2.3 - energy, flows, trophic levels, productivity
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
1st law of thermodynamics
energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.
autotrophs
organisms that produce their own food through
photo-autotrophs
photosynthesis
chemo-autotrophs
chemosynthesis
using energy from sunlight or chemical sources.
photosynthesis
photo-autotrophs convert light energy into chemical energy, producing glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water.
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
2nd law of thermodynamic
energy transformations in ecosystems are inefficient due to energy being dispersed to the environment
respiration formula
biggest loss of energy
C6H12O6 + O2 → CO2 +H2O + energy
trophic level
a position that and organism occupies in a food chain
producers (autotrophs) position
first trophic level in a food chain
consumers (heterotrophs)
organisms that feed on producers or other organisms
gain chemical energy from carbon (organic) containing compounds obtain from other organisms
occupy the second or higher trophic levels in a food chain.
decomposers/ scavengers
organisms that feed on producers or other organisms
break down dead organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
energy flow between the trophic levels
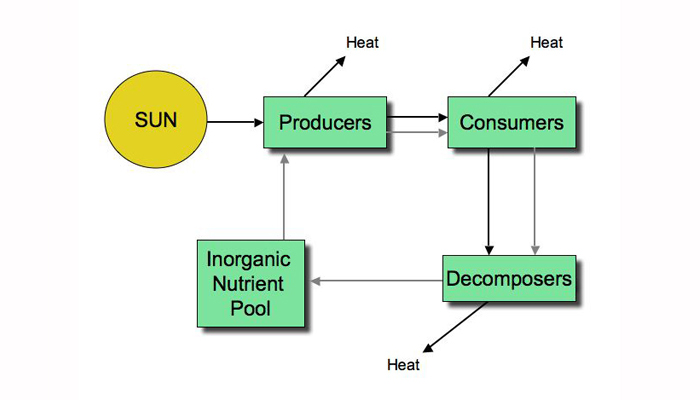
food chain
a linear sequence of organisms through which energy and nutrients pass as one organism eats another.
shows feeding relationships between species
shows energy flow
*usually up to 4 levels as lots of energy and organic matter is lost as matter is transferred along
efficiency of each transfer is typically around 10%.
ecological efficiency formula
ecological efficiency (%) = (Energy at trophic level n) / (Energy at trophic level n-1) x 100
food web
complex network of feeding relationships among various organisms in an ecosystem
illustrates how energy flows between multiple trophic levels.
biomass
the dry mass or weight of the living or once-living organisms in the environment
productivity
measure of biomass over a period of time
helps scientists to understand the energy stored at each trophic level
difficult to measure because the organism must be killed and dried to remove all water
primary productivity
the rate at which energy is converted by photosynthetic and chemosynthetic autotrophs to organic substances, typically measured in biomass.
gross primary productivity GGP
the total amount of organic matter produced by autotrophs in a given area and time.
net primary productivity NPP
the rate of energy storage by photosynthetic plants after accounting for respiration losses.
reflects biomass available for consumption
crucial for sustaining food chains
NPP = GPP - respiration
consumer and secondary productivity
gain in biomass by consumers using carbon compounds absorbed and assimilated from ingested food
gross secondary productivity GSP
total biomass that consumers obtain through ingestion of organisms
energy assimilated from the food before accounting for losses due to excretion/ undigestion
GSP = ingested food energy - energy lost through waste
net secondary productivity NSP
amount of biomass remaining after respiration and wast losses have been subtracted
energy available for growth and reproduction
NSP = GSP - respiration
role of glucose
growth
maintenance
reproduction
deposition in/around cells as new biomass