History of Psychology Exam 3
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
All of the following factors contributed to an atmosphere conducive to applied psychology in America in the late 19th century
-more experimental psychologists than laboratory positions available
-Americans believed that science should create technologies that would improve their lives
-institutional pressures to justify the cost of maintaining a laboratory
With which of the following statements would Binet agree?
mental level can be improved through specific "mental orthopedic" training
According to Binet and Simon, a débile was
a child scoring at a mental level two years below actual age
Which of the following is true of Goddard's Kallikak study?
he ignored important environmental influences that affected the fortunes of the two family lines
Goddard could be described by all of the following
-advocate of eugenics
-believed in sterilization of feebleminded
-in favor of restrictions on immigrants
Terman's studies of gifted children demonstrated that such children (at least the ones he studied)
refuted the stereotype of the brilliant child who is socially maladjusted
first translated the Binet scales into English
Goddard
was responsible for the first real standardization of the test.
Terman
According to Stern's formulation, a 5-year-old with an IQ of 80 would have a mental age of _____, while another 5-year-old, with an IQ of 120, would have a mental age of _____.
4;6
Which of the following is true of the World War I Army testing program?
it suggested that the average soldier had a mental age barely above the level of moron
In America in the early 1920s, most applied psychologists who did mental testing would agree with all of the following
-immigration, especially from Southern Europe, should be restricted
-scores on IQ tests reflect inherent biological ability
-it might be necessary to sterilize those who are mentally unfit to bear children
The gestaltists would agree with all of the following
-behavior is affected more by the behavioral environment (i.e., perception) than by the geographical environment (i.e., reality)
-perceptual organizing tendencies such as figure-ground do not have to be learned-they are an innate part of the visual system
-the whole of a perception is more than the sum of its component parts
Concerning the phi phenomenon, with which of the following statements would Wertheimer agree?
the phenomenon cannot be analyzed into constituent elements
In one study, Wertheimer used three lights lined up in a row (A, B, and C). He simultaneously turned A and C on, then off, then turned B on and off. What was the purpose of this study?
this study ruled out eye movements as an explanation for apparent motion
In the apparent motion study, what is the geographical environment?
two separate lights, each flashing on and off
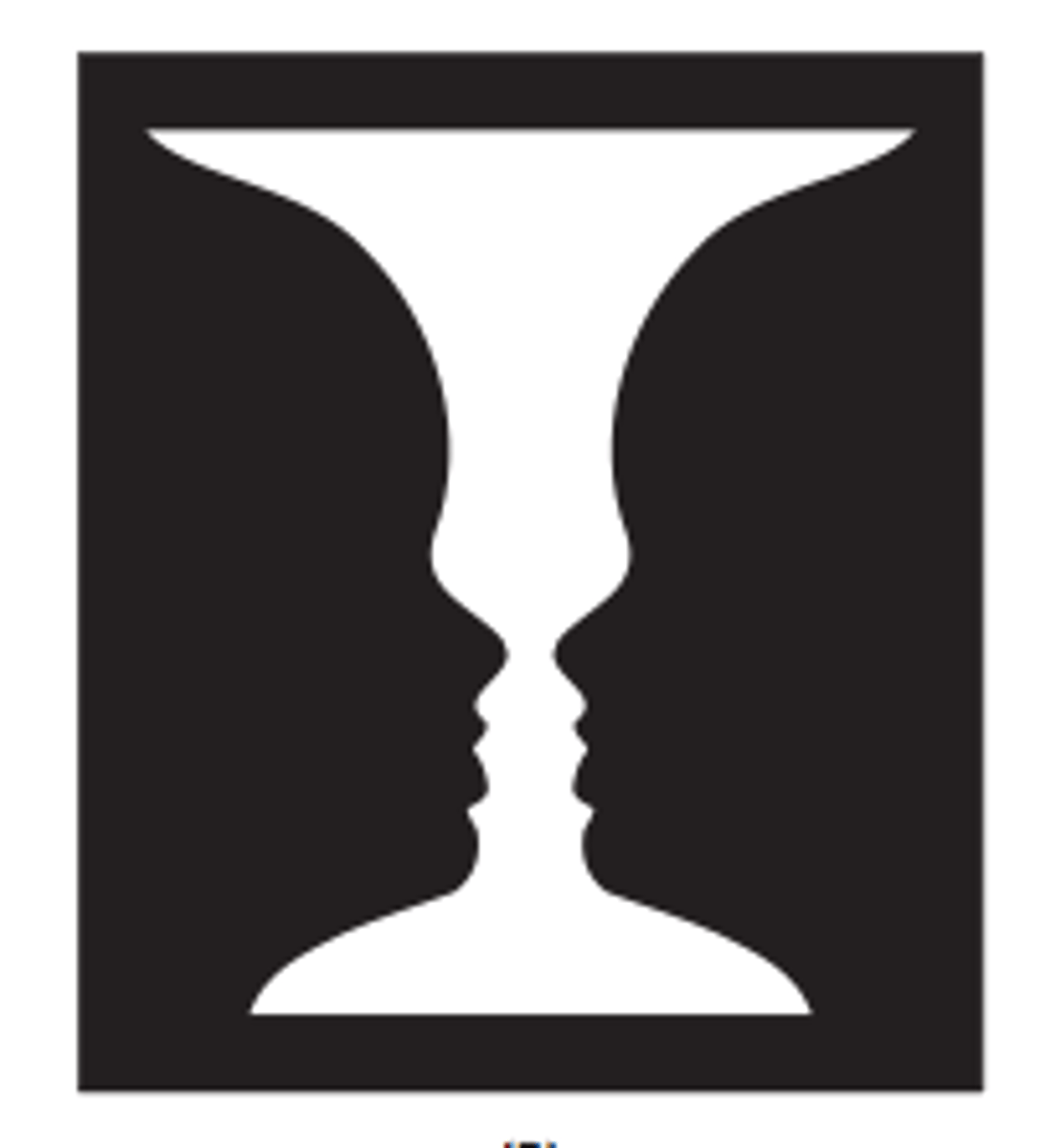
Which of the following is true about the figure-ground phenomenon?
in Rubin's vases examples, the perception is either of a vase or two faces; it is impossible toperceive both perspectives simultaneously
How did Köhler define insight?
rearranging the elements of the problem situation into a new configuration
In order for insight to occur, according to Köhler, the individual
must be able to see all the elements of the problem situation
Which of the following is true about the work of the Kurt Lewin?
he believed that understanding behavior required knowing both the person and the perceived environment
Compared to the major gestalt psychologists, Lewin was more interested in
motivation
If we think about cheating on an exam, it creates a conflict because on the one hand, we want a good grade, but on the other hand, we know it's wrong. In Lewin's terms
we are experiencing an approach-avoidance conflict
Behaviorism's roots include all of the following
-Darwinian evolution
-British empiricism/associationism (e.g., Mill)
-positivism
In Pavlovian conditioning that attempts to train a dog to salivate to a tone, the tone is called a(n)
conditional stimulus
Once a dog has been conditioned to respond to a 70 cps tone, how was differentiation accomplished (i.e., respond to 70 but not to 80)?
continue pairing the food with the CS, but don't pair food with an 80 cps tone
In Pavlov's laboratory, the phenomenon of "experimental neurosis" occurred when
stimuli that could be discriminated initially were made so similar that discrimination failed
In the behaviorist manifesto, Watson identified the goal of psychology. It was to
be able to predict and control behavior
In the manifesto, Watson first criticized structuralism and introspection. What was his attitude toward functionalism?
he criticized them for also defining psychology in terms of consciousness
In the Little Albert study, Watson and Rayner investigated all of the following
-fear acquisition
-generalization of fear
-persistence of fear (over time)
The Little Albert study has been criticized for all of the following reasons
the generalization test was contaminated by further learning trials
there is ambiguity in the description of exactly what happened procedurally
such a definitive conclusion about conditioning should not be made on the basis of astudy with just one subject
Watson and Rayner made no attempt to remove Albert's fear, but Mary Cover Jones succeeded in another case. She accomplished this by
replacing the fear response with a more pleasurable response associated with eating
Which of the following is true about Watson's "dozen infants" quote?
he overstated the case, partly to counteract the claims about inheritance that were beingmade by the mental testers
To emphasize the fact that mental abilities could change and were not endogenous or fixed, Binet and Simon used the term _______ rather than the term ________.
c. mental level; IQ
How did Terman's work with the Binet tests differ from Goddard's work?
b. Terman added the concept of IQ
The Gestaltists argued that __________
b. the whole of a perception is different and more than the sum of its component parts
Why was logical positivism attractive to American experimental psychologists?
it provided a means to study unobservable entities and still remain "scientific"
During the time of the neobehaviorists, there was general agreement among them about which of the following?
hey emphasized conditioning/learning as the prime explanation for behavior
According to Guthrie's theory of learning,
-reinforcement changes the stimulus environment, thereby preserving an S-R connection
-all learning involves contiguity of stimulus and response
-all forgetting involves new learning
Gestaltists made a distinction between behavioral and geographic environment. In the apparent motion study, what is the behavioral environment?
a. a light that moves from one position to another
Tolman believed all of the following except
a rat in a maze isn't really learning anything about the maze unless it is reinforced at theend of it
What happened in Tolman's latent learning study?
rats learned a maze regardless of whether they were rewarded or not
Hull's postulate 4 was the core of his model of learning. Hull believed all of the following
-contiguity was a key element
-habit strength builds gradually
-drive reduction is an important determinant of learning
Which of the following did Hull believe was true about reaction potential?
it was an intervening variable and it would equal zero if either habit strength or drive was zero
Which of the following is true about Skinner's radical behaviorism?
he took what could be called an non-theoretical, inductive approach to science
Which of the following best summarizes Skinner's ideas about operant conditioning?
behaviors producing positive consequences tend to occur again
Pigeons reinforced for key pecking, but only when a light is on, soon learn to key peck only when the light is on. Which of the following is true, according to Skinner?
the light has gained stimulus control over the behavior
Of the following trends, which had the least effect on the development of behaviorism?
b. the. mental testing movement
In the experimental neurosis research, how did the dogs react behaviorally?
c. either over-excited or very placid, depending on the initial temperament of the dog
In an experiment by Tolman, group A rats learn to turn right to reach food, while group B rats learn to go to a particular location for food. Those rats in group ___ learn faster, thereby illustrating what Tolman called____ learning.
b. B; place
Type R conditioning is to Type S conditioning as _________ is to _________.
b. Skinnerian; Pavlovian
How does the Binet tradition of mental testing differ from the Galton/Cattell tradition?
Galton/Cattell measured sensation and reaction time to assess intelligence; Binet used a scale of 30 tasks with increasing difficulty
Why would Binet have hated the concept of "IQ"?
He believed that intelligence in malleable through mental "orthopedics"
How did Goddard define a moron?
Someone with the mental age of 8-12 years
description of Kallikak case study
-The Kallikak study: Genealogical methods
-Vineland resident "Deborah Kallikak"
-Discovered 2 general lines in her family
-The "bad" side à high percentage of feeblemindedness
-The "good" side à virtually no feeblemindedness
Criticisms of Kallikak study
-isolated from society
- prevented breeding
- effect of preconceived biases on data interpretation
According to Stern, how is IQ calculated?
a person's mental age divided by chronological age, multiplied by 100
What did Terman discover about gifted children that discredited a traditional stereotype about them?
Found that the gifted children were generally taller, healthier, and had better social relationships, counter to the traditional concept of gifted student as bright but socially inept and prone to burnout.
Yerkes and Army Testing
-Revealed that the average soldier had the mental age of 13
-mental testing became standard for the army after WW1
Army Alpha
An intelligence test developed during World War I and used by the army for soldiers who can read.
-sub tests: commands, analogies, disarranged sentences
Army Beta Test
a nonverbal intelligence test developed during WWI by I/O psychologists to assess illiterate recruits
-subtests: picture completion, digit-symbol
phi phenomenon/apparent motion
an illusion of movement created by rapidly blinking lights
-apparent motion resists analysis
-whole> sum of parts
How did Wertheimer discredit two non-gestalt explanations of apparent motion?
eliminated eye movement as an explanation of this phenomenon; & argued against unconscious inference (too slow)
figure-ground
the organization of the visual field into objects (the figures) that stand out from their surroundings (the ground).

proximity
How did Koehler interpret Sultan's process of solving the two-stick problem?
insight learning: reorganizing the elements of the problem situation
-requires being able to view the entire field
field theory
A framework adopted by Kurt Lewin for studying the forces/factors that influence a situation
why didn't gestalt psychology have a bigger impact?
Koffka's book made many believe that Gestalt psych was more focused upon theory over data and was primarily about preception