph vessels
Epithelium
Usually Simple Columnar
Modified in some sections of canal
Muscularis Mucosae
Thin layer of smooth muscle in the Tunica Mucosa?
Lamina Propria
Consists of Areolar tissue, capillaries, and lymph vessels in the Tunica Mucosa
Epithelium
-Usually Simple columnar and is modified in some canals of the Tunica Mucosa
Esophagus
-~10 in
-Tunic Modifications
T. Mucosa = Stratified Squamous Tissue
T. Muscularis = Skeletal muscle in the upper 2/3
-Lower esophageal sphincter (Gastroesophageal Cardiac sphincter)
-Peristalsis: Surrounds cardiac orifice
Localized reflex in response to the distention of the wall by bolus
Rate of 2-4 cm/sec
Peristalsis of Esophagus
-Surrounds cardiac orifice
-Localized reflex in response to distention of wall by bolus
Rate of 2-4 cm/sec
Stomach
-Most distensible part of GI Tract
-Functions:
Store food
Initiate digestion of proteins
Kills bacteria
Converts bolus of food to paste-like chyme
Moves food (chyme) into intestine
-Empty stomach has ~50ml Volume
Can expand to 4 L
Empty, mucosa forms folds called rugae
Functions of the Stomach
Store food
Initiate digestion of proteins
Kills bacteria
Converts bolus of food to paste-like chyme
Moves food (chyme) into intestine
4 L
How much can an empty stomach expand to?
Rugae
-Gastric Folds formed by the mucosa when the stomach is empty
Structure of Stomach
-Folded Mucosa
Gastric folds/rugae
-Three Muscle layers
Outer longitudinal
Middle Circular
Inner Oblique
-Pyloric Sphincter Muscle is present
-Gastric Pits
Contain Gastric Glands
Enteroendocrine cells (secretes gastrin)
Parietal cell (secretes hydrochloric acid and intrinsic factor)
Chief cells (secretes pepsinogen
Secretes alkaline mucin
Gastric Pits
Contain Gastric Glands
Enteroendocrine cells (secretes gastrin)
Parietal cell (secretes hydrochloric acid and intrinsic factor)
Chief cells (secretes pepsinogen
Secretes alkaline mucin
Gastric Glands
What Secretes alkaline mucin
Enteroendocrine cells
*Secretes Chemical Messengers:
Acts as paracrines (local hormones)
Serotonin
Histamine,
Hormones
Somatostatin,
Gastrin
Also secretes Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Parietal Cells
Secretes Hydrochloric Acid and Intrinsic Factor
Chief Cells
Secretes Pepsinogen and Lipases
Small Intestine
-20 ft (6m) long
-Supported by mesenteries
-3 Regions
Duodenum
Jejunum
Ileum
Duodenum
*Part of the Small intestine
-1ft, Retroperitoneal
-Secretions from the gallbladder/pancreas
Jejunum
*Part of the Small intestine
-7+ ft, upper left
-Main site of absorption
Ileum
*Part of the Small intestine
-10ft, middle/lower right
Small Intestine
-Mucosa Folded
Larger Ridges = Circular Folds
Smaller Folds = Villi(Villus)
Cell Folderd = microvilli
Columnar cells absorb nutrients
-Capillaries and Lacteals
All blood from capillaries goes to liver via hepatic portal system
Circular Folds
What are large ridges in the mucosa folded part of the Small intestine?
Villi (Villus)
What are smaller folds in the mucosa folded part of the Small Intestine?
Microvilli
What are the cell folded parts of the mucosa folded part of the small intestine?
Columnar Cells
What types of cells absorb nutrients in microvilli
Large intestine
-Large, Unfolded tube
-5-6ft long
-Bulges along length = haustra
-Teniae Coli
Haustra
Bulges along length of the Large intestine
Teniae Coli
Three thickened bands of tunica muscularis
4
How many regions are the large intestine?
Cecum
*1st Region of the Large Intestine
-Contains the Ileocecal Valve
-Contains the Vermiform appendix
Colon
*2nd Region of the Large intestine
-Contains Ascending, Transverse, Descending, Sigmond, and Flexures
Rectum
*3rd Region of the Large Intestine
-7in
-Attached to Sacrum
-Lined with Stratified Squamous
Anal Cavity
*4th Region of the Large Intestine
-1in
-Internal Sphincter Muscle
-External Sphincter Muscle
Internal Structure of Large Intestine
-Contains Simple Columnar Epithelium
No Villi
-Intestinal Glands
Contains Goblet Cells
-Outer muscle layer is incomplete (teniae coli)
Splanchnic Circulation
-Serves Digestive organs
-Arteries branching off aorta
-Hepatic Portal System/ Circulation
Hepatic, splenic, left gastric arteries, Inferior and Superior Mesenteric arteries
What are the arteries that are branching off the aorta?
Hepatic Portal System/ Circulation
-Drains nutrient-rich blood from digestive organs
-Delivers blood to liver for processing
Liver
-Largest internal organ
-Regenerative
-4 Lobes
-Internal Structure
Lobules
Sinusoid Capillaries
Hepatocytes
Hepatic Portal Vein
Right and Left Lobes, Caudate Lobe, Quadrate Lobe
What are the 4 lobes of the Liver?
Lobules, Sinusoid Capillaries, Hepatocytes, and Hepatic Portal Vein
What are the internal structures of the Liver?
Gallbladder
-Small organ btwn lobes of liver
-Stores Bile
-Contraction of gallbladder ejects bile into duodenum
Via common bile duct
Bile
-Released into cystic duct and common bile duct
-Emulsifies fats (but it’s not an enzyme)
-About 250-1500 ml a day is produced by the liver
Bilirubin, spleen, bone marrow, and liver
What is bile pigment and where is it produced?
Common Bile Duct
Contraction of the gallbladder ejects bile into the duodenum via this?
Urobilinogen
What do intestinal bacteria convert bilirubin to?
Pancreas
-Leaf-like organ on duodenum
-Produces digestive enzymes from pancreatic acini
-Released into the duodenum
Mechanical Digestion
-Chewing
-Peristalsis, stomach movement (segmentation, “churning”)
Enzymatic Hydrolysis
-Enzymes use water to break chemical bonds
-Intrinsic and accessory gland enzymes