CH 20 Digital Imaging Processing
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
What are the two systems of digital radiography?
1. computed radiography (CR)
2. direct radiography (DR)
Computed Radiography (CR) uses what type of imaging plate?
photostimulable storage phosphor imaging plate (PSP)
Where is the PSP located?
inside the cassette
Once the PSP is exposed what happens next?
the cassette is taken to the reader to process image and then it is erased (two steps)
How does direct radiography work?
the image is acquired and sent directly to the display monitor for the radiographer
True/False: indirect conversions are WITH scintillator
True
What is the two-step process used by the detector of indirect conversions?
1. uses scintillator (converts incoming x-ray photons to light)
2. then photodetector (converts light into electric signal)
Indirect conversions are used in Amorphous _______ w/ a TFT
silicon
True/False: direct conversions are WITHOUT scintillator
True
True/False: the detector of direct conversions directly converts incoming x-ray photons to electronic signal
True
Direct conversions are used in Amorphous ________ w/ a TFT
selenium
What is a matrix?
series of boxes laid out in rows and columns that gives form to the image
What is a pixel?
each box of the matrix
What is a pixel also known as?
picture element
How is a pixels location determined?
by its address
True/False: a pixel is capable of representing a wide range of different shades of gray
True
What does ADC stand for?
analog to digital converter
What are the two steps that ADC is done through?
1. sampling
2. quantification
'Analog values measured at chosen sampling frequency' best describes what term?
sampling
'Sampled piece of analog data is computed and assigned a value' best describes what term?
quantification
Analog values converted to a binary digit is a ___
bit
What is the 8-bit word?
byte
What is a voxel?
a three-dimensional volume of tissue
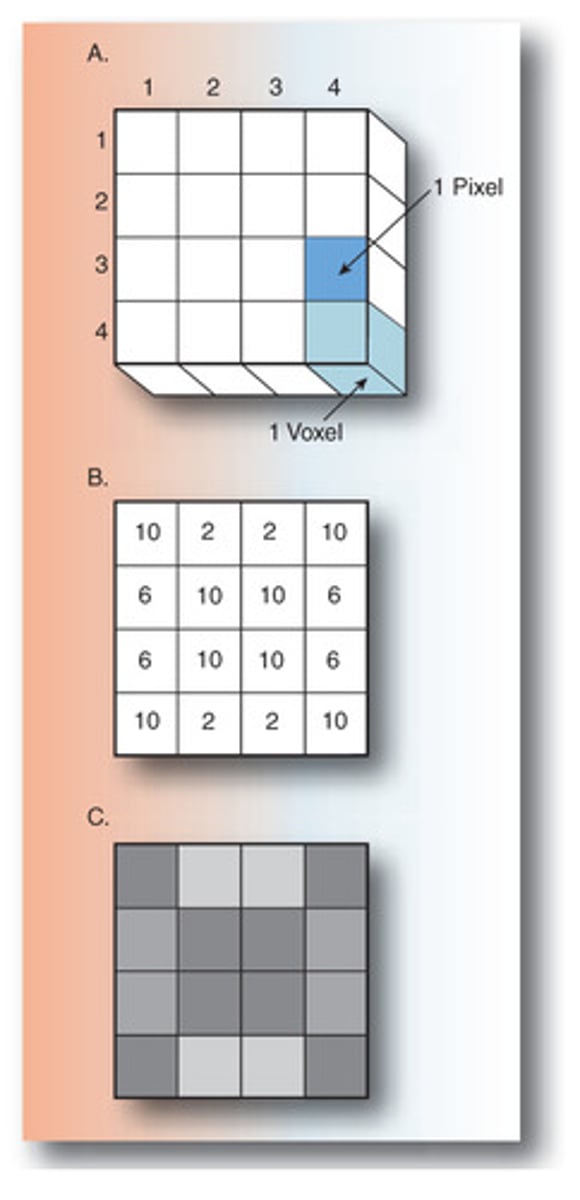
What is a voxel also known as?
volume element
Grayscale bit depth ranges from _ bits to __ bits
8; 32
What is the field of view (FOV)?
overall matrix; determined by size of the detector
If FOV remains the same, then as matrix size increases, the pixels get ____, and the resolution gets ____
smaller; sharper
True/False: the greater the matrix size for the same FOV, the better the spatial resolution
True
What is spatial resolution determined by?
pixel size
Spatial resolution is measured in what?
line pairs per millimeter (lp/mm)
What are the three processes intended to change the input values of the pixels to improve diagnostic quality of the image?
1. point processing
2. local processing
3. geometric processing
Which of the image processing systems is the most important for DR systems?
point processing
Define point processing:
performed between the receipt of the input image from the IR and the output image that is viewed on the monitor
What is a common point processing operation?
grayscale processing
What is grayscale processing?
allows for adjustments to image brightness and contrast
Grayscale processing involves the creation of (three things):
1. histogram
2. look-up-table (LUT)
3. windowing
How is a histogram generated?
the scanned area is divided into pixels and the signal intensity for each pixel is determined
Histogram, locates _______ and _______ signal within the anatomical regions of interest in the image
minimum; maximum
The shape of the histogram corresponds to what?
specific anatomy and technique used for an exam
A histogram analysis is performed to determine what two things?
1. values of interest (VOI)
2. exposure indicator (EI)
What happens if the VOI are under/overexposed?
the computer will correct the image on its own (rescaling or histogram modification)
Wide histogram indicates ______ contrast
higher
Narrow histogram indicates _____ contrast
lower
Without LUT applied, the image would display as a ___ contrast image
low
Selecting the proper LUT = proper _________
grayscale (regardless of variations in kVp and mAs)
What does windowing change?
contrast and brightness of the image on the monitor
What is window width (WW)?
range of densities that will be displayed
A narrow window width has few shades of gray and ____ contrast
high
A large window width has many shades of grays and ___ contrast
low
What is window level (WL)?
center of window width and controls brightness of image
The more the original image is changed by the Radiographer before sending to PACS, the _____ information the radiologist has to work with
less
Local processing operations is also called what?
area or group processing
What is local processing?
mathematical calculations are applied to only a small group of pixels at a time (eventually covering all pixels)
What is a kernel?
processing code that is mandatory and common to the computer system
Spatial Frequency Filtering is used to do what?
sharpen, smooth, blur, reduce noise, or pull elements of interest from image
What are the two kinds of spatial frequency filtering?
1. high-pass filtering
2. low-pass filtering
True/False: high-pass filtering is also called edge enhancement
True
What does high-pass filtering do?
- removes or suppresses low spatial frequency to produce a sharper output image
- greatly increases contrast
True/False: low-pass filtering is also called smoothing
True
What does low-pass filtering do?
- intentionally blurs the image
- reduces noise and displayed brightness
What is unsharp masking?
"blurring" subtracts a low-pass filtered image from the original
What is geometric processing used for?
to change position or orientation of pixels in the image
Digital image quality is based on what four things?
1. resolution
2. noise
3. detective quantum efficiency (DQE)
4. artifacts
Spatial resolution is controlled by what?
matrix size and how many pixels can be displayed by the monitor
If matrix size increases and pixel size decreases, what happens to spatial resolution?
it increases
Noise is classified as what (three things)?
1. system noise
2. ambient noise
3. quantum mottle noise
A high signal to noise ratio (S/N) indicates ______ noise in the image.
little
If there is an increase in noise, what happens to contrast?
decreased contrast
If there is a decrease in noise, what happens to contrast?
increased contrast
What is quantum mottle noise?
- results from an insufficient quantity of photons from an improperly set exposure factors
- produces grainy image
How do you correct quantum mottle noise?
repeat with increased technical factors
What is detective quantum efficiency the measure of?
the sensitivity and accuracy by which the IR converts the incoming data to the output viewing device
a device with 100% efficiency has DQE = 1, meaning ...
no loss of information
DR systems have a DQE between
30%, 70%
Exposure Indicators determine what?
the quantity of photons that strike the detector
What is the deviation index (DI)?
a comparison between the actual exposure and the proper exposure received by the image detector
exposure sensitivity of imaging detectors ranges from:
0.1 mR to 100 mR; or a range of 1000:1