anat lab exam 1 checklist
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
normal range of blood pH
7.35-7.45
hematocrit range
women = 42 +-5 . men = 47 +-5 %
hemoglobin concentration
women = 12-15 g/dL . men = 13-17 g/dL
WBC count range
5,000 - 10,000 cells/microliter
RBC count range
4-6 million cells/microliter
plasma
non-living fluid matrix in which formed elements are suspended
formed elements
living cells suspended in plasma (RBC, WBC, platelets)
hematocrit
volume % of RBCs
hemostasis
stops bleeding after blood vessel injury w/ clot
agglutinogens
antigens
agglutinins
antibodies - cause clumping
agglutination
process of clumping particles
leukocytosis
high WBC count
leucopenia
low WBC count
erythrocytopenia
low RBC count
polycythemia
high RBC count
hemocytometer
counts cells
leukemia
cancer w/ mutated WBCs
plasma function
transport, clot, maintain blood volume
erythrocytes function
transport oxygen + carbon dioxide
leukocytes function
protection (bacteria, infection)
neutrophil function (granulocyte)
phagocytize bacteria
eosinophil function (granulocyte)
kill parasitic worms (+allergy / asthma role)
basophil function (granulocyte)
release histamine + other mediators of inflammation
lymphocyte function (agranulocyte)
mount immune response by direct cell attack or via antibodies
monocyte function (agranulocyte)
phagocytosis + develop into macrophage in tissue
thrombocyte function (platelet)
hemostasis (blood clotting) + wound healing
intrinsic conduction system
electrical system w/in heart that keeps heart beating regularly (includes SA node, AV node, bundle of His, purkinje fibers)
autorhythmic cells (pacemaker cells)
self-excitable heart cells - make the heart beat on its own
sinoatrial (SA) node (pacemaker)
in R atrium, causes atria to contract, initiates entire cardiac cycle
atrioventricular (AV) node
delays electrical signal from SA node so atria have time to push blood into ventricles before ventricular contraction
contractile cells
produce hearts mechanical force through contraction, + propel blood
Bundle of His
conducts electrical impulses from AV node to Purkinje fibers
subendocardial conducting network (aka Purkinje fibers)
cells that transmit electrical impulses from AV node to ventricles, causing them to contract in a coordinated manner
norepinephrine (neurotransmitter + hormone)
increases HR, improves contractility, increases BP
epinephrine (hormone + neurotransmitter)
increase HR, increase contractility, increase CO
capillary beds
exchange materials (O, CO2, metabolic waste) between blood and tissues, supply myocardium w blood
arterioles
control blood flow to capillary beds (in between arteries and capillaries)
venules
very small vein, usually collecting blood from capillaries
thoroughfare channels
connects arteriole directly to venule, allowing blood to bypass capillary bed
terminal arteriole
smallest branches of arteries that directly feed into capillary beds
precapillary sphincters
regulate blood flow between arterioles and capillaries
electrocardiography (produces electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG))
medical test that records electrical activity of the heart
depolarizing
making inside cell more positive
repolarizing
cell returns to resting electrical state (-70 mv) after depolarization
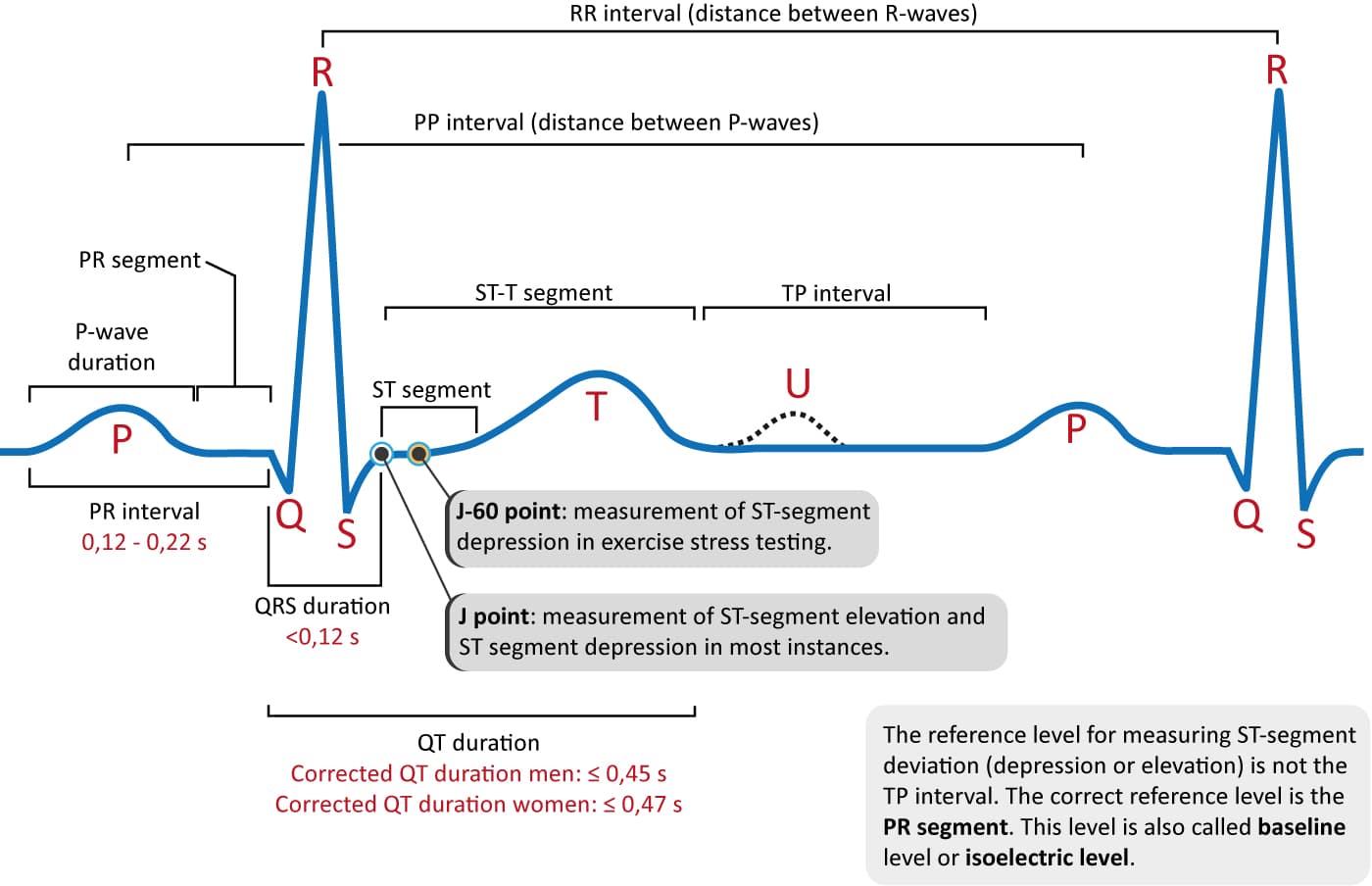
EKG segment
line between 2 waves
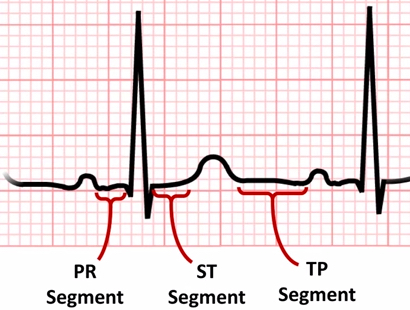
EKG interval
time that includes 1 segment and 1 or more waves
systolic pressure (squeeze)
max pressure exerted on arteries when heart contractsand pumps blood throughout body
diastolic pressure (down time)
force exerted on walls of arteries when heart Relaxes between heart beats
sphygomomanometer
automatic blood pressure machine
sounds of Korotkoff
pulsatile sounds of blood flow heard through stethoscope over brachial artery when a sphygmomanometer is deflated
tachycardia (Too fast)
abnormally fast heart rate (above 100 bpm at rest)
bradycardia (Below normal)
slow heart rate (below 60 bpm at rest)
fibrillation
rapid, irregular, and uncoordinated contraction of muscle fibers